Topic area and perimeter worksheets grade 4: Discover engaging and educational area and perimeter worksheets for Grade 4 students! These worksheets are designed to make learning geometry fun and easy, helping young learners master essential math skills. With a variety of exercises and real-life applications, students will build confidence and proficiency in calculating area and perimeter. Perfect for classroom and home practice!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 4
- Introduction
- Basic Concepts
- Perimeter Worksheets
- Area Worksheets
- Mixed Area and Perimeter Problems
- Word Problems
- Using Grids for Area and Perimeter
- Real-Life Applications
- Fun Activities and Games
- Answer Keys and Explanations
- Teacher Resources
- Home Practice Tips
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter Worksheets for Grade 4
These worksheets are designed to help Grade 4 students practice and master the concepts of area and perimeter. Below are some types of worksheets and activities included:
Types of Worksheets
- Calculating the Perimeter of Various Shapes
- Finding the Area of Rectangles and Squares
- Mixed Area and Perimeter Problems
- Word Problems Involving Area and Perimeter
- Using Grids to Find Area and Perimeter
- Real-Life Applications of Area and Perimeter
Sample Problems
Here are some examples of the problems students might encounter:
Perimeter
Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with length \(8 \, \text{cm}\) and width \(5 \, \text{cm}\):
\(P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 13 \, \text{cm} = 26 \, \text{cm}\)
Area
Find the area of a square with side length \(7 \, \text{cm}\):
\(A = s^2 = 7 \, \text{cm} \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 49 \, \text{cm}^2\)
Worksheet Features
Each worksheet includes:
- Clear Instructions
- Step-by-Step Examples
- Practice Problems
- Answer Keys
Benefits of Using These Worksheets
- Helps students understand and apply formulas for area and perimeter.
- Enhances problem-solving skills through various types of problems.
- Provides practical examples that relate to real-world scenarios.
- Encourages independent learning with answer keys for self-assessment.
These worksheets are a great resource for both classroom use and home practice, ensuring that students gain a solid understanding of area and perimeter.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive collection of area and perimeter worksheets for Grade 4 students! These worksheets are designed to help young learners grasp the fundamental concepts of geometry in a fun and engaging way. Below, you'll find detailed explanations, step-by-step instructions, and a variety of problems to solve.
In these worksheets, students will:
- Learn and apply formulas for calculating area and perimeter.
- Practice with a variety of shapes including rectangles, squares, and composite shapes.
- Engage with word problems that involve real-life scenarios.
- Use grids and diagrams to visualize and solve problems.
