Topic formula for triangle perimeter: Unlock the secrets of geometry with our comprehensive guide on the "Formula for Triangle Perimeter," a fundamental concept for students, educators, and geometry enthusiasts alike.
Table of Content
Basic Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its three sides. This fundamental geometric concept is key in various fields, including architecture and mathematics. Here\"s how to calculate it:
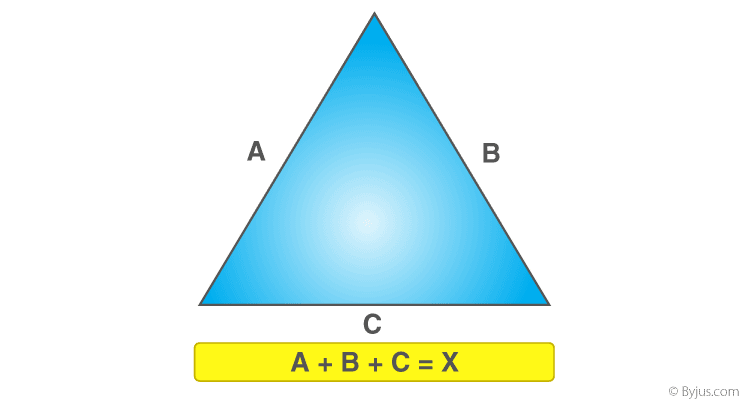
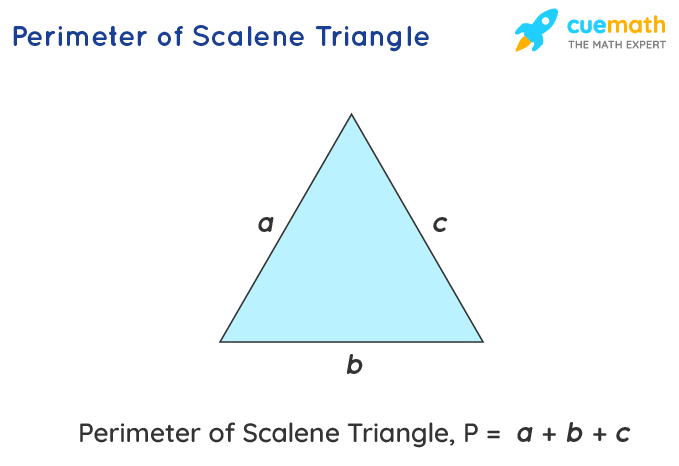
- General Formula: For any triangle with sides of lengths a, b, and c, the perimeter (P) is the sum of these side lengths: P = a + b + c.
- Special Triangles:
- For an equilateral triangle (all sides equal), if each side is \"s\", then P = 3s.
- For an isosceles triangle (two sides equal), with equal sides of length \"a\" and base \"b\", the formula is P = 2a + b.
- For a right triangle, use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of all sides if needed, and then sum them up.
- Using Angles: In cases where you know one or two angles and some side lengths, use trigonometric laws like the Sine and Cosine rules to find missing side lengths before applying the basic formula.
Understanding these formulas and when to use them helps in solving complex geometry problems efficiently.

READ MORE:
Finding the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Discover the magic of perimeter in this captivating video - learn how to calculate the total length around any shape with simple and fun examples that will leave you wanting to explore more!\"
Special Cases: Isosceles, Equilateral, and Right Triangles
Triangles come in various shapes, each with its unique perimeter formula. Let\"s explore these special cases:
- Isosceles Triangle: Characterized by two equal sides. If \"a\" is the length of the equal sides and \"b\" is the base, the perimeter is given by P = 2a + b.
- Example: For an isosceles triangle with sides 5 cm and base 4 cm, the perimeter is 2(5) + 4 = 14 cm.
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal in length. If \"s\" is the length of a side, the perimeter is P = 3s.
- Example: An equilateral triangle with each side measuring 6 cm has a perimeter of 3(6) = 18 cm.
- Right Triangle: Includes a 90-degree angle. The sides are typically referred to as the base (b), height (h), and hypotenuse (c). The perimeter is P = b + h + c. The Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find any missing side lengths.
- Example: For a right triangle with a base of 3 cm, height of 4 cm, and hypotenuse of 5 cm, the perimeter is 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 cm.
Understanding these specific formulas is crucial for accurately calculating the perimeters of various triangle types.

Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Get ready to dive into the world of geometry with this exciting video! Find out how to master both area and perimeter calculations, unlocking the secrets to measuring shapes of all sizes. Join us now and become a math whiz!\"
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Triangle with Math Mr. J
\"Welcome to the ultimate math adventure with Mr. J! In this captivating video, uncover the mysteries of area and perimeter as you embark on a thrilling journey through numbers and shapes. Prepare to be amazed by Mr. J\'s genius teaching methods.\"
Calculating Perimeter with SAS (Side-Angle-Side)
When a triangle\"s two sides and the included angle are known (SAS), the perimeter can still be calculated using trigonometry:
- Identify the Known Elements: Recognize the two given sides (a and b) and the included angle (C) between them.
- Use the Law of Cosines: To find the third side (c), use the formula: ( c = sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab cdot cos(C)} ).
- Example: For sides a = 5, b = 7 and angle C = 60°, calculate the third side.
- Calculate the Perimeter: With all three sides known, sum them up to find the perimeter: P = a + b + c.
- Continuing the example, once c is calculated, sum a, b, and c for the perimeter.
This method is particularly useful in fields like construction and engineering where precise measurements are crucial.

Calculating Perimeter with ASA (Angle-Side-Angle)
For triangles where two angles and the side between them are known (ASA), the perimeter can be calculated through a series of steps involving trigonometry:
- Determine Known Angles and Side: Identify the known side (a) and the two adjacent angles (B and C).
- Calculate the Third Angle: Since the sum of angles in a triangle is 180°, find the third angle (A) using A = 180° - B - C.
- Use the Law of Sines: To find the remaining sides (b and c), use the law of sines: ( frac{a}{sin(A)} = frac{b}{sin(B)} = frac{c}{sin(C)} ). Rearrange to find b and c.
- Example: With a = 8, B = 45°, and C = 60°, calculate b and c.
- Calculate the Perimeter: The perimeter is the sum of all three sides: P = a + b + c.
- After calculating b and c, add them with a to find the perimeter.
This approach is especially useful in fields like surveying and astronomy, where angles are more commonly measured than sides.
Practical Applications and Examples
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a triangle is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications in real life. Here are some examples:
- Architecture and Construction: Calculating the amount of materials needed for triangular architectural elements, such as gables or roofs.
- Example: Determining the amount of trim required for a triangular window.
- Land Surveying: Determining the boundaries of triangular plots of land.
- Example: Calculating the fencing required to enclose a triangular field.
- Geography and Mapping: Estimating the perimeter of triangular geographical features like islands or lakes.
- Example: Measuring the coastline of a triangular-shaped lake.
- Education: Teaching students about geometry and its real-world applications.
- Example: Classroom projects involving the calculation of perimeters of various shapes.
- Crafts and Art: Designing and creating artworks and crafts with triangular components.
- Example: Planning a triangular quilt pattern and determining the total length of the borders.
These examples illustrate how the perimeter of a triangle is a useful and practical concept in various fields.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the simplest formula for the perimeter of a triangle?
- The simplest formula is the sum of its sides: P = a + b + c, where a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle\"s sides.
- How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
- For a right triangle, calculate the lengths of all three sides (base, height, hypotenuse) and add them together. If two sides are known, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the third.
- Can you calculate the perimeter if only angles are known?
- It\"s not possible to calculate the exact perimeter with angles alone. Side length information is necessary to determine the perimeter.
- Is the formula different for equilateral and isosceles triangles?
- Yes, for an equilateral triangle (all sides equal), the formula is P = 3s (s being the side length). For an isosceles triangle, use P = 2a + b (a being the equal sides and b the base).
- How do the perimeter formulas change with units?
- The formulas remain the same regardless of units. However, ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before calculating.
- Can I calculate the perimeter using the area of the triangle?
- No, the area and perimeter of a triangle are independent measurements and calculating one from the other directly is not possible.
Mastering the formula for the perimeter of a triangle not only enhances your geometric understanding but also equips you with practical skills for everyday applications. Embrace this knowledge and open doors to a world of mathematical exploration!