Topic formula of perimeter of triangle: Explore the fascinating world of geometry as we delve into the "Formula of Perimeter of Triangle," a cornerstone concept in understanding shapes and spaces around us.
Table of Content
- Basic Concept of Perimeter in Triangles
- YOUTUBE: How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
- General Formula for Triangle Perimeter
- Perimeter Formulas for Special Triangles
- Calculating Perimeter with Different Given Parameters
- Practical Examples and Solved Problems
- FAQs and Common Misconceptions
- Interactive Tools and Resources
- Extension to Advanced Concepts
- Applications in Real Life
Basic Concept of Perimeter in Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the total distance around the triangle. It\"s calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. This measure is not only crucial in theoretical geometry but also has practical applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and design.
- General Formula: The basic formula for the perimeter of any triangle is P = a + b + c, where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" are the lengths of the triangle\"s sides.
- Types of Triangles: The calculation adjusts slightly based on the type of triangle - equilateral, isosceles, or scalene.
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal, so the perimeter is 3 times the length of one side (3 × a).
- Isosceles Triangle: With two sides equal, the perimeter is twice the length of the equal sides plus the base (2a + b).
- Scalene Triangle: All sides are different, and the perimeter is the sum of all three sides.
- Importance: Understanding the perimeter is essential for calculating other properties of triangles, such as area, and for solving real-world problems.
Grasping the concept of triangle perimeter forms the basis for further exploration into more complex geometric principles and their applications in everyday life.

READ MORE:
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Need help finding something? Watch this informative video to discover the best strategies and tools to find whatever you\'re looking for quickly and easily. Get ready to uncover hidden gems!\"
General Formula for Triangle Perimeter
The general formula for the perimeter of a triangle is a simple yet powerful tool in geometry. It is expressed as P = a + b + c, where P represents the perimeter, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle\"s sides. This formula is universally applicable to all types of triangles, whether they are scalene, isosceles, or equilateral.
- Identifying Side Lengths: The first step in applying this formula is to identify the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
- Ensuring Unit Consistency: It\"s crucial to ensure that all side lengths are measured in the same unit (e.g., meters, inches) for accurate calculation.
- Summing Up the Sides: Add the lengths of all three sides. This sum gives the total distance around the triangle, which is its perimeter.
This formula\"s beauty lies in its simplicity and universal applicability. Whether you\"re dealing with a right-angled, acute, or obtuse triangle, the method remains unchanged. It is a fundamental concept that finds application in various real-world scenarios, including construction, design, and academic research.
- Variations for Specific Triangles: While the general formula applies to all triangles, certain types of triangles have simplified formulas due to their unique properties. For example, the perimeter of an equilateral triangle can be calculated as 3 × a, where a is the length of one side.
Understanding this formula is essential for students and professionals alike, as it forms the foundation for more complex geometric calculations and theories.

How to Find the Area and Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Discover the secrets of your favorite area with this captivating video. From the trendiest neighborhoods to the top attractions, let us guide you through an immersive journey to uncover the treasures of your area.\"
Perimeter of Triangle | How to Find Perimeter of Triangle
\"Unlock the mysteries of triangles with this educational video that takes you through the fascinating world of geometric shapes. Learn how to calculate angles, find the missing side lengths, and explore the endless possibilities of triangles.\"
Perimeter Formulas for Special Triangles
In geometry, special triangles like equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles have unique characteristics that allow for specific perimeter formulas. Understanding these formulas is essential for efficient problem-solving in various geometric contexts.
- Equilateral Triangle:
- For an equilateral triangle, where all three sides are of equal length (a), the perimeter formula simplifies to P = 3a.
- Isosceles Triangle:
- In an isosceles triangle, two sides are equal in length (a), and the third side is different (b). The perimeter formula is P = 2a + b.
- Right Triangle:
- For a right triangle, the perimeter is the sum of the two legs and the hypotenuse. If the legs are a and b, and the hypotenuse is c (calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, c² = a² + b²), the perimeter is P = a + b + c.
Each of these formulas takes into account the unique properties of these triangles, making it easier to calculate their perimeters. These formulas are particularly useful in fields that require precise geometric measurements, like engineering, architecture, and design.