- Check their answers with detailed solutions provided.
These worksheets are perfect for classroom activities, homework assignments, and additional practice to reinforce learning. Let's embark on this educational journey to master area and perimeter!
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of area and perimeter is essential for Grade 4 students. Here, we break down these fundamental ideas step-by-step:
Perimeter
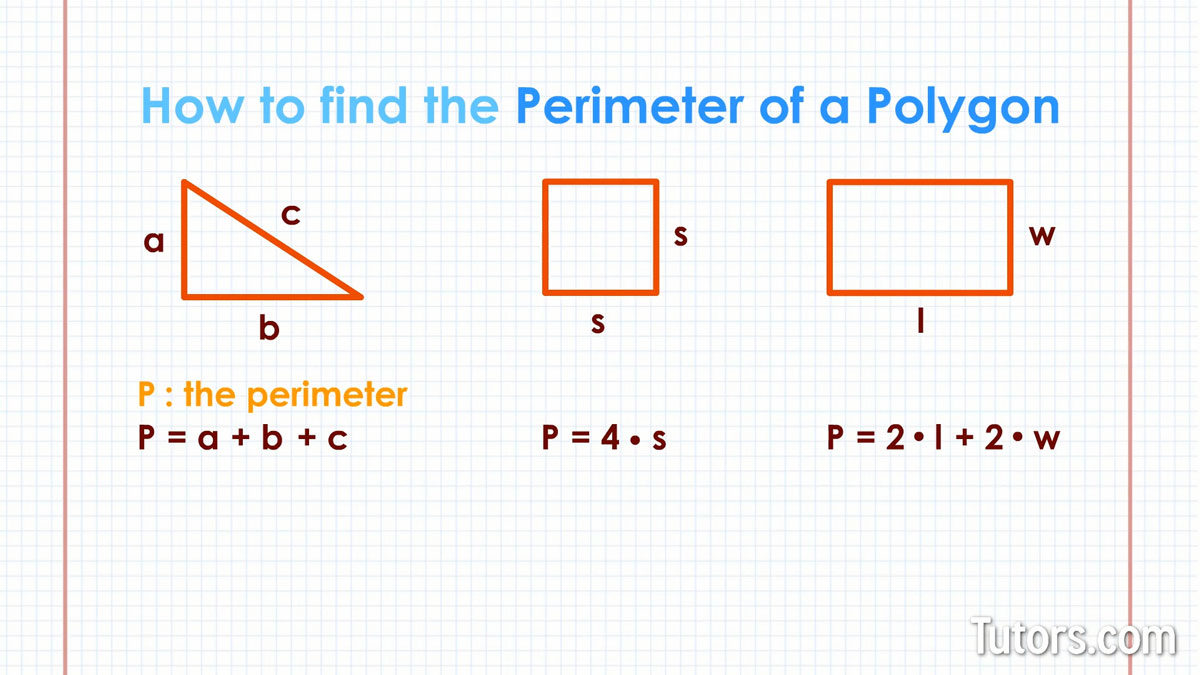
The perimeter is the distance around the edge of a shape. To find the perimeter, you add up the lengths of all the sides.
- For a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- For a square: \( P = 4 \times s \) where \( s \) is the side length.
Area
The area is the amount of space inside a shape. To find the area, you multiply the lengths of the sides.
- For a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- For a square: \( A = s^2 \) where \( s \) is the side length.
Composite Shapes
For more complex shapes, break them down into simpler shapes, calculate the area and perimeter for each, and then combine the results.
Below is a table summarizing the formulas:
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \) | \( A = l \times w \) |
| Square | \( P = 4 \times s \) | \( A = s^2 \) |
By mastering these basic concepts, students will be well-prepared to tackle a variety of problems involving area and perimeter.
Perimeter Worksheets
Our perimeter worksheets for Grade 4 are designed to help students master the concept of perimeter through a variety of engaging exercises. These worksheets provide step-by-step instructions and practice problems to build confidence and proficiency.
Worksheet Activities
- Simple Shapes: Calculate the perimeter of rectangles and squares using given side lengths.
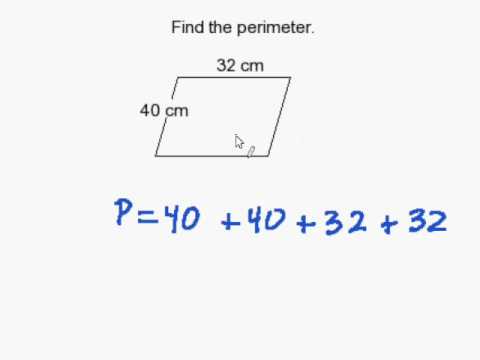
- Irregular Shapes: Find the perimeter by adding the lengths of all sides of various irregular shapes.
- Missing Side Lengths: Determine the missing side length of a shape when given the perimeter and other side lengths.
- Word Problems: Solve real-life problems involving perimeter to understand practical applications.
- Grid Exercises: Use grid paper to measure and calculate the perimeter of drawn shapes.
Sample Problems
Here are some sample problems included in the worksheets:
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with length \(10 \, \text{cm}\) and width \(6 \, \text{cm}\):
\( P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (10 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 16 \, \text{cm} = 32 \, \text{cm} \)
- Find the perimeter of a square with side length \(5 \, \text{cm}\):
\( P = 4 \times s = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
- A triangle has sides of length \(7 \, \text{cm}\), \(5 \, \text{cm}\), and \(8 \, \text{cm}\). Calculate its perimeter:
\( P = 7 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Answer Keys
Each worksheet comes with an answer key to help students check their work and understand the correct methods for solving perimeter problems.
