Topic square root of 50: The square root of 50 is a fascinating mathematical concept often encountered in algebra. This article explores various methods to find and simplify the square root of 50, including prime factorization and the long division method. We will also discuss the significance of the square root in different mathematical contexts and provide a clear understanding of its properties.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 50
- Introduction to Square Root of 50
- Simplified Form of Square Root of 50
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 50
- Applications of Square Root of 50
- FAQs on Square Root of 50
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 50. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và các bước chi tiết để giải bài toán này một cách dễ dàng.
Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 (√50) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The value of the square root of 50 is approximately 7.071 in decimal form and 5√2 in simplified radical form.
Forms of Square Root of 50
- Radical form: \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- Exponential form: \( 50^{1/2} \)
- Decimal form: 7.071
Methods to Find the Square Root of 50
There are two main methods to find the square root of 50:
1. Prime Factorization
- Express 50 as a product of its prime factors: 50 = 2 × 5 × 5
- Take the square root of both sides: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
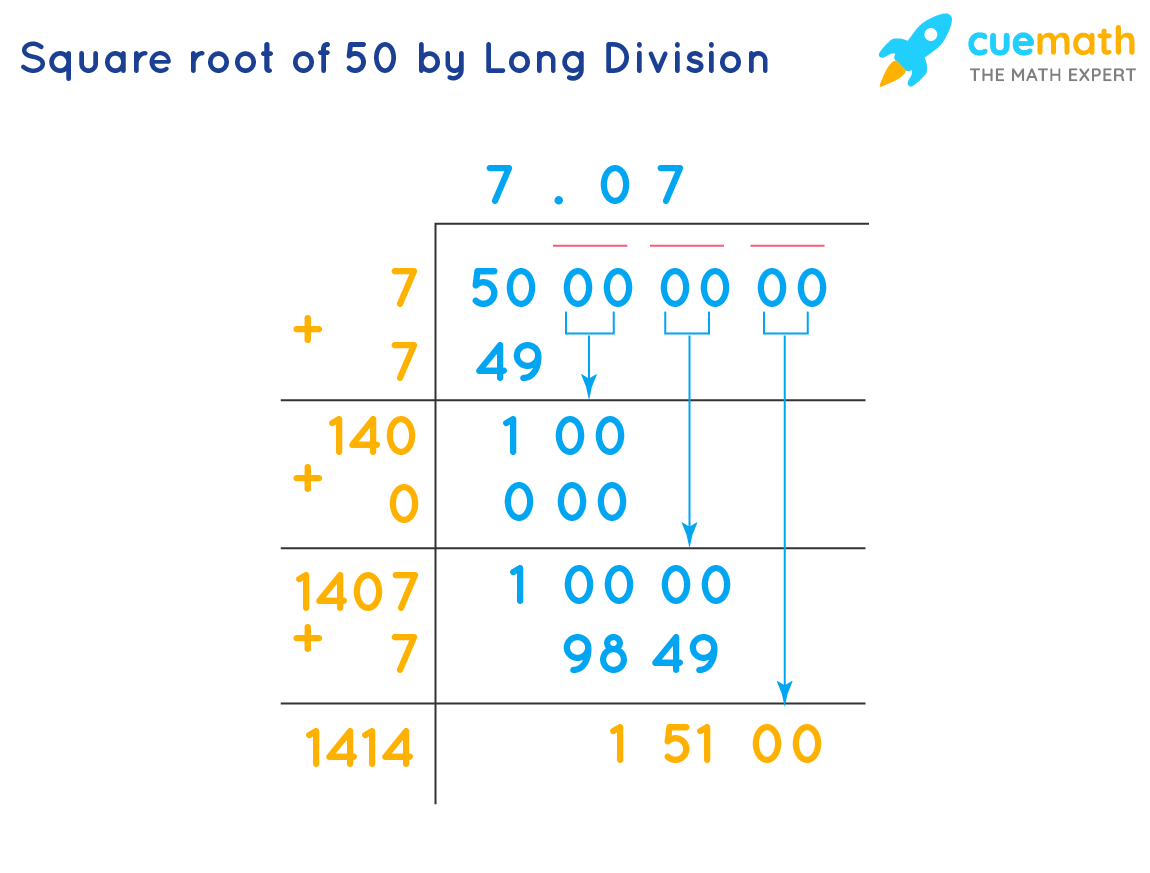
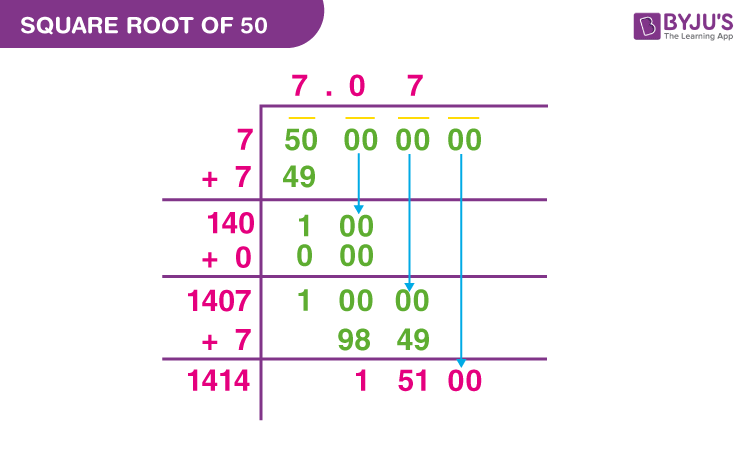
2. Long Division Method
This method involves the following steps:
- Pair the digits from right to left and find a number that, when squared, is less than or equal to 50.
- 7 × 7 = 49, so the integer part of the square root is 7.
- Put a decimal after 7 and add pairs of zeroes to continue the division.
- Follow through the steps to get a more precise value, which is approximately 7.071.
Properties of the Square Root of 50
- 50 is not a perfect square, as its square root is not an integer.
- \( \sqrt{50} \) is an irrational number because its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Examples of Other Square Roots
- Square root of 25 is 5.
- Square root of 36 is 6.
- Square root of 60 is approximately 7.746.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 50 | 7.071 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
Understanding the square root of 50 can help with various mathematical concepts and real-world applications, such as in geometry and algebra.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 is a mathematical concept that can be represented in several forms, including its radical, exponential, and decimal forms. It is an important value in various mathematical computations and real-life applications.
