Topic square root of 50 rational or irrational: Understanding the nature of the square root of 50 is crucial for students and math enthusiasts alike. This article explores whether the square root of 50 is rational or irrational, offering insights into its properties, calculation methods, and significance in mathematics.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 50: Rational or Irrational?
- Introduction
- Is 50 a Perfect Square?
- Is the Square Root of 50 Rational or Irrational?
- Simplifying the Square Root of 50
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 50
- Using a Calculator to Find the Square Root of 50
- Using a Computer to Calculate the Square Root of 50
- Rounding the Square Root of 50
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu tại sao căn bậc hai của 50 không phải là một số hợp lý và không thể biểu diễn dưới dạng phân số đơn giản.
Square Root of 50: Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 50 (\(\sqrt{50}\)) is an interesting mathematical concept that can be explored in various ways. This article provides a detailed explanation of whether the square root of 50 is a rational or irrational number, along with methods to calculate it.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because \(5 \times 5 = 25\). In the case of 50, \(\sqrt{50}\) can be simplified to \(5\sqrt{2}\).
Is \(\sqrt{50}\) Rational or Irrational?
A rational number can be expressed as the ratio of two integers (e.g., \(\frac{a}{b}\) where \(b \neq 0\)). An irrational number, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion.
The square root of 50, when simplified, is \(5\sqrt{2}\). The value of \(\sqrt{2}\) is approximately 1.41421356, which is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal. Therefore, \(\sqrt{50}\) is an irrational number.
Methods to Find \(\sqrt{50}\)
There are two primary methods to find the square root of 50:
- Prime Factorization
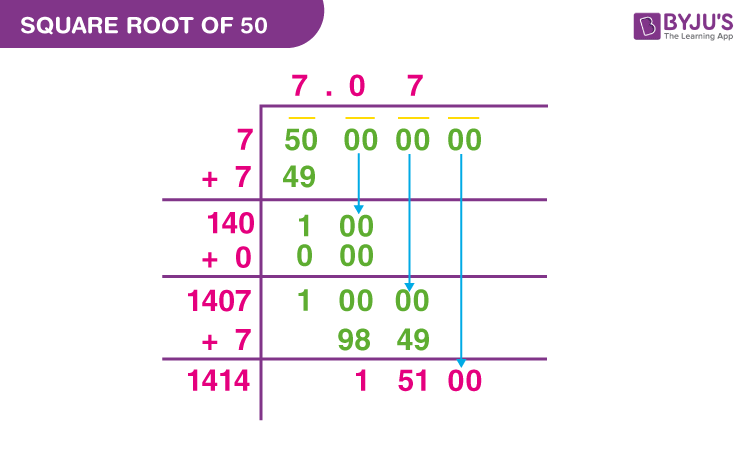
- Long Division Method
- Pair the digits of 50 from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 50. This is 7 (since \(7^2 = 49\)).
- Use the long division process to refine the value to several decimal places, resulting in approximately 7.0710678.
Express 50 as the product of its prime factors:
\(50 = 2 \times 5^2\)
Taking the square root of both sides:
\(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
This method is used to find more accurate decimal values of the square root:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 50 is \(5\sqrt{2}\) or approximately 7.0710678. Since this value is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal, \(\sqrt{50}\) is an irrational number.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 50 is an interesting number to explore, especially in understanding whether it is rational or irrational. To determine this, we need to delve into the definition of square roots, methods to calculate them, and their classification in number theory. This section will provide a detailed introduction to these concepts, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the square root of 50.
In mathematical terms, the square root of 50, represented as √50, is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives 50. This value can be expressed in several forms, including radical, exponential, and decimal. We will also explore different methods of calculating the square root, such as prime factorization and long division, to provide a step-by-step approach to finding this value.
Ultimately, we will classify the square root of 50 as either rational or irrational, based on its properties and representation. Join us in this mathematical journey to uncover the nature of the square root of 50 and enhance your understanding of square roots and their significance in mathematics.
Is 50 a Perfect Square?
To determine if 50 is a perfect square, we need to check if there exists an integer \( n \) such that \( n^2 = 50 \).
- Step 1: Take the square root of 50: \( \sqrt{50} \).
- Step 2: Calculate \( \sqrt{50} \). Approximating, we find \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071 \).
- Step 3: Check if \( \sqrt{50} \) is an integer. Since \( \sqrt{50} \) is not an integer but an irrational number, 50 is not a perfect square.
Is the Square Root of 50 Rational or Irrational?
To determine if \( \sqrt{50} \) is rational or irrational, let's analyze it step by step:
- Step 1: Prime factorize 50: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Step 2: Assume \( \sqrt{50} \) is rational, so \( \sqrt{50} = \frac{p}{q} \) where \( p \) and \( q \) are integers and \( \frac{p}{q} \) is in its simplest form.
- Step 3: Square both sides: \( 50 = \frac{p^2}{q^2} \).
- Step 4: Multiply through by \( q^2 \): \( 50q^2 = p^2 \).
- Step 5: Check the prime factorization of \( p^2 \) and \( 50q^2 \). Since the prime factors do not match, our assumption that \( \sqrt{50} \) is rational leads to a contradiction. Therefore, \( \sqrt{50} \) is irrational.
Simplifying the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 can be simplified as follows:
- Step 1: Recognize the prime factorization of 50: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Step 2: Express \( \sqrt{50} \) in terms of its prime factors: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} \).
- Step 3: Break down the square root: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5^2} \).
