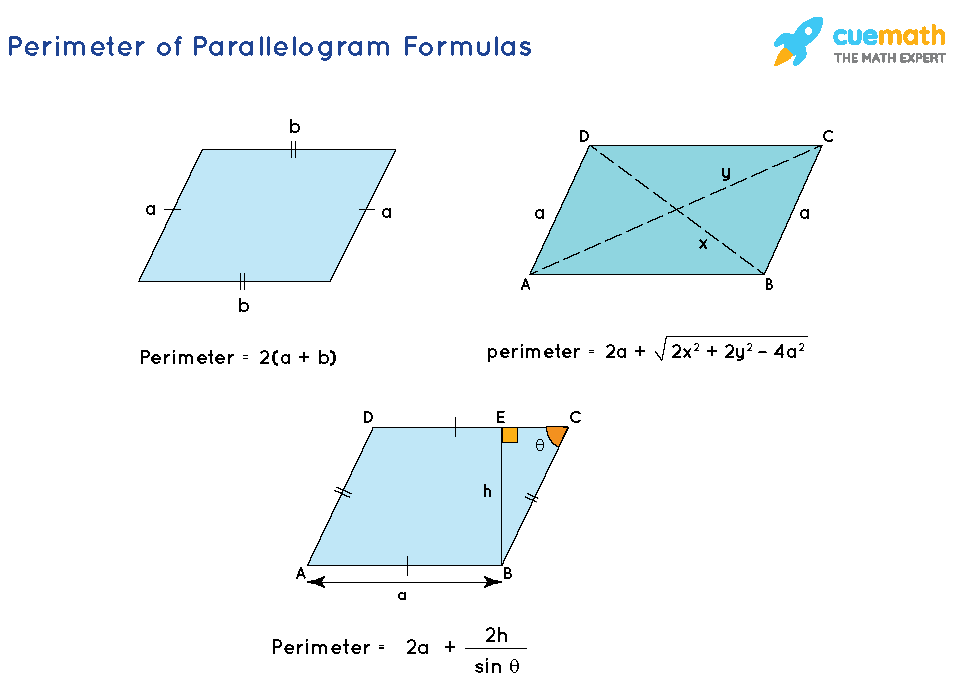
Updating information and knowledge about how do i find perimeter of a square in detail and most comprehensive, this article is currently a topic of great interest compiled by the editorial team.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Concept of Square Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
- Perimeter Formula and Calculation
- Practical Examples and Applications
- Calculating Perimeter for Different Square Sizes
- Using a Square Perimeter Calculator
- Comparison with Other Quadrilaterals
- Related Calculations: Area and Diagonal of a Square
- Visual Representation and Diagrams
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the Concept of Square Perimeter
The concept of a square\"s perimeter is fundamentally the measurement of the total distance around the boundary of the square. It represents the path that encompasses the square, essentially outlining its shape on a two-dimensional plane. The perimeter is a key aspect in various fields including mathematics, architecture, and everyday problem-solving.
Basic Definition and Formula
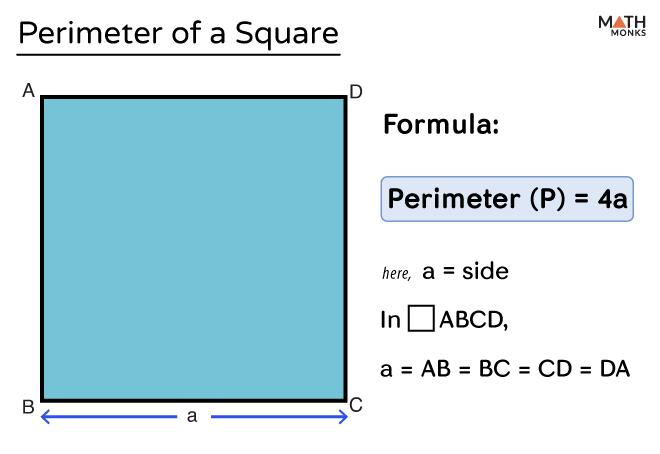
The perimeter of a square, being a four-sided polygon with equal sides, is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since each side of a square is equal, the formula simplifies to the perimeter (P) being four times the length of one side (S). Mathematically, it is expressed as:
- Perimeter of Square (P) = 4 × Side (S)
Detailed Explanation
To understand the perimeter of a square, consider it as the length of fencing needed to surround a square plot of land. Each side of this plot is of equal length, and thus, calculating the total length of fencing involves simply multiplying the length of one side by 4.
