Topic find perimeter from area: Explore the intriguing world of geometry where we unravel the secrets of finding perimeter from area, a fundamental skill in mathematics and practical applications, enriching your understanding of spatial dimensions.
Table of Content
- Basic Concepts: Understanding Perimeter and Area
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example
- Calculating Perimeter and Area for Different Shapes
- Rectangle Calculations: Finding Perimeter from Area
- Square Calculations: Relationship Between Perimeter and Area
- Perimeter and Area of Complex Shapes
- Calculating Perimeter of Circle Sectors and Ellipses
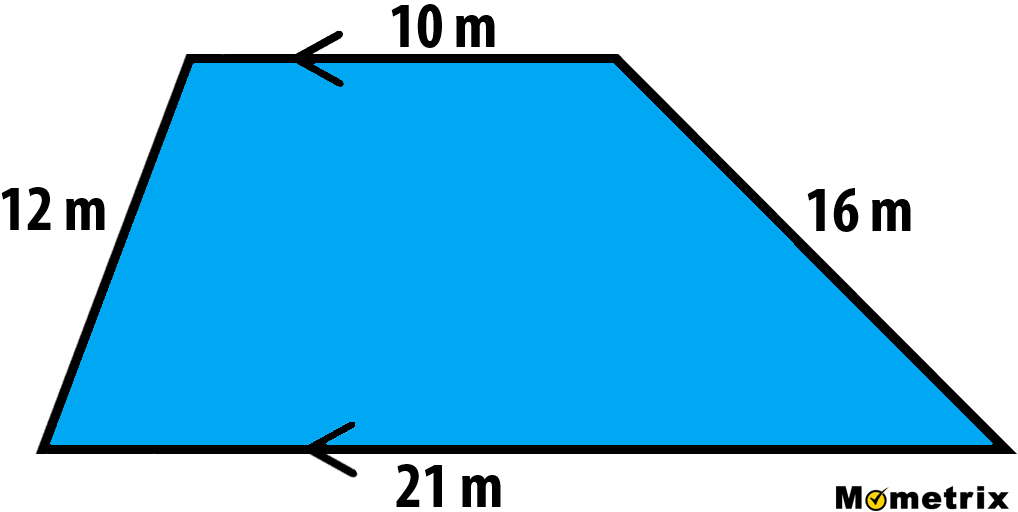
- Methods for Finding Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Practical Applications: Real-World Use of Perimeter and Area
- Advanced Topics: Reverse Calculations and Complex Figures
- Learning Resources and Tools for Perimeter and Area Calculations
Basic Concepts: Understanding Perimeter and Area
Perimeter and area are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential in various real-world applications. The perimeter of a shape refers to the total distance around its boundary, while the area represents the space occupied by the shape.
For example, in rectangles and squares, the area is calculated by multiplying the length by the width. The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of all its sides, or 2 times the sum of its length and width. In the case of a square, since all sides are equal, the perimeter is 4 times the length of one side.
When it comes to circles, the perimeter, known as the circumference, is calculated differently. The area of a circle is π times the radius squared, and the circumference is 2π times the radius. For more complex shapes like ellipses, sectors of circles, or irregular polygons, the formulas for perimeter and area become more intricate, often requiring advanced mathematical techniques.
Understanding the relationship between area and perimeter is crucial, especially when the dimensions of one aspect are used to calculate the other. This relationship, however, varies depending on the shape in question. For instance, two rectangles can have the same perimeter but different areas.
Real-life applications of these concepts are vast, ranging from calculating the amount of paint needed for a wall (area) to fencing a garden (perimeter).

READ MORE:
Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example
Discover the fascinating world of composite shapes and unleash your creativity with this captivating video! Learn how to combine different shapes to create unique and stunning designs that will leave you in awe.
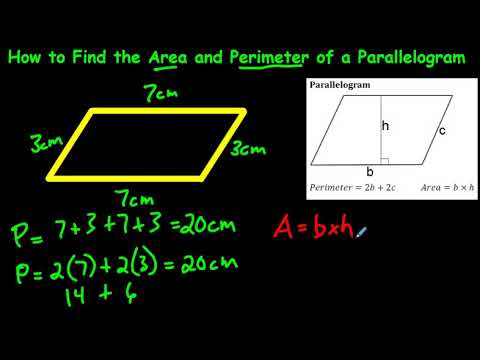
How to Find the Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle
Dive into the fundamentals of rectangles with this mesmerizing video! Explore their properties and characteristics, and unlock the secrets of their perfectly balanced proportions. Get ready to appreciate the beauty hidden within this seemingly simple shape.
