Topic parallelogram perimeter calculator: Discover the world of geometry with our "Parallelogram Perimeter Calculator," a user-friendly tool designed to simplify your calculations and enhance your understanding of parallelograms in an engaging and efficient way.
Table of Content
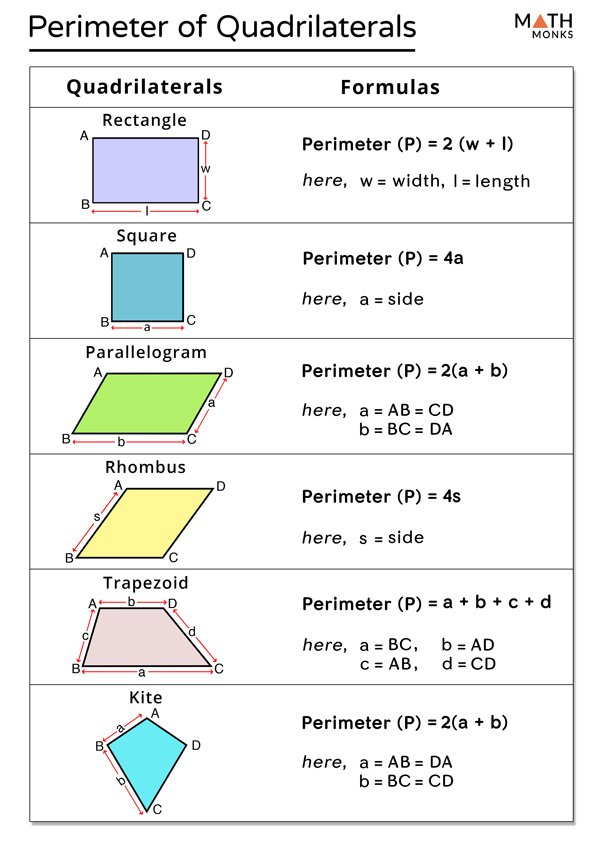
- Understanding the Parallelogram and Its Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Standard Perimeter Calculation Formula
- Calculating Perimeter with Base and Side Lengths
- Advanced Perimeter Calculations: Diagonals and Angles
- Perimeter Calculation with Base, Height, and Angles
- Interactive Parallelogram Perimeter Calculators
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using Online Calculators
- Calculation Examples for Different Parallelogram Sizes
- Evolution of Parallelogram Perimeter Calculation Methods
- Common Challenges and Errors in Perimeter Calculation
- Alternative Methods for Perimeter Calculation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Parallelograms
Understanding the Parallelogram and Its Perimeter
A parallelogram is a unique four-sided shape where opposite sides are equal in length and angles. The perimeter, which is the total distance around the parallelogram, is a key geometric measurement that can be calculated in various ways depending on the available information.
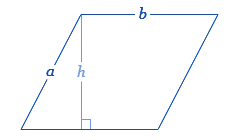
The most straightforward method for calculating the perimeter is using the basic formula: Perimeter = 2 * (base + side). This formula requires knowing the length of the base and one of the sides. For example, a parallelogram with a base of 5 units and a side of 3 units would have a perimeter of 2*(5+3) = 16 units.
However, if the lengths of the two sides are unknown, other methods are available. For instance, you can calculate the perimeter using one side and the diagonals, or by knowing the base, height, and an angle of the parallelogram. These calculations involve more complex formulas, such as using trigonometric functions or the parallelogram law, which relates the sides and diagonals of a parallelogram.
It\"s important to remember that the accuracy of these calculations can be affected by measurement errors or rounding errors, especially when dealing with larger numbers or more complex shapes. Various methods such as hand calculation, using calculators, or online tools can be employed, each with their own advantages and limitations.
For more detailed calculations and understanding, online parallelogram perimeter calculators provide step-by-step guidance. These tools are particularly useful in educational contexts or for those who are not as familiar with the mathematical concepts involved.
In summary, understanding the perimeter of a parallelogram involves knowing its properties, applying the right formula, and being aware of the potential for errors in calculation.

READ MORE:
Finding the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
Finding: \"Discover the secrets of finding your passion and purpose in life with our inspirational video that will guide you in uncovering your true calling and living a fulfilling life.\"
Parallelogram Calculator
Calculator: \"Unlock the power of numbers with our innovative calculator video that will simplify complex calculations and help you make accurate decisions, whether you\'re a student or professional.\"
Standard Perimeter Calculation Formula
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram is simple and straightforward, which can be expressed as Perimeter = 2 * (base + side). This formula requires the length of the base and one side of the parallelogram.