Practical Application
In practical terms, knowing how to calculate the perimeter of a square can be useful in everyday situations, such as determining the amount of material needed for a border around a square garden or calculating the framing required for square-shaped artwork.
Visual Representation
A square can be visually represented as a geometric shape with four equal straight sides and four right angles. To conceptualize its perimeter, imagine tracing a line along its edges without lifting your pen. The length of this continuous line represents the perimeter.
Summary
In summary, the perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the total distance around a square. It is calculated as four times the length of one side and is a critical measurement in various practical and theoretical applications.

READ MORE:
How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
Find: Unlock the mystery and discover hidden treasures as you join us on an exciting adventure to find the lost city. Watch our captivating video to embark on an unforgettable journey of exploration and discovery.
Perimeter of Square
Perimeter: Dive into the world of shapes and measurements as we unravel the secrets of perimeter. Watch our informative video to learn how to calculate perimeter with ease and enhance your mathematical skills.
Perimeter of a Square using Variables
Variables: Step into the realm of variables and witness the power of flexibility in solving complex equations. Explore the limitless possibilities and broaden your mathematical horizons by watching our enlightening video on manipulating variables.
Perimeter Formula and Calculation
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a square is straightforward and essential for various mathematical and practical applications. The perimeter (P) of a square, a measure of the total distance around its boundary, is determined by the length of one of its sides (S).
Basic Formula
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a square is:
- Perimeter (P) = 4 × Side (S)
Calculating Perimeter with Known Side Length
To calculate the perimeter when the side length is known, follow these steps:
- Note the measurement of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4.
- Express the result in the appropriate unit (cm, m, in, etc.).
Using Diagonal to Find Perimeter
If the diagonal length is known, the perimeter can be calculated using these steps:
- Note the measurement of the square\"s diagonal.
- Calculate the side length: Side = Diagonal/√2.
- Then, find the perimeter: Perimeter = 4 × Side.
Using Area to Find Perimeter
When the area of the square is given, the perimeter can be calculated as follows:
- Note the area of the square.
- Calculate the side length: Side = √Area.
- Then, find the perimeter: Perimeter = 4 × Side.
Practical Examples
Several practical examples and solved problems can help in understanding the application of these formulas. For instance, if the side of a square is 5 cm, the perimeter would be 20 cm. Similarly, if the diagonal is known to be 10 cm, the perimeter can be calculated as 20√2 cm.
Understanding these formulas and methods to calculate the perimeter of a square is fundamental in geometry and has practical implications in everyday measurements and calculations.

Practical Examples and Applications
The calculation of a square\"s perimeter has practical applications in various aspects of everyday life and different fields. Understanding these applications helps in grasping the importance and utility of this geometric concept.
Everyday Applications
- Estimating the amount of fencing needed for a square-shaped garden or plot.
- Designing furniture like square tables or cupboards where precise boundary measurements are crucial.
- Planning construction projects, such as determining the boundary of a square-shaped room or office.
- Calculating the length of materials needed for square-shaped crafts or DIY projects.
Examples in Construction and Farming
- In construction, calculating the perimeter of a square plot can help estimate the quantity of materials needed for fencing.
- Farmers use the perimeter to calculate the amount of fencing required for a square farm or plot.
Real-life Problem Solving
- If a square garden has a side of 16 feet, the perimeter (the total fencing required) would be 64 feet (16 ft × 4).
- For a square playground with a side length of 12 meters, the perimeter would be 48 meters.
- If the diagonal of a square garden is 3√2 inches, the perimeter can be calculated as 12 inches.
- In a scenario where the area of a square is 225 square units, the perimeter would be 60 units.
These examples illustrate how the concept of the perimeter of a square is applied in practical scenarios, helping in efficient planning and execution of various tasks.
