Topic is the square root of 50 a rational number: Understanding whether the square root of 50 is a rational number involves delving into the nature of irrational numbers and square roots. This article explores the characteristics of the square root of 50, its classification as irrational, and methods to approximate its value.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 50
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Calculating the Square Root of 50
- Methods for Finding Square Root
- Is the Square Root of 50 Rational or Irrational?
- Properties of the Square Root of 50
- Representation of the Square Root of 50
- Perfect Square Comparison
- Common Square Root Questions
- YOUTUBE: Xem tại sao căn bậc hai của 50 không phải là số hợp số.
Understanding the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 is a mathematical concept that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 50. This is denoted as √50.
Is the Square Root of 50 a Rational Number?
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers. In contrast, an irrational number cannot be written as a simple fraction because it has an infinite, non-repeating decimal expansion. The square root of 50 is an irrational number because it cannot be precisely expressed as a fraction of two integers.
Mathematically:
- Radical form: \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- Decimal form: \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071067811865475 \)
Why is the Square Root of 50 Irrational?
The square root of 50 simplifies to \( 5\sqrt{2} \). Since \( \sqrt{2} \) is known to be an irrational number (a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction), multiplying it by 5 (a rational number) still results in an irrational number. Therefore, \( \sqrt{50} \) is irrational.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 50
There are several methods to determine the square root of 50:
-
Prime Factorization Method
Decompose 50 into its prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5 \). Group the factors to simplify:
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
-
Long Division Method
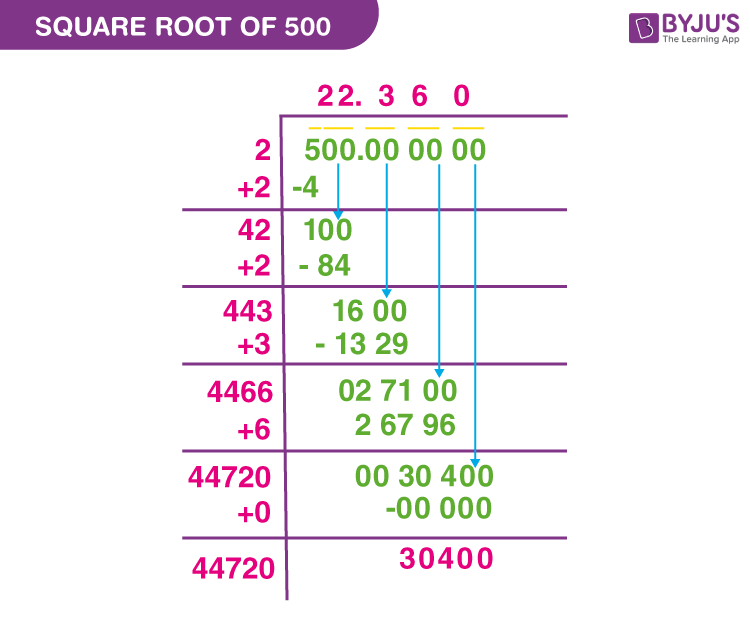
This method involves dividing 50 by successive approximations to reach a precise value:
- Place a decimal point after 50 and add pairs of zeros: 50.000000.
- Estimate the square root by finding a number whose square is close to 50 (e.g., 7 x 7 = 49).
- Refine the approximation by dividing and averaging until the desired precision is reached.
-
Estimation Method
Recognize that 50 is between the perfect squares of 49 (72) and 64 (82). Thus, \( \sqrt{50} \) is between 7 and 8.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 50 is an important mathematical concept that is irrational and can be approximated using various methods. Understanding its properties and how to calculate it is fundamental in higher mathematics.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 50, represented as √50, is a mathematical value that is not straightforward to categorize. Unlike perfect squares whose square roots are whole numbers, the square root of 50 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. Understanding why the square root of 50 is irrational and how to calculate it using various methods provides a fascinating insight into mathematical concepts and number theory.
To delve deeper, we can represent √50 in different forms, such as in its simplest radical form (5√2), in its decimal form (approximately 7.071), and as an exponent (50^(1/2)). These representations highlight the complexity and the unique nature of the square root of 50.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. It is denoted by the radical symbol √. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 × 3 = 9. The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics and has several methods for calculation:
- Square root by prime factorization
- Square root by repeated subtraction method
- Square root by long division method
- Square root by estimation method
In mathematical notation, the square root of a number \( n \) is expressed as:
$$ \sqrt{n} $$
In the case of 50, it can be expressed as:
$$ \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} = 5 \times \sqrt{2} $$
Since \( \sqrt{2} \) is an irrational number, the square root of 50 is also irrational.
Calculating the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 is a mathematical concept that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 50. This section will explain the process of calculating the square root of 50 step by step.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 50
- Prime Factorization Method
- Long Division Method
- Estimation Method
- Babylonian Method
Prime Factorization Method
- Decompose 50 into its prime factors: \(50 = 2 \times 5^2\).
