Topic what's the square root of five: What's the square root of five? This intriguing question opens the door to fascinating mathematical insights. In this article, we explore the value, methods of calculation, and the significance of the square root of five in various fields. Join us on a journey to understand this essential yet often overlooked number.
Table of Content
The Square Root of 5
The square root of 5 is an important irrational number in mathematics, commonly denoted as \(\sqrt{5}\). It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite number of decimal places.
Numerical Value
The numerical value of the square root of 5, approximated to 50 decimal places, is:
\(\sqrt{5} \approx 2.23606797749978969640917366873127623544061835961152...\)
Calculation Method
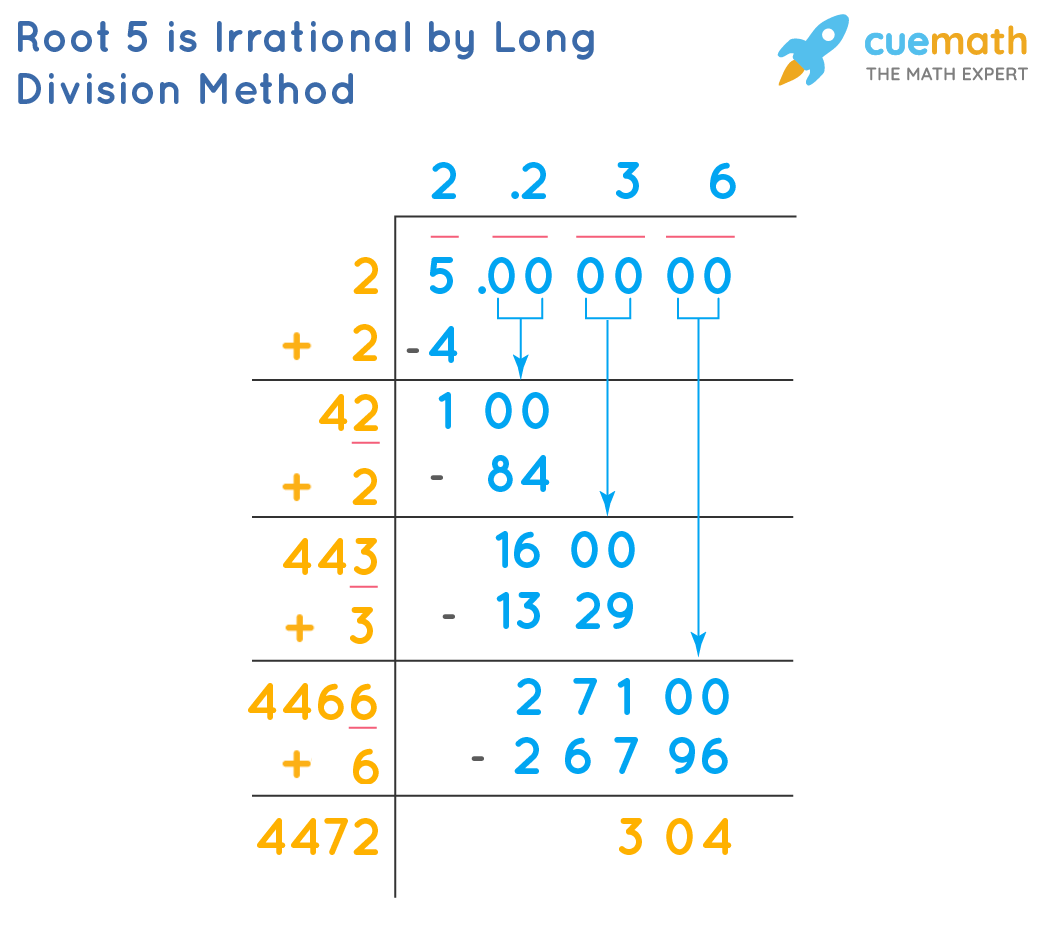
One common method to find the square root of 5 is by using the division method:
- Estimate a close value by identifying two perfect squares the number is between.
- Divide the number by one of those square roots.
- Take the average of the result and the root.
- Repeat the process until the desired accuracy is achieved.
