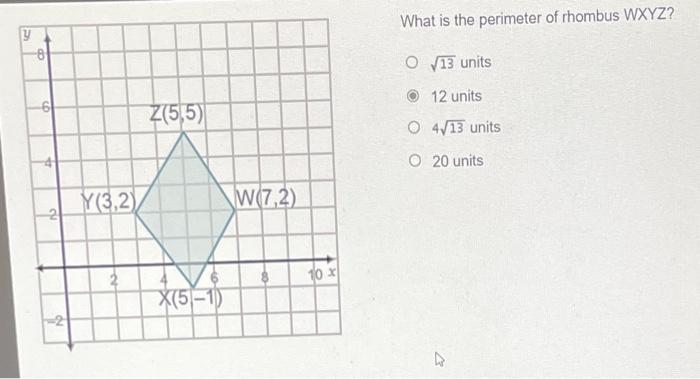
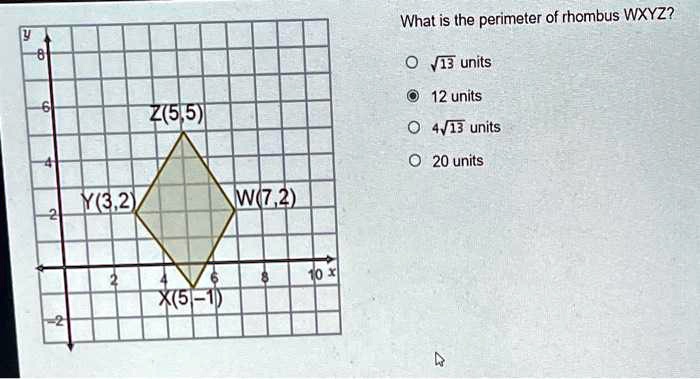
Topic what is the perimeter of rhombus wxyz: Explore the intriguing world of geometry as we delve into "What is the Perimeter of Rhombus WXYZ?", a comprehensive guide that unveils the fascinating aspects and calculation methods of rhombus perimeters, enhancing your mathematical journey.
Table of Content
- Definition and Basic Properties of a Rhombus
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Rhombus
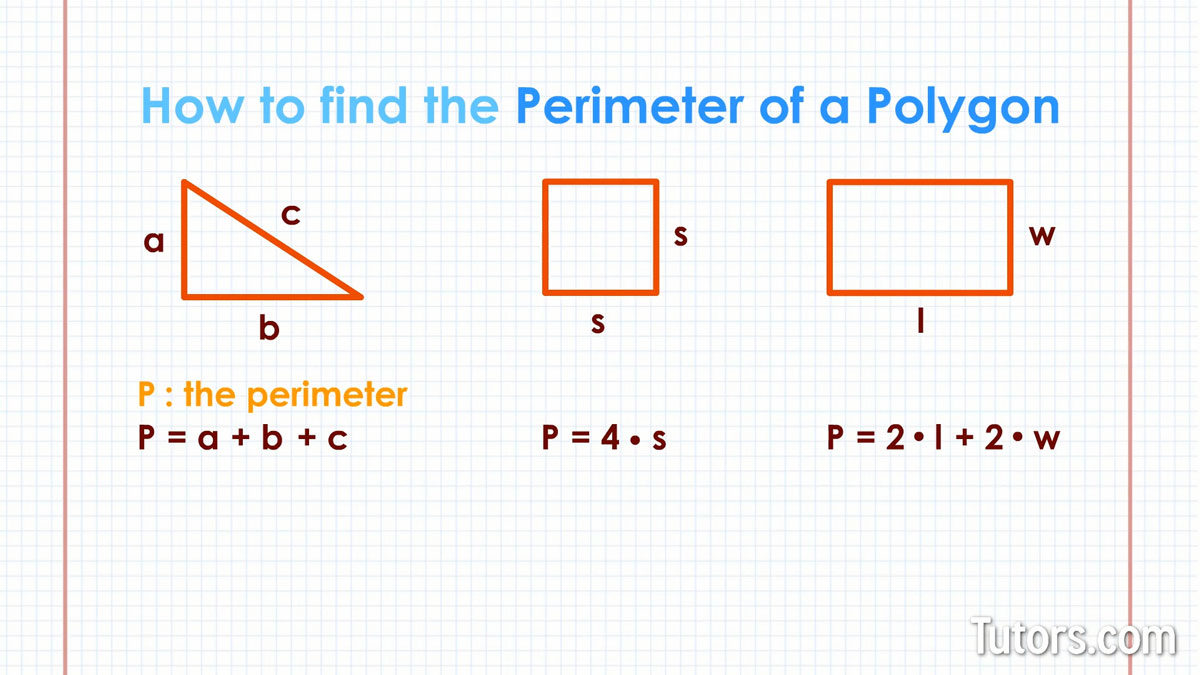
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of a Rhombus
- Calculating the Perimeter with Given Side Length
- Using Diagonals to Determine the Perimeter of a Rhombus
- Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Finding Rhombus Perimeter
- Examples and Solved Problems
- Additional Methods to Find the Perimeter
- Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
- FAQs and Common Misconceptions
- Interactive Tools and Resources for Further Learning
Definition and Basic Properties of a Rhombus
A rhombus, a fascinating quadrilateral in geometry, is known for its unique properties and symmetrical shape. It is defined by four sides of equal length, creating an intriguing geometric form often compared to a slanted square.
- Equal Sides: Each of the four sides of a rhombus is of equal length, a defining characteristic of this shape.
- Opposite Angles: The opposite angles in a rhombus are equal, contributing to its symmetry.
- Parallel Opposite Sides: In a rhombus, opposite sides are not only equal in length but also parallel to each other.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles, dividing the rhombus into four congruent right-angled triangles.
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles in a rhombus, like any quadrilateral, is 360 degrees.
Understanding these basic properties is essential for delving into more complex geometric problems, such as calculating the perimeter of a rhombus, which involves summing the lengths of all four sides.
READ MORE:
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Rhombus
