Topic what is the perimeter of trapezoid jklm: Explore the intriguing world of geometry as we dive into calculating the perimeter of Trapezoid JKLM, a fundamental yet fascinating concept for math enthusiasts and students alike.
Table of Content
- Definition and Basic Concept of a Trapezoid
- YOUTUBE: Calculating the Perimeter of Quadrilaterals
- Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
- Steps to Determine the Perimeter of Trapezoid JKLM
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations for Different Types of Trapezoids
- Understanding Isosceles, Scalene, and Right Trapezoids
- Role of Angles and Sides in Determining the Perimeter
- Practical Applications and Importance of Perimeter Calculations
- Advanced Tools and Calculators for Perimeter Calculation
- Frequently Asked Questions About Trapezoid Perimeters
Definition and Basic Concept of a Trapezoid
A trapezoid is a unique four-sided figure, known for having one pair of parallel sides, referred to as the bases. The remaining two sides, which are non-parallel, are known as the legs of the trapezoid. This geometric shape stands out because it doesn\"t necessarily have all sides or angles equal, leading to various classifications like right, isosceles, and scalene trapezoids.
- Right Trapezoids: These have a pair of right angles adjacent to each other.
- Isosceles Trapezoids: Characterized by non-parallel sides (legs) that are equal in length.
- Scalene Trapezoids: Neither the sides nor the angles of these trapezoids are equal.
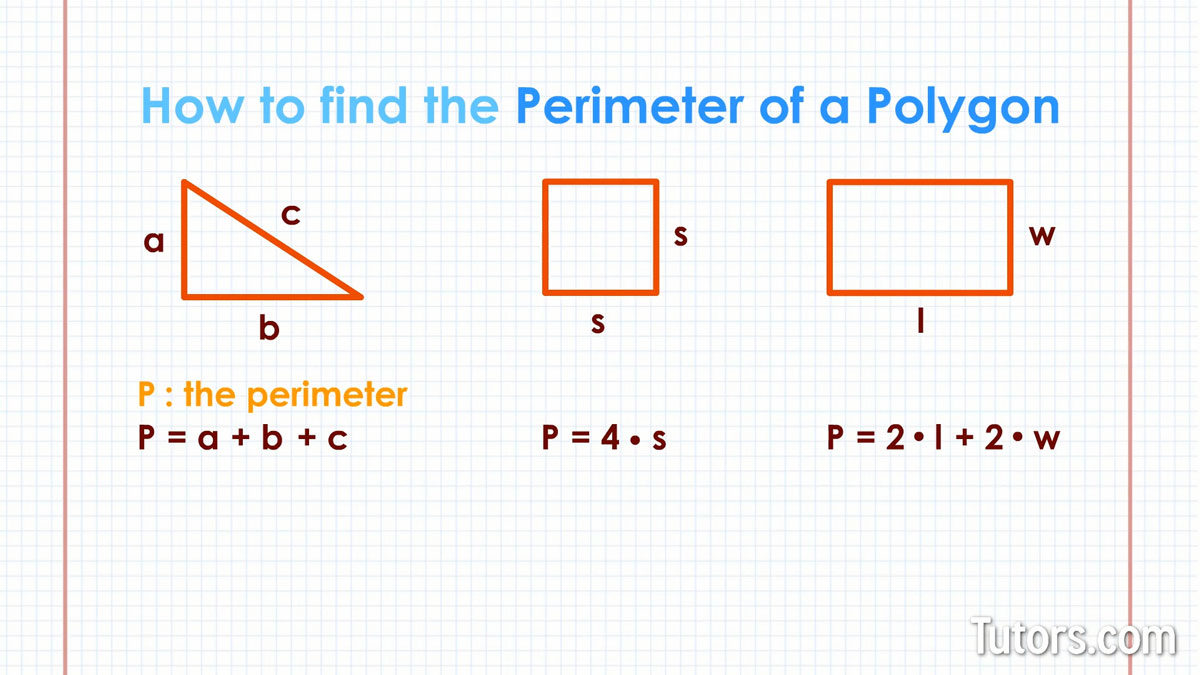
Understanding these types is crucial as they influence the properties and the formula used to calculate the perimeter of the trapezoid. The basic formula for finding the perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all its sides (P = a + b + c + d), where \"a\" and \"b\" represent the parallel sides, while \"c\" and \"d\" are the non-parallel sides. This formula can vary slightly based on the type of trapezoid and the available measurements.
Furthermore, the trapezoid\"s median or midsegment is an essential aspect, serving as a line segment that connects the midpoints of the non-parallel sides and is parallel to the bases. The median\"s length is the average of the two base lengths. The altitude or height of the trapezoid, which is the perpendicular distance between the bases, also plays a critical role in calculations involving trapezoids.
These fundamental aspects form the core of understanding and calculating the perimeter of trapezoids, paving the way for deeper exploration into their geometrical properties and applications.