For example:
\(\sqrt{5} \approx 2 + \frac{1}{2 + \frac{1}{2 + \frac{1}{2 + \frac{1}{2 + \ldots}}}}\)
Geometric Significance
Geometrically, \(\sqrt{5}\) is the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with side lengths 1 and 2, as per the Pythagorean theorem.
Relationship with Fibonacci Numbers
The square root of 5 is also related to the Fibonacci sequence. The ratio of the \(n^{th}\) Lucas number to the \(n^{th}\) Fibonacci number approaches \(\sqrt{5}\) as \(n\) increases:
\[
\lim_{{n \to \infty}} \frac{L_n}{F_n} = \sqrt{5}
\]
Applications
The square root of 5 appears in various mathematical contexts, including trigonometric constants and continued fractions.
Further Examples
| Expression | Value |
|---|---|
| \(5\sqrt{16} + 2\sqrt{25} - 2\sqrt{5}\) | 34.472 |
| \(\sqrt{5} - \sqrt{1}\) | 1.236 |
| \(20\sqrt{25} - 10\sqrt{9} - 5\sqrt{5}\) | 58.82 |
Online Calculation Tool
You can also use online tools to calculate the square root of 5. Simply enter the number 5 into a square root calculator for an instant result.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of five, denoted as \( \sqrt{5} \), is an important mathematical constant with significant implications in various fields. As an irrational number, it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The value of \( \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 2.236067977, but this approximation extends infinitely.
Mathematically, \( \sqrt{5} \) emerges naturally in several contexts. It appears in the quadratic equation \( x^2 - 5 = 0 \) and is a solution to this equation. Additionally, the square root of five is crucial in understanding the geometry of certain shapes and figures, playing a role in the calculation of the lengths and areas where it serves as a fundamental component.
The square root of five also has practical applications across various scientific and engineering disciplines. In physics, it can be found in equations describing wave functions and quantum mechanics. In computer science, algorithms that require precise calculations may involve \( \sqrt{5} \). Furthermore, it is present in the field of finance, where it is used to model growth rates and compound interest formulas.
Overall, the square root of five is more than just a numerical curiosity. Its significance extends from pure mathematics to practical applications, demonstrating its broad relevance and utility. This guide will delve into the properties, calculation methods, geometric interpretations, and diverse applications of \( \sqrt{5} \), providing a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing number.
Numerical Value and Properties
