Topic hexagon perimeter: Explore the fascinating world of hexagons with our comprehensive guide on hexagon perimeter, where we unveil the mysteries of this six-sided marvel in geometry, and its intriguing applications in various fields.
Table of Content
- Understanding Hexagons: Definitions and Types
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon: Problem of the Day
- Calculating the Perimeter of Regular Hexagons
- Perimeter of Irregular Hexagons
- Geometrical Properties of Hexagons
- Practical Applications of Hexagons
- Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing a Hexagon
- Additional Resources and Calculators
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Hexagons: Definitions and Types
A hexagon, deriving its name from Greek roots \"hex\" meaning \"six\" and \"gonia\" meaning \"angles\", is a polygon with six sides and angles. The fascinating world of hexagons includes various types and unique properties, making it a subject of interest in both mathematics and practical applications.
- Regular Hexagon: This type features six equal sides and angles, making each interior angle exactly 120°. A regular hexagon is symmetric, both in its shape and its interior angles.
- Irregular Hexagon: In contrast, irregular hexagons have sides and angles of differing lengths and measures, offering a diverse range of shapes.
- Concave Hexagon: At least one interior angle in a concave hexagon is greater than 180°, leading to an inward vertex.
- Convex Hexagon: This type of hexagon has all interior angles less than 180°, with vertices pointing outwards. Convex hexagons can be either regular or irregular.
Hexagons are renowned for their geometrical efficiency and aesthetic appeal, evident in their presence in nature and human-made structures. The regular hexagon is particularly notable for its properties, such as being able to divide into six equilateral triangles, having nine diagonals, and possessing rotational symmetry. The sum of the interior angles of any hexagon, regardless of its type, is always 720°.
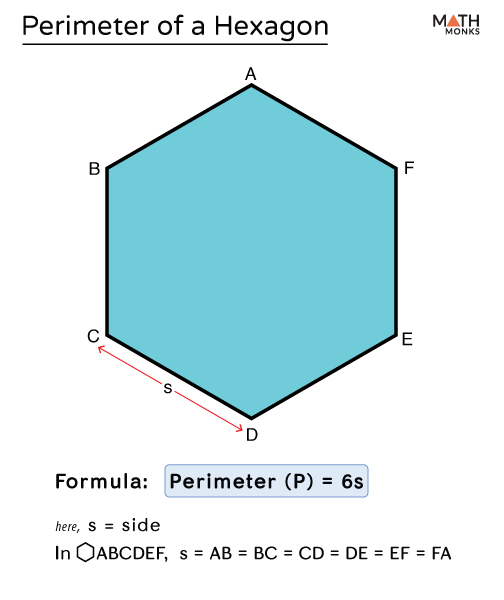
Understanding the perimeter of hexagons involves simple yet intriguing calculations. For regular hexagons, the perimeter is calculated as six times the length of one side (P = 6a). In contrast, the perimeter of an irregular hexagon is the sum of the lengths of its six sides. Such versatile properties make hexagons a fascinating topic in geometry.

READ MORE:
Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon: Problem of the Day
Are you intrigued by the mesmerizing symmetry and intricate designs of hexagons? Dive into our video and discover the hidden wonders of this fascinating geometry shape, and how it beautifully connects the natural world around us!
Perimeter of Hexagon: Regular and Irregular with Formula & Examples
Unlock the secret to finding the perimeter of any shape effortlessly with our insightful video on the perimeter formula. We\'ll guide you step-by-step through this mathematical concept, helping you become a master of measurements in no time!
Calculating the Perimeter of Regular Hexagons
The process of calculating the perimeter of a regular hexagon is straightforward and rooted in its geometric properties. A regular hexagon is characterized by having all six sides of equal length and internal angles of 120 degrees.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular hexagon is:
P = 6a
Where P represents the perimeter, and a is the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Step 1: Measure the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Step 2: Multiply this length by 6 (since a hexagon has six sides of equal length).
This method simplifies the calculation as it only requires the measurement of one side. For example, if each side of a hexagon measures 7 units, the perimeter is calculated as 6 x 7, equaling 42 units.
The simplicity of this formula makes it a versatile tool in various practical applications, such as construction, design, and even in nature, where hexagonal shapes are commonly found.
For irregular hexagons, the process involves summing the lengths of all six sides, as these hexagons do not have equal side lengths.
This approach to understanding the perimeter of regular hexagons emphasizes not only the beauty of geometry but also its practicality in everyday applications.

