Topic formula for perimeter of pentagon: Discover the intriguing world of geometry with our exploration of the "Formula for Perimeter of Pentagon." This guide illuminates the simple yet elegant methods to calculate this fundamental geometric measurement, opening doors to a clearer understanding of shapes and spaces.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Pentagon
- YOUTUBE: Perimeter of Regular Pentagon
- Regular vs Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
- Calculating Perimeter with Side Lengths
- Formula for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
- Example Calculations for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
- Formula for Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
- Understanding the Role of Apothem in Pentagon Perimeter
- Additional Parameters Related to Pentagon Perimeter
- Practical Applications and Examples of Pentagon Perimeter
- FAQs and Common Misconceptions about Pentagon Perimeter
Understanding the Perimeter of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon, a fundamental concept in geometry, represents the total distance around its boundary. This measurement is crucial in understanding the properties of pentagons, which are five-sided polygons. The calculation method varies depending on the type of pentagon - regular (with equal sides and angles) or irregular (with differing sides and angles).
For a regular pentagon, the perimeter is calculated using the formula P = 5s, where \"s\" is the length of one side. For example, if each side of a regular pentagon measures 3 cm, the perimeter would be 15 cm. This straightforward formula simplifies the process as all sides in a regular pentagon are equal in length.
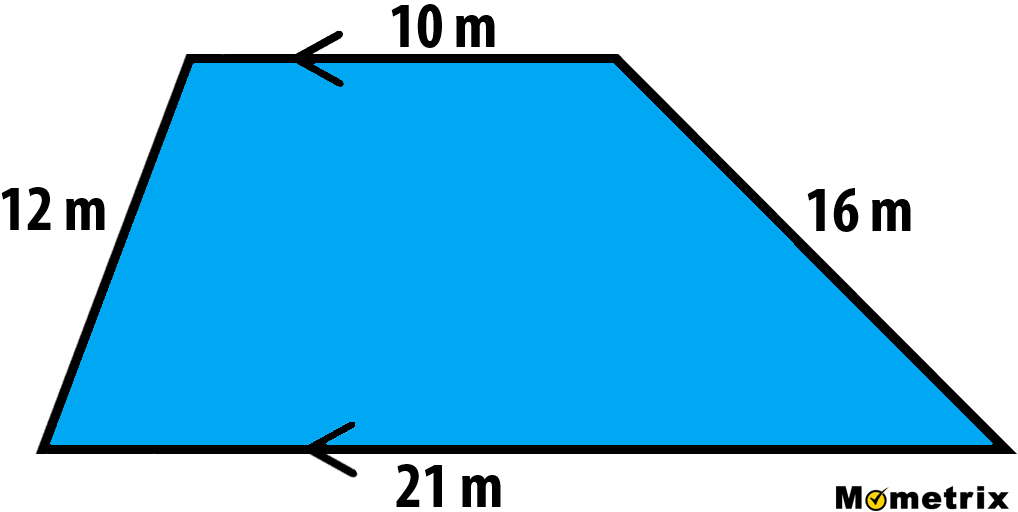
In contrast, calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon requires adding the lengths of all its sides. For instance, if an irregular pentagon has side lengths of 5, 4, 7, 3, and 6 units, its perimeter would be the sum of these measurements.
Understanding these calculations is not only essential for academic purposes but also has practical applications in various fields, including architecture and design. Regular pentagons often feature in aesthetic patterns and structures, while irregular pentagons are frequently encountered in natural formations and irregularly shaped objects.
Further extending this concept, in addition to perimeter, other properties like the area and apothem of a pentagon are also significant in comprehensive geometric studies. These aspects provide a deeper insight into the pentagon\"s structure and enable a more detailed analysis of its geometric properties.