These perimeter worksheets are a great resource for reinforcing students' understanding and helping them apply their knowledge to a variety of problems. They can be used in the classroom, for homework, or as additional practice for mastery.
Area Worksheets
Our area worksheets for Grade 4 are designed to help students understand and calculate the area of various shapes. These worksheets provide detailed explanations, step-by-step instructions, and diverse exercises to ensure a thorough grasp of the concept.
Worksheet Activities
- Simple Shapes: Calculate the area of rectangles and squares using given side lengths.
- Composite Shapes: Break down complex shapes into simpler ones and find the total area.
- Irregular Shapes: Estimate and calculate the area of irregular shapes using grids.
- Word Problems: Solve practical problems involving area to understand real-life applications.
- Grid Exercises: Use grid paper to measure and calculate the area of drawn shapes.
Sample Problems
Here are some sample problems included in the worksheets:
- Calculate the area of a rectangle with length \(12 \, \text{cm}\) and width \(7 \, \text{cm}\):
\( A = l \times w = 12 \, \text{cm} \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 84 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Find the area of a square with side length \(9 \, \text{cm}\):
\( A = s^2 = 9 \, \text{cm} \times 9 \, \text{cm} = 81 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Estimate the area of an irregular shape using a grid where each square represents \(1 \, \text{cm}^2\):
Count the full squares and partial squares to get an approximate area.
Answer Keys
Each worksheet comes with an answer key to help students check their work and understand the correct methods for solving area problems.
These area worksheets are a valuable resource for reinforcing students' understanding and helping them apply their knowledge to a variety of problems. They can be used in the classroom, for homework, or as additional practice for mastery.

Mixed Area and Perimeter Problems
Mixed area and perimeter problems are designed to help Grade 4 students apply their understanding of both concepts in various contexts. These worksheets provide a variety of problems that require students to calculate both area and perimeter, enhancing their problem-solving skills and reinforcing their knowledge.
Worksheet Activities
- Simple Calculations: Calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares using given dimensions.
- Composite Shapes: Find the area and perimeter of complex shapes by breaking them down into simpler shapes.
- Irregular Shapes: Estimate the area and perimeter of irregular shapes using grids and measurement.
- Word Problems: Solve real-life scenarios that require calculating both area and perimeter to find solutions.
- Application Problems: Use knowledge of area and perimeter to solve practical problems, such as finding the amount of material needed for a project.
Sample Problems
Here are some sample problems included in the worksheets:
- Calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length \(15 \, \text{cm}\) and width \(10 \, \text{cm}\):
Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (15 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 25 \, \text{cm} = 50 \, \text{cm} \)
Area: \( A = l \times w = 15 \, \text{cm} \times 10 \, \text{cm} = 150 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Find the area and perimeter of a square with side length \(8 \, \text{cm}\):
Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times s = 4 \times 8 \, \text{cm} = 32 \, \text{cm} \)
Area: \( A = s^2 = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 8 \, \text{cm} = 64 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Estimate the area and perimeter of an irregular shape using a grid where each square represents \(1 \, \text{cm}^2\):
Count the full squares and partial squares to get an approximate area.
Measure the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter.
Answer Keys
Each worksheet comes with an answer key to help students check their work and understand the correct methods for solving mixed area and perimeter problems.
These mixed area and perimeter worksheets are a valuable resource for helping students build confidence and proficiency in both concepts. They can be used in the classroom, for homework, or as additional practice for mastery.
Word Problems
Word problems are an excellent way for Grade 4 students to apply their knowledge of area and perimeter in real-life scenarios. These worksheets feature a variety of problems that challenge students to think critically and use their math skills effectively.
Worksheet Activities
- Simple Word Problems: Solve basic problems that require calculating the area or perimeter of given shapes.