The square root of five, denoted as \( \sqrt{5} \), is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its approximate numerical value is \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.2360679775 \).
Properties of \( \sqrt{5} \) include:
- It is the positive solution to the equation \( x^2 = 5 \).
- It is an irrational number, implying its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- It is located between 2 and 3 on the number line.
- Its continued fraction representation is \( [2; 4, 4, 4, \dots] \).
The square root of five plays a significant role in mathematics, particularly in geometric constructions involving the golden ratio and in algebraic equations where it serves as a fundamental constant.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of Five
Calculating \( \sqrt{5} \) can be approached using several methods:
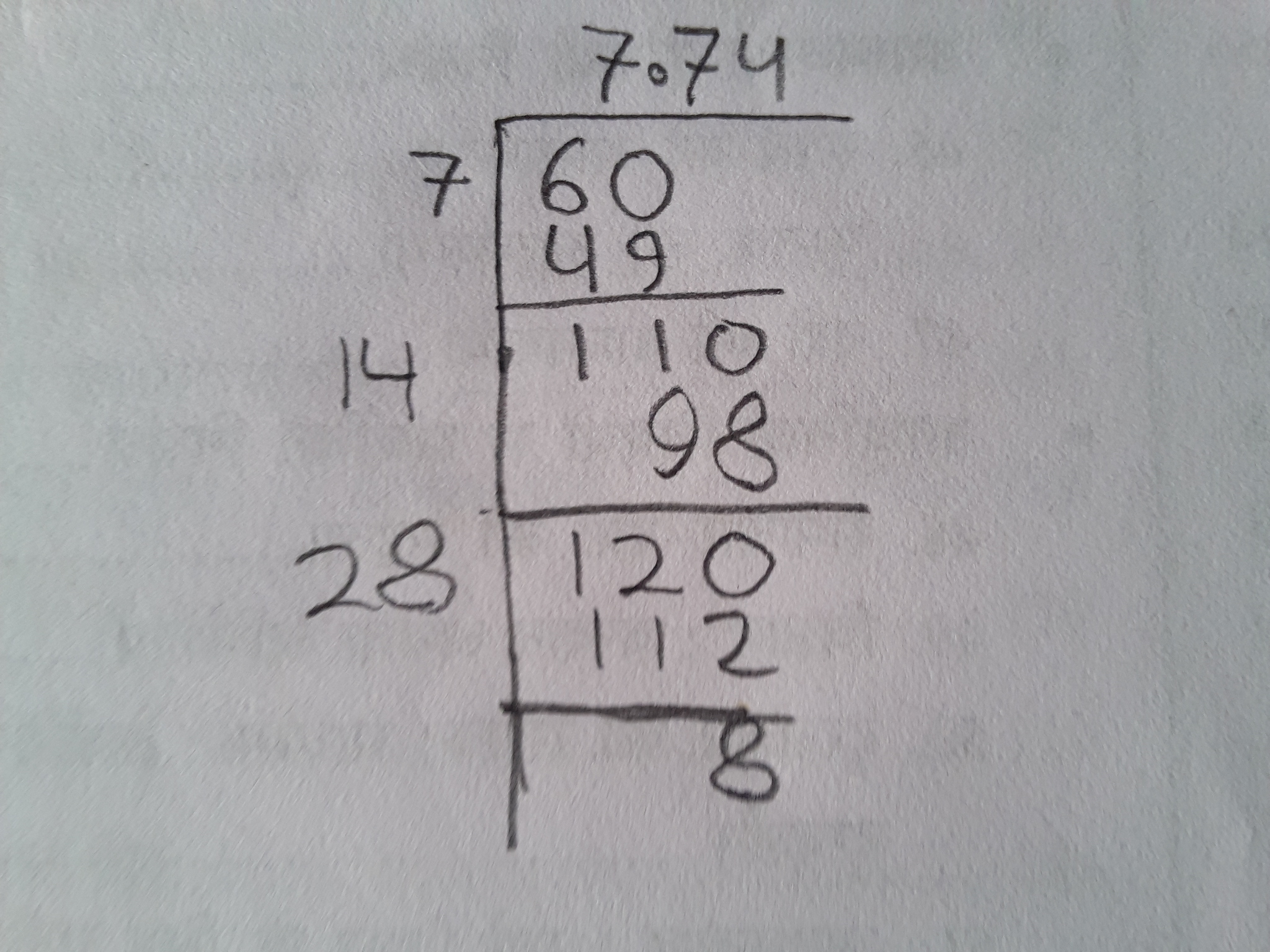
- Long Division Method: This method involves a step-by-step division process to approximate \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Newton's Method: An iterative algorithm that refines an initial guess to approximate \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Continued Fractions: Expressing \( \sqrt{5} \) as a continued fraction provides a systematic way to approximate its value.
- Binomial Expansion: Using the binomial theorem to expand \( (1+x)^{1/2} \) around \( x = 4 \) provides an approximation for \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Approximation Tables: Various mathematical tables and computational tools provide precise values of \( \sqrt{5} \).
Each method has its advantages depending on the required level of accuracy and computational resources available.
Geometric Interpretation
The square root of five, \( \sqrt{5} \), has several geometric interpretations:
- Role in the Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle with legs of length 1 unit each, the hypotenuse is \( \sqrt{2} \). Scaling such a triangle to have legs of length \( \sqrt{5} \) illustrates \( \sqrt{5} \) as the hypotenuse, demonstrating its role in the Pythagorean theorem.
- Relation to the Golden Ratio: \( \sqrt{5} \) appears in the context of the golden ratio, where it relates the length of a diagonal across a regular pentagon to the side length of the pentagon.
- Geometric Construction: \( \sqrt{5} \) can be constructed geometrically using the compass and straightedge, involving the intersection of arcs and lines.
These interpretations highlight \( \sqrt{5} \)'s significance in geometry, particularly in geometric proofs and constructions involving triangles, polygons, and ratios.