READ MORE:
Perimeter of Regular Pentagon
\"Discover the secrets hidden within the Pentagon! Join us on an extraordinary journey as we unveil the fascinating history and architecture of this iconic building in our must-watch video!\"
Perimeter of Pentagon
\"Unlock the mystery of perimeter calculations with our exciting video! Learn how to measure and calculate perimeters like a pro, as we guide you through simple and engaging examples that will leave you with a solid understanding of this fundamental concept!\"
Regular vs Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
Understanding the distinction between regular and irregular pentagons is crucial for correctly calculating their perimeters. A regular pentagon is defined by five equal sides and angles, offering simplicity in calculation. In contrast, an irregular pentagon has varying side lengths and angles, leading to a more complex calculation process.
Regular Pentagon Perimeter: For a regular pentagon, the perimeter is efficiently calculated using the formula P = 5s, where s is the length of one side. For instance, if a regular pentagon has a side length of 8 units, its perimeter is simply 5 times 8, equating to 40 units.
Irregular Pentagon Perimeter: The perimeter of an irregular pentagon requires a more meticulous approach. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. If an irregular pentagon has side lengths of a, b, c, d, and e, the perimeter is found by the formula P = a + b + c + d + e. Each side\"s length must be known or calculated for accurate measurement.
These differing methods highlight the importance of understanding the pentagon\"s structure before attempting to calculate its perimeter. Regular pentagons offer a straightforward calculation, whereas irregular pentagons demand detailed knowledge of all side lengths.

Calculating Perimeter of Pentagon
\"Are you ready to dive into the world of numbers? Let us take you on an incredible journey of calculating wonders! In our video, we\'ll explore various calculating techniques and show you practical examples to boost your math skills and make calculations a breeze!\"
Calculating Perimeter with Side Lengths
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon is a straightforward process when you know the lengths of its sides. Whether it\"s a regular pentagon with equal sides or an irregular one with different side lengths, the method varies slightly.
Regular Pentagon: For a regular pentagon, where all sides are of equal length, the perimeter is calculated using the formula: P = 5 × s, where P represents the perimeter and s is the length of a side. For example, if each side of a pentagon is 3 cm, then the perimeter is calculated as 5 × 3 = 15 cm.
Irregular Pentagon: In the case of an irregular pentagon, where the sides have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides. The formula can be represented as P = a + b + c + d + e, where a, b, c, d, and e are the lengths of the individual sides. For example, if the side lengths are 5, 4, 7, 3, and 6 units, the perimeter is the sum of these lengths.
When calculating perimeters, especially for irregular shapes, attention to detail is crucial to ensure accuracy. Moreover, understanding these calculations is not just academically beneficial but also practical in various real-life applications.
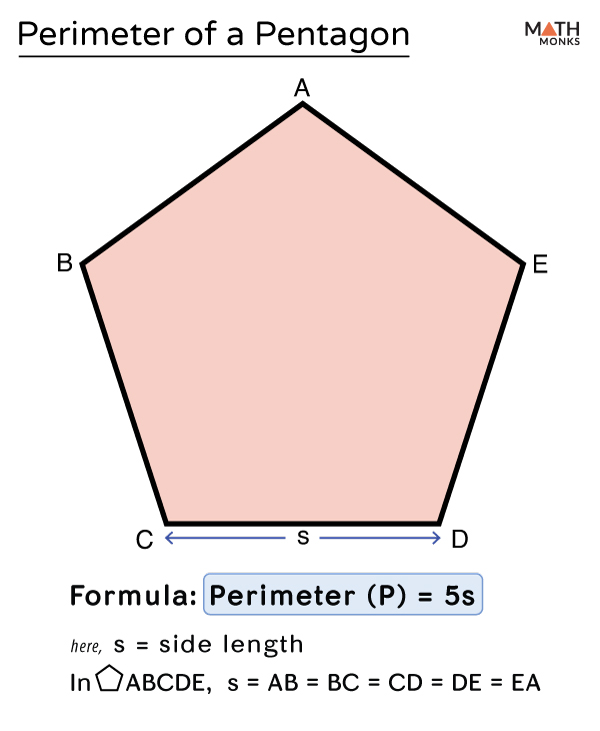
Formula for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
The perimeter of a regular pentagon, which is a polygon with five equal sides and angles, can be easily calculated using a simple formula. This formula is particularly useful as it simplifies the calculation process for regular pentagons.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon is P = 5s, where P represents the perimeter and s is the length of one of its sides. Essentially, since all sides of a regular pentagon are equal, the perimeter is five times the length of one side.
For example, if a regular pentagon has a side length of 7 cm, its perimeter would be calculated as 5 × 7 cm, resulting in 35 cm. Similarly, a pentagon with each side measuring 15 yards would have a perimeter of 75 yards.
This formula is a fundamental aspect of geometry and is widely used in various mathematical calculations and real-world applications, especially in design and architecture involving symmetrical shapes.