- Express the square root of 50 in terms of these prime factors: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2}\).
- Simplify the expression: \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
- Since \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414\), the square root of 50 is approximately \(5 \times 1.414 = 7.07\).
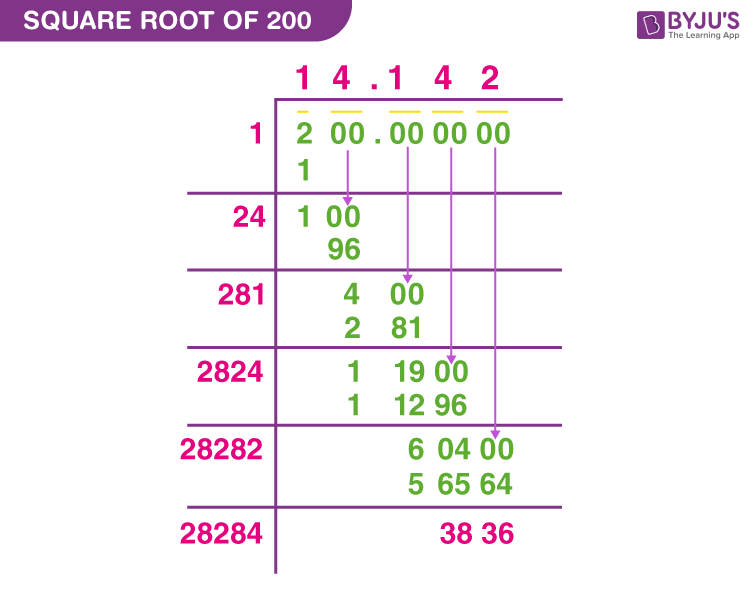
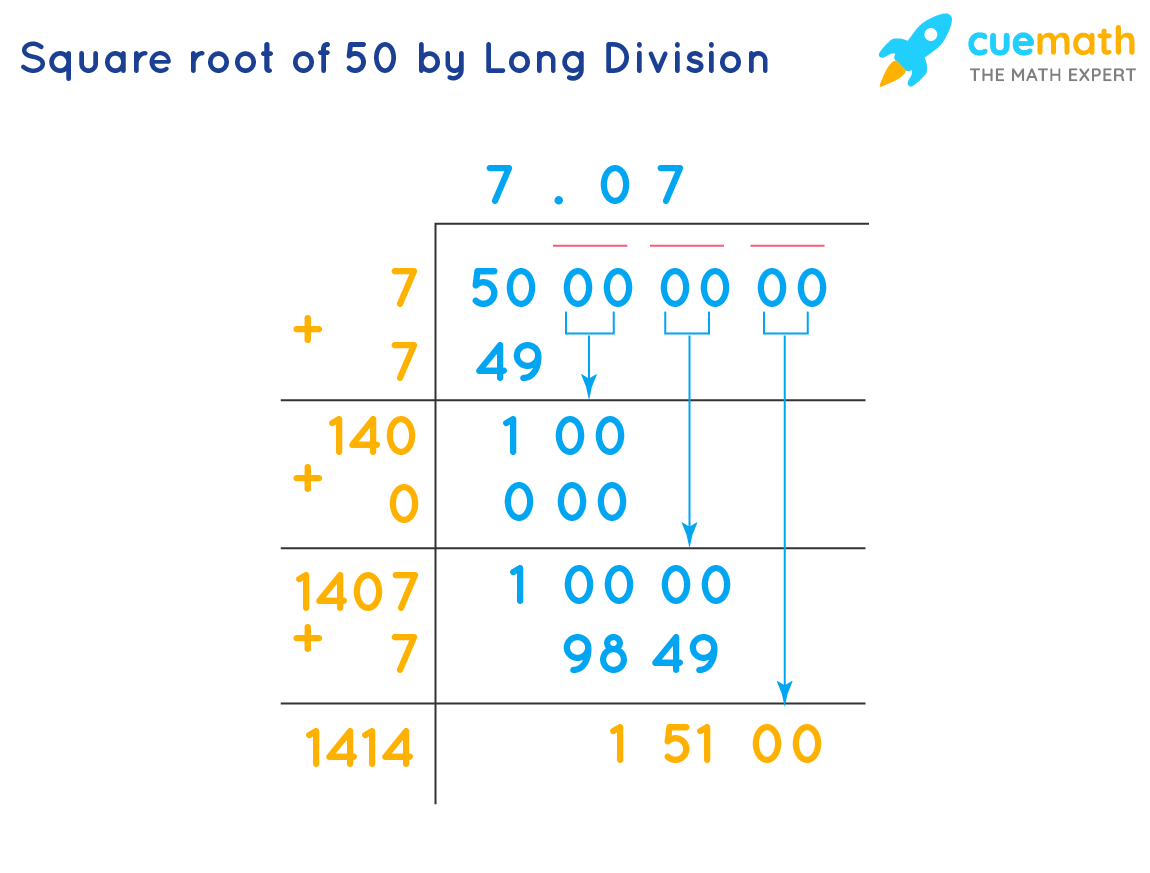
Long Division Method
- Start with 50 and place a decimal point followed by pairs of zeros: 50.00.