- Step 4: Simplify further: \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \), so \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 50
- Prime Factorization Method: Factorize 50 as \( 2 \times 5^2 \). Hence, \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
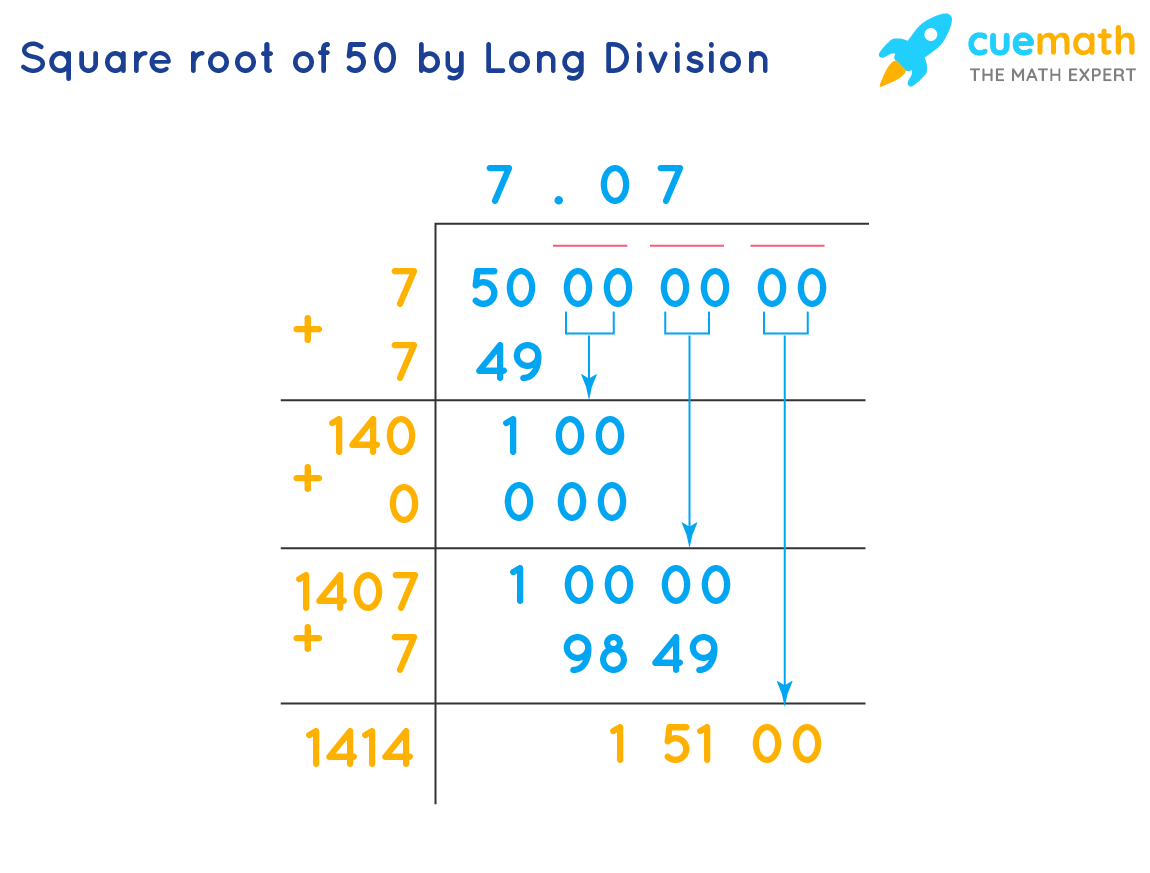
- Long Division Method: Use long division to approximate \( \sqrt{50} \) by iterative steps, refining until desired precision is achieved.
- Estimation Method: Estimate \( \sqrt{50} \) using known square roots of nearby integers, adjusting based on calculated approximations.
- Babylonian Method: Iteratively refine an initial guess to \( \sqrt{50} \) using the formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{50}{x_n} \right) \).
Using a Calculator to Find the Square Root of 50
Using a scientific calculator to find \( \sqrt{50} \) involves the following steps:
- Step 1: Turn on your scientific calculator and make sure it's in standard mode.
- Step 2: Enter the number 50.
- Step 3: Press the square root button (\( \sqrt{x} \) or similar). On most calculators, this is represented by a radical symbol.
- Step 4: Press the equals (=) button to calculate \( \sqrt{50} \).
- Step 5: Read the display. The result should show approximately \( 7.07106781187 \) or a rounded value depending on the calculator's display settings.
Using a Computer to Calculate the Square Root of 50
Computers use algorithms to calculate square roots efficiently. Here’s how a computer typically computes \( \sqrt{50} \):
- Step 1: The computer selects an initial guess for \( \sqrt{50} \).
- Step 2: It applies iterative methods like Newton's method or the Babylonian method to refine the guess until a desired level of accuracy is achieved.
- Step 3: The computer checks the result against the precision required and adjusts the calculation accordingly.
- Step 4: Finally, the computer displays \( \sqrt{50} \) as approximately \( 7.07106781187 \), or rounded to the specified decimal places.
Rounding the Square Root of 50
Rounding \( \sqrt{50} \) to a specified number of decimal places involves these steps:
- Step 1: Calculate \( \sqrt{50} \) using a calculator or computer, which gives approximately \( 7.07106781187 \).
- Step 2: Decide on the number of decimal places to round to, for example, rounding to three decimal places.
- Step 3: Identify the third decimal place: \( 7.07106781187 \) (7.071).
- Step 4: Since the fourth decimal place (6) is greater than 5, round up the third decimal place to \( 7.071 \).
- Step 5: Therefore, \( \sqrt{50} \) rounded to three decimal places is \( 7.071 \).

Xem video này để hiểu tại sao căn bậc hai của 50 không phải là một số hợp lý và không thể biểu diễn dưới dạng phân số đơn giản.
Why Square Root of 50 Is Not a Rational Number | Video Title in Vietnamese
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 50. Khám phá các bước để làm toán học dễ dàng hơn với căn bậc hai.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của Một Số | Đơn Giản Hóa Toán Học, Căn(50)