Calculating Perimeter and Area for Different Shapes
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter and area of various shapes is crucial in geometry. Each shape has specific formulas for these calculations, whether they are regular or irregular shapes.
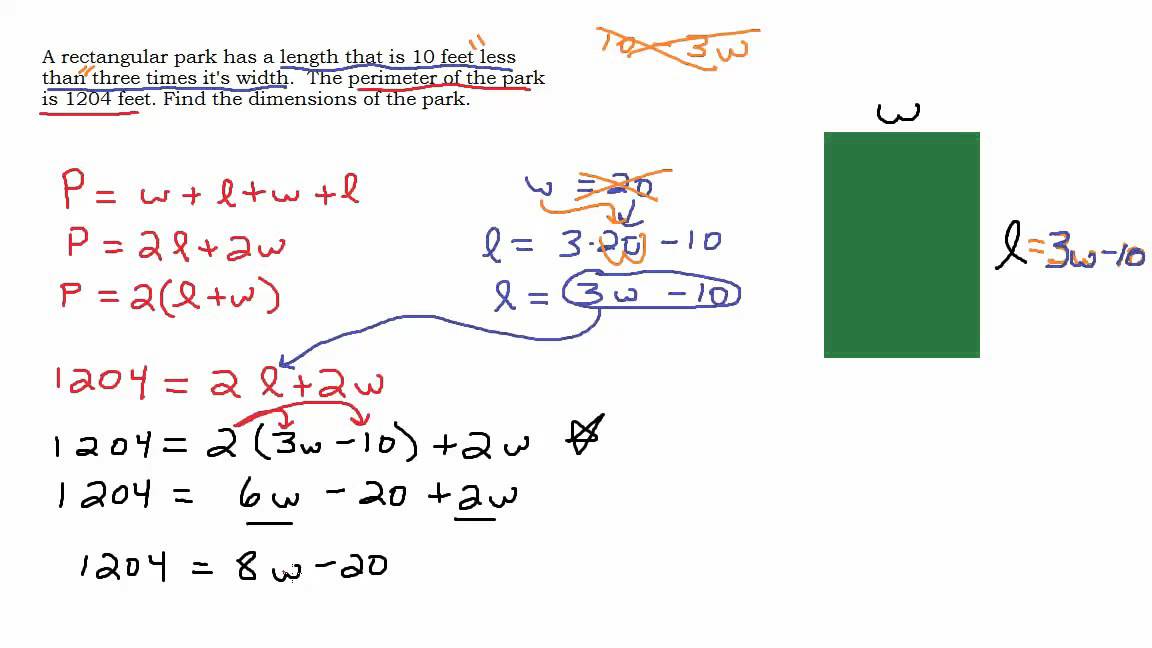
Rectangle: The area (A) of a rectangle is found by multiplying its width (w) by its length (l). Its perimeter (P) is calculated as 2 times the sum of width and length (2(w+l)). For example, if a rectangle has a width of 20 miles and an area of 500 square miles, its length would be 25 miles, leading to a perimeter of 90 miles.
Circle: The area of a circle is π times the radius squared (πr²), and the perimeter, known as the circumference, is 2π times the radius (2πr). For instance, a circle with an area of 1,000 km² would have a circumference of approximately 112.07 km.
Square: In a square, since all sides are equal, the area is the side length squared (a²), and the perimeter is four times the side length (4a).
Triangle: The area of a triangle can be found using various formulas depending on the type of triangle, with the common formula being 1/2 base times height (1/2 bh). The perimeter is the sum of all three sides (a+b+c).
Other Shapes: For complex shapes like ellipses, trapezoids, and parallelograms, specific formulas are used. The perimeter of an ellipse, for example, is calculated using the Ramanujan approximation, while for trapezoids and parallelograms, the perimeter is the sum of all their sides.
These calculations are not only academic but also have practical applications in various fields, including architecture, landscaping, and interior design.