Example Calculations for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
To illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, let\"s consider a few examples. Remember, the perimeter of a regular pentagon is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 5, since all sides are equal in length.
Example 1: Pentagon with Side Length of 4 cm
Consider a regular pentagon where each side is 4 cm long. To find the perimeter, simply multiply the side length by 5.
- Side length = 4 cm
- Perimeter = 4 cm x 5 = 20 cm
Example 2: Pentagon with Side Length of 10 inches
For a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 inches, the perimeter can be found in the same way.
- Side length = 10 inches
- Perimeter = 10 inches x 5 = 50 inches
Example 3: Pentagon with Side Length of 1.5 meters
If we have a regular pentagon with each side as 1.5 meters, we can calculate the perimeter like this:
- Side length = 1.5 meters
- Perimeter = 1.5 meters x 5 = 7.5 meters
Visualizing the Calculation
To better understand the calculation, imagine laying out five rods or sticks, each of the given length, end-to-end in the shape of a pentagon. The total length of these rods or sticks put together gives the perimeter of the pentagon.
Conclusion
These examples demonstrate that calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is straightforward as long as you know the length of one side. It\"s a simple matter of multiplication, which makes it an easy concept to grasp and apply in practical scenarios.

_HOOK_
Formula for Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
The perimeter of an irregular pentagon, where each side may have a different length, is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. This is different from a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, and the formula involves a simple multiplication.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, use the formula:
P = a + b + c + d + e
Where:
- a, b, c, d, e - Represent the lengths of the five sides of the pentagon.
Example Calculation
Suppose an irregular pentagon has sides of lengths 2.36 m, 4.01 m, 3.12 m, 3.22 m, and 4.41 m. The perimeter is calculated as:
- P = 2.36 m + 4.01 m + 3.12 m + 3.22 m + 4.41 m
- P = 17.12 m
This simple additive approach allows for the perimeter calculation of any irregular pentagon given the lengths of all its sides.

Understanding the Role of Apothem in Pentagon Perimeter
The apothem in a regular pentagon plays a critical role in geometric calculations, particularly in determining the area of the pentagon. While it\"s not directly used to calculate the perimeter, understanding its role provides deeper insights into the properties of regular pentagons.
The apothem of a pentagon is defined as the perpendicular distance from the center of the pentagon to the midpoint of one of its sides. This line segment is also considered as the radius of the pentagon\"s incircle.
Calculating the Apothem of a Pentagon
To calculate the apothem of a regular pentagon, we can use trigonometry. Here\"s a step-by-step explanation:
- The pentagon is divided into five congruent triangles.
- Each of these triangles is an isosceles triangle with the apothem serving as its height.
- By using the tangent function, the apothem (a) can be calculated using the formula: a = s / (2 * tan(36°)), where s is the side length of the pentagon.
Role of Apothem in Area Calculation
While the apothem is not used directly in calculating the perimeter, it\"s essential for finding the area of a regular pentagon. The formula for area is: Area = 1/2 * Perimeter * Apothem. Here\"s how it works:
- First, calculate the perimeter of the pentagon by multiplying the length of one side by 5.
- Then, use the apothem and the perimeter in the area formula to find the area of the pentagon.
This method highlights the importance of the apothem in understanding the geometric properties of a regular pentagon, especially in context to its area, rather than its perimeter.

