Topic square root 900: Discover the significance of the square root of 900 in mathematics, its calculation methods, and real-life applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the properties of 900, explore its perfect square nature, and provide various techniques to compute its square root effectively.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 900
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Calculation Methods
- Perfect Square and Rationality
- Simplification and Exponent Form
- Inverse Operation
- Applications and Examples
- Table of Square Roots
- FAQs
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 900 trong video này để nâng cao kiến thức toán học của bạn.
Square Root of 900
In Mathematics, the square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 900 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in 900.
Value of the Square Root of 900
The square root of 900 is expressed as √900 and is equal to 30.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 900
- Prime Factorization Method: The prime factorization of 900 is 22 × 32 × 52. Therefore, the square root of 900 is:
\[ \sqrt{900} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times (5 \times 5)} = 2 \times 3 \times 5 = 30 \]
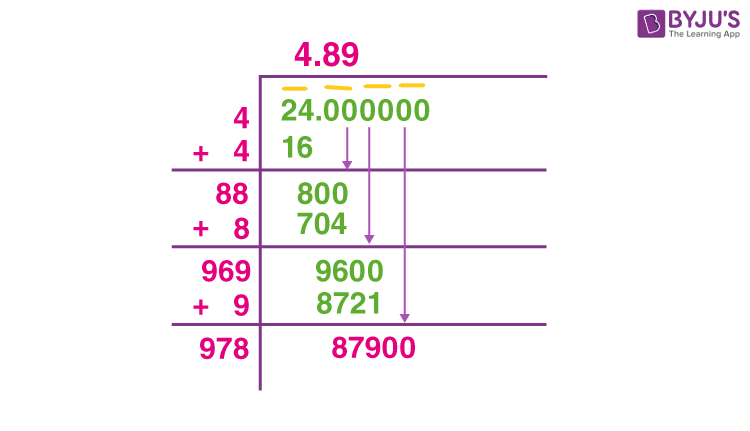
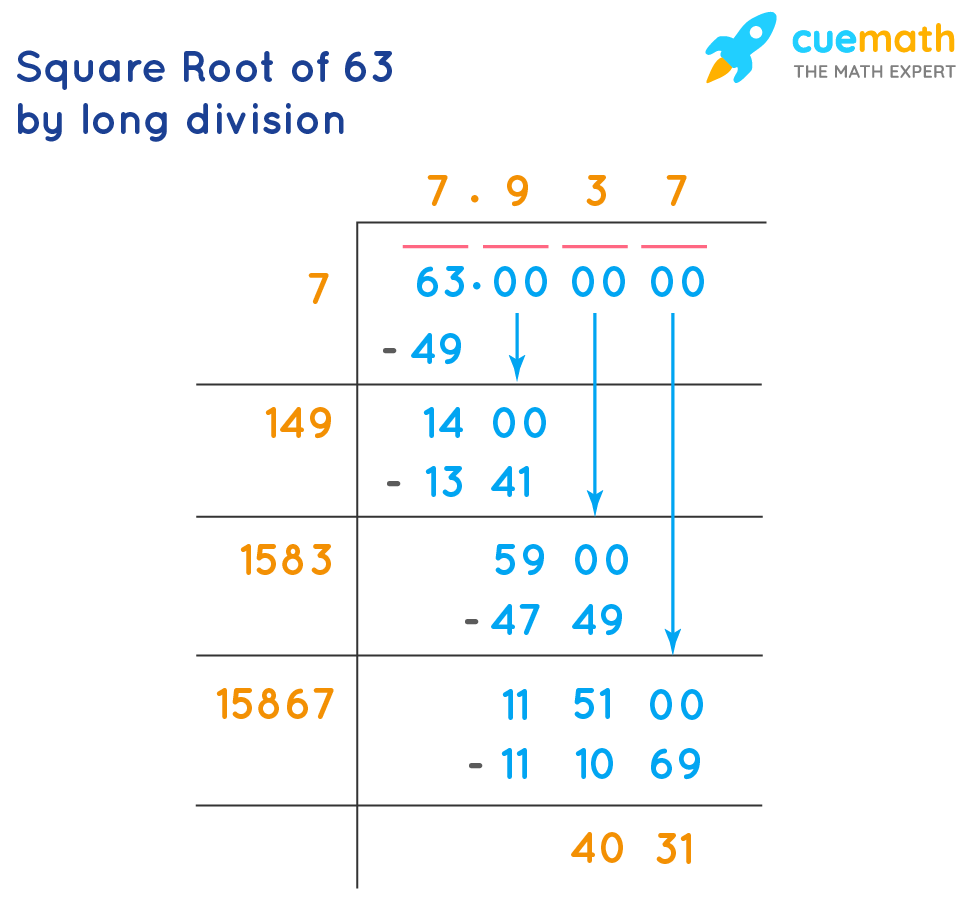
- Long Division Method:
- Pair the digits of 900 from right to left, giving us pairs (9)(00).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 9 (which is 3).
- Double the divisor (3) and get 6, bringing down the next pair (00) to get 00. Divide 00 by 60 to get 0.
- Thus, the square root of 900 is 30.
Examples
- Simplify √900 + 90:
We know √900 = 30, so √900 + 90 = 30 + 90 = 120.
- Find x if √900 - x = 10:
We know √900 = 30, so 30 - x = 10. Therefore, x = 20.
