Topic formulas for area and perimeter of all shapes: Discover the essential "Formulas for Area and Perimeter of All Shapes" in this comprehensive guide, unlocking the secrets of geometry for practical and academic success.
Table of Content
- Importance of Area and Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Area of Rectangle, Triangle, Circle, Sector, Trapezoid, Square, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Geometry
- Basic Definitions and Differences
- Formulas for Regular Shapes
- Rectangle
- Square
- Triangle
- Circle
- Parallelogram
- Rhombus
- Trapezoid
- Kite
- Regular Polygons
- Formulas for Irregular Shapes
- Applications in Real Life
- Practice Problems and Examples
- Frequently Asked Questions
Importance of Area and Perimeter
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial in both academic and everyday contexts. These concepts are fundamental in mathematics, providing a foundation for more advanced topics in algebra, trigonometry, and calculus. Area and perimeter play a significant role in various practical applications, impacting numerous fields such as architecture, engineering, and graphic design.
- Practical Applications: These measurements are essential in daily activities like planning a room layout, landscaping a garden, or constructing buildings. For instance, knowing the area helps in determining the amount of paint needed for a room or the quantity of carpeting for a floor.
- Understanding Spatial Relationships: Grasping these concepts aids in appreciating the space within boundaries and how different shapes can fit together, a skill beneficial in fields like interior design and urban planning.
- Perimeter in Daily Life: The perimeter is particularly useful in measuring distances around fields or plots of land, essential for activities like fencing, farming, or setting boundaries for construction.
- Educational Significance: These concepts are a vital part of the mathematics curriculum, helping students develop spatial awareness and problem-solving skills.
In essence, the knowledge of area and perimeter is not just limited to academic pursuits but extends to practical applications, deeply ingrained in everyday life and professional practices.

READ MORE:
Area of Rectangle, Triangle, Circle, Sector, Trapezoid, Square, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Geometry
\"Want to ace geometry like a pro? This mind-blowing video is a treasure trove of geometry formulas that will make your jaw drop. Learn the secrets of angles, triangles, and circles, and become the geometry guru you\'ve always dreamed of being!\"
Basic Definitions and Differences
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential in understanding the properties of two-dimensional shapes. Perimeter refers to the total distance around the boundary of a shape, while area describes the region occupied by it.
- Perimeter: It is the length of the outline of a shape. To calculate the perimeter, we add the lengths of all the sides of the shape. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of all its four sides, or simply, 2 times the sum of its length and width.
- Area: This represents the space enclosed within a shape. It is measured in square units (like square meters, square centimeters, etc.). The formula for the area varies based on the shape. For instance, the area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length by its width.
Distinguishing between these two concepts is crucial for various applications in mathematics and everyday scenarios, such as construction, interior designing, and land surveying.
For example, in a rectangle:
- The formula for perimeter is 2 times the sum of its length and width.
- The formula for area is the product of its length and width.
Different shapes have unique formulas for calculating area and perimeter. Understanding these formulas allows for precise calculations in real-world applications, such as calculating the amount of fencing needed for a garden or the carpet required for a room.