- Pair the digits and place a bar over them: \( \overline{50} \overline{00}\).
- Determine the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 50, which is 7 (since \(7 \times 7 = 49\)).
- Subtract 49 from 50, getting 1, and bring down the next pair of zeros, making it 100.
- Double the quotient (7), getting 14, and determine the largest digit (x) for 14x that is less than or equal to 100. The result is 140.
- Repeat the process to obtain more decimal places. The result approximates to 7.071.
Estimation Method
Since 50 is between the perfect squares of 49 (7²) and 64 (8²), the square root of 50 is estimated to be between 7 and 8. More precise estimation shows it is closer to 7.07.
Babylonian Method
- Start with an initial guess, say 7.
- Use the Babylonian formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} (x_n + \frac{50}{x_n}) \).
- Iteratively apply the formula to refine the guess until the desired precision is achieved. This method converges quickly to the accurate value of 7.071.
By understanding these methods, you can calculate the square root of 50 efficiently, whether for academic purposes or practical applications.
Methods for Finding Square Root
Finding the square root of a number can be achieved through several methods, each with its own approach and level of precision. Here are some common methods used to find the square root of 50:
-
Prime Factorization Method
- Decompose 50 into its prime factors: 2 × 5 × 5.
- Group the prime factors: √(2 × 5 × 5).
- Simplify the expression: √50 = √(25 × 2) = 5√2.
-
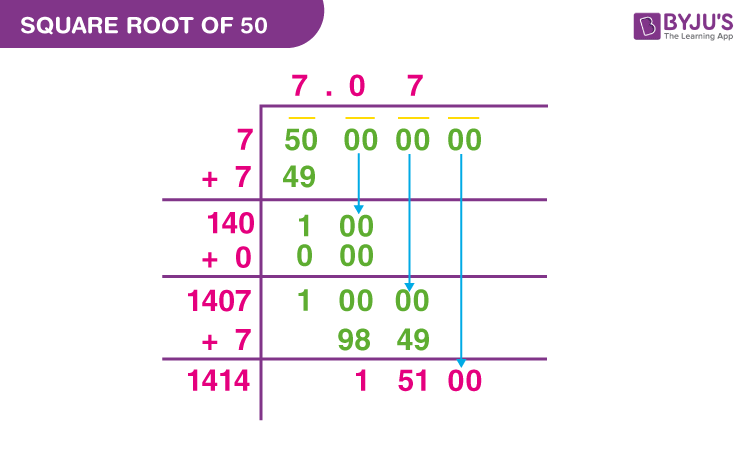
Long Division Method
- Start with an initial approximation for the square root of 50.
- Iteratively refine the approximation through successive long divisions.
- Continue adjusting the approximation until achieving the desired level of accuracy.
-
Estimation Method
- Recognize that 50 is near the square of a whole number.
- Identify nearby perfect squares: 49 (7²) and 64 (8²).
- Since 50 lies between 49 and 64, estimate its square root to be between 7 and 8.
-
Babylonian Method (Heron's Method)
- Initiate with a tentative guess for the square root of 50, such as 7.
- Use the Babylonian formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{50}{x_n} \right) \) to iteratively enhance the guess.
- Continue the iterations until reaching the desired precision level.
These methods provide clear strategies for calculating the value of the square root of 50, catering to various skill levels and preferences in mathematical reasoning. Whether you prefer a methodical approach like prime factorization or a more iterative technique like the Babylonian method, each method helps in understanding and determining the square root of numbers effectively.
Is the Square Root of 50 Rational or Irrational?
A number is considered rational if it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. An irrational number, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
To determine if the square root of 50 is rational or irrational, let's consider the nature of the square root itself:
- We start with the number 50. Its square root is represented as \( \sqrt{50} \).
- To simplify \( \sqrt{50} \), we can use prime factorization:
- The prime factors of 50 are 2 and 5 (since \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \)).
- This can be written as:
- \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{25} \)
- Since \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \), it simplifies further to:
- \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- We know that \( \sqrt{2} \) is an irrational number. Multiplying an irrational number by a rational number (5) results in an irrational number.
- Therefore, \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \) is irrational.
To conclude, the square root of 50 cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, which makes it an irrational number. This is confirmed by its decimal form, which is non-terminating and non-repeating: \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.0710678118655 \).
Properties of the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 (\(\sqrt{50}\)) has several important mathematical properties that are useful to understand.