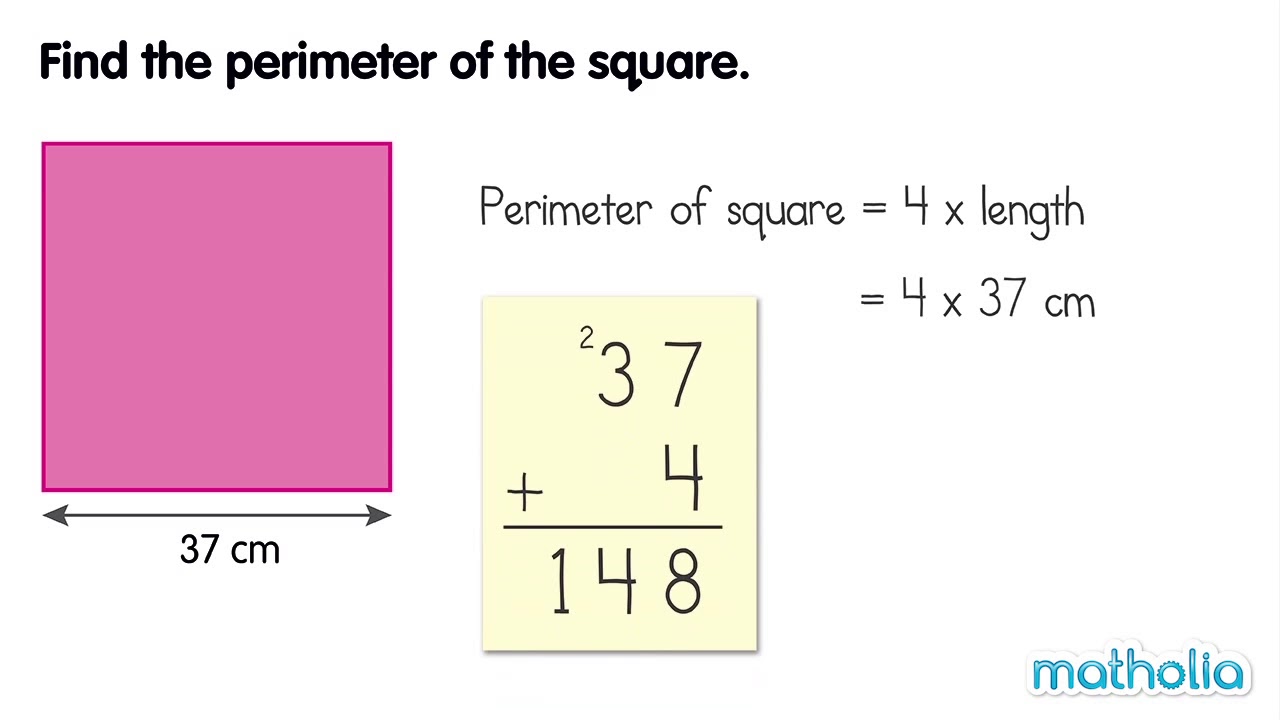
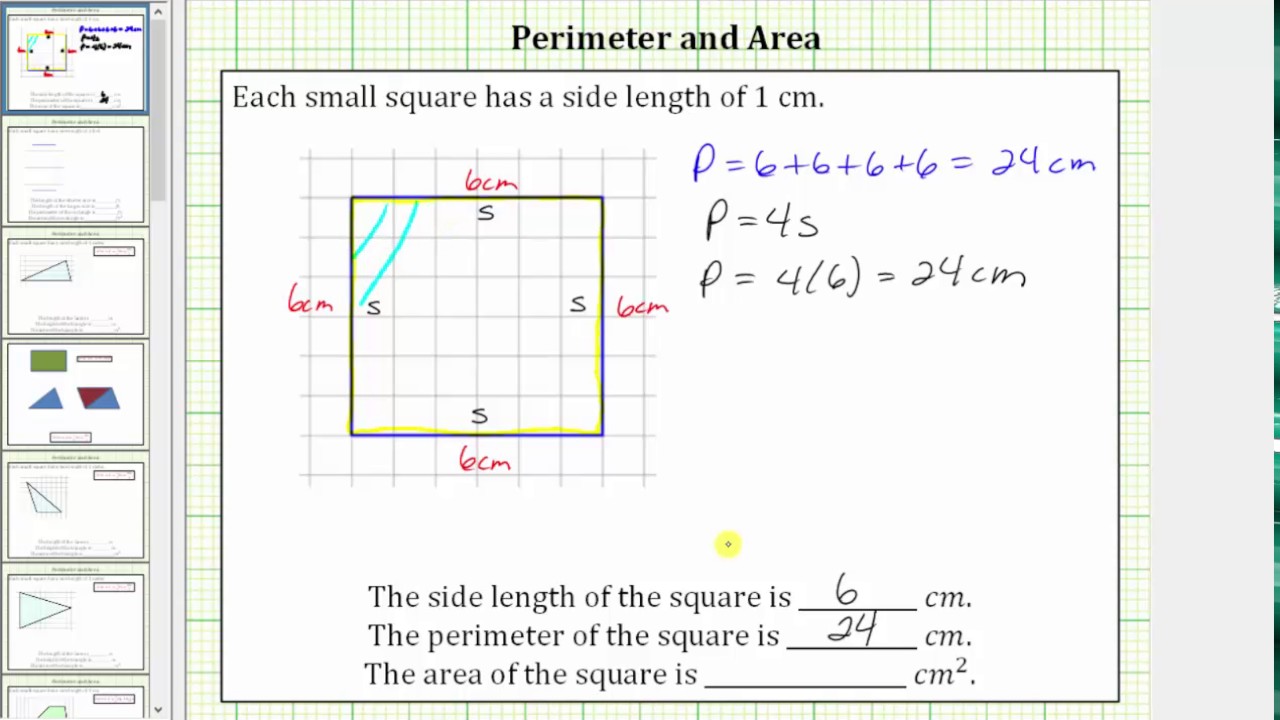
Calculating Perimeter for Different Square Sizes
The perimeter of a square is the total length of its boundaries. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. As a square has four equal sides, the perimeter can be found by multiplying the length of one side by 4.
Formula: Perimeter of a Square = 4 × Side Length
- Example 1: For a square with each side measuring 3 units, its perimeter is calculated as 4 × 3 = 12 units.
- Example 2: If a square has a side length of 5 units, its perimeter is 4 × 5 = 20 units.
- Example 3: A square with a side length of 7 feet will have a perimeter of 4 × 7 = 28 feet.
Additionally, the perimeter can also be determined using the square\"s diagonal or area:
- Using Diagonal: If the diagonal of a square is known, the side can be calculated using the formula: Side = Diagonal / √2. Then, use the perimeter formula with this side length.
- Using Area: When the area of the square is given, the side length can be found as the square root of the area (Side = √Area). Multiply this side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
It is important to remember to use consistent units when calculating the perimeter and to convert units when necessary.
| Side Length | Perimeter |
| 6 units | 24 units |
| 16 feet | 64 feet |
| 13 cm | 52 cm |
These methods and examples should help in understanding how to calculate the perimeter for different square sizes, whether the side length, diagonal, or area is known.

Using a Square Perimeter Calculator
Square perimeter calculators are easy-to-use tools that instantly calculate the perimeter of a square based on inputs such as the side length, diagonal, or area. Below is a guide on how to use these calculators effectively.
- Entering the Values: Begin by inputting a known measurement of the square. This could be the side length, the length of the diagonal, or the area of the square.
- Selecting the Units: Most calculators allow you to select the unit of measurement (e.g., meters, inches, feet). Ensure you choose the correct unit for your input value.