Calculating Perimeter with Different Given Parameters
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle can vary depending on the given parameters. Different scenarios may require different approaches, but the underlying principle remains the same: summing the lengths of the triangle\"s sides.
- Known Side Lengths:
- When all three side lengths are known, simply add them together. For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm, the perimeter is 5 + 4 + 3 = 12 cm.
- Using the Pythagorean Theorem in Right Triangles:
- If two sides of a right triangle are known, use the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²) to find the third side, and then add all three sides for the perimeter.
- Triangles with Angles and Side (SAS or ASA):
- When two sides and the included angle are known (SAS), or two angles and a side (ASA) are known, use trigonometric laws like the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines to find the missing sides, and then calculate the perimeter.
- Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles:
- For isosceles triangles with known equal sides (a) and base (b), the perimeter is 2a + b. For equilateral triangles, it\"s 3 times the length of one side.
Each method aligns with the basic principle of perimeter calculation while adapting to the specific information available about the triangle. These methods are widely used in various fields that require geometric measurements and calculations.
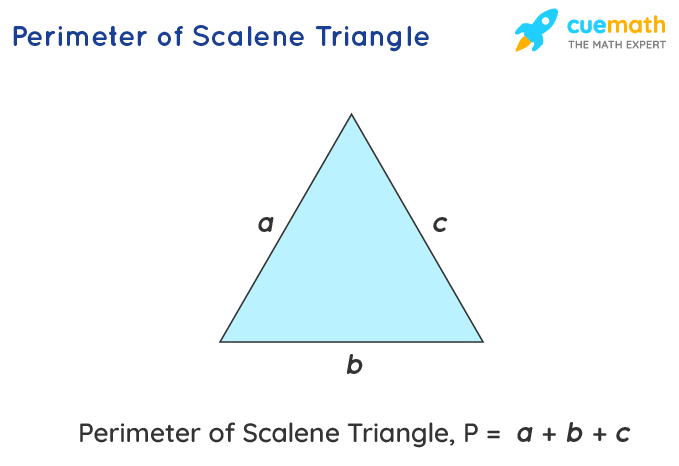
Practical Examples and Solved Problems
Applying the perimeter formulas in real-life scenarios enhances understanding. Here are varied examples illustrating how to calculate the perimeter of triangles in different situations.
- Example 1: Scalene Triangle
- Consider a triangle with sides 6 cm, 8 cm, and 12 cm. To find the perimeter, sum up the lengths of all sides. The perimeter is thus 6 + 8 + 12 = 26 cm.
- Example 2: Equilateral Triangle
- An equilateral triangle with each side measuring 6 cm has a perimeter calculated as 3 times a side length, resulting in 3 × 6 = 18 cm.
- Example 3: Isosceles Triangle
- For an isosceles triangle with two sides of 8 cm each and a perimeter of 40 cm, the length of the third side can be found using the formula 2a + b. Here, b = 40 - (2 × 8) = 24 cm.
- Example 4: Right Triangle
- A right triangle with sides 8 cm and 6 cm. Using the Pythagorean theorem, calculate the hypotenuse: √(8² + 6²) = √(64 + 36) = 10 cm. The perimeter is 8 + 6 + 10 = 24 cm.
- Example 5: Right Isosceles Triangle
- Consider a right isosceles triangle with sides 8 cm each. The hypotenuse is calculated as √2 × a = √2 × 8. The perimeter is 2a + √2 × a.
These examples cover different types of triangles and demonstrate how to apply the formulas in practical scenarios, enhancing your geometric problem-solving skills.