- Complex Word Problems: Tackle more challenging problems involving composite shapes and multiple steps.
- Real-Life Scenarios: Apply area and perimeter calculations to everyday situations, such as fencing a yard or tiling a floor.
- Mixed Problems: Work on problems that require both area and perimeter calculations to find the solution.
- Multi-Step Problems: Solve problems that involve multiple steps and require careful reading and planning.
Sample Problems
Here are some sample word problems included in the worksheets:
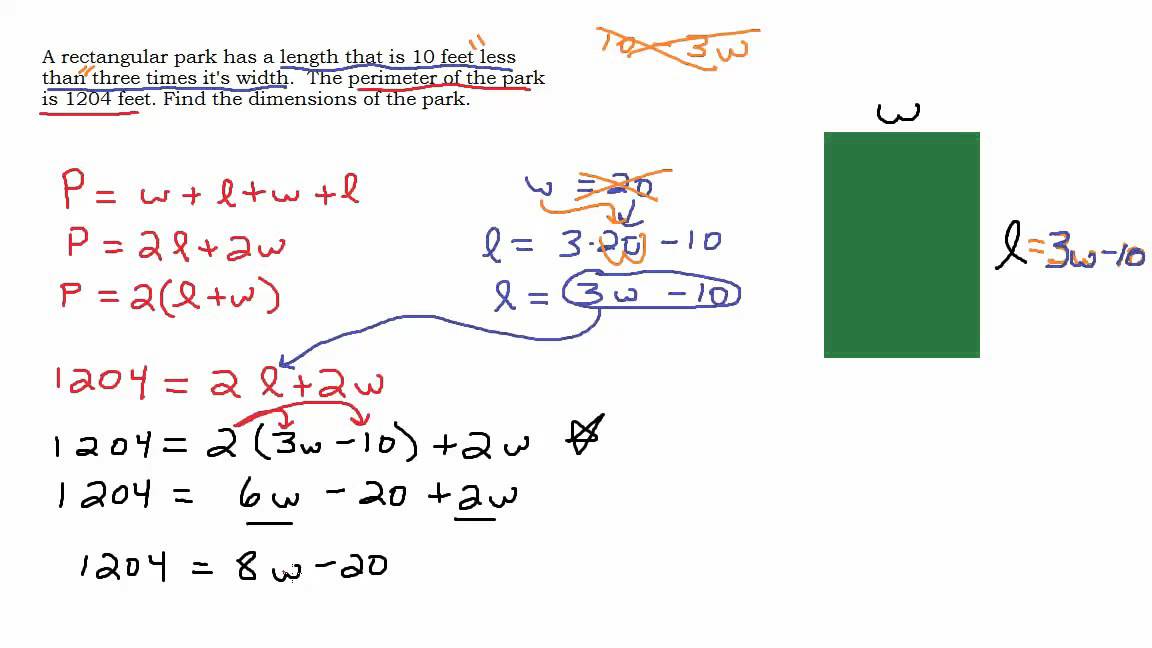
- John wants to fence his rectangular garden, which is \(20 \, \text{m}\) long and \(10 \, \text{m}\) wide. Calculate the total length of fencing he needs.
Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (20 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 30 \, \text{m} = 60 \, \text{m} \)
- Sara is tiling her kitchen floor, which is a square with a side length of \(5 \, \text{m}\). Calculate the area of the floor.
Area: \( A = s^2 = 5 \, \text{m} \times 5 \, \text{m} = 25 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- A rectangular playground measures \(30 \, \text{m}\) by \(15 \, \text{m}\). How much area is available for playing, and what is the perimeter?
Area: \( A = l \times w = 30 \, \text{m} \times 15 \, \text{m} = 450 \, \text{m}^2 \)
Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (30 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 45 \, \text{m} = 90 \, \text{m} \)
Answer Keys
Each worksheet comes with an answer key to help students check their work and understand the correct methods for solving word problems involving area and perimeter.
These word problem worksheets are a great resource for helping students connect their mathematical understanding to real-world applications. They can be used in the classroom, for homework, or as additional practice to develop problem-solving skills.