Area and Perimeter
Embark on an exciting journey into the world of area and perimeter with this educational video! Unravel the mysteries behind these essential mathematical concepts as you uncover their practical applications in everyday life. Prepare to be amazed by the incredible intricacies of shapes and measurements.
Rectangle Calculations: Finding Perimeter from Area
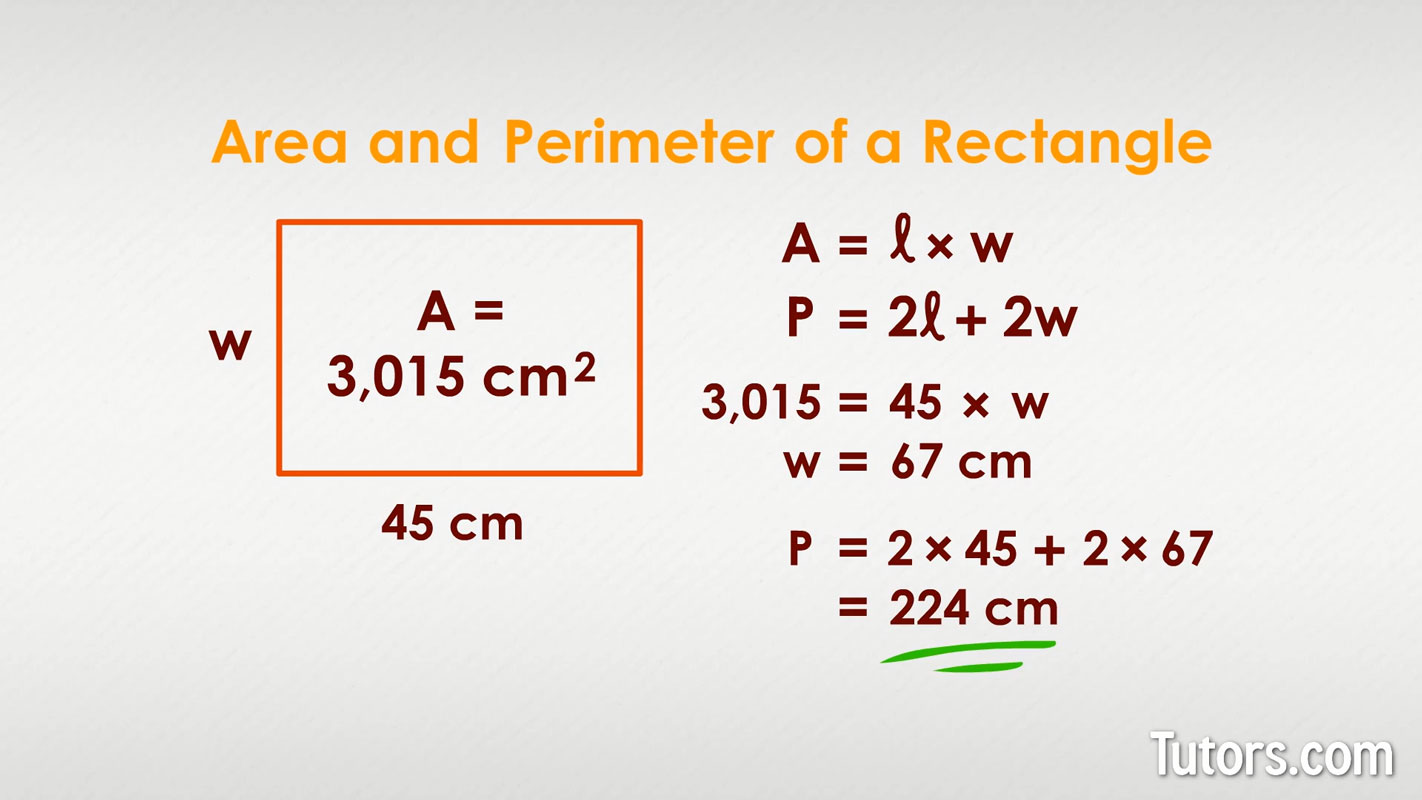
Finding the perimeter of a rectangle from its area requires additional information beyond the area itself. Specifically, you need to know at least one side length of the rectangle. This is because the formula for the area of a rectangle is Area = length × width, but the formula for its perimeter is Perimeter = 2 × (length + width). Without knowing at least one side length, it\"s impossible to determine the perimeter accurately.