Find the Perimeter of the Regular Hexagon.
Step into the world of symmetry and harmony with our captivating video on regular hexagons. Marvel at the perfect balance of angles and sides as we delve into the intriguing properties of this six-sided wonder. Get ready to be amazed!
Perimeter of Irregular Hexagons
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular hexagon, unlike regular hexagons, requires a different approach due to the variability in side lengths. An irregular hexagon is defined by its six unequal sides and differing angles. The perimeter of such a hexagon is the total length of its six sides.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular hexagon:
- Measure the length of each side of the hexagon.
- Add the lengths of all six sides.
The formula for the perimeter of an irregular hexagon is expressed as:
P = a + b + c + d + e + f
Where P is the perimeter, and a, b, c, d, e, and f are the lengths of the hexagon\"s six sides.
This approach is vital for practical applications where hexagons with varying side lengths are encountered, such as in certain architectural designs or natural formations.
It\"s important to note that the sum of the interior angles of any hexagon, whether regular or irregular, is always 720 degrees. However, the individual angles in an irregular hexagon are not equal, unlike in a regular hexagon.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate calculations and applications in fields requiring geometric precision.
Geometrical Properties of Hexagons
Hexagons, six-sided polygons, exhibit a range of fascinating geometrical properties, making them a subject of interest in mathematics and nature. They can be classified into various types based on their angles and sides, such as regular, irregular, convex, and concave hexagons.
- Regular Hexagons: In regular hexagons, all sides and angles are equal. Each interior angle measures 120 degrees, and each exterior angle measures 60 degrees. The sum of all interior angles is 720 degrees.
- Irregular Hexagons: These hexagons have unequal sides and angles. Despite this irregularity, the sum of their interior angles remains 720 degrees.
- Convex Hexagons: All interior angles in a convex hexagon are less than 180 degrees. This type of hexagon can either be regular or irregular.
- Concave Hexagons: In concave hexagons, at least one interior angle is greater than 180 degrees, leading to an inward-pointing vertex.
- Symmetry: Regular hexagons feature multiple lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry, making them inherently balanced and harmonious in shape.
- Diagonals: A hexagon, regardless of its type, has nine diagonals. The regular hexagon, in particular, has diagonals that exhibit interesting mathematical relationships.
- Tessellation: Regular hexagons are known for their ability to tessellate, or tile, a plane without gaps or overlaps. This property is evident in nature and human-made designs.
These properties highlight the hexagon\"s unique position in geometry, offering both aesthetic appeal and practical applications in various fields.

Practical Applications of Hexagons
Hexagons are a fascinating shape with a wide range of practical applications across various fields. From art and design to scientific phenomena, the unique properties of hexagons make them an intriguing subject of study and use.
- Art and Design: Hexagonal patterns are prominent in Islamic geometric designs and Chinese artifacts, symbolizing intricacy and cultural significance.
- Sacred Geometry: In religious contexts, hexagons are seen in symbols like the Star of David and the Seal of Solomon, representing harmony and balance.
- Scientific Significance: Nature frequently uses hexagonal structures, such as in bee honeycombs for efficient resource use and in rock formations like the Giant’s Causeway. Remarkably, hexagonal patterns are even observed in planetary atmospheric phenomena, like the hexagonal cloud pattern at Saturn’s North Pole.
- Mathematics and Geometry: The efficiency of hexagonal tessellations, which cover planes without gaps, finds applications in crystallography and hexagonal geometry.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and significance of hexagons in both natural and human-made structures, reflecting their unique geometrical properties and aesthetic appeal.

