Topic square root 35: The square root of 35 is a fascinating mathematical concept, representing the number which, when multiplied by itself, gives 35. This article explores the methods to calculate and approximate the square root of 35, its applications, and why it is considered an irrational number. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, dive into the intriguing properties and uses of √35.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 35
- Introduction to Square Root of 35
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 35
- Prime Factorization Method
- Estimation Method
- Long Division Method
- Iterative Methods
- Applications of Square Root of 35
- Definition and Basic Concept
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 35
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 35
- Mathematical Representation
- Applications in Mathematics
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 35
The square root of 35 is an important mathematical concept often encountered in various fields such as geometry, algebra, and calculus. Here, we will discuss the value of the square root of 35, its properties, and methods to calculate it.
Value of the Square Root of 35
The square root of 35, denoted as , is approximately equal to 5.9160797831. This value is irrational, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Properties of the Square Root of 35
- Radical Form:
- Exponential Form: 351/2
- Approximate Decimal Form: 5.9160797831
- Rational or Irrational: Irrational
Methods to Find the Square Root of 35
There are several methods to find the square root of 35:
- Prime Factorization Method:
- Express 35 as a product of its prime factors: 35 = 5 × 7
- Since both 5 and 7 are prime and their square roots are irrational, the square root of 35 cannot be simplified further.
- Estimation Method:
- Start with an initial guess, such as 6.
- Since 62 = 36 is greater than 35, adjust the guess downwards.
- Repeat the process until the approximation is satisfactory.
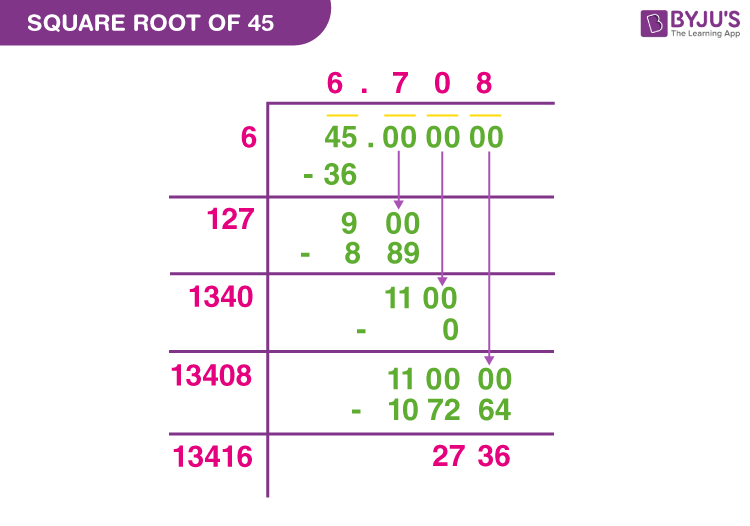
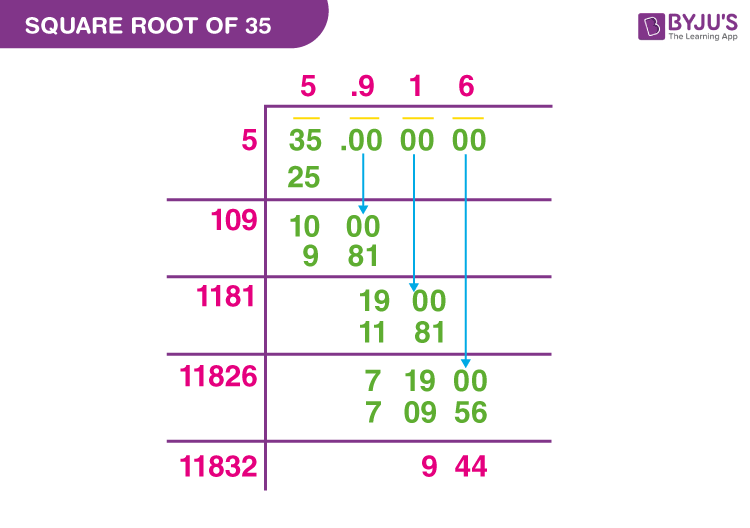
- Long Division Method:
This method provides a step-by-step approach to finding the square root of 35.
