Topic formula for right triangle perimeter: Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide to the formula for right triangle perimeter, unlocking the secrets of this fundamental concept in a simple, engaging way.
Table of Content
- What is the Perimeter of a Right Triangle?
- YOUTUBE: Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle
- Basic Formula for Right Triangle Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter with Pythagoras Theorem
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Application of Right Triangle Perimeter in Real Life
- Difference Between Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Practice Problems
What is the Perimeter of a Right Triangle?
The perimeter of a right triangle is the total distance around the triangle, which equals the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Understanding this concept is crucial in geometry, especially in the context of right triangles, known for their 90-degree angle.
- Basic Concept: A right triangle has one right angle (90 degrees) and two other angles that add up to 90 degrees, making it a unique and widely studied figure in geometry.
- Components of Perimeter: The perimeter involves adding the lengths of the three sides: the base, the height (perpendicular to the base), and the hypotenuse (the longest side opposite the right angle).
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem: When two side lengths are known, the third can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
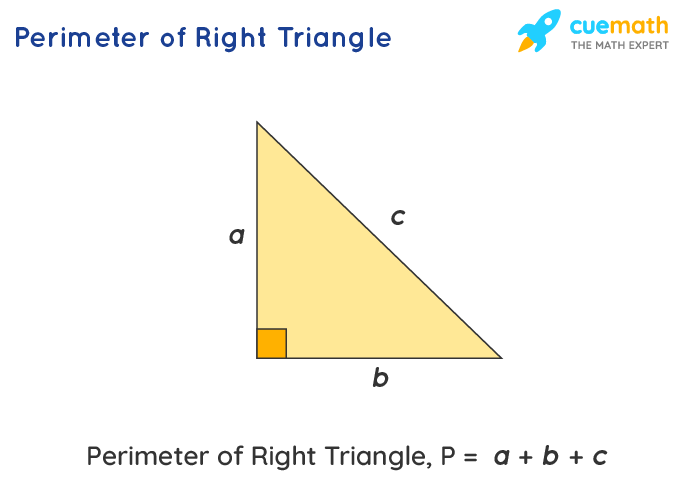
- Perimeter Formula: The formula for calculating the perimeter of a right triangle is P = a + b + c, where P is the perimeter, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides.
- Real-World Applications: Calculating the perimeter of right triangles is essential in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and even navigation.
Through these points, we can see that understanding the perimeter of a right triangle is not just a mathematical exercise but also a practical tool in various real-life applications.

READ MORE:
Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle
\"Discover the fascinating world of right triangles in this captivating video! Learn how they differ from other triangles and explore their unique properties that make them the building blocks of geometry. Get ready to be amazed by the captivating visual demonstrations that will bring the concept to life!\"
Basic Formula for Right Triangle Perimeter
The perimeter of a right triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If we denote the sides of the right triangle as a, b, and c, where c is the hypotenuse (the longest side opposite the right angle), the formula for the perimeter (P) is:
P = a + b + c
Understanding the Sides
- a and b: These are the two legs of the triangle that form the right angle.
- c (Hypotenuse): The side opposite the right angle and the longest side of the triangle.
Calculating the Hypotenuse
If only two sides are known, the length of the hypotenuse (c) can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
c² = a² + b²
This theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Alternative Formulas
If the hypotenuse (c) is not known, the perimeter can be calculated as:
P = a + b + √(a² + b²)
Similarly, if either leg (a or b) is unknown, the perimeter can be calculated by finding the missing side using modified versions of the Pythagorean theorem:
- If leg a is unknown: P = b + c + √(c² - b²)
- If leg b is unknown: P = c + a + √(c² - a²)
Examples
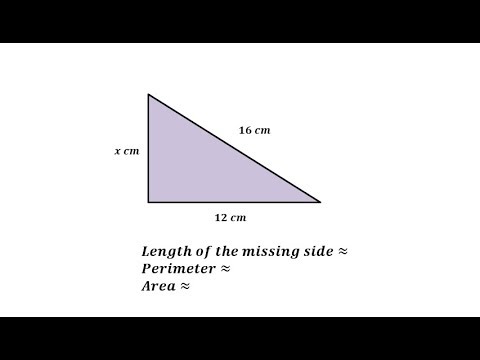
- For a right triangle with sides 4 units (a), 12 units (b), and a hypotenuse of 20 units (c), the perimeter would be P = 4 + 12 + 20 = 36 units.
- In a triangle where the base (a) is 6 units and height (b) is 8 units, first find the hypotenuse: c = √(a² + b²) = √(6² + 8²) = 10 units. Then, the perimeter is P = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 units.
- For a base of 5 units (a) and a hypotenuse of 13 units (c), first find the height (b): b = √(c² - a²) = √(13² - 5²) = 12 units. The perimeter is P = 5 + 13 + 12 = 30 units.