For instance, if a parallelogram has a base of 5 units and a side of 3 units, its perimeter can be calculated as 2 * (5 + 3), resulting in 16 units. The formula efficiently applies to parallelograms of various sizes, whether they are small (e.g., 1x1 units) or large (e.g., 100x200 units).
Despite the simplicity of this formula, its application can vary depending on the size of the parallelogram. For smaller parallelograms, the calculation can be done easily without any tools. However, for larger parallelograms, a calculator may be more suitable to ensure accuracy.
It\"s important to note that while this formula is widely applicable, it requires precise measurements of the base and side. Measurement errors can affect the accuracy of the results, especially when dealing with larger sizes or more complex shapes.
Historically, the methods of calculating the perimeter have evolved from basic hand calculations and estimations in ancient times to the use of slide rules in the 1900s, and eventually to digital calculators and online tools in the present day. Each of these methods has its own advantages and limitations in terms of ease of use, accuracy, and the level of calculation required.
Alternative methods for calculating the perimeter, such as triangulation and integration, can also be considered, particularly when dealing with more complex shapes or when a high level of accuracy is required. However, these methods might require more time and advanced mathematical skills.
In conclusion, understanding the standard perimeter calculation formula for a parallelogram is crucial for accurate measurement. The formula is not only easy to understand and apply but also forms the basis for understanding more complex geometric calculations.
Rectangle and Parallelogram Calculator
Rectangle: \"Explore the world of geometry and unlock the beauty of shapes with our captivating video that delves into the wonders of rectangles, showcasing their properties and practical applications.\"
Calculating Perimeter with Base and Side Lengths
Calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram when you know the lengths of the base and one side is a straightforward process. The fundamental formula for this calculation is given as Perimeter = 2 * (base + side). This method is applicable for parallelograms of various sizes, from small to large.
To execute this calculation, you need to measure the lengths of one base and one side of the parallelogram accurately. For example, if a parallelogram has a base of 5 units and a side of 3 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows: 2 * (5 + 3) = 16 units.
While the calculation is generally simple, it\"s important to be mindful of potential errors. Measurement errors, even small ones, can significantly affect the outcome, especially in larger parallelograms. Additionally, rounding errors can occur when dealing with decimals, impacting the precision of the calculation.
For larger parallelograms, it\"s advisable to use a calculator to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Over time, the methods for calculating the perimeter have evolved from hand calculations and basic geometry to modern tools like digital calculators and online calculators.
For complex-shaped parallelograms or when high accuracy is needed, alternative methods like triangulation or integration can be used, though these require more advanced mathematical skills and can be time-consuming.
Understanding these aspects of perimeter calculation is crucial for achieving accurate results, whether you\"re a student, educator, or professional dealing with geometrical shapes.
Advanced Perimeter Calculations: Diagonals and Angles
Calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram using diagonals and angles involves more complex formulas compared to the basic method. These advanced calculations are useful when the length of the sides is not directly known.
One such method is using the formula derived from the parallelogram law, which states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the four sides of a parallelogram equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two diagonals. The formula is: perimeter = 2 × a² + √(2 × e² + 2 × f² - 4 × a²), where a is the length of a side, and e and f are the lengths of the diagonals.
Another approach involves using the base, height, and an angle of the parallelogram. The formula for this method uses trigonometric sine function and is expressed as: perimeter = 2 × (a + (h/sin(angle))). This formula allows the calculation of the perimeter when you know one side of the parallelogram (labeled ‘a’), its corresponding height (‘h’), and one of the vertex angles.
It is important to understand the properties of parallelograms when applying these methods. For instance, the adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary, and this fact is used in the trigonometric formula mentioned above.
These advanced methods of calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram are particularly helpful in scenarios where direct measurement of all sides is not feasible, or when dealing with geometric problems that require a deeper understanding of the properties of parallelograms.
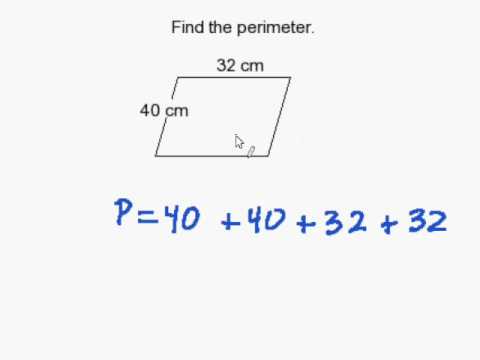
Perimeter Calculation with Base, Height, and Angles
Calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram when you have information about its base, height, and angles involves a more nuanced approach, using trigonometry and the properties of parallelograms. This method is especially useful when direct measurements of the sides are not available.
