Topic finding perimeter of a triangle: Discover the art of finding the perimeter of a triangle - a fundamental yet fascinating aspect of geometry that combines simplicity with practicality, unlocking a world of mathematical and real-world applications.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Basic Perimeter Formula
- YOUTUBE: How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Special Triangle Cases: Isosceles, Equilateral, and Right Triangles
- Advanced Perimeter Calculations: SAS and ASA Triangles
- Real-World Applications: Gardens, Fences, and More
- Triangle Perimeter with Algebra: Solving for Unknown Sides
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions in Calculating Perimeter
- Interactive Learning: Quizzes and Practice Problems
Understanding the Basic Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the edge of the triangular shape. It\"s a fundamental concept in geometry, essential in various fields such as construction, design, and even daily life calculations. The formula for finding the perimeter of any triangle is straightforward:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c
where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" represent the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
- Step 1: Measure or obtain the length of each side of the triangle.
- Step 2: Add these lengths together.
- Example: For a triangle with sides 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, the perimeter is 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 cm.
This basic formula applies to all types of triangles, whether they are scalene (with all sides of different lengths), isosceles (two sides of equal length), or equilateral (all sides equal).
- In an Equilateral Triangle, where all sides are equal (let\"s say each side is \"s\"), the perimeter formula simplifies to: P = 3s.
- For an Isosceles Triangle, with two equal sides (each of length \"l\") and the base \"b\", the formula is: P = 2l + b.
- In a Scalene Triangle, where all sides have different lengths, use the basic formula without simplification.
Understanding these variations is crucial for correctly calculating the perimeter in different scenarios, ensuring accuracy whether in academic problems or real-life applications.

READ MORE:
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Discover the fascinating world of perimeter as we explore its importance in various shapes and objects. Watch our captivating video to unravel the secrets of perimeter and how it influences the sizing and measurement of everyday items.\"
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Join us on an exciting journey into the world of triangles and unlock the mysteries behind their unique properties. Our engaging video takes you through the different types of triangles and their significance, leaving you with a newfound appreciation for these fundamental shapes.\"
How to Find the Area and Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Unleash your inner mathematician and explore the concept of area like never before! Our captivating video will guide you through a visual adventure, explaining the relevance and applications of area in everyday life. Get ready to see the world through the lens of area and be amazed!\"
Special Triangle Cases: Isosceles, Equilateral, and Right Triangles
While the general formula for the perimeter of a triangle is applicable to all types, certain types of triangles – isosceles, equilateral, and right triangles – have unique properties that simplify the calculation.
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The perimeter formula for an isosceles triangle is:
P = 2l + b
where \"l\" is the length of the equal sides and \"b\" is the base or the unequal side length.
- Step 1: Measure the lengths of the equal sides and the base.
- Step 2: Apply the formula: P = 2l + b.
Equilateral Triangle
All sides of an equilateral triangle are of equal length. Its perimeter formula is particularly simple:
P = 3s
where \"s\" is the length of one side.
- Example: If each side of an equilateral triangle measures 4 cm, the perimeter would be 3 * 4 = 12 cm.
Right Triangle
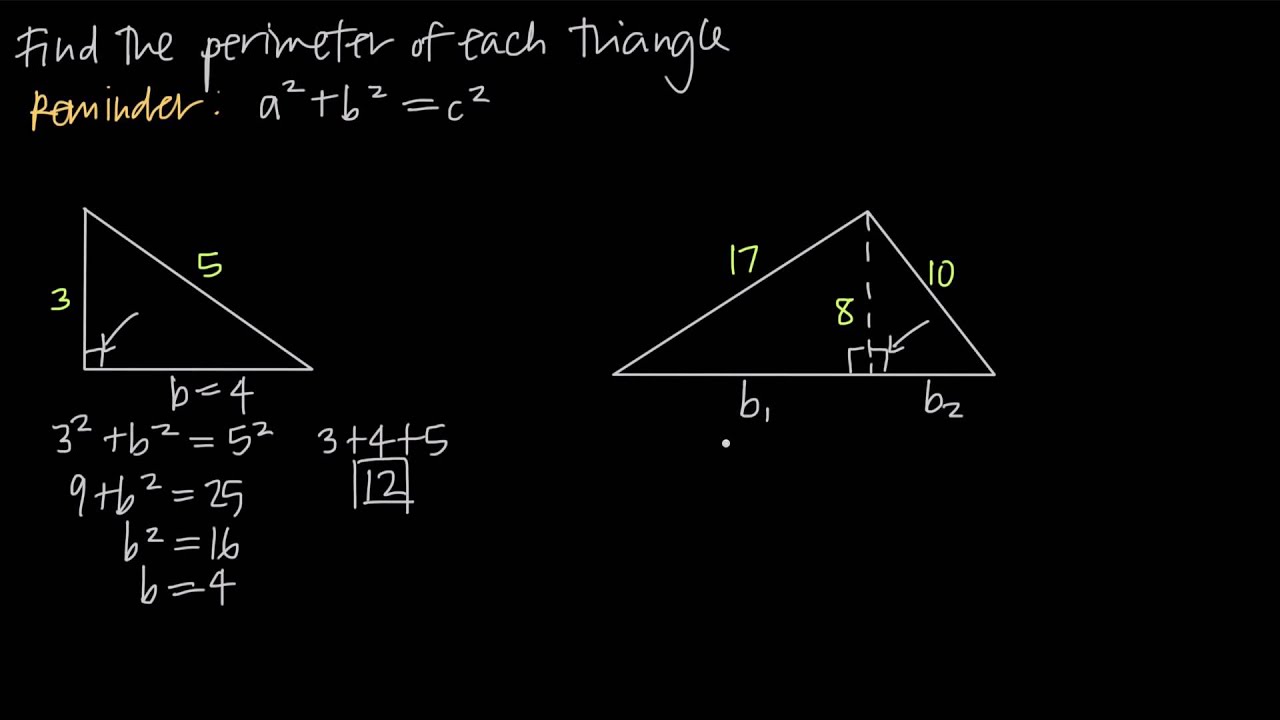