Elegant way to find the Perimeter of a right triangle - step-by-step explanation
\"Unlock the secrets of perimeter calculations with this engaging video! Dive into the world of shapes and learn how to find the perimeter by simply adding up the lengths of all sides. Get ready to see real-life examples and practical applications that will make you a perimeter expert!\"
Calculate side lengths of the right triangle - Area and Perimeter are known
\"Uncover the mysteries of side lengths in this exciting video! Explore various shapes and discover how their side lengths are interconnected. From squares and rectangles to triangles and more, you\'ll be amazed at the patterns and relationships that emerge. Get ready to dive into the world of geometry like never before!\"
Calculating Perimeter with Pythagoras Theorem
The Pythagoras Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry, particularly useful in calculating the perimeter of right triangles. This theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Pythagoras Theorem Formula
The formula is expressed as: c² = a² + b², where:
- a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides of the triangle.
- c is the length of the hypotenuse.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the lengths of two sides of the right triangle.
- Use the Pythagoras Theorem to find the length of the third side if it is not known.
- Add the lengths of all three sides to find the perimeter.
Examples
- If the lengths of two sides are known (for example, 6 units and 8 units), calculate the length of the hypotenuse (c) as: c = √(a² + b²) = √(6² + 8²) = 10 units. Then, the perimeter (P) is a + b + c = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 units.
- If the hypotenuse and one side are known (for example, hypotenuse = 13 units and one side = 5 units), calculate the other side (b) as: b = √(c² - a²) = √(13² - 5²) = 12 units. Then, the perimeter is a + b + c = 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 units.
Applications
Pythagoras Theorem has wide applications in real life, including in fields like engineering, construction, navigation, and even in security systems for facial recognition.
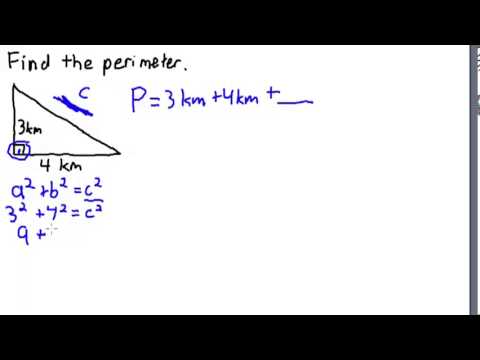
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of right triangles involves adding the lengths of all three sides. Below are some examples that illustrate how this is done in various scenarios, using the basic formula P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the sides of the triangle.
Example 1
For a triangle with a base of 4 units, height of 12 units, and hypotenuse of 20 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
Perimeter = 4 units + 12 units + 20 units = 36 units
Example 2
Consider a triangle where the base is 6 units and the height is 8 units. To find the hypotenuse (c), we apply the Pythagorean theorem:
c = √(6² + 8²) = √(36 + 64) = √100 = 10 units
Thus, the perimeter is 6 units + 8 units + 10 units = 24 units.
Example 3
In a right triangle where the base is 5 units and the hypotenuse is 13 units, we find the height (b) using the Pythagorean theorem:
b = √(13² - 5²) = √(169 - 25) = √144 = 12 units
Therefore, the perimeter is 5 units + 13 units + 12 units = 30 units.
Additional Examples
Other scenarios may include finding the perimeter of a triangle with given sides of 5 cm and 12 cm. Using the Pythagorean theorem, we find the third side to be 13 cm, leading to a perimeter of 30 cm.
In another case, if we have a triangle with a height of 10 cm and a hypotenuse of 15 cm, the base can be calculated as approximately 11.1804 cm. This results in a perimeter of approximately 36.1804 cm.
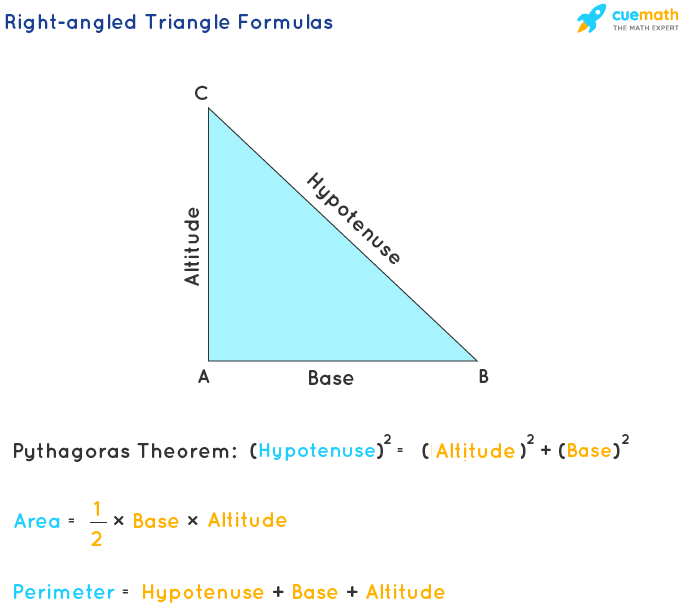
Application of Right Triangle Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of right triangles is not only a fundamental aspect of geometry, but it also has numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples of how the perimeter of right triangles is utilized in everyday life:
- Land Measurement: Farmers and builders often use the concept of perimeter to measure and mark boundaries for fields, plots, and construction sites. This measurement is crucial for activities such as fencing, planning crop areas, and laying out building foundations.
