Topic find the perimeter of a trapezoid: Discover the essentials of geometry with our guide on how to find the perimeter of a trapezoid. This article offers a straightforward approach, making it easy for learners of all levels to grasp this fundamental concept.
Table of Content
- Definition and Basic Concept of Trapezoid
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Trapezoid
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter of a Trapezoid
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Questions and Misconceptions
- Advanced Calculations: Using Angles and Height for Perimeter
- Tools and Calculators for Finding Trapezoid Perimeter
- Applications of Trapezoid Perimeter in Real Life
- Additional Resources for Geometry Learning
Definition and Basic Concept of Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a four-sided figure, known in geometry as a quadrilateral. It is unique because it has at least one pair of parallel sides, referred to as the bases. The other two sides, which are non-parallel, are known as the legs of the trapezoid. The lengths of these sides play a crucial role in determining the trapezoid\"s perimeter.
- Parallel Sides: These are the two sides of a trapezoid that run parallel to each other. In different trapezoids, these can vary in length, contributing to the shape\"s diversity.
- Non-Parallel Sides: The sides of a trapezoid that are not parallel to each other. They can be of equal or unequal lengths.
- Angles: The interior angles in a trapezoid add up to 360 degrees. The angles adjacent to the same leg are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
Trapezoids can be classified into various types based on the lengths of their sides and angles. The most common types are the isosceles trapezoid, which has equal non-parallel sides and angles, and the right trapezoid, with one pair of right angles.
Understanding the basic structure and properties of a trapezoid is essential for various applications in geometry, such as calculating area and perimeter, which are vital in fields ranging from architecture to engineering.

READ MORE:
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Trapezoid
\"Discover the beauty of your local area through breathtaking aerial shots and ground-level exploration. Watch our mesmerizing video and let us guide you on a journey of uncovering hidden gems and remarkable natural landscapes in your very own neighborhood.\"
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Right Trapezoid
\"Unravel the mysteries of the right trapezoid with our comprehensive video tutorial. Master the concepts with clear explanations and step-by-step examples, as we guide you through the properties and formulae associated with this fascinating geometric shape.\"
Formula for Calculating Perimeter of a Trapezoid
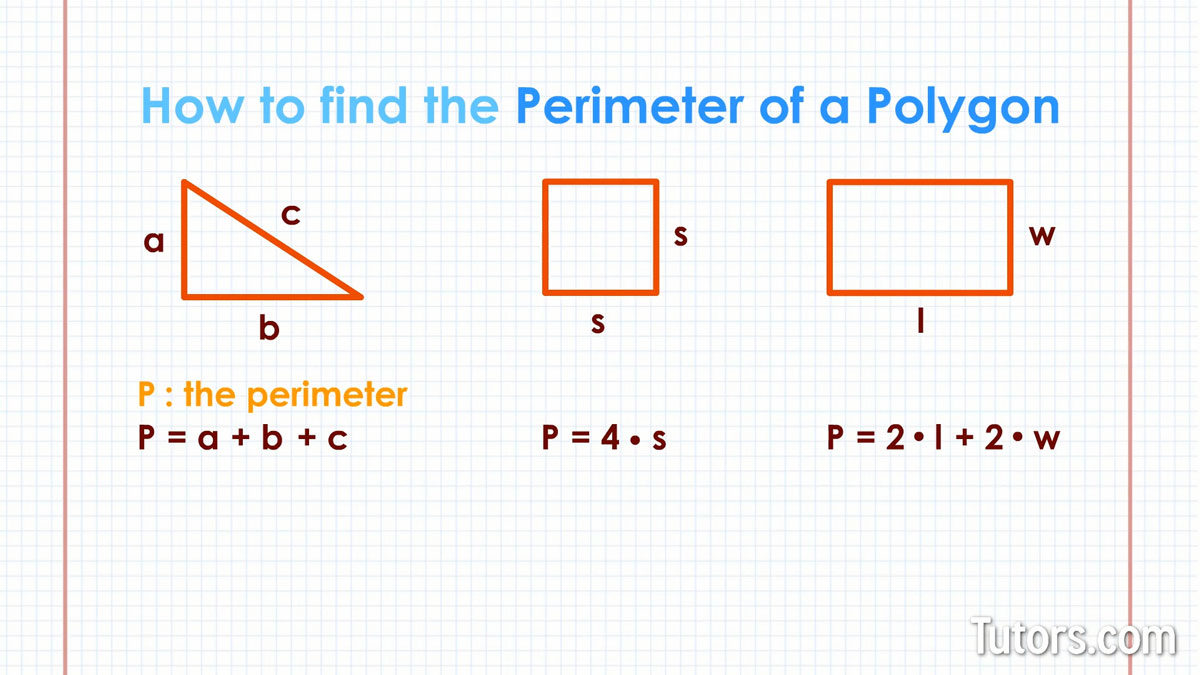
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total distance around its four sides. To calculate this, we use a simple formula:
P = a + b + c + d
- a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides (bases).
