Topic square root of 250 simplified: Discover how to simplify the square root of 250 with this comprehensive guide. Learn the methods to break down √250 into its simplest radical form, understand its decimal approximation, and see practical applications. This article will help you master the concept with clear steps and examples, ensuring a solid grasp of this fundamental mathematical skill.
Table of Content
Simplified Square Root of 250
To simplify the square root of 250, we can use prime factorization and basic algebraic principles. The steps are as follows:
Steps to Simplify √250
- Find the prime factors of 250.
- Group the factors in pairs.
- Take one factor from each pair outside the square root.
Here is the detailed breakdown:
| Prime Factorization: | 250 = 2 × 5² × 5 |
| Rewrite the square root: | √250 = √(2 × 5² × 5) |
| Simplify: | √250 = 5√10 |
Exact Form
The exact form of the square root of 250 is expressed as:
√250 = 5√10
Decimal Form
The decimal approximation of the square root of 250 is:
√250 ≈ 15.811
Examples of Usage
- Finding the side length of a square rug with an area of 250 square feet, where the length of each side is approximately 15.81 feet.
- Comparing values, such as determining that √250 is not equal to 10 times √25.
Interactive Example
To practice simplifying square roots, consider the following example:
Question: Simplify √250.
Solution: 250 = 2 × 5² × 5, so √250 = 5√10.
For more examples and interactive learning, explore educational resources like Cuemath, Mathway, and Symbolab.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 250 is often simplified to make calculations easier and to express the value in its simplest form. Simplifying the square root involves finding the largest perfect square factor of the number and then rewriting the radical. This process not only helps in mathematics but also enhances understanding of square roots and their properties.
For example, the square root of 250 can be simplified as follows:
- First, identify the factors of 250: 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50, 125, 250.
- The largest perfect square factor is 25.
- Divide 250 by 25 to get 10.
- The square root of 25 is 5.
- Thus, the square root of 250 can be simplified to \(5\sqrt{10}\).
This method is known as the prime factorization method. It shows that simplifying square roots is straightforward once you understand the process of breaking down a number into its factors and identifying perfect squares.
Understanding Square Roots
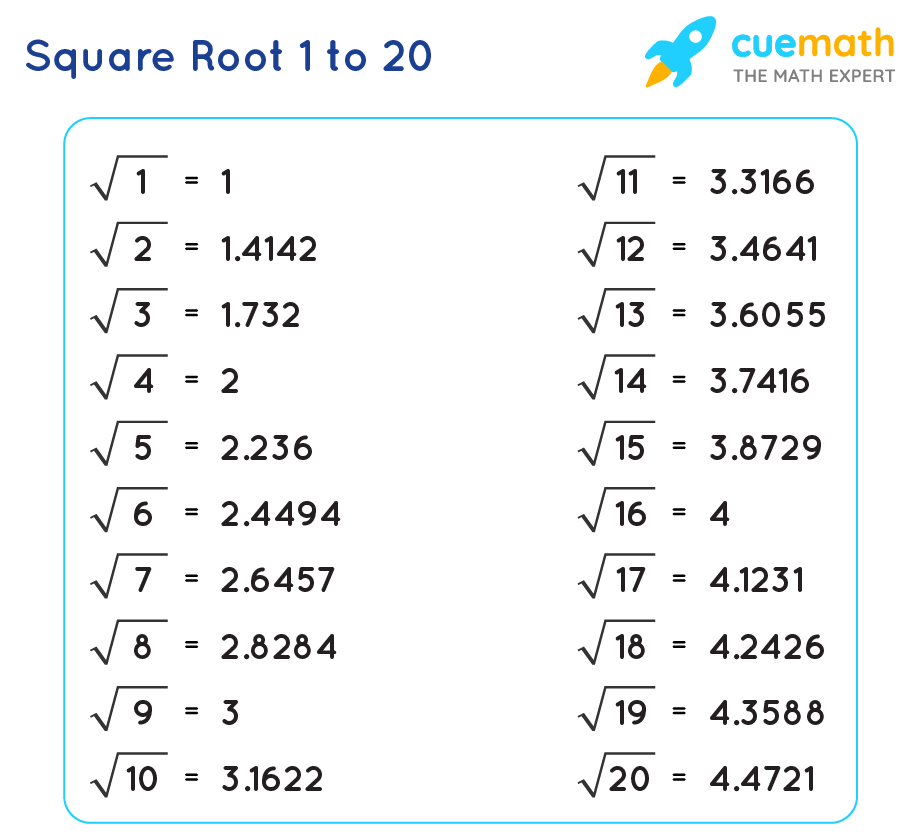
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 x 4 = 16. The symbol for the square root is √, and it is an essential concept in mathematics, used in various applications such as geometry, algebra, and calculus.