A right triangle has one 90-degree angle. The perimeter is the sum of the two legs and the hypotenuse. If the lengths of the legs are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the hypotenuse:
h² = a² + b²
where \"h\" is the hypotenuse, and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- Step 1: Measure or calculate the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse.
- Step 2: Add these three lengths to find the perimeter.
These specific formulas are invaluable for efficiently solving problems related to the perimeters of these special types of triangles.

Advanced Perimeter Calculations: SAS and ASA Triangles
While the general formula for the perimeter of a triangle is applicable to all types, certain types of triangles – isosceles, equilateral, and right triangles – have unique properties that simplify the calculation.
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The perimeter formula for an isosceles triangle is:
P = 2l + b
where \"l\" is the length of the equal sides and \"b\" is the base or the unequal side length.
- Step 1: Measure the lengths of the equal sides and the base.
- Step 2: Apply the formula: P = 2l + b.
Equilateral Triangle
All sides of an equilateral triangle are of equal length. Its perimeter formula is particularly simple:
P = 3s
where \"s\" is the length of one side.
- Example: If each side of an equilateral triangle measures 4 cm, the perimeter would be 3 * 4 = 12 cm.
Right Triangle
A right triangle has one 90-degree angle. The perimeter is the sum of the two legs and the hypotenuse. If the lengths of the legs are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the hypotenuse:
h² = a² + b²
where \"h\" is the hypotenuse, and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- Step 1: Measure or calculate the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse.
- Step 2: Add these three lengths to find the perimeter.
These specific formulas are invaluable for efficiently solving problems related to the perimeters of these special types of triangles.

Real-World Applications: Gardens, Fences, and More
While the general formula for the perimeter of a triangle is applicable to all types, certain types of triangles – isosceles, equilateral, and right triangles – have unique properties that simplify the calculation.
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The perimeter formula for an isosceles triangle is:
P = 2l + b
where \"l\" is the length of the equal sides and \"b\" is the base or the unequal side length.
- Step 1: Measure the lengths of the equal sides and the base.
- Step 2: Apply the formula: P = 2l + b.
Equilateral Triangle
All sides of an equilateral triangle are of equal length. Its perimeter formula is particularly simple:
P = 3s
where \"s\" is the length of one side.
- Example: If each side of an equilateral triangle measures 4 cm, the perimeter would be 3 * 4 = 12 cm.
Right Triangle
A right triangle has one 90-degree angle. The perimeter is the sum of the two legs and the hypotenuse. If the lengths of the legs are known, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the hypotenuse:
h² = a² + b²
where \"h\" is the hypotenuse, and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- Step 1: Measure or calculate the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse.
- Step 2: Add these three lengths to find the perimeter.
These specific formulas are invaluable for efficiently solving problems related to the perimeters of these special types of triangles.

Triangle Perimeter with Algebra: Solving for Unknown Sides
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its side lengths. In algebraic terms, if a triangle has sides of lengths a, b, and c, then its perimeter P is given by P = a + b + c. This basic formula is foundational in geometry and forms the basis for more complex calculations, especially when dealing with triangles where not all side lengths are known.
Calculating Perimeter with Known Side Lengths
For a triangle with known side lengths, simply add the lengths of all three sides. For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 5 cm, 4 cm, and 2 cm, its perimeter is calculated as 5 + 4 + 2 = 11 cm.