Using Grids for Area and Perimeter
Using grids to teach area and perimeter can help students visualize and understand these concepts better. Here are some steps and examples to guide students through using grids for calculating area and perimeter:
Understanding Grids
Grids are composed of squares of equal size. Each square can represent a unit of measurement such as 1 square centimeter or 1 square inch. By counting these squares, students can easily calculate the area and perimeter of various shapes.
Calculating Perimeter
To find the perimeter of a shape on a grid, follow these steps:
- Identify the shape on the grid.
- Count the number of unit squares along each side of the shape.
- Add the lengths of all the sides to find the perimeter.
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 4 units and a width of 3 units, its perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) = 2 \times (4 + 3) = 2 \times 7 = 14 \text{ units}
\]
Calculating Area
To find the area of a shape on a grid, follow these steps:
- Identify the shape on the grid.
- Count the number of unit squares inside the shape.
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 4 units and a width of 3 units, its area is calculated as follows:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{Length} \times \text{Width} = 4 \times 3 = 12 \text{ square units}
\]
Practical Exercises
Here are some exercises to help students practice:
- Draw a rectangle on the grid with a perimeter of 16 units. Find its dimensions and area.
- Draw different shapes (rectangles, squares, triangles) on a grid and calculate their perimeter and area.
- Compare shapes: Draw two different shapes with the same area but different perimeters, and discuss the differences.
Using Variable Scales
In some cases, grids may have different scales. For example, one square might represent 2 units instead of 1. In such cases:
- Determine the scale of the grid (e.g., 1 square = 2 units).
- Calculate the perimeter and area using the scale.
For a rectangle with a length of 3 squares and a width of 2 squares on a grid where each square represents 2 units, the calculations are:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (3 \times 2 + 2 \times 2) = 2 \times (6 + 4) = 2 \times 10 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
\[
\text{Area} = (3 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) = 6 \times 4 = 24 \text{ square units}
\]
Conclusion
Using grids to calculate area and perimeter is an effective visual method that helps students grasp these concepts more concretely. Through various exercises and examples, students can build a solid understanding and improve their math skills.
Real-Life Applications
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is not only fundamental in mathematics but also essential in various real-life scenarios. Below are some practical applications where these concepts are widely used:
- Construction of Homes and Buildings: During the planning and building phase, precise measurements of area and perimeter are crucial. This includes calculating the area for flooring, painting walls, and determining the perimeter for fencing or boundary walls.
- Landscaping: When designing gardens, parks, or outdoor spaces, landscapers use area and perimeter to plan out flower beds, lawns, and walkways efficiently.
- Buying and Selling Property: Real estate transactions often involve calculations of the area to determine property prices, especially for residential and agricultural lands.
- Construction of Roads and Bridges: Engineers use area and perimeter calculations to design roads and bridges, ensuring they fit within specific land areas and maintaining structural integrity.
- Interior Design: Interior designers calculate the area of rooms to choose the right amount of materials such as tiles, carpets, or wallpaper, and determine the perimeter for moldings and borders.
- Fashion and Art: In fashion design, measurements of area and perimeter help in creating patterns for clothing and accessories. Artists use these concepts to plan their canvases and artwork layouts.
- Agriculture: Farmers use area measurements to plan crop layouts, ensuring efficient use of land and resources. They also calculate the perimeter for fencing their fields to protect crops from animals.
These applications demonstrate the importance of learning area and perimeter, highlighting how these mathematical concepts play a vital role in various fields and everyday activities.

Fun Activities and Games
Engaging students with fun activities and games helps reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter in a memorable way. Here are some exciting ideas:
- LEGO Bricks: Use LEGO bricks to build various shapes and structures. Students can calculate the area and perimeter of their creations. This hands-on activity promotes strategic thinking and problem-solving.
- Singing Songs: Introduce catchy songs about area and perimeter to help students remember key concepts and formulas. Music can make learning more enjoyable and memorable.