Square roots can be classified into two categories:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers whose square roots are whole numbers (e.g., 1, 4, 9, 16).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers whose square roots are not whole numbers and are usually irrational (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7).
When dealing with non-perfect squares, the square root is often expressed in its simplified radical form. Simplifying square roots involves factoring the number into its prime factors and pairing identical factors.
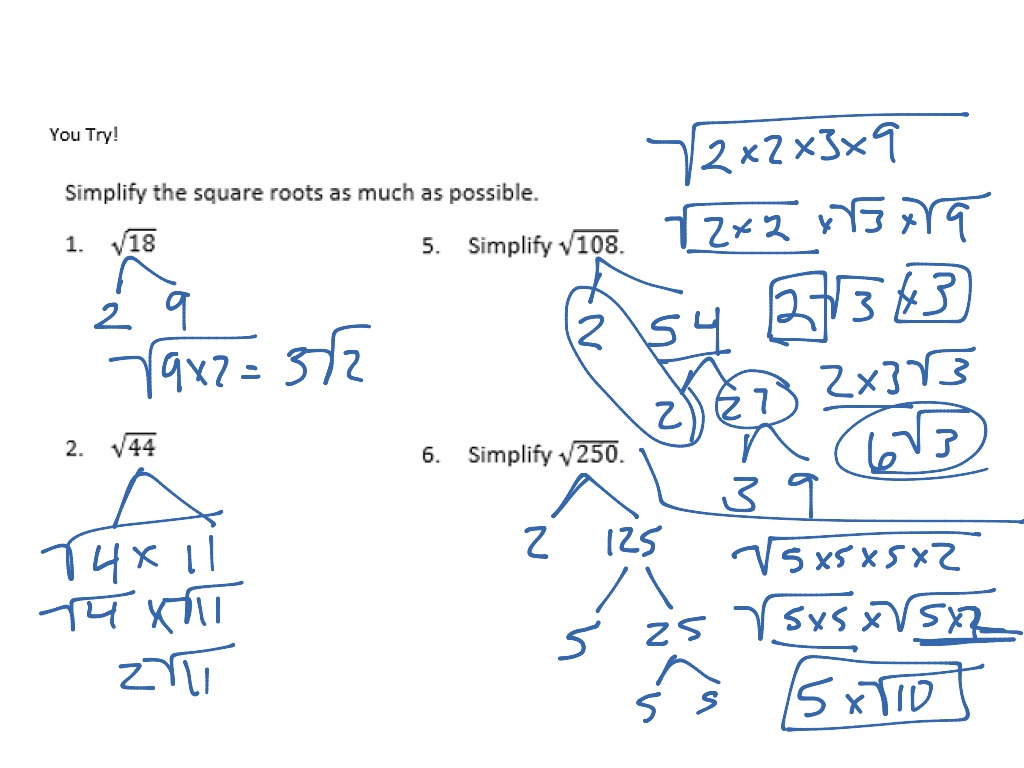
For example, the square root of 50 can be simplified as follows:
- Factor 50 into its prime factors: 50 = 2 x 5 x 5.
- Pair the identical factors: 50 = (5 x 5) x 2.
- Take one factor from each pair outside the square root: √50 = 5√2.
Similarly, the square root of 250 can be simplified by factoring it into its prime factors and applying the same steps. Understanding these principles helps in simplifying complex expressions and solving mathematical problems efficiently.
What is the Square Root of 250?
The square root of 250 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the product 250. Since 250 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal form.
