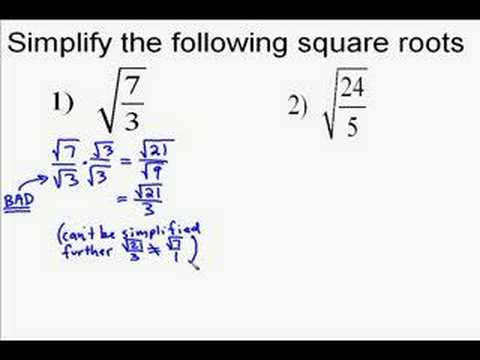
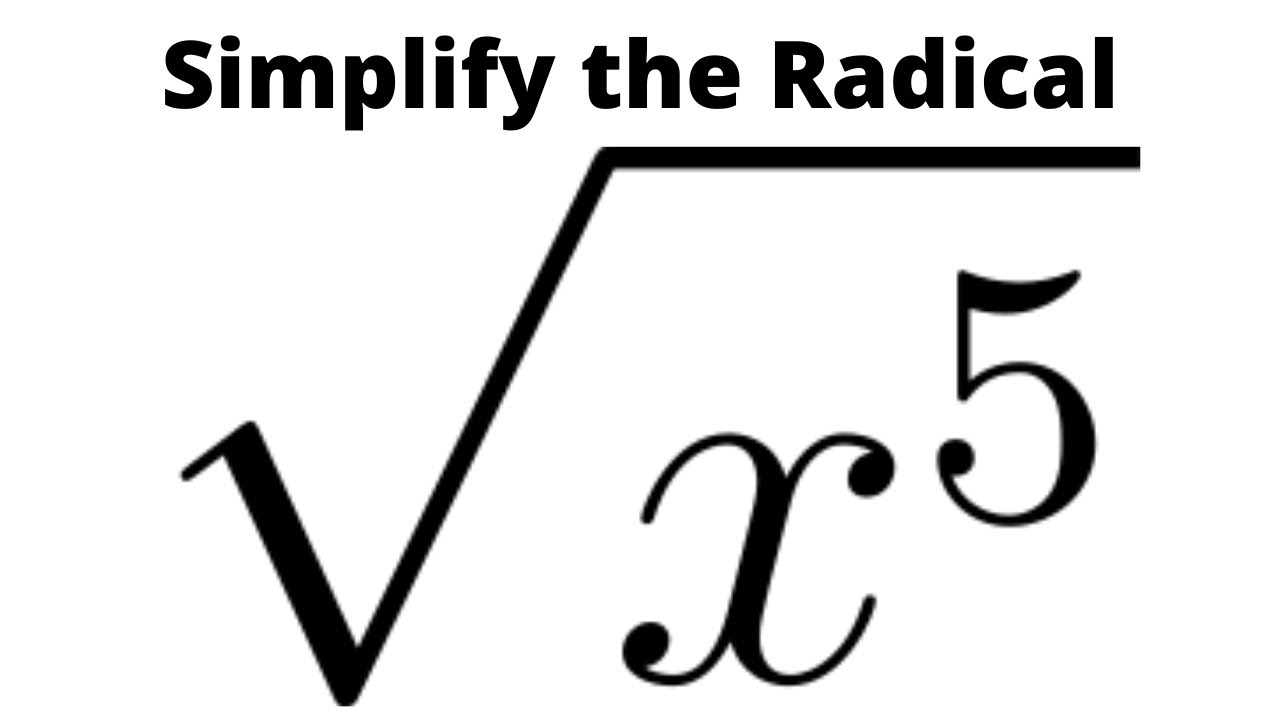Topic simplifying algebraic square roots calculator: Discover how to simplify algebraic square roots effortlessly with our comprehensive calculator. This guide will walk you through the process, providing clear explanations and examples to help you master this essential math skill. Perfect for students, educators, and math enthusiasts looking to deepen their understanding and streamline their calculations.
Table of Content
- Algebraic Square Roots Simplification Calculator
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Basic Properties of Square Roots
- Methods to Simplify Square Roots
- Simplifying Numerical Square Roots
- Simplifying Algebraic Square Roots
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Techniques for Complex Expressions
- Practical Applications of Simplifying Square Roots
- Using Online Calculators for Simplification
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai trong đại số, giúp người xem hiểu rõ và sử dụng hiệu quả.