- c and d are the lengths of the non-parallel sides (legs).
Understanding this formula is crucial for solving many geometry problems. For instance, if you have a trapezoid with bases of 5 units and 10 units, and non-parallel sides of 3 units and 7 units, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
P = 5 + 10 + 3 + 7 = 25 units
This formula remains the same regardless of the unit of measurement used, as long as the same unit is consistently applied to all sides. The calculator tools available online can assist in quickly finding the perimeter by inputting the side lengths.
It\"s important to note that while the trapezoid is a four-sided figure with two parallel sides, the lengths of these sides can vary, affecting the shape and perimeter of the trapezoid. This formula provides a straightforward method for perimeter calculation, applicable in various contexts, from academic problems to real-world applications in fields like architecture and engineering.
Determining the Perimeter and Area of a Trapezoid
\"Unlock the secrets of determining the unknown with our enlightening video. Gain valuable insights and practical tips on how to approach and solve complex problems, as we help you sharpen your problem-solving skills and boost your confidence in tackling any challenge.\"
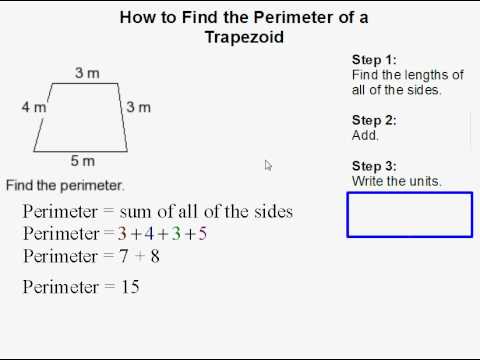
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the Sides: First, identify the lengths of the four sides of the trapezoid. Remember, a trapezoid has two parallel sides (bases) and two non-parallel sides (legs).
- Measure the Sides: If not already given, measure the lengths of the bases and legs. It\"s important to use the same unit of measurement for all sides.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula P = a + b + c + d, where \"P\" represents the perimeter, \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the bases, and \"c\" and \"d\" are the lengths of the legs.
- Add the Lengths: Add together the lengths of the four sides. For example, if the sides are 10, 6, 8, and 9 meters, the perimeter would be 10 + 6 + 8 + 9 = 33 meters.
- Consider Special Cases: In some cases, you might not have all the side lengths. You may need to use other properties of the trapezoid, like its height and angles, to calculate missing side lengths before finding the perimeter.
- Verify the Calculation: Double-check your calculations for accuracy. Using an online calculator can also be helpful for verification.
Understanding the process of calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid is crucial, as it provides a foundational knowledge in geometry that\"s applicable in various real-life scenarios.

Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid is essential in geometry. Here are some examples and practice problems to help you master this concept.
Basic Examples
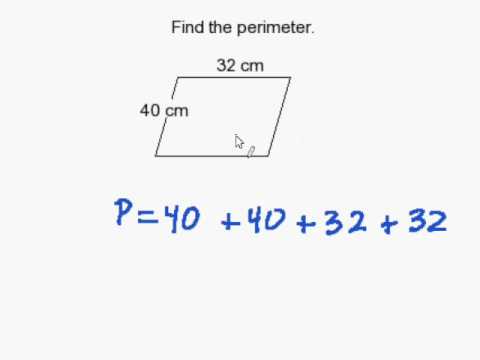
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides 10 meters, 6 meters, 8 meters, and 9 meters.
- Solution: Add all the side lengths: Perimeter = 10 + 6 + 8 + 9 = 33 meters.
- Example 2: Calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid where the sum of the non-parallel sides is 12 units and the sum of the parallel sides is 8 units.
- Solution: Perimeter = Sum of non-parallel sides + Sum of parallel sides = 12 units + 8 units = 20 units.