- Calculation: After entering the value and selecting the unit, the calculator will compute the perimeter of the square. Some calculators update the results live as you type.
- Interpreting the Results: The calculator displays the perimeter, and in some cases, it might also show other properties of the square like area and diagonal length.
These calculators are beneficial for quick calculations and are particularly useful in educational settings or in professions involving geometry and design.
Remember, the basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a square is P = 4a, where P is the perimeter and a is the length of a side of the square.
_HOOK_
Comparison with Other Quadrilaterals
When comparing a square to other quadrilaterals, it\"s important to note their distinct properties and similarities. A square is a unique type of quadrilateral with its own set of characteristics.
- Rectangle: A square is a special type of rectangle. While all squares are rectangles (having four right angles), not all rectangles are squares. A rectangle has opposite sides that are equal and parallel but does not require all sides to be of equal length as a square does.
- Rhombus: Similar to a square, a rhombus has all sides of equal length. However, a rhombus doesn\"t require right angles. A square can be considered a rhombus with the additional property of having right angles.
- Parallelogram: Both squares and parallelograms have opposite sides that are parallel. However, a parallelogram has no requirement regarding the equality of all sides or the angles being right angles, which are essential characteristics of a square.
- Trapezoid: A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides. Unlike a square, the sides and angles of a trapezoid are not necessarily equal or right angles.
- Isosceles Trapezoid: An isosceles trapezoid has non-parallel sides that are equal in length and its base angles are equal. This differs from a square which has all sides and angles equal.