Algebraic Square Roots Simplification Calculator
This calculator simplifies expressions involving square roots. Use it to break down complex square root expressions into their simplest form.
Features
- Handles both numerical and algebraic expressions
- Provides step-by-step solutions
- Supports variables and coefficients
How to Use the Calculator
- Enter the square root expression in the input box.
- Click the "Simplify" button to get the result.
- View the simplified expression and steps involved.
Example
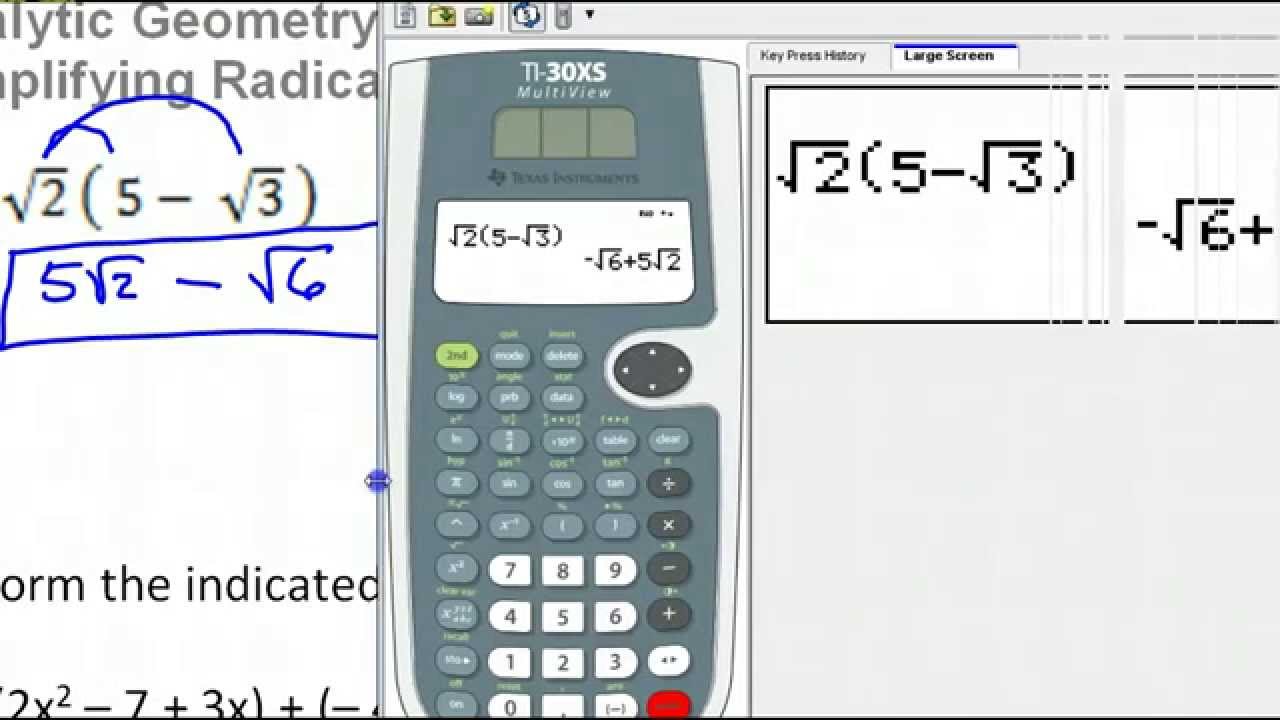
To simplify \( \sqrt{50x^2} \):
- Identify the factors of the radicand: \(50x^2 = 25 \cdot 2 \cdot x^2\).
- Apply the square root to each factor: \( \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{x^2} \).
- Simplify: \( 5 \sqrt{2} x \).