Step Description 1 Set up the number under the square root sign. 2 Estimate the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 35. In this case, it is 5 since 52 = 25. 3 Divide 35 by 5, giving approximately 7. 4 Average the quotient and the divisor: (5 + 7)/2 = 6. 5 Use this average as the next divisor and repeat the process to refine the approximation. - Iterative Methods:
- Use algorithms like Newton's method to iteratively refine an initial guess until reaching the desired precision.
Examples
Here are some examples of problems involving the square root of 35:
- Example 1: Find the length of a side of a square with an area of 35 square units.
- Solution: Let the side length be x. Then x2 = 35, so x = ≈ 5.916.
- Example 2: Simplify the expression 2.
- Solution: 2 ≈ 2 × 5.916 = 11.832.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 35
The square root of 35, denoted as √35, is an important mathematical concept. It is the value that, when multiplied by itself, results in 35. The square root of 35 is approximately 5.9160797831. This number is irrational, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. Understanding the square root of 35 is crucial for various mathematical applications, including geometry, algebra, and calculus.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 35
There are several methods to find the square root of 35:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Estimation Method
- Long Division Method
- Iterative Methods (e.g., Newton’s Method)
Prime Factorization Method
Express 35 as a product of its prime factors: \(35 = 5 \times 7\). Since 5 and 7 are prime numbers, their square roots are irrational, so the square root of 35 cannot be simplified further.
Estimation Method
Start with an initial guess, such as 6, and square it to get 36. Since 36 is greater than 35, adjust the guess downwards and repeat until reaching a satisfactory approximation.
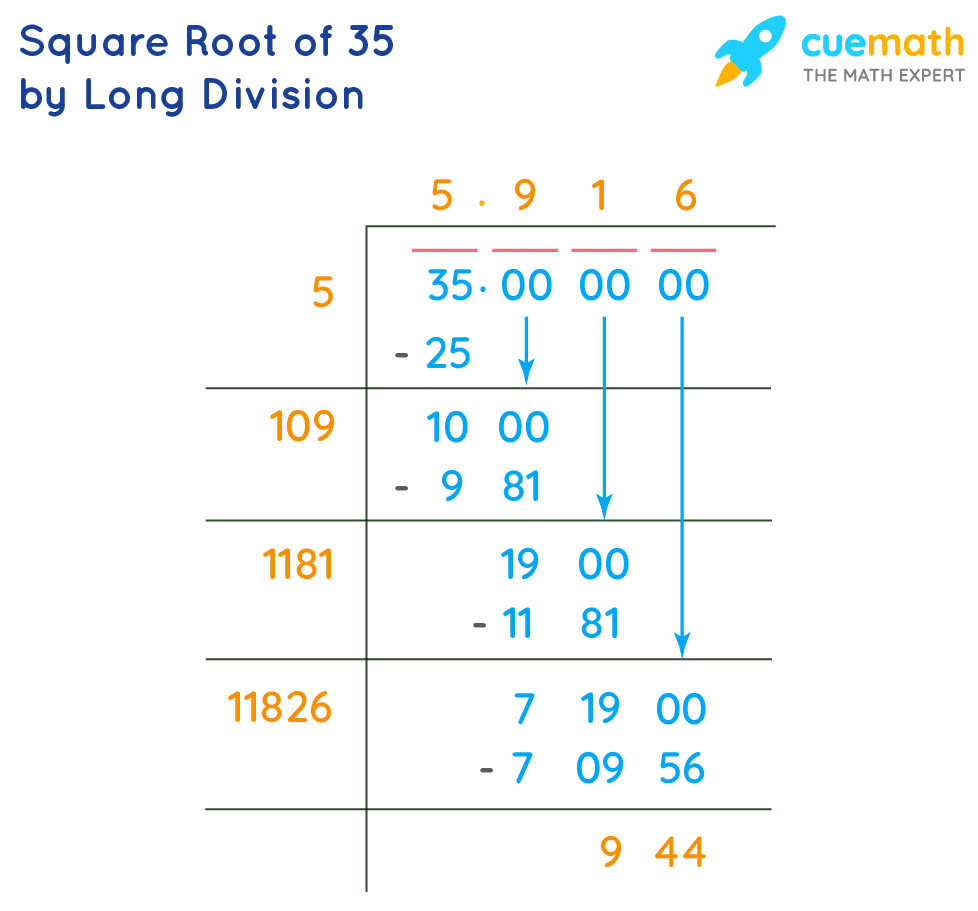
Long Division Method
Set up the number under the square root sign and estimate the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 35 (which is 5). Divide and average, then repeat the process to refine the approximation. This method results in √35 ≈ 5.916.
