Topic what is 4/3 squared: What is 4/3 squared? This common mathematical question involves raising the fraction 4/3 to the power of 2, resulting in the fraction 16/9. This article explains the steps to calculate this, converting it to decimal form, and its applications in various mathematical contexts.
Table of Content
Understanding 4/3 Squared
To find the square of a fraction like 4/3, you multiply the fraction by itself. This can be done both in fraction form and decimal form. Let's explore how this is done:
Fraction Form
The fraction form of
( \frac{4}{3} )^2 = \frac{4 \times 4}{3 \times 3} = \frac{16}{9}
Decimal Form
Alternatively, you can convert the fraction to decimal form before squaring it. The fraction
(1.3333)^2 \approx 1.7778
Steps to Square a Fraction
- Write down the fraction.
- Multiply the numerator by itself.
- Multiply the denominator by itself.
- Write the new numerator over the new denominator.
Example
Let's take the fraction
| Step | Calculation |
| Original Fraction | |
| Multiply Numerators | |
| Multiply Denominators | |
| Resulting Fraction |
Summary
The square of
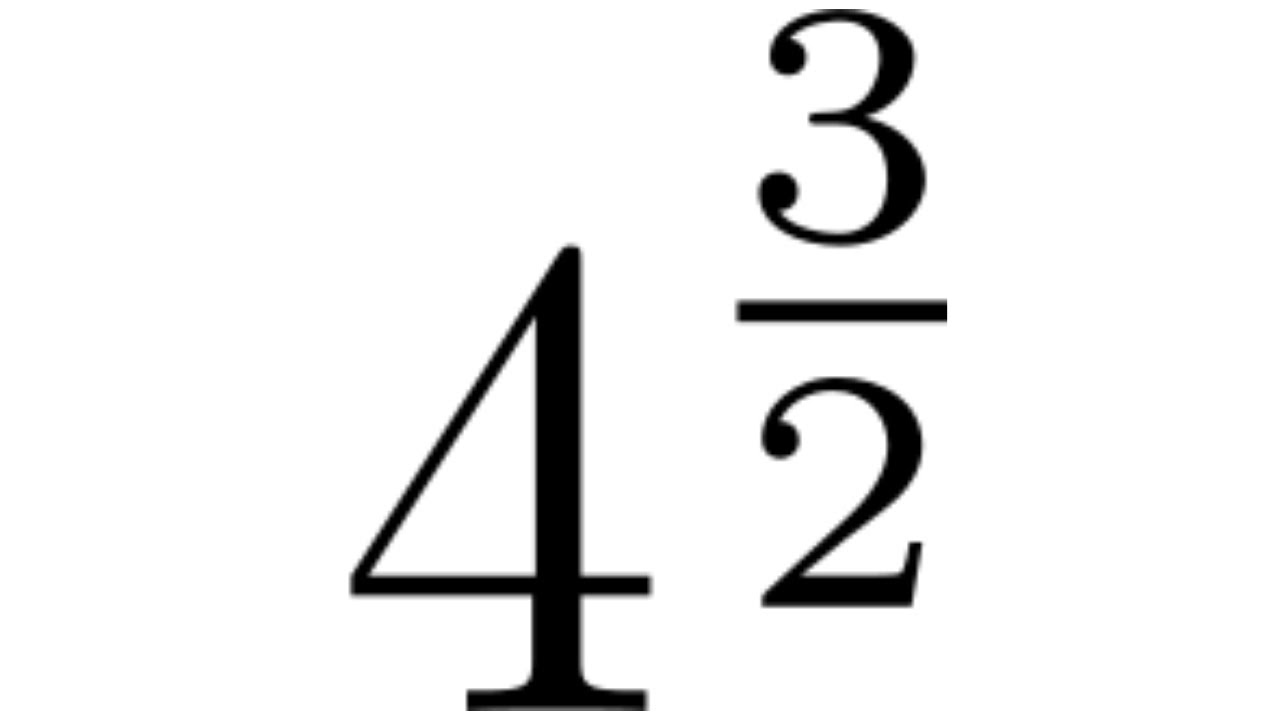
READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding how to square fractions is a fundamental aspect of mathematics. When we ask "what is 4/3 squared," we are looking to find the value of the fraction 4/3 raised to the power of 2. This is done by multiplying the fraction by itself. The process is straightforward and involves basic arithmetic operations.
To calculate (4/3)^2, we follow these steps:
- Multiply the numerator (4) by itself: 4 * 4 = 16
- Multiply the denominator (3) by itself: 3 * 3 = 9
- Combine the results to get the fraction: 16/9
Thus, (4/3)^2 = 16/9 in fraction form. To convert this into a decimal, we divide 16 by 9, which equals approximately 1.7778.
This calculation is useful in various mathematical contexts, such as solving algebraic equations and working with ratios. Understanding the concept of squaring fractions lays the groundwork for more advanced mathematical studies and applications.
Mathematical Definition
To find the square of a fraction, you multiply the fraction by itself. In this case, we are squaring the fraction \( \frac{4}{3} \).