Finding Unknown Sides
To find unknown side lengths of a triangle when the perimeter is known, algebra is used. Consider the following scenarios:
- Isosceles Triangle: In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length. If the perimeter (P) and base (b) are known, the length of each equal side (l) can be found using the formula P = 2l + b.
- Right Triangle: For right triangles, the Pythagorean theorem is often used. If two sides are known, the third side can be found using the theorem and then added to find the perimeter.
- Scalene Triangle: In scalene triangles, where all sides are of different lengths, algebraic methods such as simultaneous equations or properties of triangle types are used to find the missing lengths.
Consider an example of a right triangle with a base of 3 cm and height of 4 cm. First, calculate the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem: h = √(3² + 4²) = 5 cm. Then, the perimeter is the sum of all sides: 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 cm.
Advanced Techniques
In more complex cases, such as triangles with sides partially unknown or defined in terms of variables, algebraic techniques become essential. Equations are set up based on the known elements and solved to find the unknown lengths. This often involves solving linear or quadratic equations.
Practical Applications
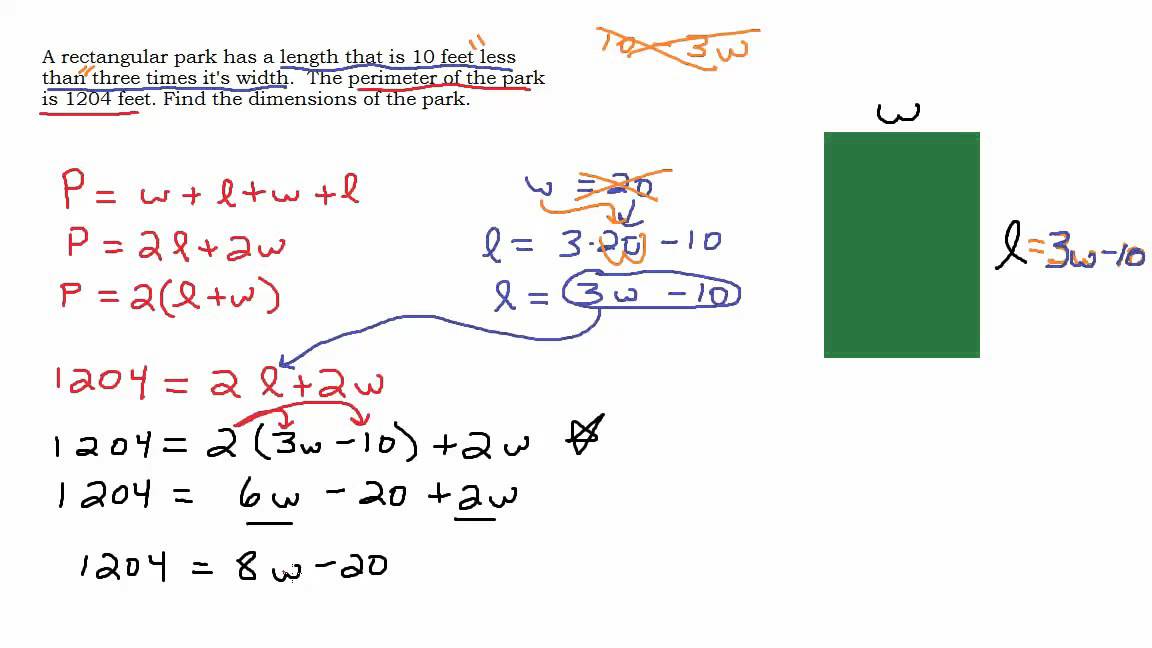
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of triangles with unknown sides is not just an academic exercise. It has practical applications in fields like engineering, architecture, and various forms of design, where dimensions of components are often interdependent.
By mastering these techniques, one can confidently tackle a wide range of geometric problems, enhancing both theoretical understanding and practical problem-solving skills.

_HOOK_
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions in Calculating Perimeter
When learning how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle, there are some common mistakes and misconceptions that can lead to incorrect answers. Understanding these can help avoid errors and increase accuracy in calculations.
- Mistake: Confusing Perimeter with Area: A frequent error is mixing up the concepts of perimeter and area. Perimeter refers to the total distance around the triangle, a one-dimensional measure, whereas area refers to the space enclosed within the triangle, a two-dimensional measure.
- Misconception: Order of Adding Sides Matters: Some might think that the order in which the sides are added affects the perimeter. However, due to the commutative property of addition, the order does not matter as long as each side is accounted for once.
- Mistake: Inconsistent Units: Using different units for sides of the triangle is a common error. Before adding the lengths, ensure all measurements are converted to the same unit.
- Misconception: Complex Calculations for Equal Sides: In cases of equilateral triangles, where all sides are equal, the perimeter can be simply calculated by multiplying the length of one side by three. This is often overlooked, leading to unnecessary calculations.