Iterative Methods
Use algorithms like Newton’s method to iteratively refine an initial guess for the square root of 35 until reaching a satisfactory approximation.
Applications of Square Root of 35
The square root of 35 is used in various mathematical equations and to find unknown sides or dimensions in geometric shapes. It is also important in fields such as engineering and physics.
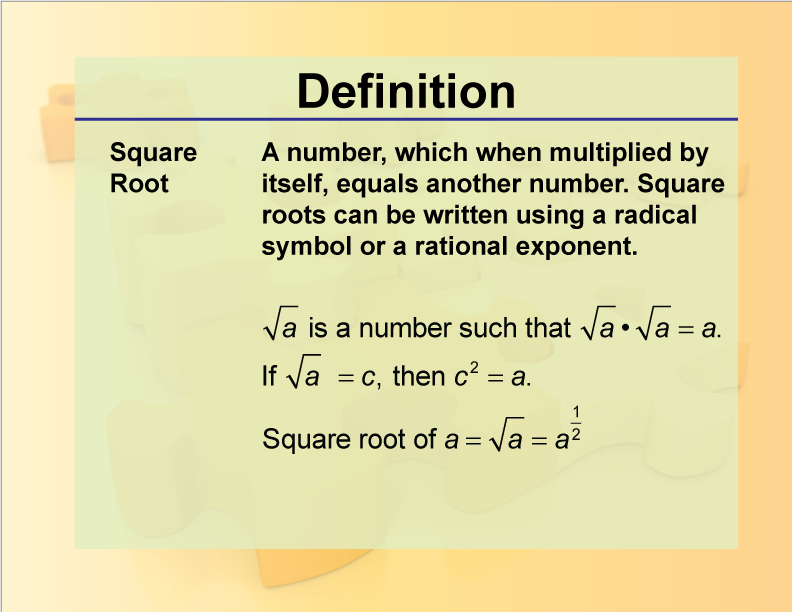
Definition and Basic Concept
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. For example, the square root of 35 is a number which, when squared, results in 35. This is represented mathematically as √35. The square root of 35 is approximately 5.9160797831, which can be rounded to 5.916 for simplicity.
Square roots are fundamental in various areas of mathematics including geometry, algebra, and calculus. The concept of square roots is closely tied to the notion of exponents, where finding the square root of a number is equivalent to raising that number to the power of 1/2.
Here are some key points about the square root of 35:
- Radical Form: √35
- Exponential Form: 351/2
- Approximate Decimal Form: 5.916
The square root of 35 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. The fact that √35 is irrational implies that it has an infinite number of decimal places without a recurring pattern.
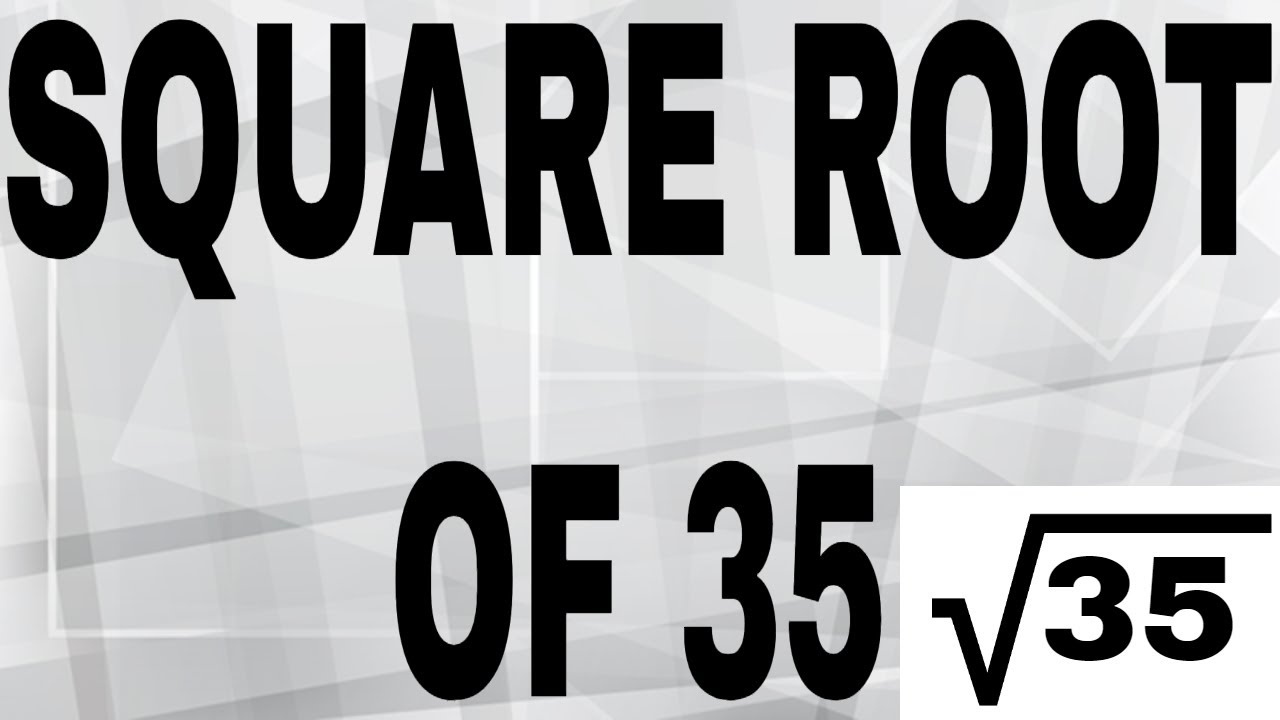
Methods to Find the Square Root of 35
Several methods can be used to find the square root of 35:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down 35 into its prime factors (5 and 7) and using their square roots. Since both 5 and 7 are primes, this method shows that √35 cannot be simplified further.
- Estimation: Starting with an initial guess, such as 6, and refining it through iterative approximation until the result is satisfactory.
- Long Division: A detailed algorithmic approach similar to traditional division but designed to find square roots with high precision.
- Iterative Methods: Techniques like Newton’s method that start with an initial guess and iteratively improve it to approximate the square root.
Understanding the square root of 35 and the methods to find it is crucial for solving mathematical problems that involve square roots and for applications in various mathematical fields.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 35