In mathematical terms, the square root of 250 can be expressed in different forms:
- Radical Form: \( \sqrt{250} \)
- Simplified Radical Form: \( 5\sqrt{10} \)
- Decimal Form: Approximately 15.81139
To understand why the simplified radical form is \( 5\sqrt{10} \), let's break down the steps:
- Prime factorize 250: \( 250 = 2 \times 5^2 \times 5 \)
- Group the factors into pairs of two: \( 250 = (5^2) \times 10 \)
- Take the square root of the pairs: \( \sqrt{250} = \sqrt{(5^2) \times 10} = 5\sqrt{10} \)
Verifying the calculation:
\[
(5\sqrt{10})^2 = 5^2 \times 10 = 25 \times 10 = 250
\]
Thus, the square root of 250 in its simplified form is \( 5\sqrt{10} \).
Methods to Simplify Square Root of 250
Simplifying the square root of 250 involves breaking it down into its prime factors and then simplifying the expression. Here are two common methods used to simplify square roots:
Prime Factorization Method
This method involves finding the prime factors of the number under the square root. Here is a step-by-step process:
- Find the prime factors of 250:
- 250 can be expressed as 25 × 10
- 25 is 52 and 10 is 2 × 5
- Therefore, 250 = 52 × 2 × 5
- Rewrite the square root of 250 using these prime factors:
- \(\sqrt{250} = \sqrt{5^2 \times 10}\)
- Separate the square root into the product of square roots:
- \(\sqrt{5^2 \times 10} = \sqrt{5^2} \times \sqrt{10}\)
- Simplify the square root of the perfect square (52):
- \(\sqrt{5^2} = 5\)
- Combine the simplified terms:
- \(\sqrt{250} = 5 \sqrt{10}\)
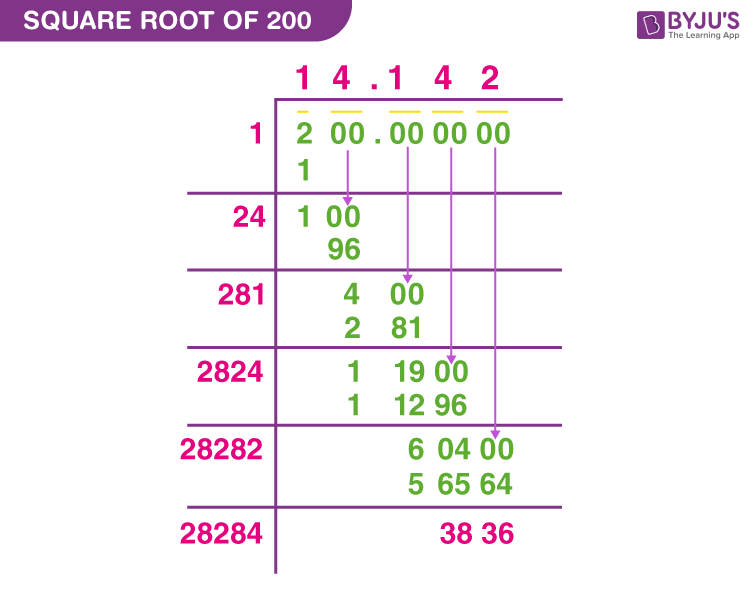
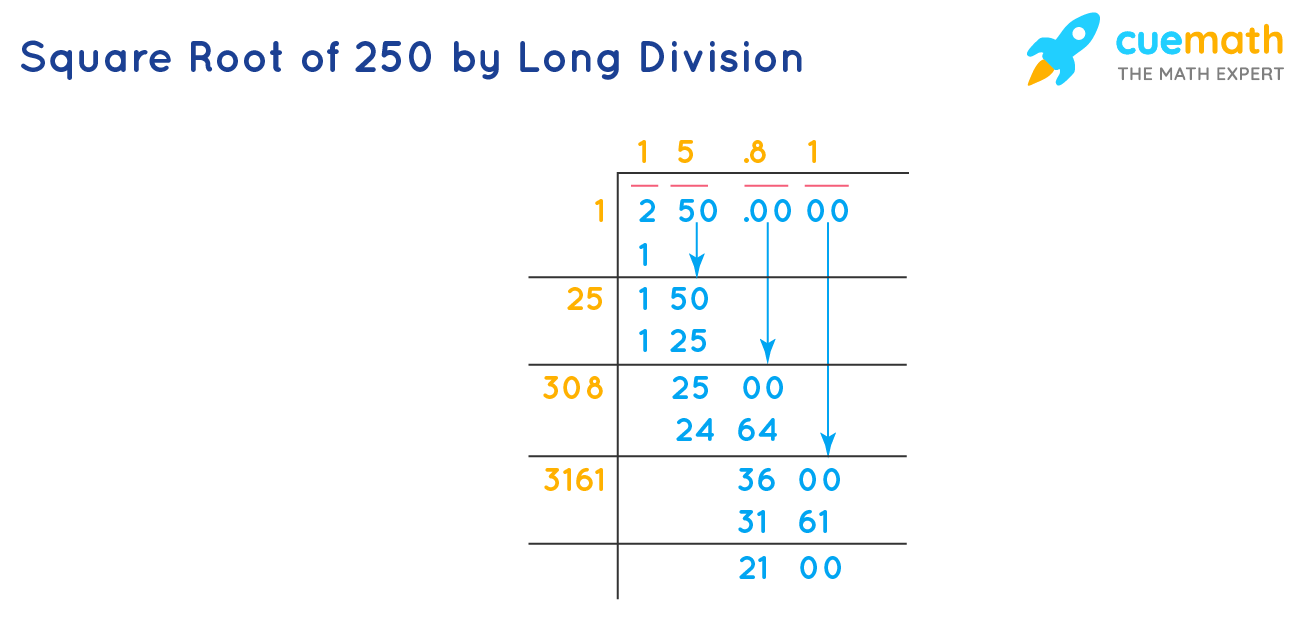
Long Division Method
This method is useful when you need a decimal approximation of the square root:
- Pair the digits of 250 from right to left (250 becomes 2 | 50).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (2). In this case, 12 = 1.
- Subtract 1 from 2, getting 1, and bring down the next pair of digits (50), making the new number 150.
- Double the divisor (1), getting 2. Find a digit (X) such that 2X multiplied by X is less than or equal to 150. The number is 7 (27 × 7 = 189).
- Subtract 189 from 150, getting a negative result, so we use the previous digit, 6. (26 × 6 = 156).
- Repeat the process for further decimal places until you reach the desired precision.