- Radical Form: The square root of 50 can be simplified to \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
- Exponential Form: In exponential notation, it is represented as \(50^{1/2}\).
- Decimal Form: The approximate decimal value of the square root of 50 is 7.071.
Because 50 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. Understanding the square root of 50 involves methods like prime factorization and the long division method.
| Method | Process | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Prime Factorization |
|
\(5\sqrt{2}\) |
| Long Division |
|
7.071... |
The square root of 50 finds its applications in geometry, particularly in calculating the side length of a square with an area of 50 square units, and in various algebraic problems. This concept is fundamental in higher mathematics and helps in understanding more complex mathematical theories.
Simplified Form of Square Root of 50
The square root of 50, represented as √50, is not a perfect square. However, it can be simplified into its simplest radical form. This process involves factoring the number into a product of its prime factors.
- Prime Factorization
First, we factor 50 into its prime factors: 50 = 2 × 5 × 5.
Next, group the factors into pairs: 50 = (5 × 5) × 2.
Then, take the square root of each group: √50 = √(5 × 5) × √2.
This simplifies to: √50 = 5√2.
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 50 is 5√2. This indicates that √50 can be expressed as 5 times the square root of 2.
Since √2 is approximately 1.414, we can also express the square root of 50 in decimal form:
√50 ≈ 5 × 1.414 = 7.07.
This decimal form is an approximation because √2 is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 50
Calculating the square root of 50 can be approached using various methods. Here are detailed steps for the most common techniques:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Decompose 50 into its prime factors: \(50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5\).
- Group the prime factors under the square root: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5}\).
- Simplify by taking the square root of perfect squares: \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
- Long Division Method
- Begin by placing a decimal after 50 followed by pairs of zeros: 50.00.
- Pair the digits and place bars over them from left to right.
- Identify a number that when squared is less than or equal to 50. Here, 7 × 7 = 49, so the quotient is 7.
- Add a decimal after 7, continue the process with pairs of zeros.