Understanding these differences is crucial in geometry for identifying and classifying different shapes based on their properties.
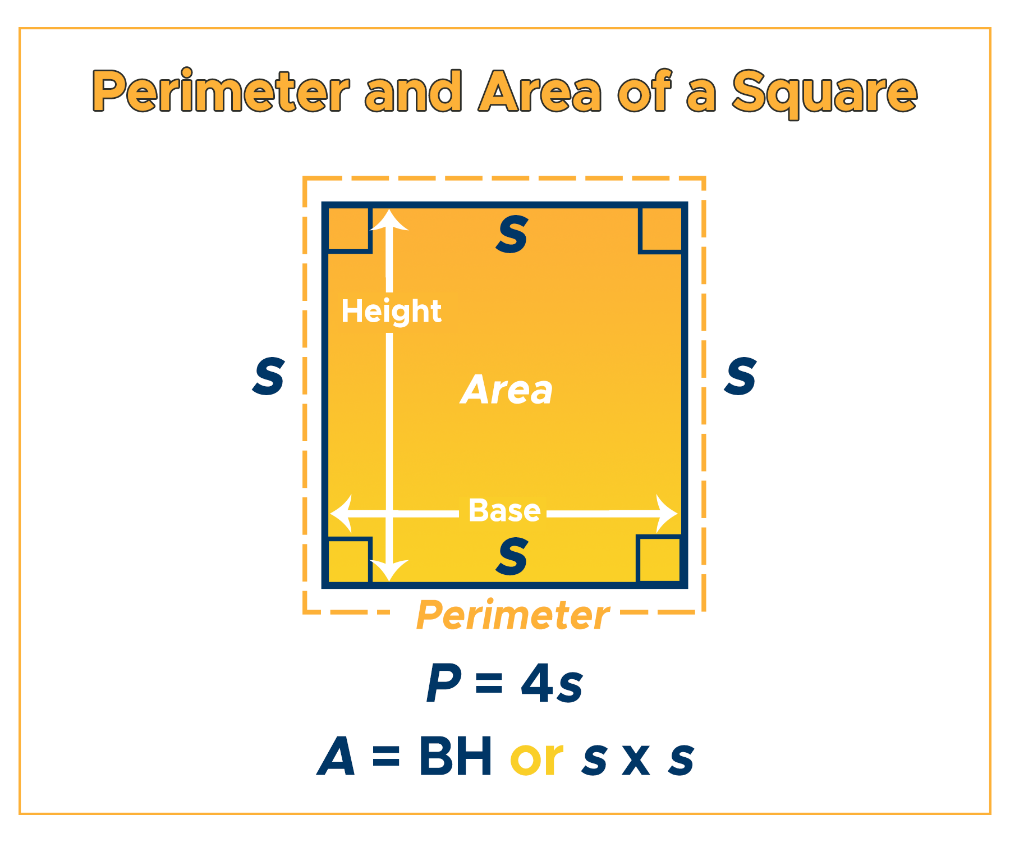
Related Calculations: Area and Diagonal of a Square
The area and diagonal of a square are closely related to its perimeter. These properties can be calculated using simple formulas based on the length of the square\"s sides.
Calculating the Area of a Square
The area of a square is calculated by squaring the length of one of its sides. The formula is:
Area (A) = side × side = a²
For example, if each side of a square is 5 units, the area would be 5² = 25 square units.
Calculating the Diagonal of a Square
The diagonal of a square can be found using the Pythagorean Theorem, since it divides the square into two congruent right triangles. The formula is:
Diagonal (d) = side × √2 = a × √2
If the side of the square is 5 units, the diagonal would be 5 × √2 ≈ 7.071 units.
Alternate Methods
- If the area of the square is known, the side can be found as the square root of the area (a = √A), and then the diagonal can be calculated using the above method.
- If the perimeter of the square is known, the side length can be found by dividing the perimeter by 4 (a = P/4), and the diagonal can be subsequently found.
These calculations are fundamental in geometry and are useful in various applications like construction, design, and mathematics.