Properties
| Square Root of 900 | 30 |
| Square of the Square Root of 900 | 900 |
| Square Root in Radical Form | √900 |
| Square Root of -900 | 30i (imaginary number) |

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 900, denoted as √900, is a fundamental mathematical calculation that serves as a building block in various mathematical and real-world applications. Understanding the square root involves finding a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 900. In this case, the square root of 900 is 30 because 30 * 30 = 900.
Exploring the concept further, the calculation methods for determining the square root of 900 include prime factorization, repeated subtraction, long division, and estimation. These methods offer different approaches to calculate square roots depending on the context and required level of precision.
Moreover, knowing that 900 is a perfect square simplifies the process since its square root is an integer, specifically 30. This characteristic makes the square root of 900 a rational number, aligning with its properties in number theory.
The significance of the square root of 900 extends beyond theoretical calculations into practical applications. For instance, it finds use in geometry to compute dimensions such as the radius of a circle with an area of 900π.
This comprehensive guide aims to elucidate various aspects of the square root of 900, from its definition and calculation methods to its practical applications and relevance across different fields of mathematics.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 900, denoted as √900, equals 30 because 30 * 30 = 900.
In mathematical terms, for a non-negative real number \( a \), the square root \( \sqrt{a} \) is defined as a number \( x \) such that \( x \geq 0 \) and \( x^2 = a \). Therefore, \( \sqrt{900} = 30 \) satisfies this condition.
Understanding square roots involves recognizing both positive and negative roots for certain numbers, though typically "square root" refers to the principal (non-negative) root in mathematical contexts.
For numbers like 900, which are perfect squares (the square of an integer), the square root is an integer. This characteristic simplifies calculations and lends itself to various applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and beyond.
Calculation Methods
Several methods can be used to calculate the square root of 900:
- Prime Factorization: Decompose 900 into its prime factors (2^2 * 3^2 * 5^2) and take the square roots of the factors (2 * 3 * 5 = 30).
- Repeated Subtraction Method: Subtract consecutive odd numbers from 900 until reaching 0 to find the square root (e.g., 900 - 1 = 899, 899 - 3 = 896, and so on).
- Long Division Method: Similar to regular long division, estimate the square root and adjust iteratively until reaching the desired precision.
- Estimation Method: Approximate the square root using known square roots of nearby perfect squares (e.g., knowing √841 ≈ 29, approximate √900 as slightly more than 29).
Perfect Square and Rationality
The number 900 is a perfect square, which means its square root is an integer. Specifically, the square root of 900 is 30 because 30 * 30 equals 900.
As a perfect square, 900 can be expressed as a product of an integer multiplied by itself (30 * 30), confirming its status as a rational number. In mathematical terms, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction \( \frac{p}{q} \) of two integers, where \( q \neq 0 \).
The square root of 900, being an integer (30), is a clear example of rationality in mathematics, contributing to its applicability in various mathematical and scientific fields.

Simplification and Exponent Form
The square root of 900 simplifies to 30, denoted as √900 = 30. This representation indicates that 30 multiplied by itself equals 900.
In exponent form, the square root of 900 can be written as 9001/2. This notation highlights the relationship between the square root operation and exponentiation, where raising a number to the power of \( \frac{1}{2} \) results in its square root.
Both forms, √900 = 30 and 9001/2, are equivalent ways to express the mathematical concept of the square root of 900, providing flexibility in mathematical calculations and representations.
Inverse Operation
The inverse operation of finding the square root of 900 is squaring the number. In mathematical terms, if \( \sqrt{900} = 30 \), then \( ( \sqrt{900} )^2 = 900 \).
This relationship demonstrates that taking the square root and squaring are inverse operations of each other. Squaring a number undoes the effect of taking its square root, returning to the original value.
Understanding the inverse relationship between squaring and taking the square root is fundamental in algebra and calculus, where these operations are widely used to solve equations and analyze functions.
Applications and Examples
The square root of 900 finds practical applications in various mathematical and real-life scenarios:
- Geometry: Calculating dimensions such as the radius of a circle with an area of 900π.
- Physics: Determining quantities related to velocity, acceleration, and energy where squares and square roots play crucial roles.
- Engineering: Solving problems related to structural design, fluid dynamics, and electrical circuits involving power calculations.
- Statistics: Analyzing data variability using standard deviation, where square roots are fundamental in calculating measures of dispersion.
- Computer Science: Implementing algorithms involving numerical methods, cryptography, and digital signal processing.
These examples illustrate the broad utility of the square root of 900 across different disciplines, showcasing its significance in problem-solving and understanding fundamental mathematical principles.
Table of Square Roots
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
| 2 | 900 | √900 | ±30 |
| 3 | 900 | ∛900 | 9.6548938461 |
| 4 | 900 | Fourth Root | ±5.4772255751 |
| 5 | 900 | Fifth Root | 3.8980598409 |
FAQs
Common questions about the square root of 900 include:
- Is 900 a perfect square?
- What is the value of the square root of 900?
- How can I calculate the square root of 900?
- What are the applications of the square root of 900?
Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 900 trong video này để nâng cao kiến thức toán học của bạn.
Căn bậc hai của 900
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tìm căn bậc hai của 900 bằng phương pháp phân tích số nguyên tố trong video này để nâng cao kiến thức toán học của bạn.
Tìm căn bậc hai của 900 bằng phương pháp phân tích số nguyên tố