Explore the fascinating world of perimeter as you embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of this mathematical concept. Watch this captivating video to discover how to calculate and utilize perimeter in everyday life situations.
Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of a Rhombus
The perimeter of a rhombus is the total distance around its edges. To calculate this, there are several formulas that can be applied depending on the dimensions available:
- Using Side Length:
- If the length of one side of the rhombus is known, say \"a\", then the perimeter (P) is given by:
- P = 4 × a
- Using Diagonals:
- When the lengths of the diagonals of the rhombus are known (denoted as p and q), the perimeter can be calculated using the formula:
- P = 2 × √(p² + q²)
- This formula derives from the fact that a rhombus can be split into four right-angled triangles by its diagonals.
- Using Trigonometry:
- When one diagonal and one interior angle of the rhombus are known, trigonometric functions can be used to calculate the length of one side, and hence, the perimeter. This method involves dividing the rhombus into two right-angled triangles and applying trigonometric ratios.
Remember, all sides of a rhombus have equal length. Therefore, knowing the length of one side is enough to determine its perimeter.
Examples and practice problems can further help in understanding how these formulas are applied in different scenarios.

Area and Perimeter of a Rhombus: Calculation with Given Measurements
Unlock the power of calculation as you delve into the realm of numbers and equations. Join us in this eye-opening video to learn invaluable techniques and strategies for mastering the art of calculation, ensuring you never struggle with math again.
Calculating Area and Perimeter in the Coordinate Plane | Geometry | Eat Pi
Step into the realm of the coordinate plane and witness the magic of visualizing mathematical concepts in a whole new way. Immerse yourself in this captivating video to unravel the mysteries of the coordinate plane and unveil how it can revolutionize your understanding of geometry.
