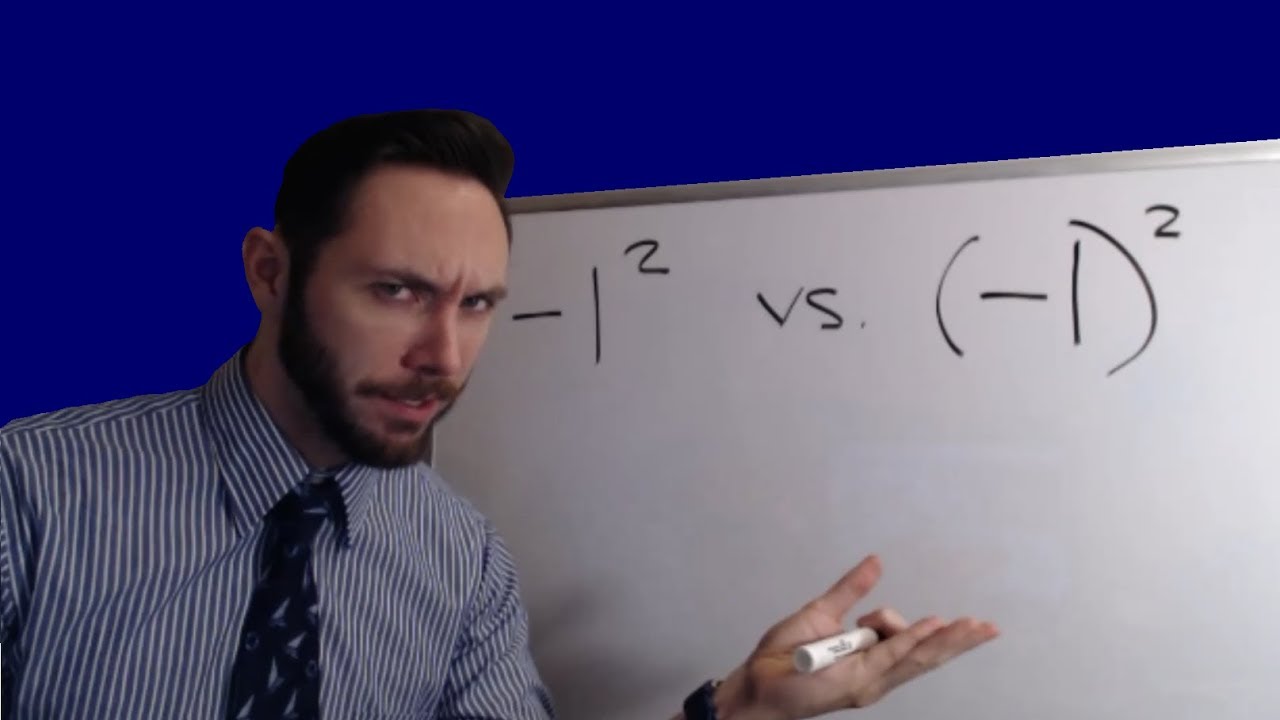Topic 7 square 2: Discover the intriguing world of squares and square roots with the concept of 7 square 2. This article delves into the calculations and applications of this mathematical operation, providing clear examples and explanations to enhance your understanding.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Concept of "7 Square 2"
- Introduction
- Mathematical Calculations
- Square Roots and Their Properties
- Practical Applications
- Step-by-Step Examples
- Using Calculators
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Xem video 'Cách Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Một Số Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán học cùng Mr. J' để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và cách tính bình phương của một số.
Understanding the Concept of "7 Square 2"
The expression "7 square 2" can be interpreted in various ways. It may refer to mathematical operations involving squaring the number 7, the concept of squaring numbers, or specific algebraic problems involving square roots.
Mathematical Interpretation
In mathematics, squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. The square of 7 is:
\( 7^2 = 7 \times 7 = 49 \)
This concept is widely used in various mathematical calculations and is fundamental in algebra and geometry.
Examples and Calculations
- Calculating the square of 7: \( 7^2 = 49 \)
- Simplifying the expression \( (7 \sqrt{2})^2 \):
First, square the coefficient and the square root separately:
\( (7 \sqrt{2})^2 = 7^2 \times (\sqrt{2})^2 = 49 \times 2 = 98 \)
Additional Mathematical Concepts
There are various tools and calculators available to help with squaring numbers and understanding their properties:
- - An online tool to find the square of any number.
- - A comprehensive math solver that provides step-by-step solutions.
- - A useful calculator for simplifying square roots.
- - An algebra problem solver for expressions involving square roots and exponents.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how to square numbers and simplify expressions involving square roots is crucial in various fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. These skills are essential for solving complex problems and understanding advanced mathematical concepts.
Conclusion
The expression "7 square 2" can be interpreted in different mathematical contexts. Whether squaring the number 7 or working with expressions involving square roots, mastering these concepts is fundamental to advancing in mathematics.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The concept of squaring a number is fundamental in mathematics. It involves multiplying the number by itself. This article delves into the details of squaring numbers, using "7 square 2" as an example to illustrate the process and its applications in various mathematical contexts.