Using these methods, you can simplify the square root of 250 to \(5\sqrt{10}\) or find its approximate decimal form.
Simplified Form of Square Root of 250
The square root of 250 can be simplified as follows:
- Start with the prime factorization of 250:
- 250 = 2 × 125
- 125 = 5 × 25
- 25 = 5 × 5
- Combine like terms under the square root:
- √(250) = √(2 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5)
- √(250) = 5√(10)
Therefore, the simplified form of √(250) is 5√(10).
Approximate Decimal Form
The square root of 250 in its approximate decimal form can be found using a calculator or through iterative methods. The approximate value of √250 is:
\[
\sqrt{250} \approx 15.81139
\]
To understand how this value is derived, here is a step-by-step explanation:
- Estimate an initial value. For √250, we know it is slightly more than √225 (which is 15) and slightly less than √256 (which is 16).
- Use a calculator or a more precise method like the Newton-Raphson method to iteratively find a more accurate value. In general, calculators quickly provide the value as:
\[
\sqrt{250} \approx 15.81139
\]
Using the long division method or a high-precision calculator, we can find that the square root of 250 is approximately 15.81139. This value is often rounded depending on the required precision in calculations, but for most practical purposes, 15.81139 is sufficiently precise.
Here is a comparison table for clarity:
| Square Root | Approximate Value |
|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{250} \) | 15.81139 |
| \( \sqrt{225} \) | 15 |
| \( \sqrt{256} \) | 16 |
Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 250 is classified as an irrational number. To understand why, let's delve into the definitions and properties of rational and irrational numbers.
- Rational Numbers:
- A rational number can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, i.e., \( \frac{a}{b} \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \).
- Examples of rational numbers include 1/2, 3, 4.5 (which is 9/2), etc.
- Irrational Numbers:
- An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Examples of irrational numbers include \( \pi \), \( \sqrt{2} \), and \( e \).
- Analyzing \( \sqrt{250} \):
- We start by simplifying \( \sqrt{250} \). The prime factorization of 250 is \( 2 \times 5^3 \).