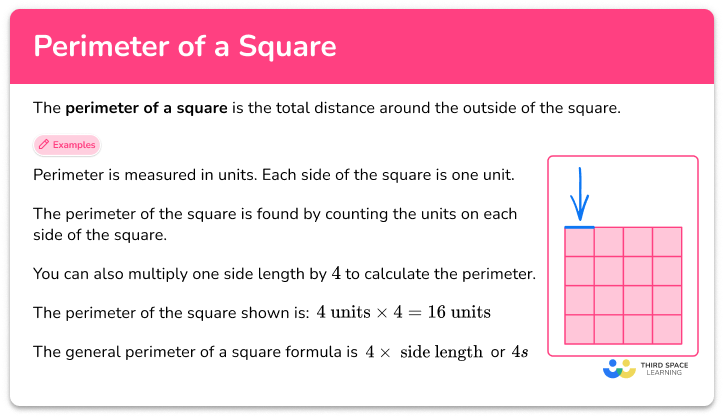
Visual Representation and Diagrams
Visual representations are crucial in understanding the concept of the perimeter of a square. They help in visualizing the process of calculating perimeter and provide an effective method for teaching and learning this geometrical concept.
Basic Diagram of a Square
A square is a four-sided figure with each side of equal length and each angle a right angle (90 degrees). A simple diagram of a square typically shows a four-sided figure with equal sides, often marked with tick marks or labels to indicate congruence.
Calculating Perimeter - Visual Steps
- Step 1: Draw a square and label all four sides with the same length (e.g., 8 feet for each side). This visually represents that all sides are equal.
- Step 2: To find the perimeter, illustrate the process of adding all side lengths. This can be shown as a repeated addition (e.g., 8 ft + 8 ft + 8 ft + 8 ft) or as a multiplication of one side length by 4 (e.g., 4 × 8 ft).
- Step 3: Show the final calculation and the resulting perimeter in the same units as the side lengths.
Examples with Diagrams
Include diagrams with different side lengths to illustrate how the perimeter changes accordingly. For instance:
- For a square with each side measuring 3 units, the perimeter will be 3 × 4 = 12 units.
- For a square with each side measuring 5 units, the perimeter will be 5 × 4 = 20 units.
These visual representations, especially when used alongside practical examples, enhance the understanding of how to calculate the perimeter of a square.
Common Mistakes and Tips
When calculating the perimeter of a square, certain common mistakes can occur, often due to misconceptions or carelessness. Understanding these errors is key to accurate calculations. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
Common Mistakes
- Incorrect Formula Application: A frequent mistake is using the wrong formula, such as using the formula for a rectangle\"s perimeter (2×(Length+Breadth)) for a square. For a square, the correct formula is 4×side length.
- Miscalculating Side Length: Errors often occur when deriving the side length from given information, like the area or diagonal. For instance, incorrectly calculating the side length from the area by forgetting to take the square root of the area.
- Unit Mismanagement: Not converting all measurements to the same unit before calculating or not including units in the final answer.
- Arithmetic Errors: Simple arithmetic mistakes in adding the lengths of sides or in multiplication can lead to incorrect answers.
Tips for Accurate Calculation
- Use the Correct Formula: Always remember that the perimeter of a square is four times one side length (P = 4×side).
- Double-Check Calculations: If given the area or diagonal, ensure the correct derivation of the side length before calculating the perimeter.
- Consistent Units: Convert all measurements to the same unit system before performing calculations and include units in your answer.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with different types of problems can help in understanding and applying the concepts correctly.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a square?
- To find the perimeter of a square, multiply the length of one side by 4. For example, if one side is 10 cm, the perimeter is 4 × 10 = 40 cm.
- Can you determine the perimeter of a square if only the area is known?
- Yes, first find the side length by taking the square root of the area. Then multiply the side length by 4 to find the perimeter. For instance, if the area is 16 square units, the side length is √16 = 4 units, and the perimeter is 4 × 4 = 16 units.
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a square?
- The formula for the perimeter of a square is 4 times the length of one side, expressed as 4a, where \"a\" is the length of a side.
- Is it possible to calculate the perimeter of a square using its diagonal?
- Yes. First, find the side length from the diagonal using the formula side = diagonal / √2. Then, calculate the perimeter using the formula 4 × side.
- What are some real-life applications of calculating the perimeter of a square?
- The perimeter of a square is useful in various real-life scenarios such as estimating the length of a garden, designing square-shaped objects (like tables, cupboards, swimming pools), in construction plans, and in agriculture for calculating fencing costs.
Discover the simplicity and practicality of calculating the perimeter of a square, an essential skill in geometry and beyond. Our comprehensive guide provides clear explanations, examples, and tips to master this fundamental concept with ease and confidence.
_HOOK_