The square root of 35 can be determined using various methods. Here, we will explore three primary methods: the long division method, the prime factorization method, and the Newton-Raphson method.
- Long Division Method
- Start by pairing the digits of 35 from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the number in the leftmost group, which is 35. Here, 52 is less than 35.
- Subtract the square of this number from 35, giving a remainder of 10. Bring down a pair of zeros.
- Double the divisor (5) and write it as 10. Determine the largest digit to append to 10 to form a number that, when multiplied by itself, is less than or equal to 1000.
- Continue this process to get a more accurate value of the square root. The approximation converges to about 5.916.
- Prime Factorization Method
- Express 35 as a product of its prime factors: 35 = 5 × 7.
- Since there are no pairs of prime factors, we can't simplify further.
- This method shows that 35 is not a perfect square.
- Newton-Raphson Method
- Start with an initial guess, \( x_0 = 6 \).
- Use the formula \( x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f'(x_n)} \) where \( f(x) = x^2 - 35 \) and \( f'(x) = 2x \).
- Calculate: \( x_1 = 6 - \frac{6^2 - 35}{2 \times 6} = 5.917 \).
- Repeat for more accuracy: \( x_2 = 5.917 - \frac{5.917^2 - 35}{2 \times 5.917} = 5.9161 \).
- Continue this iteration to achieve the desired precision. The square root converges to approximately 5.916.
By employing these methods, one can determine the square root of 35 with a high degree of accuracy. While the prime factorization method quickly shows that 35 is not a perfect square, the long division and Newton-Raphson methods provide a more precise value.
Mathematical Representation
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Mathematically, the square root of 35 is represented as:
\[ \sqrt{35} \]
In this representation:
- The symbol \( \sqrt{} \) is known as the radical sign.
- The number under the radical sign (35 in this case) is called the radicand.
The square root of 35 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating. The approximate value of the square root of 35 is:
\[ \sqrt{35} \approx 5.916 \]
This value is derived using various methods, including prime factorization, long division, or approximation techniques.