Mathematical Calculations
Understanding the mathematical operations involved in squaring and simplifying expressions with the number 7 and the square root of 2 is essential for various applications in algebra and geometry. Below, we will explore detailed steps for performing these calculations.
-
Step 1: Squaring the Number 7
The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself. For 7, this is calculated as:
\[ 7^2 = 7 \times 7 = 49 \]
-
Step 2: Squaring the Square Root of 2
The square root of a number, when squared, returns the original number. Thus, for \(\sqrt{2}\), we have:
\[ (\sqrt{2})^2 = 2 \]
-
Step 3: Simplifying the Expression \(7\sqrt{2}\)
To simplify \(7\sqrt{2}\), recognize that the expression is already in its simplest form. However, if we want to square this entire term, we follow these steps:
\[ (7\sqrt{2})^2 = 7^2 \times (\sqrt{2})^2 \]
Using the results from Step 1 and Step 2, we get:
\[ (7\sqrt{2})^2 = 49 \times 2 = 98 \]
-
Step 4: Verifying the Simplified Result
To ensure the calculations are correct, we recheck the steps and calculations:
- Square of 7: \( 7^2 = 49 \)
- Square of \(\sqrt{2}\): \( (\sqrt{2})^2 = 2 \)
- Combining these, \( (7\sqrt{2})^2 = 49 \times 2 = 98 \)
Summary
By following these steps, we have demonstrated that squaring the term \(7\sqrt{2}\) yields the result 98. These calculations are crucial in algebraic manipulations and solving problems involving exponents and radicals.
Square Roots and Their Properties
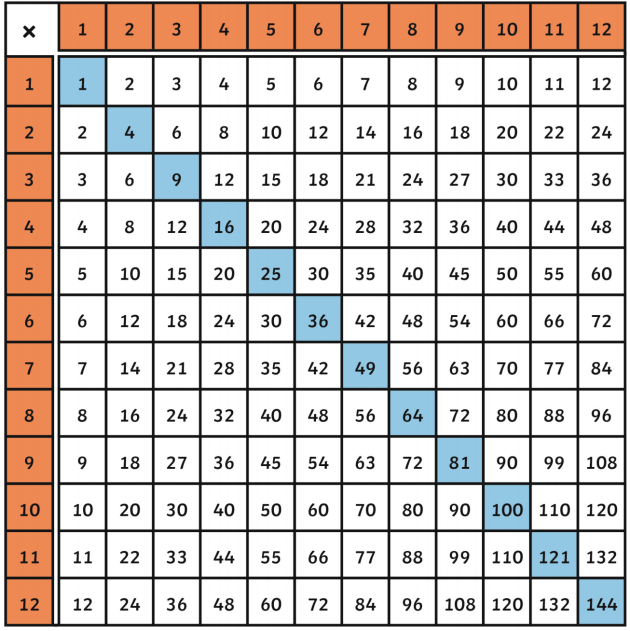
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\). The square root symbol, known as the radical symbol (√), denotes this operation.
Square roots have several properties:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, etc., are perfect squares because their square roots are whole numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, respectively).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers like 2, 3, 5, etc., do not have whole numbers as their square roots. These square roots are irrational numbers, meaning their decimal forms are non-repeating and non-terminating.
- Product Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots. Mathematically, this is expressed as: \(\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\). For example, \(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3}\).
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\). For example, \(\sqrt{\frac{9}{4}} = \frac{\sqrt{9}}{\sqrt{4}} = \frac{3}{2}\).
- Addition and Subtraction: Square roots can be added or subtracted if they have the same radicand. For instance, \(2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3} = 5\sqrt{3}\).
- Simplification: Simplifying square roots involves factoring out perfect squares. For example, \(\sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2}\).
Understanding these properties is fundamental in algebra and higher-level mathematics, as they provide the basis for more complex operations and problem-solving techniques.
Practical Applications
The concept of 7 square 2, represented mathematically as \(7\sqrt{2}\), finds applications in various fields. Understanding how to work with this expression can be useful in solving real-world problems and in academic contexts. Below are detailed practical applications:
- Geometry: In geometric calculations, especially in finding the length of the diagonal of a square, the expression \(7\sqrt{2}\) is often used. For example, if the side of a square is 7 units, the diagonal will be \(7\sqrt{2}\) units.
- Physics: This expression appears in physics when calculating distances or speeds involving square roots. For instance, in problems involving the Pythagorean theorem in physics, such as determining the resultant velocity or displacement.
- Engineering: Engineers use \(7\sqrt{2}\) in design and analysis, particularly in areas like signal processing, structural engineering, and when dealing with vectors and forces.
- Architecture: Architects might use this expression when designing certain elements of structures that involve right-angled triangles or in calculating the spacing of elements in a design.