Advanced Problems
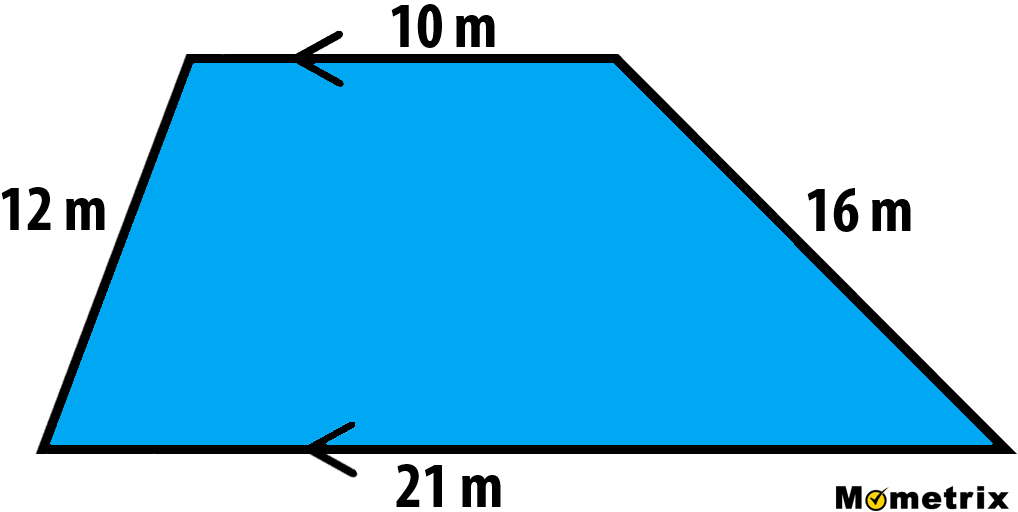
- Example 3: Find the perimeter of a trapezoid ABCD with sides AB = 120 m, DE = 50 m, EF = 120 m, FC = 80 m, and BF = 90 m, considering missing sides.
- Use the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the missing sides AD and BC.
- Once all sides are known, add them to find the perimeter.
- Example 4: Calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid given the coordinates of its vertices in a coordinate plane.
- Use coordinate geometry techniques to find the lengths of all sides.
- Add these lengths to find the perimeter.
Practice Problems
Now, try these problems on your own to practice finding the perimeter of trapezoids:
- Find the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides of 15 m, 7 m, 10 m, and 12 m.
- Calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid where the parallel sides are 18 units and 22 units, and the non-parallel sides are both 15 units.
- A trapezoid has a perimeter of 40 units, with three sides measuring 8 units, 10 units, and 12 units. Find the length of the fourth side.
Common Questions and Misconceptions
This section addresses some of the common questions and misconceptions about the perimeter of trapezoids to enhance your understanding of this geometrical concept.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How is the perimeter of a trapezoid calculated? - The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total distance around its edge, calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Can the Pythagorean theorem be used in calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid? - Yes, it can be used to find the lengths of missing sides when other dimensions are known, which are then summed to find the perimeter.
- What are the different types of trapezoids? - Trapezoids can be classified as isosceles, scalene, or right trapezoids, based on their side lengths and angles.
Common Misconceptions
- All Sides of a Trapezoid are Equal: - This is not true; only in an isosceles trapezoid are the non-parallel sides equal.
- Area and Perimeter are Measured the Same Way: - The perimeter is measured in linear units (like meters), while the area is measured in square units (like square meters).
- Trapezoid and Parallelogram are the Same: - A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides, whereas a parallelogram has two pairs of parallel sides.

_HOOK_
Advanced Calculations: Using Angles and Height for Perimeter
When the dimensions of a trapezoid are not directly given, we can still calculate its perimeter using angles and height. This section explores such advanced calculation methods.
Using Angles and Height
To find the perimeter of a trapezoid when angles and one base are known, we can use trigonometric functions and the Pythagorean theorem. This method involves calculating the height and the projections of the non-parallel sides on the base.
Example:
- Given a trapezoid with one base (a), two angles (α and δ), and the lengths of the non-parallel sides (c and d), first calculate the height (h) using the sine function: h = c * sin(α).
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the projections of the sides on the base.
- Calculate the length of the other base and use the formula for the perimeter: P = a + b + c + d.
Using the Height and a Side
If the height and lengths of one of the non-parallel sides are known, we can use similar triangles and trigonometric identities to find missing sides and thus calculate the perimeter.
Steps for Calculation:
- Determine the height of the trapezoid using perpendicular lines from the bases.
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem in the formed right triangles to find the lengths of the missing sides.
- Add up the lengths of all sides for the perimeter.
Note: The above methods require a basic understanding of trigonometry and the Pythagorean theorem. In cases of right trapezoids, the height is simply the leg adjacent to the right angle.

Tools and Calculators for Finding Trapezoid Perimeter
There are various online tools and calculators available to help you easily determine the perimeter of a trapezoid. These calculators are particularly useful when you have specific measurements like sides, angles, or height and need to calculate the perimeter accurately.
Popular Trapezoid Perimeter Calculators
- Omnicalculator Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator: This tool allows you to input the lengths of each side of the trapezoid or a combination of sides, angles, or height to calculate the perimeter. It also has an advanced mode for more complex calculations involving angles and height.
