Topic 5 square 5: Unlock the secrets of squaring numbers with our comprehensive guide. From basic concepts to practical applications, delve into the world of square roots, calculating square footage, and more. Whether you're a student brushing up on math skills or a curious mind exploring mathematical properties, this article has something for everyone.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Concept of 5 Square 5
- Introduction to Squaring Numbers
- Basic Concepts of Square Roots
- Calculating Square Footage
- Formulas for Area of a Square
- Practical Applications of Squaring Numbers
- Simplifying Square Roots
- Square Roots in Algebra
- Mathematical Properties of Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: Hãy khám phá bảng ma thuật 5x5 đầy kỳ diệu trong video này! Bạn sẽ được tận hưởng những trải nghiệm thú vị và học hỏi về cách xây dựng ma trận ma thuật 5x5.
Understanding the Concept of 5 Square 5
The keyword "5 square 5" can be explored in different contexts, including mathematics and geometry. Here, we dive into the mathematical and geometric meanings and calculations related to squaring the number 5.
Mathematical Concept
In mathematics, squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. For the number 5, this can be represented as:
\[
5^2 = 5 \times 5 = 25
\]
Squaring a number is a fundamental arithmetic operation that results in a perfect square, which is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself.
Geometry and Square Shape
In geometry, a square is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with all sides of equal length and all angles equal to 90 degrees. The area and perimeter of a square can be calculated using the side length.
- Side length: \( a \)
- Area: \( A = a^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \)
- Diagonal: \( q = a\sqrt{2} \)
Square Root of 5
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 5 is an irrational number, often approximated as:
\[
\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236
\]
This value is non-repeating and non-terminating, making it an important concept in various mathematical calculations and applications.
Practical Examples
Let's consider some practical examples involving the number 5 and its square:
- If a square has a side length of 5 units, its area would be:
\[
A = 5^2 = 25 \text{ square units}
\] - If the side length of a square is given, the perimeter can be calculated as:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\] - The diagonal of the square with side length 5 units is:
\[
q = 5\sqrt{2} \approx 7.071 \text{ units}
\]
Using Calculators for Squaring
Online calculators can help easily find the square of a number or the area and perimeter of a square. These tools are useful for quick computations and verifying manual calculations.
| Operation | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Square of 5 | \( 5^2 \) | 25 |
| Area of Square | \( A = a^2 \) | 25 square units |
| Perimeter of Square | \( P = 4a \) | 20 units |
| Diagonal of Square | \( q = a\sqrt{2} \) | 7.071 units |
READ MORE:
Introduction to Squaring Numbers
Squaring numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics that involves multiplying a number by itself. When we square a number, we essentially find the area of a square with side lengths equal to that number. Let's take the example of 5 squared (5²), which is calculated by multiplying 5 by itself: 5 * 5 = 25.
Understanding how to square numbers is crucial in various mathematical operations, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus. It forms the foundation for solving equations, finding areas, and analyzing geometric shapes.
Basic Concepts of Square Roots
Understanding square roots is essential in mathematics, offering insights into the inverse operation of squaring numbers. When we talk about the square root of a number, we're essentially asking: "What number multiplied by itself equals this number?" For instance, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 * 5 = 25.
Key concepts related to square roots include:
- Principal square root: The non-negative square root of a real number.
- Rational and irrational numbers: Square roots can result in either rational or irrational numbers, depending on the original number.
- Radical notation: Expressing square roots using the radical symbol (√).
- Estimating square roots: Techniques for approximating square roots without using a calculator.
Understanding these concepts lays the groundwork for advanced mathematical operations and problem-solving techniques.
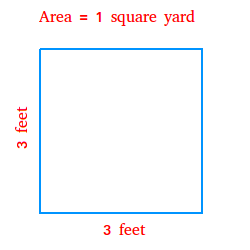
Calculating Square Footage
Calculating square footage is a crucial skill in various fields, including construction, real estate, and interior design. It involves determining the area of a space in square units, typically square feet or square meters. Here's how to calculate square footage:
- Measure the length and width of the area in feet (or meters).
- Multiply the length by the width to find the area in square units.
- For example, if a room measures 10 feet by 12 feet, the square footage is calculated as follows:
| Length (ft) | Width (ft) | Area (ft2) |
| 10 | 12 | 10 * 12 = 120 |
So, the square footage of the room is 120 square feet.
Understanding how to calculate square footage is essential for determining material quantities, estimating costs, and planning spatial layouts.