Area and Perimeter Formulas: Rectangle, Circle, Mensuration Formulas, Geometry Shorts Feed
\"Looking to up your mensuration game? Look no further! This incredible video will unveil a world of mensuration formulas that will blow your mind. From the volume of spheres to the area of complex shapes, this video has it all. Get ready to conquer mensuration like a true mathematical genius!\"
Formulas for Regular Shapes
Regular shapes have specific formulas for calculating their area and perimeter. These formulas are essential for various applications in mathematics, science, engineering, and everyday life. Understanding these formulas allows for accurate measurements and calculations.
- Square:
- Perimeter = 4s (where \"s\" is the length of a side)
- Area = s^2
- Rectangle:
- Perimeter = 2w + 2l (where \"w\" is the width and \"l\" is the length)
- Area = l × w
- Triangle:
- Perimeter = a + b + c (where \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\" are the lengths of the sides)
- Area = (1/2) × base × height
- Circle:
- Circumference (Perimeter) = 2πr (where \"r\" is the radius)
- Area = πr^2
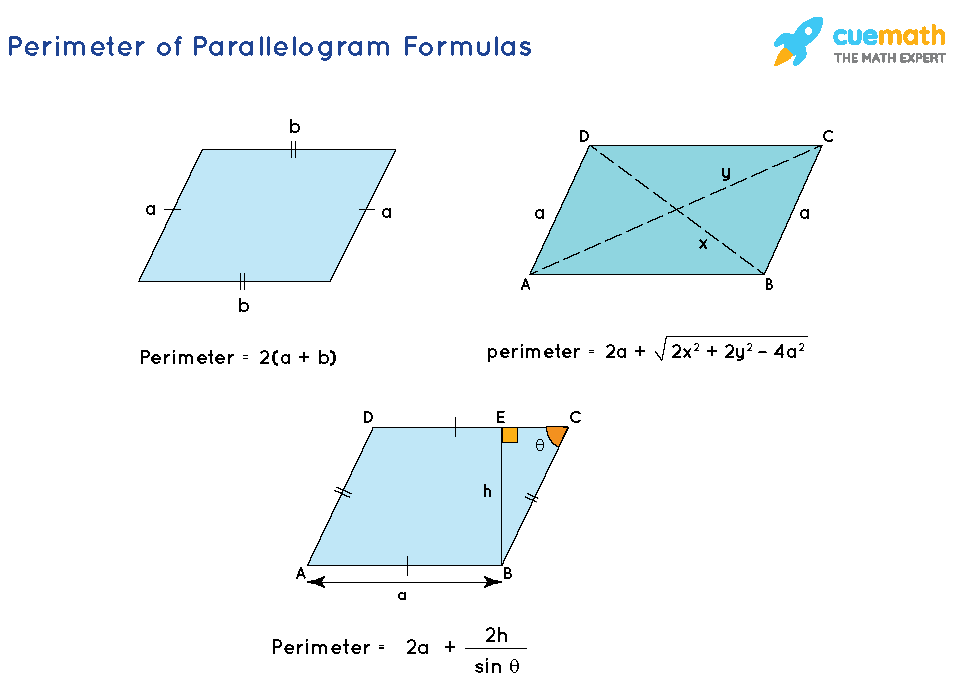
- Parallelogram:
- Area = base × height
- Perimeter = 2(base + side length)
- Trapezoid:
- Area = (1/2) height × (base1 + base2)
- Perimeter = sum of all sides
- Rhombus:
- Area = (diagonal1 × diagonal2) / 2
- Perimeter = 4 × side length
Each of these formulas is crucial for solving problems related to geometry, whether in academic settings or in practical applications like construction and design. For example, knowing the area formula of a circle is essential in determining the material needed for a circular garden plot, while the perimeter formula of a rectangle can help in fencing a rectangular yard.

Rectangle
The rectangle is a fundamental shape in geometry, characterized by having four sides with opposite sides being equal and parallel. Each angle in a rectangle is a right angle (90 degrees).
Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length (l) by its width (w). The formula is:
- Area = length × width
- Area = l × w
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 5 meters and a width of 3 meters, its area will be 5 × 3 = 15 square meters.
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around its edges. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, the formula is:
- Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
- Perimeter = 2 × (l + w)
For the same rectangle with a length of 5 meters and a width of 3 meters, its perimeter will be 2 × (5 + 3) = 16 meters.

Square
A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are of equal length. Each angle in a square is a right angle (90 degrees).
Area of a Square
The area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one of its sides. The formula is:
- Area = side × side
- Area = s²
For example, if a square has a side length of 4 meters, its area will be 4² = 16 square meters.
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total distance around its edges. Since all sides of a square are equal, the formula is:
- Perimeter = 4 × side
- Perimeter = 4s
For a square with a side length of 4 meters, its perimeter will be 4 × 4 = 16 meters.

_HOOK_
Triangle
A triangle is a three-sided polygon with three angles. The properties and formulas for triangles vary based on the type of triangle (scalene, isosceles, equilateral).
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using the base and height of the triangle. The formula is:
- Area = 1/2 × base × height
- Area = 1/2 b × h
For example, if a triangle has a base of 6 meters and a height of 4 meters, its area will be 1/2 × 6 × 4 = 12 square meters.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. The formula is:
- Perimeter = a + b + c
Where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. For instance, if the sides of a triangle are 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters, its perimeter will be 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 meters.

Circle
A triangle is a three-sided polygon with three angles. The properties and formulas for triangles vary based on the type of triangle (scalene, isosceles, equilateral).
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using the base and height of the triangle. The formula is:
- Area = 1/2 × base × height
- Area = 1/2 b × h
For example, if a triangle has a base of 6 meters and a height of 4 meters, its area will be 1/2 × 6 × 4 = 12 square meters.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. The formula is:
- Perimeter = a + b + c
Where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. For instance, if the sides of a triangle are 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters, its perimeter will be 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 meters.

Parallelogram
A triangle is a three-sided polygon with three angles. The properties and formulas for triangles vary based on the type of triangle (scalene, isosceles, equilateral).
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using the base and height of the triangle. The formula is:
- Area = 1/2 × base × height
- Area = 1/2 b × h
For example, if a triangle has a base of 6 meters and a height of 4 meters, its area will be 1/2 × 6 × 4 = 12 square meters.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. The formula is:
- Perimeter = a + b + c
Where a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. For instance, if the sides of a triangle are 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters, its perimeter will be 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 meters.