The key formula used in such calculations is: perimeter = 2 × (a + (h/sin(angle))). This formula leverages the trigonometric sine function and the principle that the sum of the angles in a parallelogram is 180°, making the adjacent angles supplementary. Therefore, you can use either of the angles in this calculation, as sin(angle) equals sin(180° - angle).
To apply this formula, you need to know the length of one side (labeled ‘a’), the corresponding height (‘h’), and one of the internal angles. First, solve for the unknown side using the trigonometric relationship and then apply the perimeter formula.
For example, if you have a parallelogram with a side of 10 units, a height of 5 units, and an angle of 30°, you first calculate the length of the adjacent side using the sine function and then calculate the perimeter using the formula.
This method of calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram is particularly useful in geometric problem-solving and in situations where complete side length data is not available.
_HOOK_
Interactive Parallelogram Perimeter Calculators
Discovering the perimeter of a parallelogram is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Our interactive calculators simplify this process, accommodating various inputs to calculate the perimeter accurately.
Basic Perimeter Calculation
For the most straightforward approach, if you know the lengths of the adjacent sides (a and b), use the formula: Perimeter = 2 * (a + b). This method relies on the property that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length.
Advanced Calculations
- Using Diagonals and a Side: If the diagonals (e and f) and one side (a) are known, the perimeter can be calculated using a more complex formula derived from the parallelogram law.
- Using Base, Height, and Angle: When you have the base (a), height (h), and an angle, the perimeter can be found using trigonometric functions, specifically the sine function.
Step-by-Step Guide for Using the Calculators
- Identify the available measurements you have for the parallelogram (sides, diagonals, angles, etc.).
- Select the appropriate calculator section based on your available data.
- Enter the values into the calculator. For example, if you have side (a) and two diagonals (e, f), input these values.
- The calculator will process the inputs and provide the perimeter. If the entered values do not form a valid parallelogram, the calculator will notify you.
Example Calculations
For illustrative purposes, consider a parallelogram with sides of 10 ft and 20 ft. The perimeter is calculated as 2 * (10ft + 20ft) = 60 ft.
Alternative Methods and FAQs
Besides standard calculations, alternative methods like triangulation offer high accuracy, albeit being more time-consuming. Common questions such as the applicability of the calculator for different parallelogram types (including rhombuses) are addressed, confirming the tool\"s versatility.
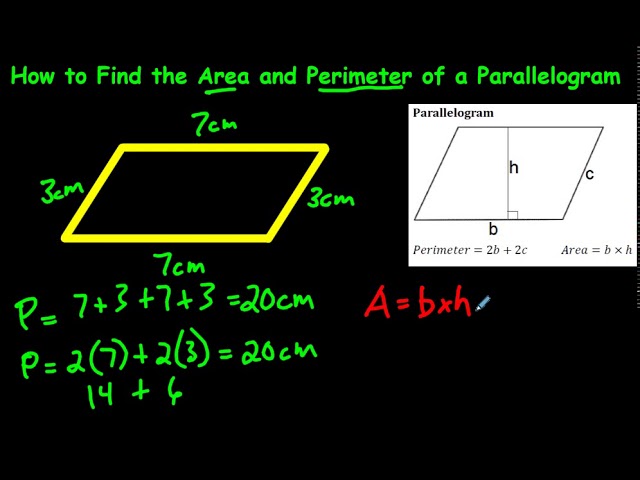
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Online Calculators
Discovering the perimeter of a parallelogram is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Our interactive calculators simplify this process, accommodating various inputs to calculate the perimeter accurately.
Basic Perimeter Calculation
For the most straightforward approach, if you know the lengths of the adjacent sides (a and b), use the formula: Perimeter = 2 * (a + b). This method relies on the property that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length.
Advanced Calculations
- Using Diagonals and a Side: If the diagonals (e and f) and one side (a) are known, the perimeter can be calculated using a more complex formula derived from the parallelogram law.
- Using Base, Height, and Angle: When you have the base (a), height (h), and an angle, the perimeter can be found using trigonometric functions, specifically the sine function.
Step-by-Step Guide for Using the Calculators
- Identify the available measurements you have for the parallelogram (sides, diagonals, angles, etc.).
- Select the appropriate calculator section based on your available data.
- Enter the values into the calculator. For example, if you have side (a) and two diagonals (e, f), input these values.