- Radical Form: The simplest radical form of \(\sqrt{50}\) is \(5\sqrt{2}\). This simplification is derived from the factorization of 50 into \(25 \times 2\), where 25 is a perfect square.
- Decimal Form: The approximate decimal value of \(\sqrt{50}\) is 7.0710678118655. This is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal, indicating that it is an irrational number.
- Exponential Form: The exponential form of \(\sqrt{50}\) is \(50^{1/2}\).
- Irrational Nature: Since \(\sqrt{50}\) cannot be expressed as a fraction \(\frac{p}{q}\) where \(p\) and \(q\) are integers, it is classified as an irrational number. This is because it includes \(\sqrt{2}\), which is itself irrational.
Prime Factorization
The square root of 50 can be understood through prime factorization:
- Factorize 50 into prime factors: \(50 = 2 \times 25 = 2 \times 5 \times 5\).
- Express \(\sqrt{50}\) using these prime factors: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
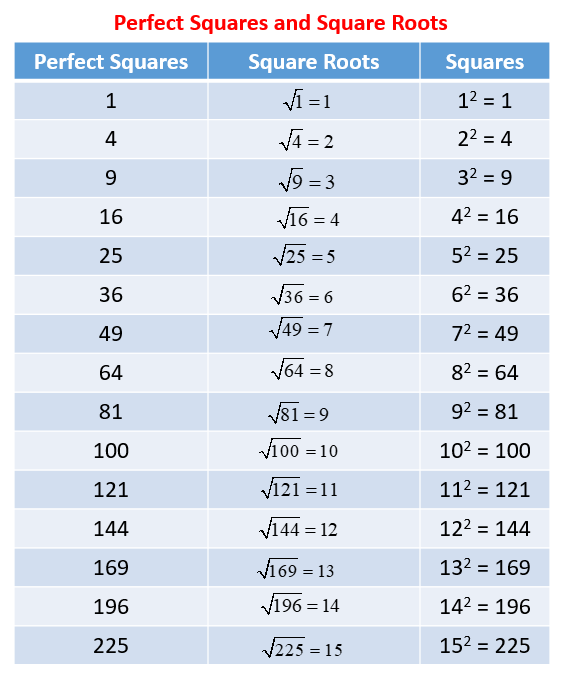
Comparison with Perfect Squares
Understanding how \(\sqrt{50}\) compares with nearby perfect squares can also be insightful:
- \(\sqrt{49} = 7\)
- \(\sqrt{64} = 8\)
- \(\sqrt{50}\) lies between these two values, closer to 7.
Continued Fraction Representation
The square root of 50 can also be represented as a continued fraction, which is a way to express it as a series of fractions that provide progressively better approximations:
\(\sqrt{50} = 7 + \frac{1}{14 + \frac{1}{14 + \frac{1}{14 + \cdots}}}\)
This form highlights the regularity and pattern in the approximations of \(\sqrt{50}\).
Numerical Approximations
For practical calculations, \(\sqrt{50}\) is often approximated to a few decimal places, such as 7.07, which is sufficient for many real-world applications.
Representation of the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50, denoted as √50, can be represented in different forms:
- Radical Form: √50 = 5√2
- Decimal Approximation: √50 ≈ 7.0710678118655
In radical form, √50 simplifies to 5 times the square root of 2. This representation shows the exact value of the square root of 50 in terms of its prime factors.
The decimal approximation of √50 provides a numerical value that is approximately 7.0710678118655. This decimal form is useful for practical calculations and measurements where an exact radical form is not necessary.
Perfect Square Comparison
The square root of 50 is not a perfect square. Perfect squares are numbers that can be expressed as the square of an integer, such as 1, 4, 9, 16, etc. Since 50 is not a perfect square, its square root, √50, is an irrational number.
To determine if a number is a perfect square, you can check if its prime factorization includes only even powers of its prime factors. In the case of 50, its prime factorization is 2 × 5^2, which includes an odd power of 5 (5^2). Therefore, 50 is not a perfect square.
Common Square Root Questions
- Is the Square Root of 50 a Perfect Square?
- Can the Square Root of 50 be Simplified?
- How to Calculate the Square Root of 50 Using a Calculator?
No, the square root of 50 (√50) is not a perfect square because 50 itself is not a perfect square.
Yes, the square root of 50 can be simplified. √50 = 5√2, where 5 is outside the radical sign and √2 is inside. This is the simplest radical form.
To calculate √50 using a calculator, simply input the number 50 and press the square root (√) button. The result will be approximately 7.0710678118655.
Xem tại sao căn bậc hai của 50 không phải là số hợp số.
Why Square Root of 50 Is Not a Rational Number - Video
READ MORE:
Xem giải thích về căn bậc hai của số 50 và tính chất của nó.
Căn bậc hai của 50 (Giải thích)