READ MORE:
Calculating the Perimeter of Quadrilaterals
Perimeter: \"Discover the fascinating world of perimeter calculations and unlock the secrets of shapes and distances in this captivating video that will redefine your understanding of the perimeter concept.\"
Trapezoids
Trapezoid: \"Unearth the beauty of trapezoids and unravel the mystery behind their unique characteristics in this enlightening video that will leave you mesmerized by the intricate nature of these four-sided wonders.\"
Formula for Calculating the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total distance around its edges. It\"s a simple but essential concept in understanding trapezoids, which are quadrilaterals with one pair of parallel sides. The formula for calculating the perimeter is straightforward, encompassing the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
To express this formula, we use:
- P for perimeter,
- a and b for the lengths of the parallel sides (bases),
- c and d for the lengths of the non-parallel sides (legs).
Therefore, the formula for the perimeter (P) of a trapezoid is given by:
P = a + b + c + d
This formula is universally applicable regardless of the type of trapezoid, whether it is right, isosceles, or scalene. In the case of an isosceles trapezoid, where the non-parallel sides are equal, the formula can be slightly modified to P = a + b + 2c, where c is the length of one of the equal sides.
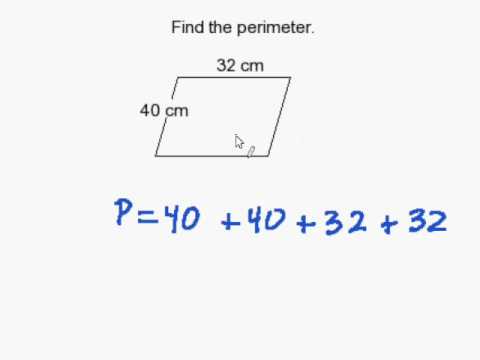
For example, to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides 10 meters, 6 meters, 8 meters, and 9 meters, we simply add these lengths together. In this case, the perimeter would be 10 + 6 + 8 + 9 = 33 meters.
It\"s important to note that the units of the perimeter will match the units used for the sides of the trapezoid, whether they are meters, centimeters, inches, or any other linear measurement.
Moreover, there are various combinations of sides, angles, and heights that can be used to calculate the perimeter if not all side lengths are known. Tools like the trapezoid perimeter calculator can assist in these calculations by allowing input of different combinations of known values.

Geometry Notes - Properties of Trapezoids
Geometry: \"Embark on an exciting journey through the realm of geometry and delve into a world where shapes and patterns come to life. This mind-opening video will open your eyes to the wonders of geometry like never before.\"
Steps to Determine the Perimeter of Trapezoid JKLM
- Determine the Lengths of All Sides: Measure or obtain the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid, labeled a, b, c, and d. Here, a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides, while c and d are the lengths of the non-parallel sides.
- Calculate the Perimeter: Use the perimeter formula P = a + b + c + d. Add the lengths of all four sides together to find the perimeter of the trapezoid.
- Consider Special Cases: In the case of an isosceles trapezoid, where the non-parallel sides are equal, the formula can be simplified to P = a + b + 2c.
- Utilize Advanced Calculations if Necessary: If not all side lengths are known, you may need to calculate them using other properties of the trapezoid, such as angles, height, or the properties of right triangles. For example, the height can be found using trigonometric functions in the case of known angles, or by using the Pythagorean theorem.
- Apply Units of Measurement: Remember that the perimeter is a linear measurement. Therefore, ensure that all side lengths are in the same unit (e.g., meters, centimeters, inches) before calculating the perimeter.
Note: The steps outlined are a general guide to calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid, including trapezoid JKLM. Depending on the specific properties of trapezoid JKLM, some steps may require adjustments or additional calculations.