_HOOK_
Step-by-Step Guide to Drawing a Hexagon
Drawing a hexagon can be achieved through two main methods: using a compass and ruler for a precise construction or drawing by hand for a more freehand approach. Here\"s a guide to help you draw a perfect hexagon.
Drawing a Hexagon with a Compass
- Draw a Circle: Start by drawing a cross with two guidelines at a right angle. Then, using your compass, draw a circle from where the lines intersect.
- Mark the Top Two Corners: Keep your compass at the same radius and draw a semicircle from the top intersection of the circle. Mark the points where this semicircle intersects the circle.
- Mark the Bottom Two Corners: Repeat the above step for the bottom intersection of the circle to mark the remaining two points of the hexagon.
- Connect the Points: Join the six intersecting points with straight lines to complete your regular hexagon.
Drawing a Hexagon by Hand
- Draw a Triangle: Start with an equilateral triangle where all sides are of equal length.
- Add Two Upside-Down Triangles: Add two triangles of the same size on each side of the starting triangle, drawing them upside down.
- Add Two More Triangles on Top: Draw two more triangles, standing on the flat side, with their points up. Extend the side lines of the first triangle past the center of the hexagon and then draw the outer sides.
- Complete the Hexagon: Add a line at the top to complete the hexagon. You can erase the triangle guidelines if needed.
This guide offers a structured approach to drawing a hexagon, whether you prefer precise geometric construction or a more artistic freehand method.

Additional Resources and Calculators
For those interested in exploring or calculating various aspects of hexagons, several online resources and calculators are available. These tools can help in computing areas, perimeters, and other properties of hexagons efficiently and accurately.
- Hexagon Calculators: Online calculators like the ones found on OmniCalculator and MathPortal offer easy-to-use interfaces to calculate parameters such as area, perimeter, side length, and diagonals of hexagons. These calculators often include options for converting units to suit different measurement systems.
- Area and Perimeter Formulas: Websites like Calculat.org and CalcResource provide detailed formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of regular hexagons. These formulas are especially useful for educational purposes or in situations where precise calculations are needed.
- Custom Calculations: For specific measurement needs, tools like SpikeVM\"s calculator allow for inputs in feet and inches, offering results in various units including square feet, inches, and meters. This can be particularly useful in construction or design projects involving hexagonal shapes.
- Drawing Guides: For those interested in the geometric construction of hexagons, resources are available that guide through the process of drawing perfect hexagons using tools like a compass. This is useful for artistic, architectural, and educational endeavors.
These resources provide comprehensive support for anyone working with hexagons, whether for academic, professional, or recreational purposes. They offer a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application, making the study of hexagons more accessible and engaging.

READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a hexagon?
- The formula for calculating the perimeter of a regular hexagon is P = 6a, where \"a\" represents the length of a side of the hexagon.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a hexagon with a given side length?
- To calculate the perimeter of a hexagon with a known side length, simply multiply the length of one side by 6. For example, if each side of the hexagon is 12 cm, the perimeter is 6 * 12 = 72 cm.
- What are the different types of hexagons?
- Hexagons can be classified as regular (all sides and angles are equal), irregular (sides and angles are not equal), concave (at least one interior angle is greater than 180 degrees), and convex (no interior angle is greater than 180 degrees).
- How many diagonals does a hexagon have?
- A hexagon has a total of 9 diagonals. These diagonals form six equilateral triangles within the hexagon.
- What is the sum of the interior angles of a regular hexagon?
- The sum of all interior angles of a regular hexagon is 720 degrees, with each interior angle measuring 120 degrees.
- How is the area of a hexagon calculated?
- The area of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula: Area = (3√3/2) * s², where \"s\" is the length of a side.
These questions cover the basic concepts and calculations related to hexagons, providing essential information for understanding their geometric properties.
Discover the intriguing world of hexagons, a shape integral to nature and mathematics. Our comprehensive guide on hexagon perimeters not only educates but also inspires, opening doors to geometric wonders. Join us in exploring this six-sided marvel!