Calculating the Perimeter with Given Side Length
To calculate the perimeter of a rhombus when the length of its side is known, a straightforward formula is used. This formula is based on the property that all sides of a rhombus are equal in length. The perimeter is simply the sum of the lengths of all four sides.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a rhombus (P) when the length of a side (a) is known:
P = 4 × a
Here\"s a step-by-step explanation:
- Determine the length of one side of the rhombus (denoted as \"a\").
- Multiply this length by 4, as there are four sides in a rhombus and they are all equal in length.
- The resulting product is the perimeter of the rhombus.
Example Calculations:
- If the side length of a rhombus is 10 inches, then its perimeter is 4 × 10 = 40 inches.
- For a rhombus with a side length of 7 units, the perimeter would be 4 × 7 = 28 units.
- In a scenario where the perimeter is known (for example, 36 feet), and the side length needs to be found, divide the perimeter by 4. Thus, a rhombus with a 36-foot perimeter has sides each measuring 9 feet (36 ÷ 4).
Understanding this formula is crucial in solving various geometry problems related to rhombuses, especially in situations where the side length is the only dimension provided.

Using Diagonals to Determine the Perimeter of a Rhombus
To calculate the perimeter of a rhombus using its diagonals, a specific formula derived from the Pythagorean theorem is employed. This method is applicable when the lengths of the diagonals are known.
The formula for calculating the perimeter (P) of a rhombus when the lengths of the diagonals (p and q) are known:
P = 2 × √(p² + q²)
Here is a detailed explanation:
- Determine the lengths of the diagonals of the rhombus, denoted as p and q.
- Square both p and q, then add the results together.
- Take the square root of the sum obtained in step 2.
- Multiply the result by 2 to get the perimeter of the rhombus.
Example Calculations:
- For a rhombus with diagonals of lengths 6 inches and 8 inches, the perimeter is calculated as 2 × √(6² + 8²) = 2 × √(36 + 64) = 2 × √100 = 20 inches.
- If a rhombus has diagonals measuring 12 cm and 16 cm, its perimeter is 2 × √(12² + 16²) = 2 × √(144 + 256) = 2 × √400 = 40 cm.
This formula is a practical and efficient way to calculate the perimeter of a rhombus when the side lengths are not directly known but the diagonals are.

Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Finding Rhombus Perimeter
The Pythagoras Theorem plays a crucial role in calculating the perimeter of a rhombus, especially when the diagonals of the rhombus are known. A rhombus can be divided into four congruent right-angled triangles by its diagonals. These diagonals bisect each other at right angles, which is key to applying the Pythagoras Theorem.
Consider a rhombus ABCD with diagonals p and q. The diagonals bisect each other at right angles, creating four congruent right-angled triangles. For example, in triangle AOD, we can denote half the length of the diagonals as p/2 and q/2.
Using Pythagoras Theorem in triangle AOD:
- The side length (a) of the rhombus can be calculated using the formula: (a = sqrt{left(frac{p}{2}
- ight)^2 + left(frac{q}{2}
- ight)^2}).
- Expanding this, we get: (a = frac{sqrt{p^2 + q^2}}{2}).
Once the side length is determined, the perimeter (P) of the rhombus can be easily calculated since all sides of a rhombus are equal. The formula for the perimeter is P = 4a.
Thus, substituting the value of a in the perimeter formula, we get:
Perimeter of the rhombus = (4 imes frac{sqrt{p^2 + q^2}}{2}) = (2sqrt{p^2 + q^2}).
Example:
Let\"s consider a rhombus with diagonals measuring 8 inches and 6 inches respectively.
- First, calculate the side length using the diagonals and Pythagoras Theorem.
- Then, apply the perimeter formula to find the total boundary length.
In this example, the perimeter calculation would proceed as follows:
- Side length calculation: (a = frac{sqrt{8^2 + 6^2}}{2}).
- Perimeter calculation: Perimeter = (4 imes a).
Therefore, the perimeter of this rhombus would be 20 inches.