- The calculator will process the inputs and provide the perimeter. If the entered values do not form a valid parallelogram, the calculator will notify you.
Example Calculations
For illustrative purposes, consider a parallelogram with sides of 10 ft and 20 ft. The perimeter is calculated as 2 * (10ft + 20ft) = 60 ft.
Alternative Methods and FAQs
Besides standard calculations, alternative methods like triangulation offer high accuracy, albeit being more time-consuming. Common questions such as the applicability of the calculator for different parallelogram types (including rhombuses) are addressed, confirming the tool\"s versatility.

Calculation Examples for Different Parallelogram Sizes
Discovering the perimeter of a parallelogram is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Our interactive calculators simplify this process, accommodating various inputs to calculate the perimeter accurately.
Basic Perimeter Calculation
For the most straightforward approach, if you know the lengths of the adjacent sides (a and b), use the formula: Perimeter = 2 * (a + b). This method relies on the property that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length.
Advanced Calculations
- Using Diagonals and a Side: If the diagonals (e and f) and one side (a) are known, the perimeter can be calculated using a more complex formula derived from the parallelogram law.
- Using Base, Height, and Angle: When you have the base (a), height (h), and an angle, the perimeter can be found using trigonometric functions, specifically the sine function.
Step-by-Step Guide for Using the Calculators
- Identify the available measurements you have for the parallelogram (sides, diagonals, angles, etc.).
- Select the appropriate calculator section based on your available data.
- Enter the values into the calculator. For example, if you have side (a) and two diagonals (e, f), input these values.
- The calculator will process the inputs and provide the perimeter. If the entered values do not form a valid parallelogram, the calculator will notify you.
Example Calculations
For illustrative purposes, consider a parallelogram with sides of 10 ft and 20 ft. The perimeter is calculated as 2 * (10ft + 20ft) = 60 ft.
Alternative Methods and FAQs
Besides standard calculations, alternative methods like triangulation offer high accuracy, albeit being more time-consuming. Common questions such as the applicability of the calculator for different parallelogram types (including rhombuses) are addressed, confirming the tool\"s versatility.
Evolution of Parallelogram Perimeter Calculation Methods
The calculation of the perimeter of parallelograms has evolved significantly over time. Initially, the process was manual and heavily reliant on fundamental geometric principles.
Early Methods
In the 1800s and earlier, calculations were primarily performed by hand. Basic arithmetic was employed to sum up the lengths of the sides of parallelograms.
Mid 20th Century Advancements
The introduction of tools like the slide rule in the 1900s offered a more efficient means for calculation, streamlining the process while maintaining accuracy.
Modern Technology
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw a significant leap with the advent of digital calculators and computers. This era marked a transition to quick, precise, and user-friendly methods for perimeter calculations.
Online Calculators
Online calculators, emerging in the 2000s, have provided an accessible platform for users to input values and instantly obtain results. Websites like Omni Calculator, Calculator Soup, and Owl Calculator offer user-friendly interfaces for calculating parallelogram perimeters using various formulas and parameters.
Current Trends
Presently, the calculation methods have become more diverse, accommodating various scenarios like missing side lengths, known diagonals, or angles. These methods leverage advanced mathematical concepts like trigonometry and the parallelogram law to provide accurate results.
Future Outlook
As technology continues to advance, we anticipate further enhancements in calculation methods, possibly integrating more sophisticated mathematical models and algorithms for even greater accuracy and efficiency.
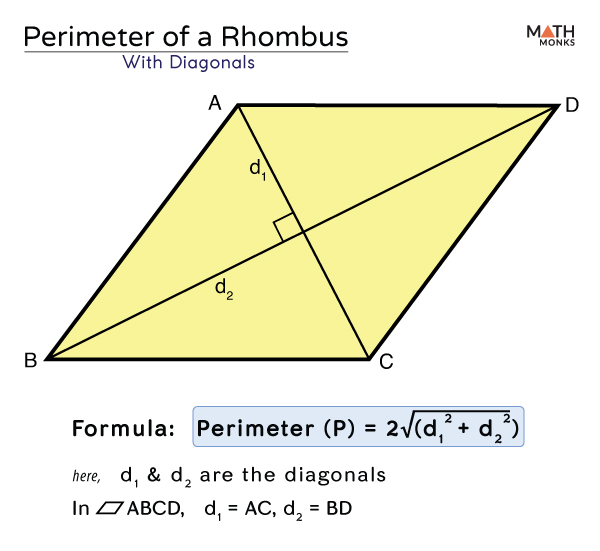
Common Challenges and Errors in Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram, while straightforward, can often present challenges and lead to errors. Understanding these common pitfalls can help improve accuracy and efficiency in calculations.