- Architecture and Carpentry: In architecture and carpentry, the principles of right triangle perimeters are used to ensure that walls are straight and corners are accurately square. This is essential for fitting interior elements correctly and for overall structural integrity.
- Navigation and Surveying: Navigators and surveyors apply the concepts of right triangles in determining distances. This is particularly important for tasks such as estimating the distance of a ship from the shore, or calculating the height of a building using trigonometric functions.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use the principles of right triangle perimeters to measure the orbits and movements of planets. This helps in understanding the distances between celestial bodies and their motion in space.
- Graphic Design: In graphic design, particularly in computer-aided design, the concept of perimeter is used to draw precise graphics, shapes, and characters, significantly impacting fields like gaming, advertising, and educational content creation.
- Fashion and Art: In the fashion industry, designers utilize the concept of perimeter for tasks like cutting fabrics. Similarly, in art, the perimeter concept helps in achieving accurate proportions and dimensions in artistic works.
- Mathematical Education: Teaching right triangles and their perimeters provides a practical context for students to understand and apply geometric and trigonometric principles, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications.
These applications demonstrate the importance of understanding right triangle perimeters in various professional and everyday contexts, making it a valuable concept in both educational and practical realms.

_HOOK_
Difference Between Area and Perimeter of a Right Triangle
Understanding the difference between the area and perimeter of a right triangle is crucial in geometry. While both are fundamental properties of a triangle, they represent different aspects and are calculated using different formulas.
- Area of a Right Triangle: The area is a measure of the total space enclosed within the triangle. It is calculated using the formula: Area = 1/2 × Base × Height. In a right triangle, one of the sides adjacent to the right angle is considered as the base, and the other as the height. The area is expressed in square units.
- Perimeter of a Right Triangle: The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of the triangle. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides of the triangle: Perimeter = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" are the lengths of the sides. The perimeter is expressed in linear units.
The key difference lies in their conceptual understanding: area relates to the space contained within the triangle, while perimeter concerns the distance around it. Both properties are used in different contexts and have various applications in mathematics, engineering, and other fields.
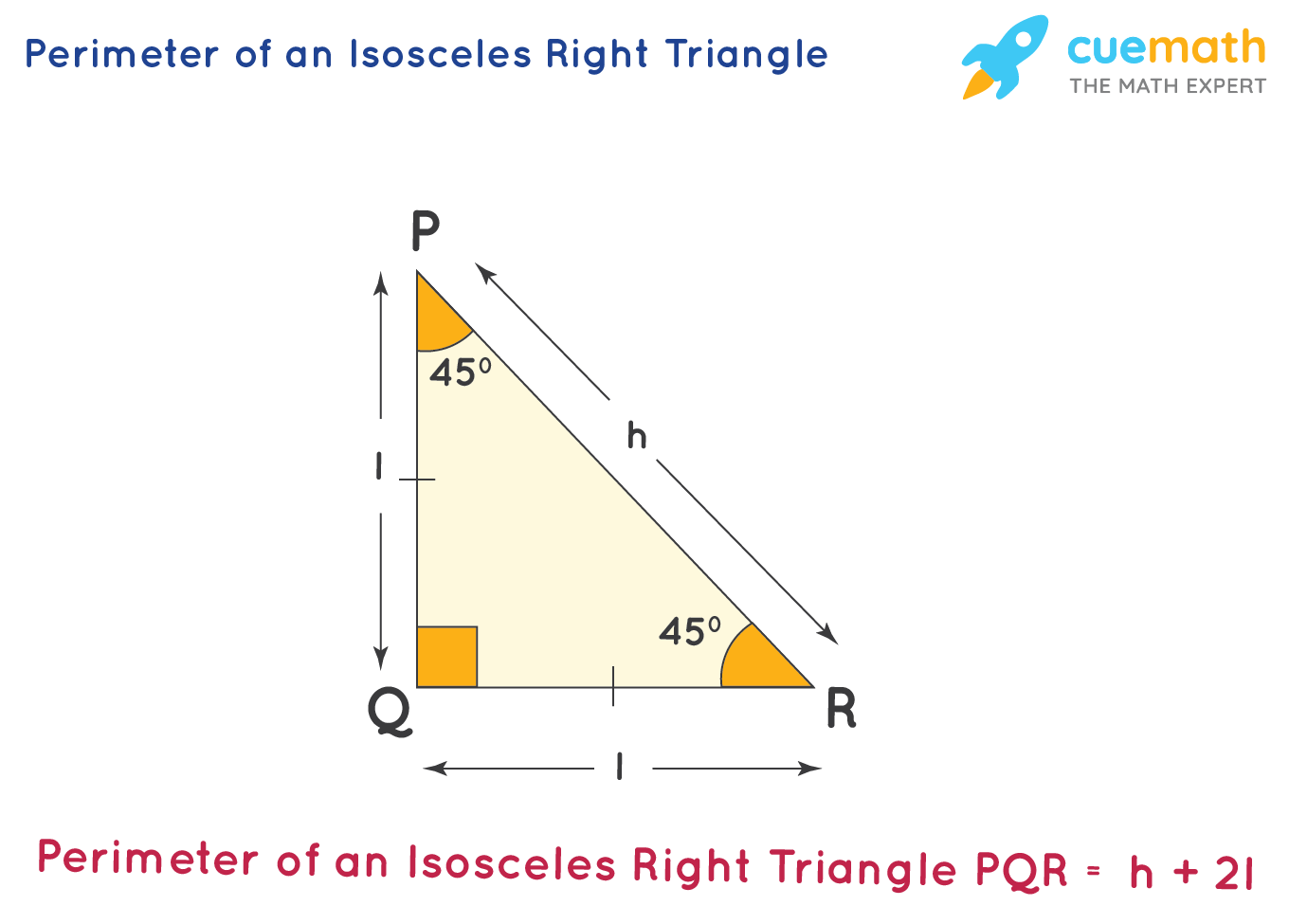
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for finding the perimeter of a right triangle?
- The perimeter of a right triangle is found by adding the lengths of its three sides. The formula is given as P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" represent the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- How is the Pythagoras theorem applied in a right triangle?
- The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This is expressed as c² = a² + b², where \"c\" is the hypotenuse and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- How can you calculate the area of a right triangle?