Examples of Perimeter Calculations for Different Types of Trapezoids
- Regular Trapezoid:
- For a trapezoid with side lengths a = 10 meters, b = 6 meters, c = 8 meters, and d = 9 meters, the perimeter is calculated by adding all the side lengths. Here, P = 10 + 6 + 8 + 9 = 33 meters.
- Isosceles Trapezoid:
- In an isosceles trapezoid with bases a = 34.4 cm, b = 16.4 cm, and equal legs c (each 12.5 cm), the perimeter is calculated as P = a + b + 2c, which equals 34.4 + 16.4 + 2 × 12.5 = 75.8 cm.
- Trapezoid with Known Sides and Angles:
- For a trapezoid with sides c = 4, d = 3, base a = 10, and angle α = 30°, first calculate the height h = c * sin(α) = 4 * sin(30°) = 2. Then, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the projections of the sides on base a, subtract these from base a to find b, and then calculate the perimeter as P = a + b + c + d.
- Right Trapezoid:
- Consider a right trapezoid with base lengths a = 8 inches, b = 5 inches, and side d = 3 inches, and angles α = 90° and δ = 45°. In this case, the side c is perpendicular to the bases, thus equal to the height h. Using trigonometric functions and the Pythagorean theorem, the perimeter can be determined.
These examples illustrate the versatility of the perimeter formula for trapezoids, accommodating various types and specific measurements of trapezoids. The key lies in accurately determining the lengths of the sides, which may involve additional geometric calculations or measurements.

Understanding Isosceles, Scalene, and Right Trapezoids
Trapezoids, also known as trapezia, are four-sided figures with at least one pair of parallel sides, known as the bases. The other two sides are termed as legs. This unique structure leads to different types of trapezoids, each with distinct properties.
- Isosceles Trapezoids: These trapezoids are characterized by their non-parallel sides (legs) being of equal length. This equality of legs also leads to equal angles on each of the bases. One key property of isosceles trapezoids is that their diagonals are equal in length.
- Scalene Trapezoids: In scalene trapezoids, neither the sides nor the angles are equal. This lack of symmetry means each side and angle can have different measurements, making it the most general form of a trapezoid.
- Right Trapezoids: These trapezoids have a pair of right angles. Typically, these right angles are adjacent to each other, making one of the non-parallel sides perpendicular to the bases. This perpendicular side effectively becomes the height of the trapezoid.
The properties of trapezoids extend beyond their shape. The median or midsegment of a trapezoid, a line connecting the midpoints of the non-parallel sides, is parallel to the bases and its length equals the average of the two base lengths. The height or altitude, essential in area calculations, is the perpendicular distance between the bases. In the case of right trapezoids, determining the height is straightforward as it\"s the length of the leg perpendicular to the bases. In contrast, for scalene and isosceles trapezoids, more complex calculations involving trigonometric functions or the Pythagorean theorem might be required to find the height.