- Block Letter Names: Have students draw their names on grid paper, then calculate the area and perimeter of each letter. This activity combines creativity with mathematical calculations.
- Floor Tiles: Create shapes on the floor using painter's tape and have students calculate the area and perimeter. They can also create their own shapes for others to solve.
- Pentominoes: Using Tetris-like pentomino blocks, students can trace shapes on grid paper and calculate their area and perimeter. This activity is great for understanding irregular shapes.
- Kite Building: Students can design and build kites, then measure and calculate the area and perimeter of their designs. This activity integrates math with a fun outdoor activity.
- Interior Design: Challenge students to design a room layout with furniture, ensuring all items fit within the given area and perimeter constraints. This real-life application shows practical uses of math.
- City Building: Students work together to create a miniature city, calculating the area and perimeter of each building. This collaborative project incorporates volume and teamwork.
- Island Conquer: In this game, students plot rectangles (islands) on a grid and calculate their area and perimeter. The player with the most island area wins.
- Food Shapes: Use snacks like cheese crackers or marshmallows to form different shapes. Students can calculate the area and perimeter of their edible creations, making learning tasty and fun.
- School Scavenger Hunt: Create various shapes with painter's tape around the school and organize a scavenger hunt where students solve area and perimeter problems to find clues.
These activities not only make learning about area and perimeter fun but also help students see the practical applications of these mathematical concepts in real-life situations.
Answer Keys and Explanations
Providing clear and detailed answer keys and explanations for area and perimeter worksheets is essential for helping students understand and learn from their mistakes. Below are the steps and strategies used in solving typical area and perimeter problems, along with example answers.
Steps for Solving Area and Perimeter Problems
- Identify the Shape:
Determine the type of shape (e.g., square, rectangle, triangle) to use the correct formulas.
- Measure Dimensions:
Measure or note down the necessary dimensions such as length, width, base, and height.
- Apply Formulas:
- For the area of a rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- For the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
- For the area of a triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- For the perimeter of a triangle: \( P = \text{side1} + \text{side2} + \text{side3} \)
- Calculate:
Perform the calculations using the formulas and the dimensions provided.
- Verify:
Double-check the calculations to ensure accuracy.
Example Problems and Solutions
Here are some example problems with step-by-step solutions:
Example 1: Rectangle
| Given: | Length = 8 cm, Width = 5 cm |
| Area Calculation: | \( A = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 40 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
| Perimeter Calculation: | \( P = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 26 \, \text{cm} \) |
Example 2: Triangle
| Given: | Base = 10 cm, Height = 6 cm, Side1 = 10 cm, Side2 = 8 cm, Side3 = 6 cm |
| Area Calculation: | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \, \text{cm} \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 30 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
| Perimeter Calculation: | \( P = 10 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm} \) |
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Misidentifying Shapes:
Ensure that students correctly identify the shape before applying formulas.
- Incorrect Measurements:
Double-check measurements to avoid errors in calculations.
- Formula Misapplication:
Remind students to use the appropriate formula for each shape and context.
- Arithmetic Errors:
Encourage students to re-calculate to catch any arithmetic mistakes.
Teacher Resources
Teaching area and perimeter to grade 4 students can be engaging and effective with the right resources and strategies. Here are some helpful tools and activities for teachers:
Interactive Activities
- Math Mosaics: Use square sticky notes to create mosaics on a grid. Have students calculate the area and perimeter of their designs. This hands-on activity combines creativity with math practice.
- LEGO Bricks: Utilize LEGO bricks to teach area and perimeter. Students can build shapes and calculate their dimensions, making learning fun and interactive.
- Floor Tiles: Use blue painter's tape on square floor tiles to create shapes. Students can then measure and calculate the area and perimeter of each shape.
Real-Life Examples
- Interior Design Project: Have students design a room layout on grid paper, placing furniture and calculating the area and perimeter of each piece to ensure everything fits.
- Building a City: Create a class project where students build a miniature city with buildings. They calculate the area and perimeter of each building, integrating volume for a comprehensive learning experience.