Input Format
Use the following format for input expressions:
- For square roots:
\(\sqrt{a}\) - For variables:
x, y, z - For exponents:
x^2, y^3
Example Inputs
| Input | Simplified Form |
|---|---|
| \(\sqrt{72}\) | \(6\sqrt{2}\) |
| \(\sqrt{45x^2}\) | \(3x\sqrt{5}\) |
| \(\sqrt{98y^4}\) | \(7y^2\sqrt{2}\) |

READ MORE:
Introduction
Welcome to the Comprehensive Guide to Simplifying Algebraic Square Roots. This guide is designed to help you master the art of simplifying square roots, both numerical and algebraic, using a step-by-step approach. Whether you're a student looking to improve your math skills or a teacher seeking comprehensive resources, this guide will provide you with the tools and knowledge you need.
Square roots are fundamental in algebra and mathematics in general. Simplifying square roots is an essential skill that allows for easier manipulation and understanding of more complex expressions. This guide will take you through the basics of square roots, their properties, and various methods to simplify them.
To get started, let's briefly discuss what square roots are and why they are important. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 multiplied by 3 equals 9. Algebraic square roots involve variables and can be simplified using similar principles.
Throughout this guide, we will cover:
- Understanding Square Roots: Basic definitions and concepts.
- Basic Properties of Square Roots: Key properties that make simplification possible.
- Methods to Simplify Square Roots: Various techniques and strategies.
- Simplifying Numerical Square Roots: Step-by-step processes for numerical examples.
- Simplifying Algebraic Square Roots: Applying the same principles to algebraic expressions.
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process: Detailed procedures for simplifying complex expressions.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Tips to prevent common errors in simplification.
- Advanced Techniques for Complex Expressions: Tackling more difficult problems with advanced methods.
- Practical Applications of Simplifying Square Roots: Real-world uses of these mathematical techniques.
- Using Online Calculators for Simplification: Leveraging technology to simplify square roots.
- Examples and Practice Problems: Practice problems to test your understanding and improve your skills.
- Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing common queries and concerns.
- Conclusion: Summarizing key points and encouraging further learning.
- Additional Resources: Further reading and tools to expand your knowledge.
By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of how to simplify algebraic square roots and be well-equipped to handle a variety of mathematical challenges. Let's dive in and start simplifying!
Understanding Square Roots
The concept of a square root is fundamental in mathematics, especially when dealing with algebraic expressions. A square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). In other words, it is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
Square roots are often represented using the radical symbol \(\sqrt{}\). For example, \(\sqrt{16} = 4\) because \(4^2 = 16\).
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-negative results: The square root of a non-negative number is also non-negative. For instance, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\).
- Multiplication: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots. This can be written as \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\).
- Division: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\).
- Simplification: Square roots can be simplified by factoring out perfect squares. For example, \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \cdot 2} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
Examples
Consider the expression \(\sqrt{50}\). To simplify, we find the factors of 50:
- Identify the factors: \(50 = 25 \cdot 2\).
- Apply the property of multiplication: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
Algebraic Expressions with Square Roots
When dealing with algebraic square roots, the principles remain the same. For example, to simplify \(\sqrt{a^2 \cdot b}\), we can use the property of multiplication:
- Apply the property: \(\sqrt{a^2 \cdot b} = \sqrt{a^2} \cdot \sqrt{b}\).
- Simplify: \(a \cdot \sqrt{b}\).
Using Online Calculators
There are many online calculators available that can simplify square roots for you. These tools can handle both numerical and algebraic expressions, providing step-by-step solutions. For example, entering \(\sqrt{72}\) into an online calculator will show you the factorization and simplification process, resulting in \(6\sqrt{2}\).
Understanding the basic properties and methods for simplifying square roots is crucial for solving more complex mathematical problems efficiently. Practice and familiarity with these concepts will enhance your problem-solving skills.
Basic Properties of Square Roots
Understanding the basic properties of square roots is essential for simplifying and working with them in various mathematical contexts. Here are the fundamental properties:
- Non-Negative Numbers: The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative. For any positive real number \( a \in \mathbb{R}_+ \), the principal square root is denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \) and is non-negative.