Rhombus
A rhombus is a four-sided shape where all sides have equal length. Additionally, opposite sides are parallel, and opposite angles are equal. A rhombus is sometimes referred to as a diamond or lozenge shape.
Area of a Rhombus
The area of a rhombus can be calculated by using the lengths of its diagonals. The formula is:
- Area = (diagonal 1 × diagonal 2) / 2
For example, if a rhombus has diagonals of lengths 10 cm and 8 cm, its area will be (10 × 8) / 2 = 40 square cm.
Perimeter of a Rhombus
The perimeter of a rhombus is the total length of its boundaries. Since all sides of a rhombus are equal, the formula is:
- Perimeter = 4 × side length
If the side length of a rhombus is 5 cm, then its perimeter will be 4 × 5 = 20 cm.

Trapezoid
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium in some countries, is a four-sided shape with at least one pair of parallel sides. The formulas for its area and perimeter are distinct due to its unique shape.
Area of a Trapezoid
The area of a trapezoid is calculated using the lengths of its bases (the parallel sides) and its height (the perpendicular distance between the bases). The formula is:
- Area = 1/2 × (base 1 + base 2) × height
- Area = 1/2(a + b) × h
For example, if a trapezoid has base lengths of 8 meters and 5 meters, and a height of 4 meters, its area will be 1/2 × (8 + 5) × 4 = 26 square meters.
Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all its four sides. This calculation is straightforward if all side lengths are known.
- Perimeter = sum of all sides
- Perimeter = a + b + c + d
Where a, b, c, and d are the lengths of the four sides of the trapezoid.