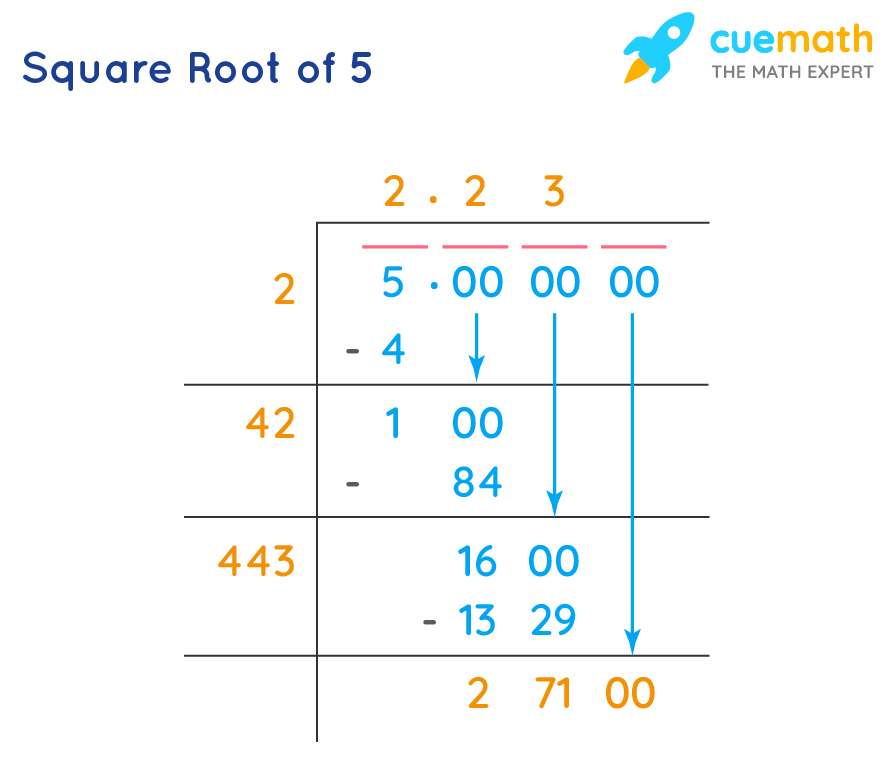
Applications in Mathematics and Science
The square root of five, \( \sqrt{5} \), finds applications across various fields of mathematics and science:
- Trigonometry: \( \sqrt{5} \) appears in trigonometric identities and calculations involving right triangles and complex angles.
- Algebra: It serves as a fundamental constant in algebraic equations and expressions, influencing polynomial roots and quadratic equations.
- Geometry: \( \sqrt{5} \) relates to geometric constructions, the Pythagorean theorem, and the golden ratio, contributing to geometric proofs and theorems.
- Physics: In physics, \( \sqrt{5} \) may appear in calculations related to waveforms, resonance frequencies, and dimensional analysis.
- Engineering: Engineers utilize \( \sqrt{5} \) in structural design, optimization problems, and signal processing applications.
Understanding \( \sqrt{5} \)'s mathematical properties and applications is crucial for advancing scientific research and practical applications in various disciplines.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the square root of five?
The square root of five, denoted as \( \sqrt{5} \), is approximately 2.2360679775. It is the positive solution to the equation \( x^2 = 5 \). - Is the square root of five a rational number?
No, \( \sqrt{5} \) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. - How to approximate the square root of five?
\( \sqrt{5} \) can be approximated using methods such as long division, Newton's method, continued fractions, or referencing mathematical tables for precise values.
Conclusion
The square root of five, \( \sqrt{5} \), embodies mathematical elegance and practical significance across various disciplines. From its geometric interpretations in the Pythagorean theorem and the golden ratio to its applications in trigonometry, algebra, physics, and engineering, \( \sqrt{5} \) serves as a fundamental constant and a key element in mathematical equations and constructions. Understanding its properties as an irrational number and its approximate value enhances our ability to solve complex problems and explore new mathematical frontiers.
With its rich mathematical heritage and versatile applications, \( \sqrt{5} \) continues to inspire researchers, educators, and enthusiasts alike, contributing to advancements in science and technology.
Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của số 5 và các phương pháp đơn giản hóa nó.
Căn Bậc Hai Của Số 5 Được Đơn Giản Hóa
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của số 5 bằng phương pháp chia dài một cách dễ dàng và chính xác. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết từng bước.
Cách Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 5 bằng Phương Pháp Chia Dài