Additional Parameters Related to Pentagon Perimeter
Beyond the basic formulas for calculating the perimeter of regular and irregular pentagons, there are additional parameters that can be used to determine the perimeter of a pentagon in various contexts. These include calculations based on the radius (circumradius) and apothem of the pentagon.
Perimeter Calculation Using Radius
For a pentagon inscribed in a circle (circumscribed pentagon), the radius (distance from the center to a vertex) can be used to determine the side length and, consequently, the perimeter. The side length in this case is derived using the formula: Side length = 2r × Sin(180/n), where r is the radius, and n is the number of sides (5 for a pentagon). Once the side length is determined, the perimeter is simply 5 times this length.
Perimeter Calculation Using Apothem
When the apothem (the perpendicular distance from the center to a side) of the pentagon is known, it can also be used to calculate the perimeter. The formula to find the side length in this scenario is: Side length = 2a × tan(180/n), where a is the apothem. The perimeter is then calculated by multiplying this side length by 5.
These methods are particularly useful in scenarios where the direct measurement of the side lengths is not feasible but the radius or apothem can be determined or is given.

Practical Applications and Examples of Pentagon Perimeter
The concept of a pentagon\"s perimeter is not just limited to mathematical theory but finds practical applications in various fields. Understanding these applications helps appreciate the relevance of geometry in our daily lives.
Architecture and Design
In architecture, the pentagon shape is used for aesthetic and functional purposes. The perimeter of pentagons and other polygons helps architects determine the dimensions and layout of structures, including unique building designs.
Urban Planning
Urban planners use geometric shapes, including pentagons, to design public spaces, parks, and layout city blocks. The perimeter of these shapes assists in calculating the area and spatial relationships necessary for effective planning.
Art and Decoration
Artists and designers often incorporate pentagons and other geometric shapes into their work. The perimeter and area of these shapes play a role in creating symmetrical designs and patterns in artworks, textiles, and decorative items.
Sports Fields
The layout of certain sports fields and courts involves geometry. While a pentagon shape may not be directly used, understanding its properties can aid in designing and marking sports fields with precision.
Technology
In technology, particularly in graphic design and digital art, geometric shapes including pentagons are used to create visually appealing and structurally sound designs. The perimeter of these shapes is crucial in maintaining proportion and balance.
These are just a few examples of how the perimeter of a pentagon and other polygons are used in practical applications, showcasing the importance of geometric concepts in various aspects of life.

READ MORE:
FAQs and Common Misconceptions about Pentagon Perimeter
The concept of the perimeter of a pentagon, while straightforward, often brings about several questions and misconceptions. Understanding these can enhance our comprehension and application of geometric concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is the perimeter of a regular pentagon always larger than an irregular one with the same side length?No, the perimeter of a pentagon depends on the length of its sides. A regular pentagon has equal sides, but an irregular pentagon can have sides of varying lengths that could result in a larger or smaller perimeter.
- Can you calculate the perimeter of a pentagon without knowing all side lengths?In a regular pentagon, knowing one side length is sufficient as all sides are equal. However, in an irregular pentagon, you need the length of each side to calculate the perimeter.
- Is the perimeter of a pentagon always five times its side length?This is true only for regular pentagons. For irregular pentagons, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
Common Misconceptions
- Misconception: A square is not a rectangle.Contrary to this common belief, a square is a special type of rectangle where all sides are equal. This misconception often arises due to the standard orientation of shapes in teaching materials.
- Misconception: Similar shapes are always congruent.Similar shapes have the same shape but not necessarily the same size, whereas congruent shapes are both the same shape and size.
- Misconception: 2D and 3D shapes with similar appearances are unrelated.Many students struggle to recognize that 2D and 3D shapes with similar appearances (like a square and a cube) are closely related, with the latter being a 3D extension of the former.
- Misconception: The orientation of a shape changes its type.Some students believe that a shape\"s orientation (like a square positioned as a diamond) changes its type. However, a shape\"s type is determined by its sides and angles, not its orientation.
Addressing these FAQs and misconceptions helps clarify the understanding of pentagon perimeters and geometric concepts in general, aiding in a more comprehensive grasp of geometry.
Discover the world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the formula for the perimeter of a pentagon. Enhance your understanding, unravel common misconceptions, and explore practical applications in a way that\"s both engaging and informative.
_HOOK_