The mathematical operation can be represented as:
\[
\left( \frac{4}{3} \right)^2 = \frac{4}{3} \times \frac{4}{3}
\]
Step by step, the calculation is as follows:
- Multiply the numerators: \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
- Multiply the denominators: \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \).
Thus, the result in fraction form is:
\[
\left( \frac{4}{3} \right)^2 = \frac{16}{9}
\]
Converting this fraction to a decimal, we get:
\[
\frac{16}{9} \approx 1.7778
\]
Therefore, the square of \( \frac{4}{3} \) is \( \frac{16}{9} \) or approximately 1.7778.
Calculation Steps
The calculation of \( \left(\frac{4}{3}\right)^2 \) involves squaring the numerator and the denominator separately. Here are the detailed steps:
Start with the fraction: \( \frac{4}{3} \).
Square the numerator: \( 4^2 = 16 \).
Square the denominator: \( 3^2 = 9 \).
Combine the squared numerator and denominator to form the new fraction: \( \frac{16}{9} \).
Convert the fraction to decimal form by dividing the numerator by the denominator: \( \frac{16}{9} \approx 1.7778 \).
Thus, \( \left(\frac{4}{3}\right)^2 \) equals \( \frac{16}{9} \) in fraction form and approximately 1.7778 in decimal form.
Examples of Squaring Fractions
Squaring fractions involves multiplying the fraction by itself. This section provides detailed examples to help you understand the process step by step.
- Example 1:
- Consider the fraction \(\frac{4}{3}\).
- Square the fraction: \(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right)^2\).
- Multiply the numerator by itself: \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Multiply the denominator by itself: \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
- The result is \(\frac{16}{9}\).
- Example 2:
- Consider the fraction \(\frac{5}{2}\).
- Square the fraction: \(\left(\frac{5}{2}\right)^2\).
- Multiply the numerator by itself: \(5 \times 5 = 25\).
- Multiply the denominator by itself: \(2 \times 2 = 4\).
- The result is \(\frac{25}{4}\).
- Example 3:
- Consider the fraction \(\frac{7}{5}\).
- Square the fraction: \(\left(\frac{7}{5}\right)^2\).
- Multiply the numerator by itself: \(7 \times 7 = 49\).
- Multiply the denominator by itself: \(5 \times 5 = 25\).
- The result is \(\frac{49}{25}\).
These examples illustrate that squaring a fraction is a straightforward process involving multiplying the numerator and the denominator by themselves. This method can be applied to any fraction to find its square.

Applications
Squaring fractions, such as \(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right)^2\), is a fundamental operation in various fields. Here are some common applications:
- Mathematics and Education: Understanding the squaring of fractions is essential in learning algebra and calculus. It helps students grasp concepts of exponents and fractional arithmetic.
- Physics: Squaring fractions is used in equations dealing with proportions, scaling, and dimensional analysis. For instance, in calculating areas and volumes where sides are given in fractional units.
- Engineering: In engineering, precise calculations often involve squaring fractional measurements, such as in signal processing, where power calculations involve squaring amplitude ratios.
- Economics and Finance: Squaring fractions is used in economic models and financial formulas. For example, in compound interest calculations where growth rates are represented as fractions.
- Computer Science: Algorithms for data compression and error correction often involve squaring operations, especially when dealing with probabilities and statistical models.
Conclusion
Squaring the fraction \(\frac{4}{3}\) is a straightforward mathematical operation that involves multiplying the fraction by itself. This process yields a new fraction with the numerator and denominator each raised to the power of 2. Here are the detailed steps to understand this operation:
- Begin with the fraction \(\frac{4}{3}\).
- Square the numerator: \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Square the denominator: \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
- The resulting fraction is \(\frac{16}{9}\).
- To convert \(\frac{16}{9}\) to a decimal, divide 16 by 9, resulting in approximately 1.7778.
This example illustrates the basic principle of squaring fractions, which involves multiplying the fraction by itself. The result \(\frac{16}{9}\) is a rational number that can also be expressed as a repeating decimal 1.7778.
Understanding how to square fractions is essential in various mathematical applications. It allows for the simplification and solving of more complex equations in algebra, calculus, and other fields. The process demonstrates the importance of fundamental arithmetic operations and their role in broader mathematical contexts.
In conclusion, squaring the fraction \(\frac{4}{3}\) results in \(\frac{16}{9}\), highlighting the utility and simplicity of this basic mathematical operation. This concept not only underpins many areas of mathematics but also aids in the comprehension of more advanced topics.
Video hướng dẫn cách bình phương một số và giải thích ý nghĩa của việc bình phương một số. Học toán với Thầy J, dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn.
Cách Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Một Số Có Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa phân số khi được nâng lên lũy thừa hữu tỉ và cách xử lý phân số được nâng lên phân số khác.
Đơn Giản Hóa Phân Số Được Nâng Lên Lũy Thừa Hữu Tỉ, Phân Số Nâng Lên Phân Số