_HOOK_
Role of Angles and Sides in Determining the Perimeter
The perimeter of a trapezoid, a key geometric concept, is influenced by both the lengths of its sides and the angles between them. Understanding how these elements interplay is crucial in accurately determining the perimeter.
- Importance of Side Lengths: The most direct way to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid is by adding the lengths of all four sides. This method is straightforward when all side lengths are known. For example, the perimeter of a trapezoid with side lengths of 10 meters, 6 meters, 8 meters, and 9 meters is simply the sum of these measurements, resulting in a perimeter of 33 meters.
- Angles and Height in Calculations: When not all side lengths are known, angles can play a pivotal role in determining missing dimensions. For instance, the height of the trapezoid can be found using trigonometric functions if an angle and one side length are known. This height can then be used to calculate missing side lengths, especially in right trapezoids where one of the legs forms a right angle with the bases.
- Advanced Calculations: For more complex scenarios, such as when only angles and one base are known, advanced geometric and trigonometric methods may be required. These might involve calculating the height using trigonometric functions and then determining the projections of the sides on the bases.
- Using Perimeter Calculators: In situations where manual calculations become cumbersome, perimeter calculators can be invaluable. These tools often require inputs like side lengths, angles, or height and provide the perimeter as output. They can handle various configurations of trapezoids, including isosceles, scalene, and right trapezoids.
In summary, while the basic formula for the perimeter of a trapezoid is straightforward, the role of angles and sides can significantly influence the method used to determine it. Understanding these geometric principles is key to accurate calculations.

Practical Applications and Importance of Perimeter Calculations
Perimeter calculations, particularly for trapezoids, are essential in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and land surveying. These calculations help in accurately determining the boundary lengths of plots, gardens, and construction sites. Understanding trapezoid perimeters is crucial in designing roofs, bridges, and other structures where non-rectangular forms are present.
In educational contexts, the study of trapezoid perimeters enhances geometrical understanding, providing a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. It also fosters problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
- Architecture and Construction: Determining material quantities, ensuring structural balance.
- Land Surveying: Accurate boundary measurements for plots and properties.
- Education: Enhancing understanding of geometry and fostering analytical skills.
- Engineering: Essential in the design of mechanical parts, roads, and bridges where trapezoidal shapes are common.
Overall, the ability to calculate trapezoid perimeters is not just a mathematical skill but a practical tool in various real-world applications, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of geometry.

Advanced Tools and Calculators for Perimeter Calculation
In the realm of geometry and mathematics, advanced tools and calculators have significantly simplified the process of calculating the perimeter of trapezoids. These tools offer precision and ease, especially in complex scenarios where manual calculations are cumbersome or prone to error.
- Online Trapezoid Perimeter Calculators: These user-friendly online tools allow for quick and accurate perimeter calculations by inputting the lengths of the trapezoid\"s sides.
- Geometric Software Programs: Software like GeoGebra provides dynamic geometry environments where one can visually construct trapezoids and calculate their properties, including perimeters.
- Spreadsheet Tools: Excel and similar spreadsheet programs can be used to create formulas for perimeter calculations, useful for repeated calculations or variations in trapezoid dimensions.
- Mobile Applications: Various geometry-related mobile apps offer perimeter calculation tools that are convenient for on-the-go use, particularly useful for educators and students.
- Graphing Calculators: Advanced graphing calculators often have built-in functions to assist in geometry calculations, including the perimeter of trapezoids.
These tools not only provide accuracy but also foster a deeper understanding of geometric principles through visual and interactive means, making them indispensable in educational and professional settings.

READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions About Trapezoid Perimeters
This section addresses common queries regarding the calculation and understanding of trapezoid perimeters, helping to clarify doubts and enhance comprehension of this geometric concept.
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a trapezoid? The perimeter of a trapezoid is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Can I calculate the perimeter if I only know the lengths of the bases? No, you need the lengths of all four sides for an accurate calculation of the perimeter.
- How does the height of a trapezoid affect its perimeter? The height of a trapezoid does not directly affect its perimeter but is essential for calculating the area.
- Is the perimeter calculation different for an isosceles trapezoid? The formula remains the same, but the equal length of the non-parallel sides simplifies the calculation.
- Can the perimeter of a trapezoid be calculated using angles? Angles alone are not sufficient; side lengths are necessary for perimeter calculation.
- Are there online tools to calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid? Yes, there are various online calculators that can compute the perimeter when the side lengths are provided.
These FAQs aim to provide quick answers to common questions, aiding in a better understanding of the principles and methods involved in calculating trapezoid perimeters.
Unravel the mysteries of trapezoid JKLM\"s perimeter through our comprehensive guide. Delve into the world of geometry and uncover practical insights, expert tools, and engaging FAQs. Join us in this intriguing exploration!