Formulas for Area of a Square
Calculating the area of a square is straightforward and involves using simple formulas. The most common formula to find the area of a square is:
- Using side length: If you know the length of one side of the square (let's call it "s"), you can find the area by squaring this length: Area = s2.
- Using diagonal length: If you know the length of the diagonal (d) of the square, you can find the area using the formula: Area = (d2) / 2.
For example, let's consider a square with a side length of 5 units:
| Side Length (s) | Area (s2) |
| 5 | 5 * 5 = 25 |
So, the area of the square is 25 square units.
These formulas are fundamental in geometry and are used extensively in various applications, including architecture, engineering, and design.

Practical Applications of Squaring Numbers
The concept of squaring numbers finds numerous practical applications across various fields, showcasing its importance beyond theoretical mathematics. Some notable applications include:
- Area Calculation: Squaring numbers is essential for finding the area of squares, rectangles, and other geometric shapes. This is crucial in fields such as construction, architecture, and urban planning.
- Physics Formulas: Many physics equations involve squaring numbers, such as formulas for calculating velocity, acceleration, and energy. Understanding these concepts is vital for students and professionals in physics-related fields.
- Financial Analysis: Squaring numbers is utilized in various financial calculations, including determining compound interest, analyzing investment returns, and forecasting future values.
- Signal Processing: In telecommunications and digital signal processing, squaring numbers is used in tasks like signal modulation, noise reduction, and spectral analysis.
- Machine Learning: Squaring numbers is a fundamental operation in machine learning algorithms, where it's often used in optimization techniques, regression analysis, and error calculation.
These practical applications highlight the significance of understanding and applying the concept of squaring numbers in real-world scenarios.
Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves expressing them in their simplest form, often involving factors that are perfect squares. Here's how to simplify square roots step by step:
- Identify perfect square factors: Look for factors of the radicand (the number under the square root) that are perfect squares.
- Break down the radicand: Rewrite the square root expression by splitting the radicand into its perfect square factors.
- Apply the square root property: Take the square root of each perfect square factor and combine them if possible.
For example, let's simplify √50:
| Radicand | Perfect Square Factor | Square Root of Factor |
| 50 | 25 | √25 = 5 |
So, √50 can be simplified as 5√2.
Mastering the skill of simplifying square roots is essential in algebra, calculus, and various mathematical applications, enabling easier manipulation of expressions and equations.
Square Roots in Algebra
In algebra, square roots play a significant role in solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding fundamental concepts. Here's how square roots are used in algebra:
- Equation Solving: Square roots are often involved in solving quadratic equations, where the solutions may include both positive and negative square roots.
- Expression Simplification: Square roots appear in expressions involving variables, where they can be simplified using algebraic techniques such as factoring.
- Radical Equations: Equations containing square roots, known as radical equations, are solved by isolating the radical term and squaring both sides of the equation to eliminate the square root.
- Complex Numbers: Square roots are also used to define complex numbers, where the square root of negative numbers is represented as imaginary numbers.
For example, consider the equation x² = 25. By taking the square root of both sides, we get two solutions: x = ±√25, which simplifies to x = ±5.
Understanding how to work with square roots in algebra is essential for mastering various topics in mathematics, including algebraic manipulation, equation solving, and graphing functions.
Mathematical Properties of Square Roots
Square roots possess several important mathematical properties that are essential for understanding their behavior and applications. Here are some key properties:
- Non-Negativity: The square root of a non-negative real number is always non-negative. In other words, √x ≥ 0 for all x ≥ 0.
- Product Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots of the factors. That is, √(ab) = √a * √b.
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots of the numerator and denominator. In other words, √(a/b) = √a / √b, provided that b ≠ 0.
- Radical Form: Any positive real number can be expressed as the square root of another real number. For example, √x² = |x| for all real numbers x.
- Index Property: The square root is the most common example of a radical, but similar properties apply to higher-order roots, such as cube roots or nth roots.
Understanding these properties is crucial for manipulating expressions involving square roots, simplifying mathematical calculations, and solving various mathematical problems.

Hãy khám phá bảng ma thuật 5x5 đầy kỳ diệu trong video này! Bạn sẽ được tận hưởng những trải nghiệm thú vị và học hỏi về cách xây dựng ma trận ma thuật 5x5.
5 x 5 Magic Square | Bảng Ma Thuật 5 x 5 | Ma Trận Ma Thuật 5x5 | Ma Trận Ma Thuật
READ MORE:
Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 5 một cách dễ dàng và chi tiết. Hãy xem để nắm vững khái niệm này!
Căn bậc hai của 5 Đơn giản hóa