Here\"s a step-by-step guide to finding a rectangle\"s perimeter from its area:
- Start with the area of the rectangle. Let\"s denote this as A.
- Assume you know the length or the width of the rectangle. Let\"s call this known side L (if it\"s the length) or W (if it\"s the width).
- Using the area formula, express the unknown side in terms of the known side and area. If you know the length, the width W = A / L, and vice versa.
- Once you have both sides, use the perimeter formula: Perimeter = 2 × (L + W).
- Substitute the known values and calculate the perimeter.
Example: Let\"s say you have a rectangle with an area of 200 square units and a length of 20 units. To find the width: Width = 200 / 20 = 10. Then, the perimeter is Perimeter = 2 × (20 + 10) = 60 units.
It\"s important to note that for a rectangle, knowing the area alone is not sufficient to determine the perimeter because the same area can be achieved with different combinations of length and width.
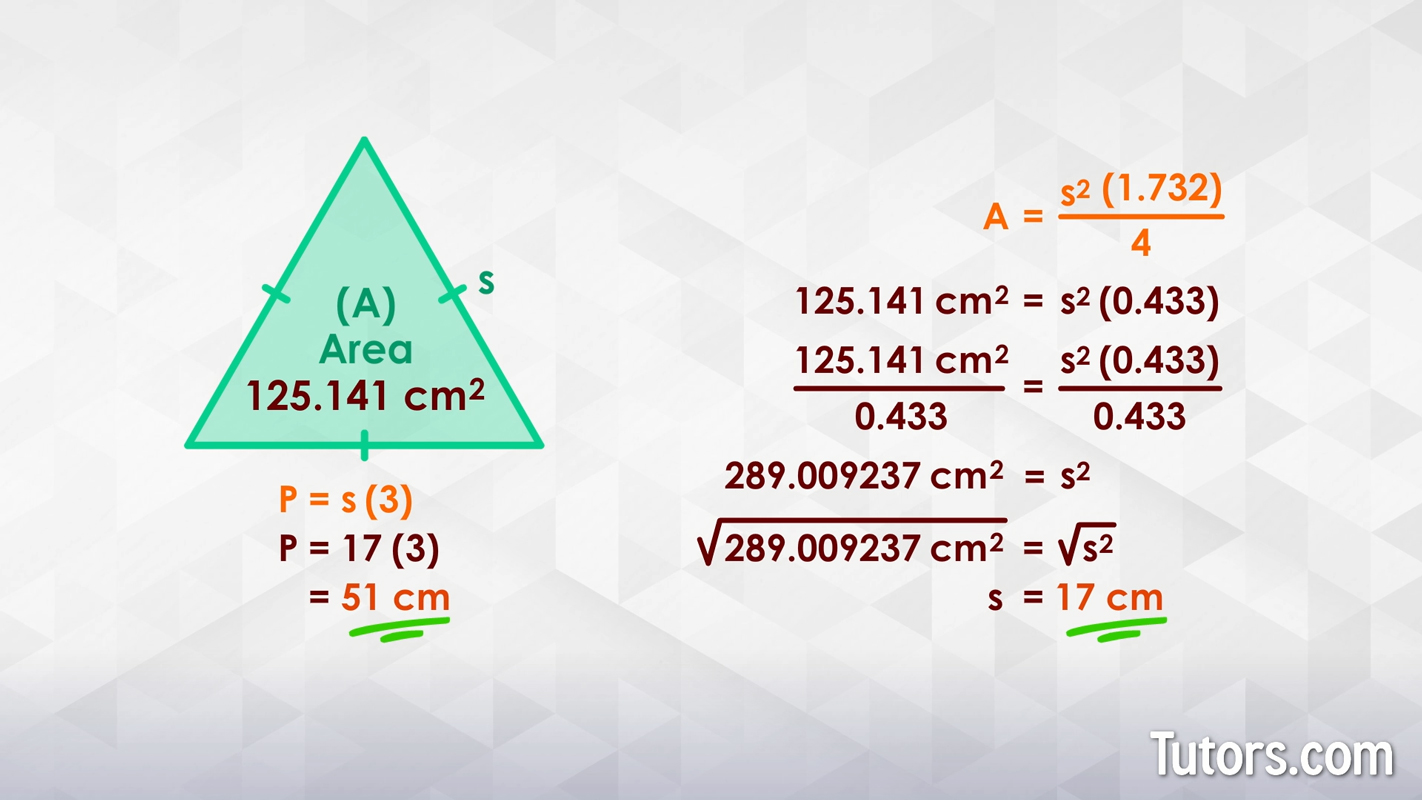
Square Calculations: Relationship Between Perimeter and Area
In geometry, understanding the relationship between the perimeter and area of a square is essential. A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length. The formulas for the perimeter and area of a square are interconnected, based on the length of its sides.