- Mistake: Incorrect Application of Formulas: Misusing formulas, especially in special triangles (isosceles, equilateral, right), is common. For example, not correctly applying the Pythagorean theorem in right triangles can lead to wrong perimeter values.
- Misconception: Perimeter Depends on Triangle Type: While the formula to find the perimeter (sum of all sides) is the same for all triangles, the approach to find missing sides may vary. This does not imply that the basic perimeter formula changes with the triangle type.
- Mistake: Overlooking Triangle Properties: In solving problems, especially those involving algebra, overlooking the properties of different types of triangles (such as the angles in an isosceles triangle) can lead to incorrect solutions.
Understanding these common mistakes and misconceptions can significantly improve proficiency in calculating the perimeter of triangles. It is important to practice different types of problems to develop a deeper understanding and avoid these errors.

READ MORE:
Interactive Learning: Quizzes and Practice Problems
Engaging with interactive learning resources can significantly enhance the understanding of how to find the perimeter of a triangle. Below are various types of interactive exercises and practice problems that can be useful for students at different levels of their learning journey.
Interactive Exercises and Examples
- Basic Perimeter Calculation: Practice finding the perimeter of triangles with given side lengths. For instance, calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides of 5 cm, 9 cm, and 11 cm. This type of problem helps in reinforcing the basic concept of perimeter as the sum of all side lengths.
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons: Some resources provide exercises for finding the perimeter of regular polygons, including equilateral triangles. This involves multiplying the number of sides by the length of one side.
Worksheets and Practice Problems
Worksheets are an excellent tool for practice and reinforcement. They can range from simple problems to more complex ones involving different types of triangles and varying units of measurement.
- Perimeter with Integers: Worksheets that focus on finding the perimeter of triangles with dimensions given as integers, suitable for grade 2 to grade 8 students.
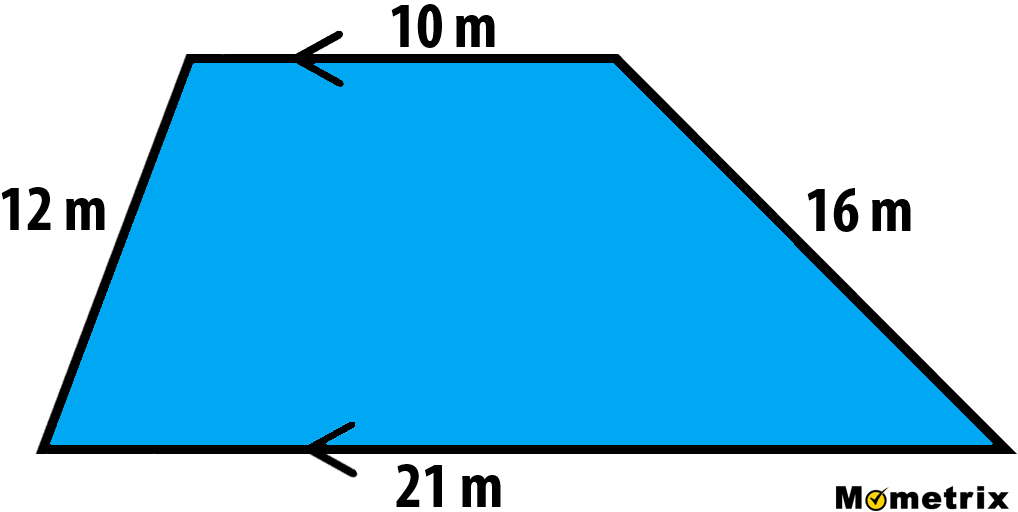
- Real-World Applications: Some worksheets include scenarios where students need to apply their understanding of perimeter to solve real-world problems.
- Decimal Dimensions: For more advanced students, worksheets that involve calculating the perimeter of triangles with decimal side lengths can be very beneficial.
Interactive Digital Activities
Digital resources offer an engaging way for students to practice finding the perimeter. These activities often include self-checking features and can be used for both individual practice and classroom teaching.
- Shape Identification: Interactive activities where students identify the shapes and calculate their perimeters. These can include triangles and other polygons.
- Real-World Examples: Engage students with perimeter calculations of shapes that they might encounter in everyday life, like parks or playgrounds.
- Classroom Integration: Digital activities that are perfect for lesson introductions or wrap-ups, helping students apply perimeter concepts in a variety of contexts.
These interactive resources, quizzes, and worksheets are invaluable for building a strong foundation in geometry, particularly in understanding and calculating the perimeter of triangles.
Discovering the perimeter of a triangle is a journey through geometry that blends practicality with intrigue. Whether you\"re a student, educator, or just a curious mind, our comprehensive guide offers the keys to unlocking this fundamental aspect of mathematics. Explore, learn, and master the art of perimeter calculations with us!