- Product Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots of each factor. For any non-negative numbers \( a \) and \( b \): \[ \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \]
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator. For any non-negative numbers \( a \) and \( b \) (where \( b \neq 0 \)): \[ \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \]
- Power of a Square Root: The square root of a number squared is the absolute value of the original number. For any real number \( a \): \[ \sqrt{a^2} = |a| \]
- Simplification: A square root can be simplified by factoring out perfect squares. For example: \[ \sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2} \]
These properties form the foundation for more advanced operations and simplifications involving square roots, allowing for efficient computation and manipulation of radical expressions.
Methods to Simplify Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is a fundamental skill in algebra that can be approached through several methods. Here are the most common techniques:
- Prime Factorization:
- Factor the number under the square root into its prime factors.
- Group the factors into pairs.
- Move each pair of factors outside the square root.
- Multiply the factors outside the root.
Example: \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = 3\sqrt{4 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2}\)
- Using Perfect Squares:
- Identify and extract perfect square factors from the number under the square root.
- Simplify the square root of these perfect squares.
- Leave the remaining factors inside the root.
Example: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
- Rationalizing the Denominator:
- Multiply the numerator and the denominator by the same square root to eliminate the square root in the denominator.
Example: \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions:
- Factorize the algebraic term under the square root.
- Extract and simplify any perfect square factors.
- Combine the simplified parts.
Example: \(\sqrt{18x^2} = \sqrt{9 \times 2 \times x^2} = 3x\sqrt{2}\)
- Using Online Calculators:
For complex expressions, using an online calculator can be helpful. These calculators can factorize the expression, simplify the square roots, and even handle algebraic expressions with variables.
Example: Input \(\sqrt{45y^2}\) into a calculator to get \(3y\sqrt{5}\).
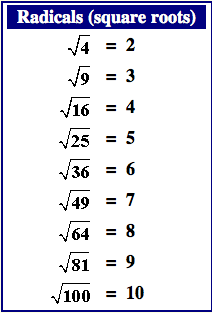
Simplifying Numerical Square Roots
Square roots are used extensively in mathematics, especially in algebra and geometry. Simplifying square roots involves expressing the root in its simplest form, which often includes a radical symbol (√) and potentially involves factoring out squares.
Steps to Simplify Numerical Square Roots
-
Factor the Number: Begin by factoring the number under the square root into its prime factors. For example, to simplify √72:
- 72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
-
Group the Factors: Group the factors into pairs of identical numbers:
- √72 = √(2 × 2) × √(3 × 3) × √2
-
Extract the Square Roots: Simplify by taking the square root of each pair:
- √72 = 2 × 3 × √2 = 6√2
Examples
Simplifying √50:
- 50 = 2 × 5 × 5
- √50 = √(5 × 5) × √2 = 5√2
Simplifying √45:
- 45 = 3 × 3 × 5
- √45 = √(3 × 3) × √5 = 3√5
Special Cases
For perfect squares, the square root is an integer:
- √25 = 5
- √144 = 12
Using Calculators
Online calculators can simplify square roots by factoring and simplifying the radical expression. These tools are useful for quickly finding the simplest form of square roots and verifying manual calculations.
Practice Problems
- Simplify √98
- Simplify √128
- Simplify √200
Simplifying Algebraic Square Roots
Simplifying algebraic square roots involves reducing the expression under the square root to its simplest form. The process can be broken down into a few straightforward steps:
Basic Steps to Simplify Algebraic Square Roots
-
Identify Perfect Squares: Look for perfect square factors within the radicand (the number inside the square root). For instance, in \(\sqrt{50x^2}\), 50 can be factored into 25 (a perfect square) and 2.
-
Rewrite the Expression: Express the radicand as a product of its factors. Using the previous example, \(\sqrt{50x^2} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2 \cdot x^2}\).
-
Separate the Square Roots: Use the property \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\). Thus, \(\sqrt{25 \cdot 2 \cdot x^2} = \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{x^2}\).
-
Simplify Each Part: Simplify the square roots of the perfect squares. In this case, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) and \(\sqrt{x^2} = x\). The expression becomes \(5x\sqrt{2}\).
Handling Variables
When variables are involved, apply the same principles:
- If the variable's exponent is even, the square root is straightforward. For example, \(\sqrt{x^4} = x^2\).
- If the variable's exponent is odd, factor it into an even exponent and 1. For example, \(\sqrt{x^5} = \sqrt{x^4 \cdot x} = x^2\sqrt{x}\).