The area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one of its sides. The formula is:
- Area = side × side or Area = a², where a is the length of a side.
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is four times the length of one side. The formula for the perimeter is:
- Perimeter = 4 × side or Perimeter = 4a, where a is the length of a side.
Understanding the relationship between these two measurements involves recognizing how the length of the side of a square affects both its area and perimeter. If the side length of a square is known, both the area and perimeter can be easily calculated using these formulas.
For example, if a square has a side length of 5 units:
- The area would be 5² = 25 square units.
- The perimeter would be 4 × 5 = 20 units.
Conversely, if you know the area of a square, you can find the side length by taking the square root of the area, and then calculate the perimeter. For instance, if a square has an area of 36 square units:
- The side length is the square root of 36, which is 6 units.
- The perimeter is then 4 × 6 = 24 units.
These calculations are crucial in various practical applications, such as construction, where knowing the amount of materials needed to cover a square area or the length of fencing required around a square plot is essential.

Perimeter and Area of Complex Shapes
Understanding the perimeter and area of complex shapes involves applying principles and formulas to various geometrical figures. Different shapes have unique formulas for calculating their area and perimeter.
Triangle
For an equilateral triangle, the perimeter can be derived from its area. The area formula is (A = frac{4s^2sqrt{3}}{4}), where (s) is the side length. To find the side length from a known area, rearrange the formula and solve for (s). The perimeter, (P), is then calculated as (P = s imes 3).
Square
The perimeter of a square is simpler to derive from its area. If the area, (A), of a square is known, the perimeter, (P), is calculated as (P = 4 imes sqrt{A}).
Rectangle
Calculating the perimeter of a rectangle from its area requires additional information - either the length or the width. The area, (A), of a rectangle is (A = length imes width). Knowing one dimension and the area, the other dimension can be found. The perimeter, (P), is calculated as (P = 2 imes (length + width)).
Circle
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, (C), can be found from the area, (A), using the formula (C = 2 imes sqrt{pi imes A}).
Applications
These calculations have practical applications in various fields such as construction, design, and landscaping. For instance, knowing the perimeter is essential for fencing a garden or laying out a track, while the area is crucial for flooring or painting a surface.
Conclusion
While these formulas provide a basis for calculating perimeter and area of basic shapes, complex figures may require a combination of these principles or advanced geometric methods for accurate measurements.
_HOOK_
Calculating Perimeter of Circle Sectors and Ellipses
Understanding the calculation of the perimeter of circle sectors and ellipses is essential in geometry and real-world applications such as design and construction.
Perimeter of Circle Sectors
A circle sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. The perimeter of a circle sector includes the length of the arc plus the lengths of the two radii.
- Formula for Perimeter of Circle Sector: Perimeter = Radius + Radius + Arc length
- Calculation Example: For a sector with radius 5.2 units and arc length 2 units, the perimeter is 5.2 + 5.2 + 2 = 12.4 units.
Calculating Arc Length in Circle Sectors
If the arc length is unknown, it can be calculated using the formula Arc length = radius × θ (angle in radians).
- Conversion: To convert an angle from degrees to radians, use the formula Radians = Degrees × π / 180.
- Example: For a 90° sector with a 7 cm radius, the arc length is 11 cm (after converting degrees to radians).
Perimeter of Ellipses
The calculation of an ellipse\"s perimeter is more complex due to its shape. Several approximation formulas exist for this purpose.
- Ramanujan\"s Approximation: A famous method by mathematician Ramanujan provides a closer approximation of an ellipse\"s perimeter.
- Formula: p ≈ π(a + b) (1 + 3h / (10 + √(4 - 3h))), where h = (a - b)² / (a + b)².