Mistakes in Using Formulas
- Inaccurate Measurements: Incorrectly measuring the sides of the parallelogram can lead to significant errors in the final perimeter calculation.
- Using Wrong Formulas: Applying inappropriate formulas for specific parallelogram types (like confusing the formulas for a rectangle or a rhombus with those for a general parallelogram) can result in incorrect calculations.
- Misunderstanding Diagonals: Errors can occur when calculating the perimeter using diagonals and angles without a clear understanding of the parallelogram law (the sum of the squares of the lengths of the sides equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the diagonals).
Computational Errors
- Arithmetic Mistakes: Simple arithmetic errors during manual calculations can lead to incorrect results.
- Rounding Errors: Inaccurate rounding of decimal or fractional values can slightly skew the final perimeter value.
Challenges with Angles and Sides
- Angle Confusion: Misinterpretation of angles in a parallelogram, especially when using trigonometric functions, can result in incorrect calculations.
- Unknown Side Lengths: Challenges arise when not all side lengths are known, requiring the use of additional information like diagonals or angles for accurate calculation.
Technological Limitations
- Calculator Limitations: Online calculators are immensely helpful but may be limited in handling complex cases or specific parallelogram types.
- User Input Errors: Incorrectly inputting values into a calculator can lead to erroneous results.
Conclusion
Understanding these challenges and errors can significantly enhance the accuracy of perimeter calculations for parallelograms. It\"s important to approach calculations methodically, double-check measurements and formulas, and use reliable tools and resources.

_HOOK_
Alternative Methods for Perimeter Calculation
While the standard method for calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram involves summing twice the sum of its base and side lengths, there are alternative methods that can be used, especially in situations where certain dimensions are unknown or when seeking more accuracy in complex shapes.
Using Diagonals and Angles
- Diagonal-Based Calculations: If diagonals and one side are known, the perimeter can be calculated using the parallelogram law. This law states that the sum of the squares of the sides of a parallelogram equals the sum of the squares of its diagonals.
- Trigonometric Methods: When the base, height, and an angle are known, trigonometric functions like sine can be used to find the perimeter.
Geometric Approaches
- Triangulation: This method involves dividing the parallelogram into triangles, calculating their perimeters, and then summing these up. This is more accurate for complex shapes but can be time-consuming.
- Integration: A more advanced method, suitable for parallelograms with curved sides or variable side lengths, where integration can provide a precise perimeter measurement.
Technological Aids
- Online Calculators: For a quick and accurate calculation, online parallelogram perimeter calculators can be used. These tools often require just the length of the sides or base and side to compute the perimeter.
- Software Programs: Advanced software tools can calculate the perimeter based on digital models of the shape, providing high accuracy, especially in engineering and design fields.
Conclusion
Each method has its advantages and is suitable for different scenarios. While hand calculations and basic formulas are sufficient for simple cases, more complex shapes might require advanced geometric or computational approaches.
READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Parallelograms
- What is a parallelogram?
- A parallelogram is a four-sided figure with opposite sides that are equal in length and opposite angles that are equal in measure.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a parallelogram?
- The perimeter of a parallelogram can be calculated using the formula: Perimeter = 2 * (Side A + Side B).
- Do all parallelograms have the same perimeter?
- No, the perimeter varies depending on the lengths of the sides.
- Why is a square a parallelogram?
- A square is a specific type of parallelogram where all sides are equal in length and all angles are right angles.
- Can a parallelogram have right angles?
- Yes, a rectangle is a type of parallelogram that has right angles.
- What units are used to measure the perimeter of a parallelogram?
- Any unit of length can be used to measure the perimeter of a parallelogram, such as feet, meters, inches, etc.
- What is the difference between the perimeter and area of a parallelogram?
- The perimeter is the distance around the outside of the parallelogram, while the area is the amount of space inside the parallelogram.
- How can I improve the accuracy of my perimeter calculations?
- Ensuring accurate measurements, using precise tools, and reducing rounding errors can all improve the accuracy of perimeter calculations.
- What are some alternative methods for calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram?
- Some alternative methods include triangulation and geometric methods.
- Are the formulas for calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram and rectangle the same?
- Yes, they are the same as both are calculated as 2 * (Side A + Side B).
Discover the world of parallelogram perimeters with ease! Our comprehensive guide and calculators make mastering this essential geometry skill both engaging and accessible. Explore now to enhance your understanding and calculation abilities!