Topic perimeter and area formula of all shapes: Explore the fascinating world of geometry with our definitive guide on "Perimeter and Area Formula of All Shapes," offering clear, concise formulas and engaging insights for learners and enthusiasts alike.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter and Area
- YOUTUBE: Area and Perimeter of all Shapes: Rectangle, Square, Triangle, Circle
- Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
- Area Formulas for Various Shapes
- Application and Practical Examples of Perimeter and Area
- Perimeter and Area in Irregular Shapes
- Interactive Examples and Problems
- Tools and Calculators for Perimeter and Area
- Perimeter and Area in Advanced Mathematics
- Teaching Resources and Strategies for Perimeter and Area
- Historical Context and Development of Perimeter and Area Concepts
Understanding Perimeter and Area
The concepts of perimeter and area are fundamental in geometry, each describing a distinct aspect of shapes. Perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary of a shape, while area measures the space enclosed within that boundary. These measurements are crucial in various fields, from architecture to land surveying, and form the basis for more advanced mathematical concepts.
- Perimeter: It is the sum of the lengths of all sides of a shape. For circles, referred to as the circumference, it is calculated based on the radius or diameter.
- Area: This is the space contained within a shape\"s boundaries. It is measured in square units and varies based on the shape\"s dimensions and type.
Different shapes have specific formulas for calculating perimeter and area. Regular shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles have well-defined formulas. For example, the area of a rectangle is the product of its length and width, while the perimeter is the sum of all its sides.
In contrast, irregular shapes might require more complex methods such as dividing the shape into regular components or using integral calculus in more advanced scenarios. Understanding these concepts not only aids in practical applications but also enhances spatial awareness and problem-solving skills.
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
| Rectangle | 2(length + width) | Length x Width |
| Circle | 2πr (r = radius) | πr² |
| Triangle | Sum of all sides | ½(base x height) |
| Square | 4 x side | Side² |
It\"s important to note that these formulas serve as a foundation for exploring more complex geometric shapes and concepts, providing a valuable toolkit for both academic study and practical application.

READ MORE:
Area and Perimeter of all Shapes: Rectangle, Square, Triangle, Circle
Are you curious about the fascinating world of shapes? Join us as we explore the mesmerizing patterns and symmetry hidden within various shapes in this captivating video. Get ready to be amazed!
Finding the Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape: L-Shaped Example - Geometry - Math with Mr. J
Dive into the realm of composite shapes and discover the beauty that lies in their intricate combination of different figures. Unleash your creativity and learn how to create stunning composite shapes in this visually stunning video.
Area and Perimeter Formulas: Rectangle, Circle - Mensuration Formulas - Geometry Shorts Feed
Unlock the secret to solving complex mathematical problems with our comprehensive guide to formulas. From solving algebraic equations to calculating the area of different shapes, this video will equip you with the essential tools. Get ready to ace those math tests with ease!
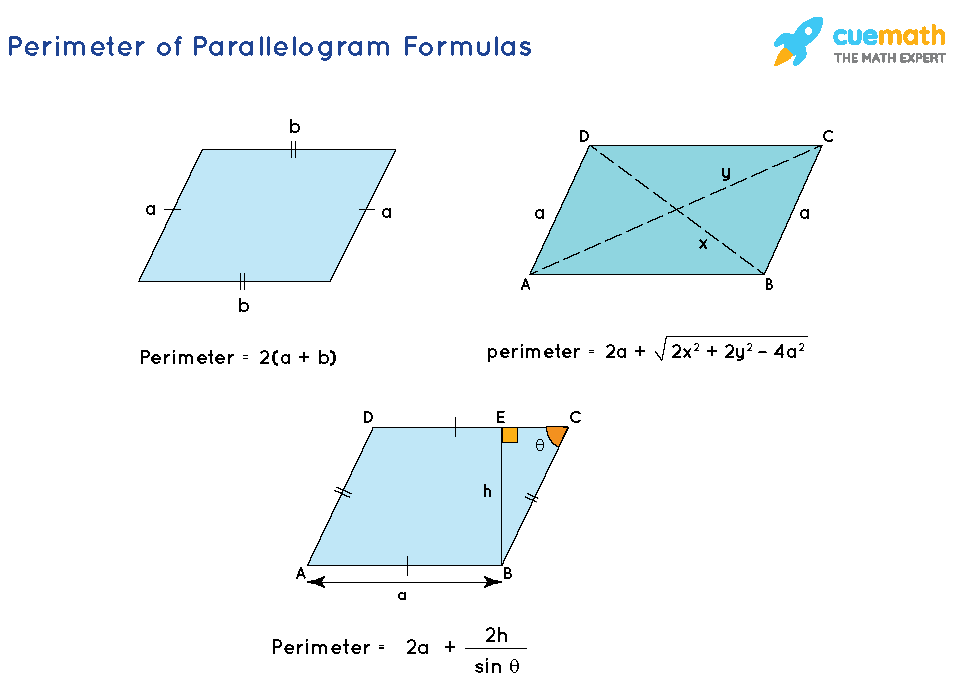
Perimeter Formulas for Common Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes is a key aspect of geometry, involving adding the lengths of all the sides of a shape. Each shape has a specific formula for its perimeter, making it easier to calculate this linear measurement. Here are the formulas for some common shapes:
It\"s important to note that these formulas apply to regular shapes with defined dimensions. For irregular shapes, the perimeter may require additional calculations or measurements. Understanding these formulas is not just essential for academic purposes but also practical in various real-life applications such as construction, crafting, and more.

Area Formulas for Various Shapes
Understanding the area formulas for different shapes is crucial for various mathematical and practical applications. The area of a shape is a measure of the space inside its perimeter. Each shape has a unique formula to calculate its area, depending on its specific properties. Below are the formulas for the area of some common shapes:
| Shape | Area Formula |
| Rectangle | Length × Width |
| Square | Side length² |
| Circle | πr² (r = radius) |
| Triangle | ½(base × height) |
| Parallelogram | Base × Height |
| Trapezoid | ½(sum of parallel sides) × height |
| Rhombus | ½(product of diagonals) |
| Polygon (Regular) | ½(perimeter × apothem) |
These formulas are essential for calculating the area in various fields such as architecture, land development, and in everyday situations like gardening or interior design. They also form the foundation for more advanced topics in geometry and mathematics.