Topic what is the perimeter of hexagon acefgh: Discover how to calculate the perimeter of hexagon ACEFGH, whether it's a regular or irregular hexagon. This guide will provide step-by-step instructions and examples to ensure you understand the process and can apply it to any hexagon calculation.
Table of Content
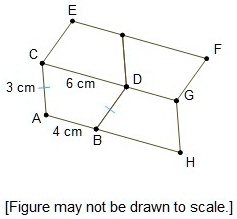
Perimeter of Hexagon ACEFGH
The perimeter of a hexagon is the total distance around its edges. For a regular hexagon, where all sides are equal, the formula is straightforward. However, for an irregular hexagon, each side length needs to be individually measured and summed up.
Formula for Regular Hexagon
If the hexagon is regular (all sides equal), the perimeter (P) is given by:
\[ P = 6 \times a \]
where \(a\) is the length of one side.
Example Calculation for Regular Hexagon
Consider a hexagon ACEFGH with each side of length \(7.3\) cm:
\[ P = 6 \times 7.3 = 43.8 \, \text{cm} \]
Formula for Irregular Hexagon
For an irregular hexagon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e + f \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e,\) and \(f\) are the lengths of the sides of the hexagon.
Example Calculation for Irregular Hexagon
Suppose the lengths of the sides of hexagon ACEFGH are:
- AB = 4.2 cm
- BC = 4.3 cm
- CD = 1.52 cm
- DE = 5.4 cm
- EF = 9.2 cm
- FA = 3.1 cm
The perimeter is calculated as:
\[ P = 4.2 + 4.3 + 1.52 + 5.4 + 9.2 + 3.1 = 27.72 \, \text{cm} \]
Special Case: Hexagon Inscribed in a Circle
If a regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle, and the radius of the circle is known, the side length \(a\) of the hexagon is equal to the radius of the circle \(r\). Thus, the perimeter can be calculated using:
\[ P = 6 \times r \]
For example, if the radius of the circle is 1 unit, then:
\[ P = 6 \times 1 = 6 \, \text{units} \]

READ MORE:
Introduction
The perimeter of a hexagon ACEFGH is the total distance around the shape, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. For regular hexagons, each side is equal, simplifying the calculation. However, irregular hexagons require adding each unique side length. This guide will explain both methods in detail, providing clear, step-by-step instructions and examples.
- For a regular hexagon with side length \(a\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
- \(P = 6a\)
- For an irregular hexagon with side lengths \(a, b, c, d, e, f\), the perimeter \(P\) is:
- \(P = a + b + c + d + e + f\)
Let's explore these calculations through examples and detailed steps to ensure a comprehensive understanding of how to determine the perimeter of hexagon ACEFGH.
Definition of a Hexagon
A hexagon is a six-sided polygon characterized by six angles and six vertices. There are several types of hexagons, each defined by the properties of their sides and angles.
- Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has six equal sides and six equal angles. The perimeter of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula \( P = 6a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Irregular Hexagon: An irregular hexagon has sides and angles that are not all equal. The perimeter of an irregular hexagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides, calculated as \( P = a + b + c + d + e + f \), where \( a, b, c, d, e, \) and \( f \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Concave Hexagon: A concave hexagon has at least one interior angle greater than 180°. This type of hexagon has a shape that "caves" inward.
- Convex Hexagon: In a convex hexagon, all interior angles are less than 180°, and the vertices point outwards.
Overall, the perimeter of any hexagon is determined by summing the lengths of its six sides, regardless of whether it is regular, irregular, concave, or convex.
Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon is a polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles. This uniformity simplifies the calculation of its perimeter, making it straightforward and quick. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a regular hexagon is given by:
\[ P = 6a \]
where \( a \) represents the length of one side of the hexagon. Each side is identical in length, contributing to the overall symmetry and balance of the shape.
Let's walk through a detailed step-by-step calculation:
- Measure the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Multiply this length by 6 to account for all six sides of the hexagon.
- The result is the perimeter of the hexagon.
For example, if the side length \( a \) is 5 units, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as follows:
- Side length \( a = 5 \) units
- Perimeter \( P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \) units
This method ensures that the perimeter is accurately determined with minimal steps, emphasizing the efficiency of the formula for regular hexagons.
Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measures. Unlike a regular hexagon, where all sides and angles are equal, an irregular hexagon lacks this symmetry, making its perimeter calculation unique.
To find the perimeter of an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all its sides:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c + d + e + f
- Identify and measure each side length individually.
- Ensure accurate measurements to get an exact perimeter value.
- Add the lengths of all six sides to find the total perimeter.
For example, if the side lengths of hexagon ACEFGH are 4.2, 4.3, 1.52, 5.4, 9.2, and 3.1 units respectively, the perimeter is calculated as:
Perimeter (P) = 4.2 + 4.3 + 1.52 + 5.4 + 9.2 + 3.1 = 27.72 units
This straightforward method allows you to determine the perimeter of any irregular hexagon, provided you have the measurements of all its sides.

Properties of Hexagon
- Six equal sides and angles (for regular hexagons)
- Sum of interior angles is 720°
- Each interior angle is 120° (for regular hexagons)
- Nine diagonals can be drawn
- The perimeter of hexagon ACEFGH can be calculated by summing the lengths of its six sides, where ACEFGH represents the vertices of the hexagon.
Calculation Examples
Based on search results, the perimeter of hexagon ACEFGH can vary depending on the lengths of its sides. Here are some examples:
- For a hexagon with side lengths 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 units:
- For a hexagon with side lengths 10, 12, 15, 20, 22, and 25 units:
- For a hexagon with side lengths 3.5, 4.2, 6.1, 7.8, 9.3, and 11.2 units:
Perimeter (P) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 39 units
Perimeter (P) = 10 + 12 + 15 + 20 + 22 + 25 = 104 units
Perimeter (P) = 3.5 + 4.2 + 6.1 + 7.8 + 9.3 + 11.2 = 42.1 units
Types of Hexagons
- Regular Hexagon: All sides and angles are equal.
- Irregular Hexagon: Sides and angles are not equal.
- Concave Hexagon: At least one interior angle is greater than 180°.
- Convex Hexagon: All interior angles are less than 180°.
- Hexagon ACEFGH: Referring to the specific hexagon mentioned, its properties and classification would depend on the lengths and measures of its sides and angles.
READ MORE:
Applications of Hexagons
- Beehive Cells: The hexagonal shape allows bees to build efficient honeycomb structures, maximizing storage space while minimizing material usage.
- Tiles and Flooring: Hexagonal tiles are commonly used in flooring due to their ability to create visually appealing patterns and efficient coverage of space.
- Graphite Structures: Hexagonal structures are fundamental in the formation of graphite, a versatile material used in various applications including pencils, lubricants, and composite materials.
- Nut and Bolt Heads: Hexagonal heads provide better grip and torque transfer, making them commonly used in fasteners such as nuts and bolts for mechanical assemblies.
- Hexagon ACEFGH: Depending on its context and properties, this specific hexagon could find applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, or mathematics.