- Infinite Series Approach: More exact formulas involve infinite series calculations, providing higher accuracy but requiring more complex computations.
Both circle sectors and ellipses play a vital role in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design, making the understanding of their perimeters crucial for accurate planning and execution of projects.

Methods for Finding Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Finding the perimeter of irregular shapes, which are shapes with sides and angles of varying lengths and sizes, requires a different approach compared to regular shapes.
Basic Method
The most straightforward method for finding the perimeter of an irregular shape is to simply add up the lengths of all its outer sides. This method applies to any irregular polygon, regardless of the number of sides or the specific measurements of each side.
Step-by-Step Approach
- Identify the shape and determine that it is irregular (sides and angles are not all equal).
- Measure the length of each side of the shape accurately.
- Add up all the side lengths to get the total perimeter of the shape.
- Ensure to cross off each side length as it is added to avoid any miscalculation.
Tips for Accurate Calculation
- Start from one corner and move around the shape to keep track of the sides measured.
- For larger numbers, use strategies like number bonds or compensation addition to simplify calculations.
- If there are multiple sides of the same length, consider multiplying the length by the number of sides.
Dividing Into Simpler Shapes
In more complex cases, you may divide an irregular polygon into smaller, regular shapes such as triangles and rectangles. Calculate the perimeter or area of these smaller shapes individually and then add them together to find the total perimeter or area of the original irregular shape.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes has practical applications in fields like architecture, interior design, landscaping, and more.

Practical Applications: Real-World Use of Perimeter and Area
The concepts of perimeter and area are not just confined to the pages of a mathematics textbook. They have numerous applications in our daily lives, in various fields such as agriculture, construction, and urban planning.
Measurement of Land or Fields
In agriculture, determining the perimeter of fields is crucial for activities like fencing, which helps in protecting crops from animals. On the other hand, calculating the area of land is fundamental in real estate for buying and selling property, be it residential or agricultural land.
Construction of Homes and Buildings
In construction, the perimeter and area calculations are integral in designing homes and buildings. Perimeter helps in estimating materials needed for constructing boundaries like walls and fences, while area measurements are vital in planning the interior space of buildings and rooms.
Construction of Roads and Bridges
Roads and bridges require meticulous planning and surveying, where the area and perimeter measurements are essential. These calculations help ensure the symmetry and structural integrity of these infrastructures, which is critical for safety.
Determining Material Requirements
Whether it\"s installing tiles in a room, painting walls, or setting up a tent, the area helps estimate the amount of material required. Similarly, the perimeter is used to measure the length of materials needed for fences, doors, or cabin glasses.
Computer Graphics and Gaming
In computer graphics and gaming, area and perimeter play a significant role in creating accurate and visually appealing graphical representations, enhancing the user\"s experience.
Art and Fashion
The world of art and fashion also utilizes these concepts. Designers use area and perimeter measurements for apparel designing and accessory creation, ensuring precision in their work.
Educational Value
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter enhances analytical thinking, logical reasoning, and problem-solving skills. It fosters the ability to practically and logically evaluate various real-life scenarios.
Conclusion
Area and perimeter are more than mathematical concepts; they are tools that help us navigate and shape the world around us. Their applications span multiple domains, underscoring their importance in practical and educational settings.
Advanced Topics: Reverse Calculations and Complex Figures
Reverse calculating perimeter from the area is a complex yet intriguing aspect of geometry, particularly when dealing with various shapes. This advanced topic requires a thorough understanding of the basic formulas of area and perimeter for different shapes. Let’s delve into some examples to illustrate this concept.
Rectangles and Squares
For rectangles and squares, determining the perimeter from the area can be straightforward if one dimension is known. For a square, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is simply four times the square root of the area. In the case of a rectangle, however, knowing one dimension (length or width) is essential as the sides are not equal.
- Rectangle: Perimeter = 2 x (Length + Width). Knowing one dimension and the area, the other dimension can be determined and thus the perimeter.
- Square: Perimeter = 4 x √Area. Since all sides of a square are equal, finding the perimeter from the area is more straightforward.
Triangles
Triangles pose a more challenging scenario. For an equilateral triangle, knowing the area can lead to finding the side length using the formula: Side = √((4 x Area) / √3). The perimeter is then thrice the side length.