_HOOK_
Kite
A kite is a fascinating and unique shape in geometry, characterized by its distinctive properties and measurements. To fully understand the kite and how to calculate its area and perimeter, it\"s essential to grasp its defining features.
Defining Characteristics of a Kite
- A kite is a quadrilateral, meaning it has four sides.
- It has two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal in length.
- The diagonals of a kite intersect at right angles.
- One of the diagonals bisects the other.
Area of a Kite
To calculate the area of a kite, you need the lengths of its diagonals. The formula is quite straightforward:
Area = (Diagonal 1 x Diagonal 2) / 2
This formula works because when you draw the diagonals of a kite, they form four right-angled triangles. The area of the kite is equivalent to the sum of the areas of these triangles.
Perimeter of a Kite
Calculating the perimeter of a kite involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Since a kite has two pairs of adjacent sides of equal length, the formula is:
Perimeter = 2 x (Length of one pair of adjacent sides + Length of the other pair of adjacent sides)
It\"s important to note that the sides referred to here are the adjacent sides that are equal in length.
Practical Applications
Understanding the area and perimeter of kites has practical implications in various fields, including architecture, design, and even kite making. This knowledge is crucial for creating balanced and aesthetically pleasing designs.
Conclusion
The kite, with its unique properties, offers an interesting study in geometry. Calculating its area and perimeter can be a fun and educational exercise, reinforcing the principles of shape and measurement.
Regular Polygons
Regular polygons are fascinating figures in geometry, characterized by equal sides and equal angles. The formulas for calculating their area and perimeter vary based on the number of sides and specific dimensions such as side length, apothem, or radius.
Area of Regular Polygons
The area of a regular polygon can be determined using various formulas depending on the information available:
- For polygons with known side length: Area = [l2n]/[4tan(180/n)]
- With circumradius (r): Area = (nr2/2) sin (2π/n)
- Using the apothem (a): Area = (a x p)/2, where p is the perimeter.
These formulas utilize trigonometric functions and require precise measurements for accurate calculations.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
The perimeter of a regular polygon is simpler to calculate and is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. It can be calculated as:
Perimeter = Number of sides x Length of one side
Examples
Here are some examples to illustrate these concepts:
- Calculating the area of a regular hexagon with a side length of 2 cm.
- Finding the area of a regular pentagon with a circumradius of 4 cm.
- Determining the perimeter of a regular decagon with each side measuring 6 cm.
Application in Real Life
Knowledge of these formulas is not just academically interesting but also practical in fields like architecture, design, and engineering, where precise calculations of space and boundaries are crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding regular polygons and their area and perimeter calculations is a key aspect of geometry, offering insights into the symmetry and balance inherent in these shapes.
Formulas for Irregular Shapes
Calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes requires a different approach than regular shapes due to their non-uniform sides and angles. The following methods provide a step-by-step guide to effectively tackle these calculations.
Area of Irregular Shapes
To determine the area of an irregular shape:
- First, decompose the irregular shape into familiar regular shapes like triangles, rectangles, circles, etc.
- Calculate the area of each decomposed shape using their respective formulas.
- Add the areas of all these shapes to obtain the total area of the irregular shape.
- In some cases, using a grid method by dividing the shape into unit squares can be helpful to approximate the area.
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
For the perimeter:
- Measure the length of each external side of the irregular shape.
- Add all these lengths to get the total perimeter.
Real-Life Application
Understanding these methods is crucial in various fields, such as architecture, land surveying, and design, where working with irregular shapes is common.
Conclusion
Though irregular shapes don\"t conform to standard geometric rules, these methods allow for effective calculation of their area and perimeter, providing valuable insights into their spatial properties.
Applications in Real Life
The concepts of area and perimeter are fundamental in our daily lives and are applied in various fields. Here are some practical applications:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and engineers use area and perimeter calculations to design buildings and structures. They need to know the floor area for designing layouts and the perimeter for estimating the materials required for construction, such as fencing.
- Agriculture: Farmers use these measurements to determine the size of their fields, which helps in planning the distribution of crops, irrigation systems, and the amount of seeds and fertilizers required.
- Interior Design: When designing an interior space, knowing the area is essential for fitting furniture appropriately and ensuring efficient use of space.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors use area and perimeter measurements to determine property boundaries and for land division.
- Sports: The design and layout of sports fields and courts require precise area and perimeter measurements to meet standard regulations.
- Geographical Mapping: Geographers and cartographers calculate the area and perimeter of various geographical features for map making and resource management.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, these concepts are used for material estimation, layout planning of manufacturing units, and optimizing the use of raw materials.
- Education: Area and perimeter serve as foundational concepts in mathematics education, essential for advanced studies in geometry, trigonometry, and calculus.
- Art and Craft: Artists and craftsmen use area and perimeter calculations in designing and creating artworks and crafts, ensuring proportional and aesthetic appeal.
Understanding the practical applications of area and perimeter not only helps in solving real-life problems but also enhances spatial reasoning and analytical skills.
Practice Problems and Examples
Practicing problems on area and perimeter enhances understanding of these concepts. Below are examples with solutions:
- Rectangle Area and Perimeter: For a rectangular field with a length of 12 m and a breadth of 10 m, calculate its area and perimeter.
- Circle Perimeter: Determine the perimeters of circles with radii of 14 cm, 10 m, and 4 km.
- Rhombus Area: A rhombus with a base of 10 cm and a height of 7 cm - find its area.
- Area of a Square Park: If a square park has a perimeter of 320 m, what is its area?
- Area of Rhombus by Diagonals: Calculate the area of a rhombus when the lengths of the diagonals are given.
- Area and Perimeter of Various Shapes: Practice finding area and perimeter for different shapes using specific formulas.
These exercises are designed to cover basic to slightly advanced problems, helpful for students and anyone looking to refresh their knowledge.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why are area and perimeter important in mathematics and real life?
- Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, crucial for understanding more complex mathematical theories and practical applications in various fields such as architecture, land surveying, and everyday activities like gardening or interior designing.
- How can I calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle?
- To calculate the area of a rectangle, multiply its length by its breadth. The perimeter is the sum of all its sides, calculated as 2 times the sum of its length and breadth.
- What is the formula for the area of a circle?
- The area of a circle is given by πr², where r is the radius of the circle.
- How do you determine the perimeter of irregular shapes?
- The perimeter of irregular shapes can be found by summing the lengths of all its sides. For circular segments, the circumference formula can be used as part of the calculation.
- Can the area and perimeter of a shape be the same?
- Yes, in certain cases, the numerical values of area and perimeter can be the same, but they represent different physical quantities and are measured in different units.
- How is the area of a triangle calculated?
- The area of a triangle is calculated as 1/2 multiplied by its base and height (Area = 1/2 × base × height).
- What are the applications of learning area and perimeter?
- Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for practical tasks like construction planning, agricultural planning, designing, and even in sports for determining the playing area.
- How can I find the area of a square if I know its perimeter?
- To find the area of a square from its perimeter, first divide the perimeter by 4 to get the length of one side, and then square this length (Area = (Perimeter/4)²).
- Is the formula for perimeter the same for all shapes?
- No, the formula for perimeter varies depending on the shape. Generally, it involves summing the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
Unlock the world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on area and perimeter formulas for all shapes, a valuable resource for students, educators, and geometry enthusiasts. Dive in to explore and master these fundamental concepts in a fun and engaging way!