- The area of a right triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height. In this formula, the base and height are the lengths of the two sides that form the right angle.
- What is the difference between the area and perimeter of a right triangle?
- The area of a right triangle measures the space within the triangle, calculated as 1/2 × base × height. The perimeter measures the boundary of the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle with two sides and the hypotenuse?
- To find the perimeter when two sides and the hypotenuse are known, use the formula P = a + b + h, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the two known sides and \"h\" is the hypotenuse.
- What are some applications of right triangle formulas?
- Right triangle formulas are widely used in various fields such as construction, trigonometry, engineering, and navigation, where calculations involving angles and distances are essential.
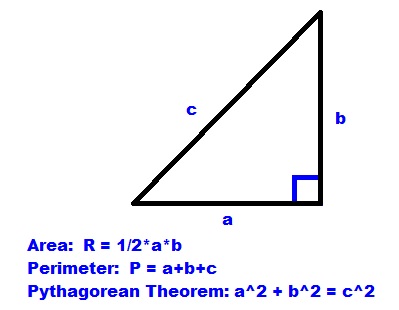
READ MORE:
Practice Problems
- What is the formula for finding the perimeter of a right triangle?
- The perimeter of a right triangle is found by adding the lengths of its three sides. The formula is given as P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" represent the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- How is the Pythagoras theorem applied in a right triangle?
- The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This is expressed as c² = a² + b², where \"c\" is the hypotenuse and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
- How can you calculate the area of a right triangle?
- The area of a right triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height. In this formula, the base and height are the lengths of the two sides that form the right angle.
- What is the difference between the area and perimeter of a right triangle?
- The area of a right triangle measures the space within the triangle, calculated as 1/2 × base × height. The perimeter measures the boundary of the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
- How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle with two sides and the hypotenuse?
- To find the perimeter when two sides and the hypotenuse are known, use the formula P = a + b + h, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the two known sides and \"h\" is the hypotenuse.
- What are some applications of right triangle formulas?
- Right triangle formulas are widely used in various fields such as construction, trigonometry, engineering, and navigation, where calculations involving angles and distances are essential.
The perimeter of a right triangle is found by adding the lengths of its three sides. The formula is given as P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" represent the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This is expressed as c² = a² + b², where \"c\" is the hypotenuse and \"a\" and \"b\" are the other two sides.
The area of a right triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = 1/2 × base × height. In this formula, the base and height are the lengths of the two sides that form the right angle.
The area of a right triangle measures the space within the triangle, calculated as 1/2 × base × height. The perimeter measures the boundary of the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
To find the perimeter when two sides and the hypotenuse are known, use the formula P = a + b + h, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the two known sides and \"h\" is the hypotenuse.
Right triangle formulas are widely used in various fields such as construction, trigonometry, engineering, and navigation, where calculations involving angles and distances are essential.