- Mathematics: In mathematical problems and proofs, simplifying expressions involving square roots is common, and understanding how to manipulate \(7\sqrt{2}\) is fundamental. This knowledge is particularly useful in algebra and calculus.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and importance of mastering the concept of square roots, particularly expressions like \(7\sqrt{2}\), in various scientific and practical domains.

Step-by-Step Examples
Understanding how to solve expressions involving square roots and exponents is crucial in mathematics. Here are detailed, step-by-step examples to help clarify the process.
- Example 1: Simplifying \(7 \sqrt{2}\)
- Step 1: Write down the expression \(7 \sqrt{2}\).
- Step 2: Since \(\sqrt{2}\) is already in its simplest form, multiply 7 by \(\sqrt{2}\).
- Result: \(7 \sqrt{2}\).
- Example 2: Squaring \(7 \sqrt{2}\)
- Step 1: Write the expression \((7 \sqrt{2})^2\).
- Step 2: Apply the exponent to both 7 and \(\sqrt{2}\), resulting in \(7^2 \times (\sqrt{2})^2\).
- Step 3: Calculate \(7^2 = 49\) and \((\sqrt{2})^2 = 2\).
- Step 4: Multiply the results, \(49 \times 2 = 98\).
- Result: \( (7 \sqrt{2})^2 = 98 \).
- Example 3: Solving \((x - 7)^2\)
- Step 1: Write the expression \((x - 7)^2\).
- Step 2: Expand using the FOIL method:
- First: \(x \cdot x = x^2\)
- Outer: \(x \cdot (-7) = -7x\)
- Inner: \((-7) \cdot x = -7x\)
- Last: \((-7) \cdot (-7) = 49\)
- Step 3: Combine like terms, resulting in \(x^2 - 14x + 49\).
- Result: \((x - 7)^2 = x^2 - 14x + 49\).
Using Calculators
Using calculators can simplify complex mathematical calculations and ensure accuracy. Whether you're working with square roots, powers, or other mathematical functions, calculators are invaluable tools. Here's a step-by-step guide to using calculators for various mathematical purposes.
- Square Root Calculations:
- Enter the number for which you want to find the square root.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- Read the result displayed on the calculator screen.
- Square Calculations:
- Enter the number you want to square.
- Press the power (x²) button.
- Observe the result, which is the number multiplied by itself.
- Using Online Calculators:
- Navigate to a reliable online calculator, such as CalculatorSoup or Mathway.
- Select the type of calculation you need (e.g., square root, square).
- Enter your values into the provided fields and press the calculate button.
- Review the results, which may be presented in both exact and decimal forms.
- Advanced Calculations:
- For more complex calculations, such as finding the square of sums or differences, use a scientific calculator.
- Input the entire expression using parentheses to ensure correct order of operations.
- Press the equals button (=) to get the result.
Using calculators can help streamline your mathematical processes, save time, and reduce errors, making them an essential tool for students, professionals, and anyone dealing with numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to the expression "7 square 2", along with detailed answers to help you understand the concepts better.
-
What does "7 square 2" mean?
The expression "7 square 2" can be interpreted in different ways depending on the context. It might refer to squaring the number 7, which means calculating \( 7^2 \). Alternatively, it might be referring to the number 7 multiplied by the square root of 2, written as \( 7\sqrt{2} \).
-
How do you calculate \( 7^2 \) (7 squared)?
To square a number, you multiply the number by itself. Therefore, \( 7^2 = 7 \times 7 = 49 \).
-
How do you simplify \( 7\sqrt{2} \)?
Simplifying \( 7\sqrt{2} \) involves leaving it as is because it is already in its simplest form. The value can be approximated as \( 7 \times 1.414 = 9.899 \).
-
How do you calculate \( (7\sqrt{2})^2 \)?
To evaluate \( (7\sqrt{2})^2 \), follow these steps:
- First, square the coefficient: \( 7^2 = 49 \).
- Next, square the square root: \( (\sqrt{2})^2 = 2 \).
- Multiply the results: \( 49 \times 2 = 98 \).
Thus, \( (7\sqrt{2})^2 = 98 \).
-
What is the difference between "square" and "square root"?
"Square" refers to multiplying a number by itself, while "square root" is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square of 4 is \( 4^2 = 16 \), and the square root of 16 is \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
What is the principal square root?
The principal square root of a number is its non-negative root. For instance, while both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16, the principal square root is 4.
-
How do calculators handle negative squares?
When squaring negative numbers, it is essential to use parentheses to ensure the correct interpretation. For example:
- \(-5^2\) without parentheses means the negative of 5 squared, resulting in \(-(5 \times 5) = -25\).
- \((-5)^2\) with parentheses means negative 5 squared, resulting in \((-5) \times (-5) = 25\).
Xem video 'Cách Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Một Số Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán học cùng Mr. J' để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và cách tính bình phương của một số.
Cách Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Một Số Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán học cùng Mr. J
READ MORE:
Xem video 'Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán học cùng Mr. J' để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và cách tính căn bậc hai của một số.
Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán học cùng Mr. J