Circles
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, can be found from the area by the formula: Circumference = 2 x π x √(Area / π).
Complex Figures
More complex shapes, such as irregular polygons or composite figures, require a combination of geometric knowledge and creative problem-solving. The approach often involves decomposing the figure into simpler shapes, calculating individual areas and perimeters, and then combining them to get the final measurements.
Understanding these concepts is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for real-world applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and design.
Practical Application and Problem-Solving
- Identify the type of shape or figure.
- Apply the appropriate area formula to find one or more missing dimensions.
- Use these dimensions to calculate the perimeter.
- In the case of complex shapes, decompose into simpler shapes, if necessary.
Mastery of these advanced concepts opens the door to a deeper understanding of geometry and its practical applications.
READ MORE:
Learning Resources and Tools for Perimeter and Area Calculations
Mastering the concepts of perimeter and area is essential in mathematics. A variety of interactive and engaging resources are available to aid learners in understanding and applying these concepts effectively. Here, we explore some of the most effective learning tools and resources.
Interactive Simulations
Interactive simulations such as those provided by PhET Interactive Simulations offer a dynamic way for students to explore the relationship between perimeter and area. These tools allow learners to create their own shapes using colorful blocks, compare areas and perimeters, and understand these concepts in a visually engaging manner.
Digital Games and Puzzles
Digital puzzles and games, like those available on Teach Starter, present a hands-on approach for practicing area and perimeter calculations. These games often involve calculating the perimeter and area of various shapes, enhancing understanding through interactive and fun challenges.
Mnemonic Devices and Tricks
Employing mnemonic devices can be an effective way to remember complex concepts. For example, associating the word “perimeter” with its outer rim can help students recall that perimeter relates to the boundary of a shape. Similarly, associating “area” with a square (e.g., “squarea”) can assist in remembering that area is the space within a shape.
Comprehensive Online Courses
Online educational platforms like Khan Academy offer structured courses covering area and perimeter. These courses include a variety of learning materials such as video lessons, practice exercises, and quizzes, providing a comprehensive learning experience.
Classroom Activities and Real-World Applications
Hands-on classroom activities, such as estimating and calculating the area needed to wrap a box, can greatly aid in understanding the real-world applications of these mathematical concepts. Such activities help in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical usage.
Teaching Strategies
Effective teaching strategies, including explicit teaching, questioning, and mathematical investigation, can significantly enhance students\" understanding of area and perimeter. These strategies involve clear communication of learning intentions, encouraging a culture of questioning, and engaging students in problem-solving activities.
Utilizing these resources and tools can make learning about perimeter and area an engaging and informative experience for students of all ages.
Mastering the concepts of perimeter and area is essential in mathematics. A variety of interactive and engaging resources are available to aid learners in understanding and applying these concepts effectively. Here, we explore some of the most effective learning tools and resources.
Interactive simulations such as those provided by PhET Interactive Simulations offer a dynamic way for students to explore the relationship between perimeter and area. These tools allow learners to create their own shapes using colorful blocks, compare areas and perimeters, and understand these concepts in a visually engaging manner.
Digital puzzles and games, like those available on Teach Starter, present a hands-on approach for practicing area and perimeter calculations. These games often involve calculating the perimeter and area of various shapes, enhancing understanding through interactive and fun challenges.
Employing mnemonic devices can be an effective way to remember complex concepts. For example, associating the word “perimeter” with its outer rim can help students recall that perimeter relates to the boundary of a shape. Similarly, associating “area” with a square (e.g., “squarea”) can assist in remembering that area is the space within a shape.
Online educational platforms like Khan Academy offer structured courses covering area and perimeter. These courses include a variety of learning materials such as video lessons, practice exercises, and quizzes, providing a comprehensive learning experience.
Hands-on classroom activities, such as estimating and calculating the area needed to wrap a box, can greatly aid in understanding the real-world applications of these mathematical concepts. Such activities help in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical usage.
Effective teaching strategies, including explicit teaching, questioning, and mathematical investigation, can significantly enhance students\" understanding of area and perimeter. These strategies involve clear communication of learning intentions, encouraging a culture of questioning, and engaging students in problem-solving activities.
Utilizing these resources and tools can make learning about perimeter and area an engaging and informative experience for students of all ages.
_HOOK_