_HOOK_
FAQs and Common Misconceptions
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle involves addressing common questions and clarifying misconceptions. Here are some frequently asked questions and important clarifications to deepen your understanding of triangle perimeters.
- What is the perimeter of a triangle?
- The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its outer edges, which is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. This measurement is crucial in geometry for understanding the size and scale of the triangle.
- How do you find the perimeter of a triangle?
- To calculate the perimeter, add the lengths of the triangle\"s three sides. The calculation method varies slightly depending on the triangle type, such as scalene, isosceles, equilateral, or right triangle. Each type has a specific formula for calculating its perimeter.
- Common Misconception: Order of Adding Sides Matters
- It\"s a common misconception that the order of adding the sides of a triangle affects the perimeter. However, due to the commutative property of addition, the order does not matter. All sides should be added only once, in any order.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area
- Another frequent confusion is mixing up the concepts of perimeter and area. Remember, the perimeter is a one-dimensional measure representing the length around a triangle, while the area is a two-dimensional measure of the space within a triangle.
- Dealing with Different Units
- When calculating the perimeter, ensure that all side lengths are in the same unit before adding them. If the sides are in different units, convert them to a common unit first.
- Calculating Perimeter with SAS (Side-Angle-Side)
- In cases where two sides and the included angle are known (SAS), use the law of cosines to find the third side and then calculate the perimeter.
Addressing these FAQs and misconceptions helps in accurately understanding and calculating the perimeter of triangles in various contexts.
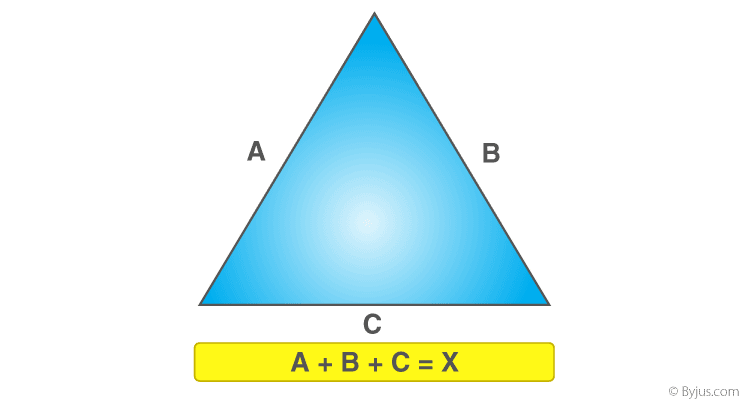
Interactive Tools and Resources
For anyone looking to delve deeper into the topic of triangle perimeters, a variety of interactive tools and resources are available. These can enhance understanding and provide practical applications of the concepts learned.
- Online Perimeter Calculators:
- Websites like Omni Calculator offer an interactive perimeter of a triangle calculator. This tool simplifies the process by allowing you to input known values (like side lengths or angles) to easily compute the perimeter of various types of triangles.
- Educational Websites:
- Platforms such as Cuemath provide in-depth explanations, examples, and practice problems. These resources are great for both students and educators, offering visual aids and step-by-step guides for calculating perimeters of different triangle types.
- Worksheets and Problem Sets:
- For hands-on practice, there are numerous worksheets available online that cover various scenarios. These can range from simple perimeter calculations to more complex problems involving different types of triangles.
- Interactive Learning Platforms:
- Several educational platforms offer interactive courses and tutorials. These platforms often include visual tools and games to make learning about triangle perimeters more engaging and fun.
These tools and resources not only aid in understanding the concept of triangle perimeters but also help in applying these concepts to solve real-world problems effectively.
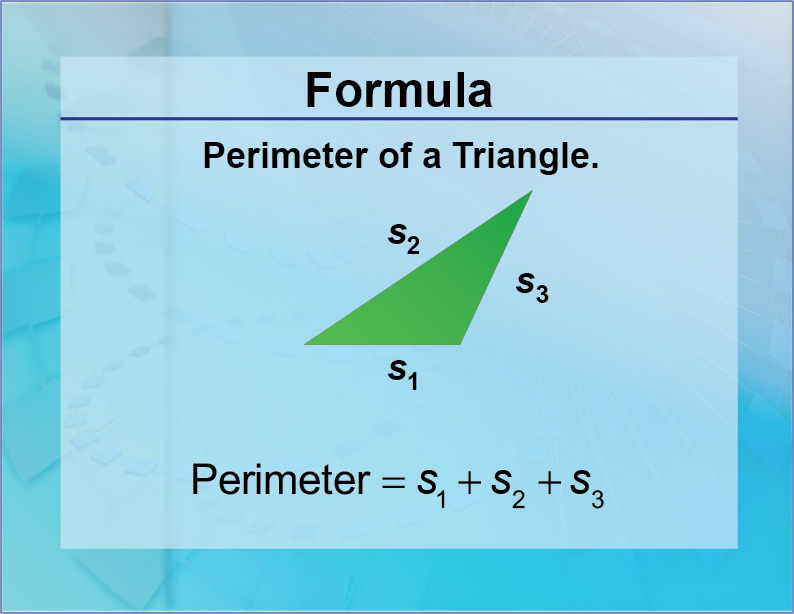
Extension to Advanced Concepts
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle can serve as a foundation for exploring more advanced mathematical concepts. Let\"s explore some of these extensions:
- Application in Trigonometry:
- The principles of trigonometry can be applied to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when not all sides are known. For example, in right-angled triangles, the Pythagorean theorem is used to find missing sides, and in non-right triangles, laws like the Law of Sines and Cosines come into play.
- Perimeter Formulas in Different Polygons:
- Expanding from triangles, the concept of perimeter applies to various polygons like squares, rectangles, trapezoids, and kites, each with its specific formula. For instance, the perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of all its four sides, and for a kite, it\"s calculated by adding the lengths of its pairs of sides.
- Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry:
- In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a triangle can be calculated by first determining the lengths of its sides using the distance formula, given the coordinates of its vertices.
- Complex Problem Solving:
- Advanced problems may involve finding the perimeter of triangles in more complex figures, or under constraints, such as maximising or minimising the perimeter given certain conditions.
These advanced applications not only broaden the understanding of the concept of perimeter but also illustrate the interconnectedness of different areas in mathematics.

READ MORE:
Applications in Real Life
The concept of the perimeter of a triangle has numerous practical applications in real life. It is not just a mathematical concept confined to textbooks but plays a significant role in various fields. Here are some of the key applications:
- Architecture and Engineering:
- In construction, understanding the perimeter of triangular structures or components is crucial. It helps in determining the amount of materials needed, like fencing around a triangular plot or tiles for a triangular floor area.
- Design and Art:
- The concept is used in graphic design, art, and fashion, especially when working with triangular shapes or patterns. Accurate perimeter calculation ensures the proper fitting and aesthetic appeal of designs.
- Land Surveying:
- Surveyors often use the concept of perimeter to calculate the boundaries of land plots, which may involve triangular shapes due to irregularities in terrain or property lines.
- Educational Tools:
- In education, understanding the perimeter of triangles aids in developing problem-solving and analytical skills. It is a fundamental concept in geometry that students learn and apply in various math problems.
These real-life applications of the perimeter of a triangle highlight its importance beyond the classroom, emphasizing its role in practical problem-solving and creative design.
Mastering the formula of the perimeter of a triangle opens doors to a world of geometric understanding and practical applications, from architecture to design. Embrace this foundational concept and unlock the potential of shapes in both academic and real-world scenarios.