- Double the quotient (7) and find a suitable number to multiply with the new divisor. Continue iterating to refine the approximation.
- Example: Start with 50 as the dividend, 7 as the quotient: \(7.07\) (approximation).
- Estimation Method
- Recognize nearby perfect squares: 49 (7²) and 64 (8²).
- Estimate \(\sqrt{50}\) lies between 7 and 8. A rough estimate gives \(7.07\).
- Babylonian (Heron's) Method
- Start with an initial guess, for example, 7.
- Use the iterative formula: \(x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2}(x_n + \frac{50}{x_n})\).
- Repeat the process until reaching the desired precision.
- Example: Start with 7, iterate to refine: \(7.071\) (approximation).
Each method provides a pathway to accurately determine the square root of 50, catering to different levels of mathematical proficiency and precision requirements.
Applications of Square Root of 50
The square root of 50, approximately 7.071, finds applications in various fields. These applications utilize the mathematical properties of square roots in practical and theoretical contexts.
- Geometry and Area Calculation: When determining the side length of a square with a known area, the square root of the area is used. For example, if the area is 50 square units, the side length is the square root of 50.
- Physics and Free Fall: In physics, square roots are used to calculate the time it takes for an object to fall from a certain height under gravity. The time (t) to fall from a height (h) can be calculated using the formula . If an object is dropped from a height of 50 feet, the time to hit the ground is seconds.
- Engineering and Design: Engineers often use square roots in designing systems and structures where precise measurements are required. For instance, calculating the diagonal of a square with a side length derived from the square root of 50 can be essential in layout planning.
- Accident Investigations: Forensic investigators use the square root to calculate vehicle speed from skid marks. The speed (v) can be found using , where d is the length of the skid marks. If skid marks are 50 feet, the speed is miles per hour.
These examples illustrate the diverse applications of the square root of 50, highlighting its importance in various scientific and practical domains.
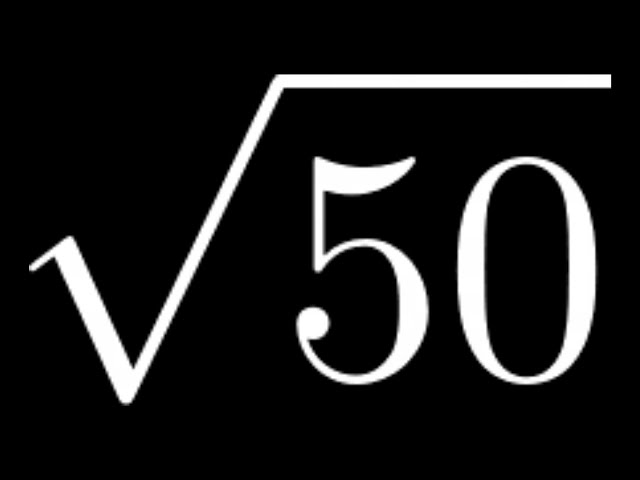
FAQs on Square Root of 50
Understanding the square root of 50 can raise many questions. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify this mathematical concept:
- What is the square root of 50?
The square root of 50 is approximately 7.071, which means √50 ≈ 7.071. In simplified radical form, it is expressed as 5√2.
- Is the square root of 50 a rational number?
No, the square root of 50 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- How do you simplify the square root of 50?
To simplify √50, you factor it into √(25 * 2) which equals 5√2.
- What are the properties of the square root of 50?
Some key properties include:
- It is an irrational number.
- It can be simplified to 5√2.
- It is approximately equal to 7.071.
- How do you calculate the square root of 50 using a calculator?
Simply enter 50 into the calculator and press the square root (√) function to get the approximate value of 7.071.
- What is the principal square root of 50?
The principal square root of 50 is the positive value, which is approximately 7.071.
- Can the square root of 50 be negative?
Yes, the square root of 50 can also be -7.071, but the principal square root refers to the positive value.
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 50. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và các bước chi tiết để giải bài toán này một cách dễ dàng.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 50: Căn(50)
READ MORE:
Giải thích cách tính căn bậc hai của 50 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Hướng dẫn từng bước để bạn có thể nắm vững kiến thức này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 50 (Giải Thích)