Note: This method is particularly useful when the side lengths are not directly given but the diagonals are known. It demonstrates the versatility of the Pythagoras Theorem in geometry.

_HOOK_
Examples and Solved Problems
Exploring examples and solved problems can provide a deeper understanding of how to calculate the perimeter of a rhombus. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Calculating Perimeter with Side Length
Find the perimeter of a rhombus with a side length of 8 inches.
Solution:
- Perimeter of a rhombus = 4 × side length.
- Thus, Perimeter = 4 × 8 inches = 32 inches.
Example 2: Using Diagonals to Find Perimeter
Find the perimeter of a rhombus with diagonals measuring 8 inches and 6 inches respectively.
Solution:
- First, find the side length using the Pythagoras theorem: a = sqrt((p/2)^2 + (q/2)^2) where p and q are the diagonals.
- For diagonals 8 inches (p) and 6 inches (q), side length a = sqrt((8/2)^2 + (6/2)^2) = 5 inches.
- Then, Perimeter = 4 × side length = 4 × 5 inches = 20 inches.
Example 3: Perimeter with Given Side Length
A rhombus ABCD has a side length of 7 units. What is its perimeter?
Solution:
- Perimeter of a rhombus = 4 × side length.
- Thus, Perimeter = 4 × 7 units = 28 units.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems for you to try:
- Calculate the perimeter of a rhombus with each side measuring 6 units.
- Find the perimeter of a rhombus whose diagonals measure 3 units and 4 units.
- If the perimeter of a rhombus is 48 units, determine the length of its side.
- What is the perimeter of a rhombus with diagonals 16 inches and 30 inches?
- Determine the perimeter of a rhombus if the sum of the squares of its diagonals is 68 units.

Additional Methods to Find the Perimeter
In addition to the standard method of multiplying the side length by 4, there are other methods to calculate the perimeter of a rhombus when certain information is available. These methods utilize the unique properties of rhombuses.
Using Diagonals
If the lengths of the diagonals of the rhombus are known, you can calculate the perimeter using this formula:
P = 2√(d1² + d2²)
where d1 and d2 are the lengths of the diagonals. This method involves using the Pythagorean theorem in each of the triangles formed by the diagonals.
Diagonal and Vertex Angle
When one diagonal and a vertex angle are known, trigonometric functions can be used to find the perimeter:
- Divide the diagonal in half, as diagonals bisect each other in a rhombus.
- Use the sine of the vertex angle and the half diagonal to find the side length.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
Base-Height Method
When the area and height of a rhombus are known, the perimeter can be determined by:
- Dividing the area by the height to find the length of one side.
- Multiplying this length by 4 to find the perimeter.
Sin of Angle Method
If the area and one interior angle are known, the perimeter can be calculated by:
- Using the formula: P = 4[area/sin(interior angle)].
- Calculating the sine of the angle and dividing the area by this sine.
- Multiplying the result by 4 to get the perimeter.
Diagonal Formula
When the diagonals are known, use the following steps:
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem using half the lengths of each diagonal to find the side length.
- Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
These methods provide flexibility in calculating the perimeter of a rhombus, depending on the available information.

Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The rhombus shape, characterized by equal side lengths and often congruent angles, finds its application in various aspects of daily life, architecture, and design. Understanding its perimeter plays a crucial role in these applications.
Architecture and Building Design
Architects and engineers use the rhombus shape for aesthetic and functional purposes. For instance, rhombus-shaped windows in buildings like the Louvre in Paris not only enhance the building\"s appearance but also optimize the distribution of natural light. Similarly, rhombus-shaped roofs are used in construction due to their ability to distribute loads effectively, making them suitable for heavy-duty structures like bridges.
Interior and Fashion Design
In interior design, rhombus-shaped tiles create visually appealing patterns on floors and walls, adding sophistication to the space. In fashion, the symmetry and elegance of rhombus shapes are evident in jewelry designs such as earrings and pendants, adding a touch of refinement to the pieces.