- Owlcalculator Trapezoid Perimeter Calculator: A user-friendly calculator where you enter the lengths of the parallel sides and the non-parallel sides to get the perimeter. It automatically computes the perimeter based on the input values.
- HelpingWithMath Trapezoid Calculator: This calculator not only helps find the perimeter but also offers insights into calculating the area of a trapezoid. It is useful for educational purposes.
- BYJU\"S Trapezoid Calculator: Known for its educational tools, BYJU\"S offers a simple and efficient trapezoid perimeter calculator.
- MathPortal Trapezoid Calculator: This calculator is comprehensive, showing all the steps involved in the calculation, which can be particularly educational for students learning geometry.
- Easyerra Trapezoid Calculator: This tool simplifies the calculation of the trapezoid\"s perimeter, area, diagonal, and angles, making it a versatile option for various geometrical calculations.
These calculators are beneficial for students, teachers, and professionals who deal with geometrical calculations in their work or studies. They simplify the process, ensuring accuracy and saving time.

Applications of Trapezoid Perimeter in Real Life
Trapezoids, with their unique geometric properties, find applications in various real-life scenarios. Understanding the perimeter of a trapezoid enhances our appreciation of its practical uses in diverse fields.
Architecture and Construction
In architecture, the trapezoidal shape is often used in the design of roofs. Its distinctive shape offers efficient water drainage and structural stability, making it ideal for sloped and gabled roofs.
Engineering and Structural Design
Trapezoids play a crucial role in engineering, particularly in bridge and truss construction. Their load-bearing capacity and stability are essential for supporting heavy loads and distributing forces.
Graphics and Computer Modeling
In computer graphics and modeling, trapezoids aid in rendering 2D shapes and creating visual effects, forming the basis for various algorithms in computer-aided design and animation.
Art and Design
Trapezoidal shapes inspire artistic expression, being used in graphic design to create dynamic compositions that convey movement and balance.
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, trapezoidal profiles are common in conveyor belts and timing belts, where their shape ensures a secure grip and efficient motion transfer.
Surveying and Land Measurement
Surveyors often use trapezoidal calculations to accurately measure land areas, especially in plots with irregular shapes.
Everyday Objects
Many everyday objects have trapezoidal shapes, such as glasses, lamps, flowerpots, and handbags, illustrating the geometric figure\"s prevalence in our daily lives.
Mathematics and Geometry Education
Studying trapezoids in geometry helps students understand fundamental concepts such as parallel lines, angles, and quadrilaterals, enhancing their mathematical knowledge.
Physics and Mechanics
In physics and mechanics, trapezoidal configurations are seen in pulley systems, where trapezoidal belts or chains are used for efficient power transmission.
Pattern Making and Sewing
In garment design, trapezoidal patterns are often used to shape and fit clothing to different body contours, such as in sleeves and skirts.
Finance and Economics
The trapezoidal rule is a mathematical method used in finance for estimating the area under a curve, which assists in financial calculations like option pricing or risk measurement.

READ MORE:
Additional Resources for Geometry Learning
Exploring geometry can be both fascinating and enriching. To assist in this journey, a variety of online resources are available, catering to different learning styles and levels. Whether you are a student, educator, or simply someone interested in mathematics, these resources offer a wealth of information and interactive experiences to enhance your understanding of geometry.
Comprehensive Courses and Lessons
- Khan Academy: Offers a broad range of geometry topics with interactive lessons and practice exercises.
- Mathigon: Known as \"The Mathematical Playground\", it provides an engaging and interactive approach to learning geometry.
- School Yourself: Features free online lessons in geometry, offering an interactive, personalized learning experience.
Interactive Learning and Practice
- Edutopia: Recommends various math apps and online tools that include geometry-related activities, suitable for different grade levels.
- SplashLearn: Offers interactive learning resources in geometry, making the subject easy and fun for children.
Advanced Learning Platforms
- edX: Provides online courses in geometry that can advance professional skills in various fields.
- Lessonface: Offers access to online teachers for one-on-one geometry learning sessions.
- Study.com: Features comprehensive geometry courses, including crash courses and nano-degree programs.
Specialized Geometry Education
- DoodleLearning: Includes resources for parents, teachers, and students, focusing on geometry for K-5 students.
- Art of Problem Solving: Offers math classes for different school levels, with a focus on problem-solving in geometry.
- Mathplanet: A free online platform providing video classes, written content, and exercises in geometry.
Each of these resources offers unique approaches to learning geometry, from foundational concepts to advanced applications. By exploring these platforms, you can deepen your understanding and appreciation of this fundamental area of mathematics.
Discovering the perimeter of a trapezoid opens doors to a fascinating world of geometry, blending practical applications with mathematical intrigue. Join us in unraveling this geometric mystery and enhancing your mathematical journey!