To denote both the positive and negative square roots, we use the ± symbol:
\[ \pm \sqrt{35} \]
Here, \( +\sqrt{35} \) represents the principal (positive) square root, and \( -\sqrt{35} \) represents the negative square root.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 35 | \[ \sqrt{35} \approx 5.916 \] |
Applications in Mathematics
The square root of 35 has various applications in mathematics, particularly in geometry, physics, and algebra. Here are some of the key applications:
- Geometry: In geometry, square roots are often used to find the lengths of sides in right triangles and other polygons. For example, the Pythagorean theorem involves square roots to determine the length of a hypotenuse.
- Area and Perimeter: Square roots can be used to determine the side length of a square when the area is known. For instance, if the area of a square is 35 square units, the side length is √35 units.
- Distance Formula: In coordinate geometry, the distance between two points in a plane can be calculated using the distance formula, which includes a square root. The formula is D = √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²).
- Physics: In physics, square roots appear in formulas involving motion and force. For example, the time it takes for an object to fall a certain distance under gravity can be calculated using a formula that includes a square root.
- Quadratic Equations: The quadratic formula, which is used to solve quadratic equations, involves square roots. The formula is x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a.
- Engineering and Construction: In engineering and construction, square roots are used in various calculations such as determining the length of a diagonal support in structures or the slope of a roof.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics and game development, square roots are used to calculate distances and render objects accurately in a 3D space.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you understand the concept of the square root of 35 better:
Example 1: Approximating the Square Root
Find the approximate value of √35 using the estimation method.
- Identify two perfect squares between which 35 lies. These are 25 (5²) and 36 (6²).
- Since 35 is closer to 36, we can estimate that √35 is slightly less than 6.
- Refine the estimate by averaging:
\(5.9^2 = 34.81\) (too low)
\(5.95^2 = 35.4025\) (too high)
Therefore, √35 ≈ 5.92.
Example 2: Using Long Division Method
Calculate √35 using the long division method up to 2 decimal places.
- Set up 35 as the number and 6 as the initial divisor (since 6² is close to 35).
- Divide 35 by 6 to get a quotient of 5.83.
- Use 5.83 as the new divisor and continue the process to refine the quotient.
- After repeating the process, √35 ≈ 5.92.
Practice Problems
Try solving these practice problems on your own:
- Approximate the square root of 35 using the iterative method (Newton's Method).
- Express the square root of 35 in exponential form and radical form.
- Determine if √35 is a rational or irrational number and justify your answer.
- Use the prime factorization method to explain why √35 is an irrational number.
Practice Problem Solutions
Here are the solutions to the practice problems:
-
Iterative Method (Newton's Method):
Initial guess: \(x_0 = 6\)
Formula: \(x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left(x_n + \frac{35}{x_n}\right)\)
Iteration 1: \(x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left(6 + \frac{35}{6}\right) = 5.9167\)
Iteration 2: \(x_2 = \frac{1}{2} \left(5.9167 + \frac{35}{5.9167}\right) ≈ 5.916\)
Therefore, √35 ≈ 5.916. -
Exponential and Radical Form:
Exponential form: \(35^{0.5}\)
Radical form: \(\sqrt{35}\) -
Rational vs. Irrational:
√35 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers. -
Prime Factorization Method:
35 = 5 × 7 (both are prime)
Since there is no pair of primes, √35 cannot be simplified to a rational number, confirming it is irrational.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of 35 simplified?
The square root of 35 cannot be simplified further. It remains as \(\sqrt{35}\).
-
What is the square of 35?
The square of 35 is \(35^2 = 1225\).
-
What is the approximate square root of 35?
The approximate square root of 35 is 5.916.
-
Is the square root of 35 a rational number?
No, the square root of 35 is an irrational number because its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
-
Is the square root of 35 a real number?
Yes, the square root of 35 is a real number.
-
How do you calculate the square root of 35 using the long division method?
To calculate the square root of 35 using the long division method, follow these steps:
- Set up 35 under the square root symbol.
- Estimate the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 35. Here, it's 5 because \(5^2 = 25\).
- Divide 35 by 5, giving 7. Add 5 (quotient) and 7 (divisor), then divide by 2 to get the average: \(\frac{5 + 7}{2} = 6\).
- Use 6 as the next divisor. Divide 35 by 6 to get approximately 5.833.
- Refine this process until you reach the desired level of accuracy.
The resulting approximation for \(\sqrt{35}\) is about 5.916.
Căn bậc hai của 35
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai của số 35 trong video này, được giải thích chi tiết và dễ hiểu để thu hút người xem.
Căn bậc hai của 35