Everyday Objects and Recreation
- Home Décor: Items like mirrors, wall patterns, and quilts often feature rhombus shapes, enhancing the aesthetics of living spaces.
- Sports Fields: The perimeter of a rhombus can be used to calculate dimensions in sports, like the distance of a pitcher’s spot from the striker in a baseball field shaped like a rhombus.
- Kites: The rhombus shape is common in kite designs, where its geometry helps achieve stability and balance in the air.
Educational Tools
In education, understanding the perimeter of a rhombus aids in teaching geometry and mathematics. It offers a practical way to explain complex mathematical concepts through real-world examples like tile patterns, window grills, and other household items.
Nature and Art
The rhombus shape is not limited to man-made objects; it is also found in natural patterns, such as the arrangement of leaves or butterfly wings. In art, rhombus shapes are used to create intricate patterns and designs, showcasing the versatility of this geometric figure.
In conclusion, the practical applications of the rhombus shape and its perimeter span across various fields, highlighting the importance of geometric principles in our everyday lives.

FAQs and Common Misconceptions
When learning about the perimeter of a rhombus, many students have questions and sometimes misunderstand the concepts. Here are some frequently asked questions and clarifications to help deepen your understanding.
- What is the perimeter of a rhombus?
- The perimeter of a rhombus is the total length of its boundaries, calculated as the sum of all its sides. Since a rhombus has four equal sides, the perimeter is 4 times the length of one side.
- Can you calculate the perimeter of a rhombus using its diagonals?
- Yes, it\"s possible to find the perimeter of a rhombus using its diagonals. The formula is P = 2√(p² + q²), where \"p\" and \"q\" are the lengths of the diagonals. This formula is derived from the properties of the rhombus and the Pythagorean theorem.
- Is it always necessary to use the diagonal method to find the perimeter?
- No, using diagonals is just one of the methods. The perimeter can also be calculated simply as 4 times the length of a side if the side length is known.
- What are some common misconceptions about the perimeter of a rhombus?
- One common misconception is that the perimeter of a rhombus can be different for each rhombus. In reality, it\"s always 4 times the length of a side.
- Another misconception is that calculating the perimeter using diagonals is complex. However, with the formula P = 2√(p² + q²), it\"s quite straightforward.
- How does the Pythagorean theorem apply to a rhombus?
- The Pythagorean theorem is used in the method of finding the perimeter of a rhombus through its diagonals. Since the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles, forming four right-angled triangles, the theorem helps in calculating the side length.
- Can the perimeter of a rhombus be the same as that of a square?
- Yes, if the side length of both the square and the rhombus are the same, their perimeters will also be the same, since both are calculated as 4 times the side length.
READ MORE:
Interactive Tools and Resources for Further Learning
To enhance your understanding of the perimeter of a rhombus, here are some interactive tools and resources. These platforms provide engaging and educational activities to help solidify your knowledge of rhombus properties and perimeter calculations.
- Mathigon\"s Polypad
- An interactive tool that offers a range of manipulatives for geometry learning. Polypad includes various features such as fraction circles, algebra tiles, and customisable shapes, allowing students to visually explore and understand the properties of a rhombus and its perimeter.
- Visit Mathigon\"s Polypad
- PhET Interactive Simulations - Area Builder
- This simulation allows you to create shapes using colorful blocks, helping you explore the relationship between area and perimeter. It\"s a fun way to understand the concepts of perimeter for various shapes, including rhombuses.
- Explore PhET Area Builder
- Math is Fun - Interactive Quadrilaterals
- This interactive tool lets you play with various quadrilaterals, including rhombuses. You can rotate and view these shapes from different angles, aiding in a comprehensive understanding of their properties.
- Visit Math is Fun
Discover the intriguing world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the perimeter of Rhombus WXYZ. Our engaging content, enriched with interactive tools and examples, promises to transform your understanding and appreciation of this fascinating geometric concept.

_HOOK_