- Island Conquer Game: This game involves plotting rectangles on a grid to create "islands" and calculating their area and perimeter. The student with the most area wins.
Printables and Worksheets
Provide students with worksheets that cover various aspects of area and perimeter. Here are some types of exercises:
- Basic Calculations: Worksheets that require students to calculate the area and perimeter of simple shapes like rectangles and squares.
- Irregular Shapes: Activities that involve finding the area and perimeter of more complex, irregular shapes to challenge students' problem-solving skills.
- Volume Introduction: As students become comfortable with area and perimeter, introduce the concept of volume with activities that require calculating the volume of rectangular prisms.
Visual Aids and Tools
Incorporate visual aids to enhance understanding:
- Grid Paper: Use grid paper for drawing shapes and calculating their dimensions, helping students visualize the concepts.
- Charts and Diagrams: Display charts that explain the formulas for area, perimeter, and volume, providing a quick reference for students.
Helpful Tips
- Relate to Real Life: Show students how these concepts apply to everyday situations, like measuring rooms for furniture or designing a garden layout.
- Use Technology: Incorporate educational apps and online tools that provide interactive exercises and instant feedback.
- Engage with Projects: Encourage students to take on projects that involve designing, measuring, and calculating to reinforce their learning.
Professional Development
Stay updated with the latest teaching strategies by participating in professional development workshops and webinars focused on mathematics education. Networking with other educators can provide new insights and ideas for teaching area and perimeter effectively.
By using these resources and strategies, teachers can create a dynamic and engaging learning environment that helps students master the concepts of area, perimeter, and volume.
Home Practice Tips
Practicing area and perimeter problems at home can be both fun and educational for fourth graders. Here are some practical tips to help students improve their skills:
- Create a Study Schedule: Set aside a specific time each day for math practice. Consistency helps reinforce learning.
- Use Everyday Objects: Measure the perimeter and area of household items like books, tables, or rooms to make learning more relatable.
- Interactive Games: Incorporate math games and apps that focus on area and perimeter. These can make learning more engaging.
- Practice with Worksheets: Print or create worksheets that offer a variety of problems, from basic to advanced, to keep the practice challenging.
- Math Journals: Encourage students to keep a math journal where they can solve problems and write down strategies and solutions.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to quiz students on key concepts and formulas related to area and perimeter.
- Real-Life Scenarios: Pose real-life problems, such as planning a garden or arranging furniture, that require calculating area and perimeter.
- Reward System: Set up a reward system to motivate students. Rewards can be as simple as stickers or extra playtime.
- Group Study: Organize study groups where students can work on problems together, discuss strategies, and learn from each other.
- Parental Involvement: Parents should participate in the learning process by helping with homework and providing additional practice problems.
By incorporating these tips into their daily routine, students can enhance their understanding of area and perimeter, making math practice at home both effective and enjoyable.

Conclusion
Understanding and mastering the concepts of area and perimeter are crucial components of a Grade 4 math curriculum. These concepts not only help students improve their mathematical skills but also prepare them for real-world applications. By practicing with a variety of worksheets, students can reinforce their knowledge and gain confidence in solving problems related to area and perimeter.
The use of visually appealing worksheets that allow students to work at their own pace is highly beneficial. These worksheets often include a range of problems, from basic calculations to more complex word problems, ensuring that students can gradually build their skills. Additionally, incorporating real-life examples and practical applications into the worksheets can make learning more engaging and relevant for students.
In conclusion, Grade 4 area and perimeter worksheets are essential tools for both teachers and students. They provide a structured approach to learning, offer ample practice opportunities, and help students develop a deeper understanding of these fundamental math concepts. By using these worksheets consistently, students can achieve better results in their exams and gain valuable skills that will benefit them in their academic journey and beyond.
Bài Hát Về Diện Tích Và Chu Vi Cho Trẻ Em | Lớp 3 - 4
READ MORE:
Tìm Chu Vi Và Diện Tích Của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán Học Với Thầy J