- This can be written as \( \sqrt{2 \times 5^3} \). Using the property of square roots, this becomes \( \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5^3} = \sqrt{2} \times 5\sqrt{5} = 5\sqrt{10} \).
- Since \( \sqrt{10} \) cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, it is irrational.
- Therefore, \( 5\sqrt{10} \) is also irrational because the product of a rational number (5) and an irrational number (\( \sqrt{10} \)) is irrational.
In conclusion, \( \sqrt{250} \) is an irrational number.
Application Examples
Understanding the square root of 250 and its simplified form \( 5\sqrt{10} \) can be very useful in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples to illustrate its application:
- Comparison with Square Root of 25:
By comparing \( \sqrt{250} \) with \( \sqrt{25} \), we can better understand the relative sizes of these values.
- The square root of 25 is 5, as \( 25 = 5^2 \).
- The square root of 250 is \( 5\sqrt{10} \), which is approximately 15.81139.
- This comparison shows that \( \sqrt{250} \) is about three times larger than \( \sqrt{25} \).
- Real-World Problem: Finding Rug Side Length:
Suppose you have a square rug with an area of 250 square units, and you want to find the side length of the rug.
- The area \( A \) of a square is given by \( A = s^2 \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- To find \( s \), we take the square root of the area: \( s = \sqrt{250} \).
- Simplifying, \( s = 5\sqrt{10} \), which is approximately 15.81139 units.
- Thus, the side length of the rug is about 15.81139 units.
- Mathematical and Scientific Calculations:
The square root of 250 often appears in various mathematical and scientific formulas.
- In physics, it might be used in equations involving energy, where square roots of large numbers are common.
- In geometry, it could be used to calculate distances or dimensions where exact square roots are needed.
These examples show how understanding \( \sqrt{250} \) and its properties can be applied in practical and theoretical contexts.
Interactive Questions
Test your understanding of the square root of 250 and its simplification with these interactive questions:
- What is the simplified form of \( \sqrt{250} \)?
- \( 5\sqrt{10} \)
- \( 10\sqrt{5} \)
- \( \sqrt{25 \times 10} \)
- \( \sqrt{125 \times 2} \)
- Is the square root of 250 a rational or irrational number?
- Rational
- Irrational
- Calculate the approximate decimal form of \( \sqrt{250} \).
- 15.5
- 16
- 15.811
- 15.9
- If a square has an area of 250 square units, what is the length of one side?
- 15 units
- 5√10 units
- 16 units
- 10√5 units
- Compare \( \sqrt{250} \) with \( \sqrt{25} \). How much larger is \( \sqrt{250} \) approximately?
- 1 times larger
- 2 times larger
- 3 times larger
- 4 times larger
Check your answers and see how well you understand the concept of the square root of 250 and its applications!
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the square root of 250 simplified?
The square root of 250 simplified is \( 5\sqrt{10} \). This simplification is achieved by finding the prime factorization of 250, which is \( 2 \times 5^3 \). By grouping the factors, we get \( 5\sqrt{10} \).
- How do you find the square root of 250?
To find the square root of 250, you can use the prime factorization method or a calculator. For simplification:
- Prime factorize 250: \( 250 = 2 \times 5^3 \).
- Group the factors to form a perfect square: \( 250 = (5^2) \times 10 = 25 \times 10 \).
- Take the square root of the perfect square: \( \sqrt{250} = \sqrt{25 \times 10} = 5\sqrt{10} \).
- Is the square root of 250 a real number?
Yes, the square root of 250 is a real number. It is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, but it is still a valid number on the real number line.
- What is the approximate decimal form of the square root of 250?
The approximate decimal form of \( \sqrt{250} \) is 15.81139. This value can be found using a calculator or through iterative methods like the Newton-Raphson method.
- How is the square root of 250 used in real-world applications?
The square root of 250 can be used in various real-world applications, such as:
- Determining the side length of a square with an area of 250 square units.
- Comparing with other square roots, such as \( \sqrt{25} \), to understand relative sizes.
- Applying in scientific and engineering calculations where exact square roots are necessary.
READ MORE:
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai và Căn Bậc Ba