Examples
- \(\sqrt{72x^3}\): Factor 72 into 36 (a perfect square) and 2. Also, factor \(x^3\) as \(x^2 \cdot x\).
\(\sqrt{72x^3} = \sqrt{36 \cdot 2 \cdot x^2 \cdot x} = \sqrt{36} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{x^2} \cdot \sqrt{x} = 6x\sqrt{2x}\)
- \(\sqrt{50a^2b^5}\): Factor 50 into 25 (a perfect square) and 2, and factor \(b^5\) as \(b^4 \cdot b\).
\(\sqrt{50a^2b^5} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2 \cdot a^2 \cdot b^4 \cdot b} = 5a^2b^2\sqrt{2b}\)
Using Online Calculators
Several online calculators can help simplify algebraic square roots, providing step-by-step solutions. Tools like the ones from , , and are highly recommended.
Conclusion
Simplifying algebraic square roots is a valuable skill that can make solving equations and understanding expressions more manageable. By breaking down the process into clear steps and utilizing online resources, you can simplify even the most complex square root expressions.
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
Simplifying algebraic square roots involves breaking down the expression into its simplest form. Here is a detailed step-by-step process:
-
Identify Perfect Squares: Break the expression under the square root into factors, looking for perfect squares.
For example, consider \( \sqrt{50x^4} \). The factors of 50 are 25 and 2, and the factor of \( x^4 \) is \( (x^2)^2 \).
- \( 50x^4 = 25 \cdot 2 \cdot (x^2)^2 \)
-
Separate the Perfect Squares: Write the square root of each perfect square separately.
- \( \sqrt{50x^4} = \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{(x^2)^2} \)
-
Simplify the Square Roots: Calculate the square roots of the perfect squares.
- \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
- \( \sqrt{(x^2)^2} = x^2 \)
-
Combine the Results: Multiply the simplified square roots with the remaining factors.
- \( 5 \cdot x^2 \cdot \sqrt{2} = 5x^2\sqrt{2} \)
Following these steps, we can simplify various algebraic square root expressions. Let’s look at another example:
Example: Simplify \( \sqrt{72a^6} \).
-
Factorize the expression under the square root:
- \( 72a^6 = 36 \cdot 2 \cdot (a^3)^2 \)
-
Separate the perfect squares:
- \( \sqrt{72a^6} = \sqrt{36} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{(a^3)^2} \)
-
Simplify the square roots:
- \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \)
- \( \sqrt{(a^3)^2} = a^3 \)
-
Combine the results:
- \( 6 \cdot a^3 \cdot \sqrt{2} = 6a^3\sqrt{2} \)
This method can be applied to simplify any algebraic square root expression. Practice with different examples to become more proficient in this process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Simplifying algebraic square roots can be challenging, and many students make common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are some key mistakes to watch out for:
- Not Fully Simplifying: Often, students stop the simplification process too early. Ensure you have extracted and simplified all possible factors.
- Ignoring Prime Factorization: Skipping the step of prime factorization can lead to missing perfect square factors, resulting in an incomplete simplification.
- Misapplying Properties: Incorrectly applying the product or quotient properties can lead to errors. Remember that \(\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\) and \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\), and apply these properties correctly.
- Combining Unlike Terms: Attempting to combine terms under the square root that aren’t alike is a mistake. Only like terms outside the radical can be combined.
- Forgetting About Variables: When simplifying square roots with variables, it’s essential to apply the same principles as with numerical values, including checking for and simplifying perfect square factors among the variables.
- Overlooking Negative Signs: Be cautious with negative numbers under the square root, as this involves imaginary numbers. Ensure you’re applying the correct rules for simplification.
- Assuming Additivity: A common mistake is to assume \(\sqrt{x + y} = \sqrt{x} + \sqrt{y}\). This is incorrect. Simplify each term under the square root individually.
- Canceling Errors: To cancel terms, they must be common factors of both the numerator and the denominator. For example, in \(\frac{3x^3 - x}{x}\), factor out the \(x\) before canceling.
By being aware of these common pitfalls and proceeding methodically, you can greatly improve your accuracy and confidence in simplifying square roots.
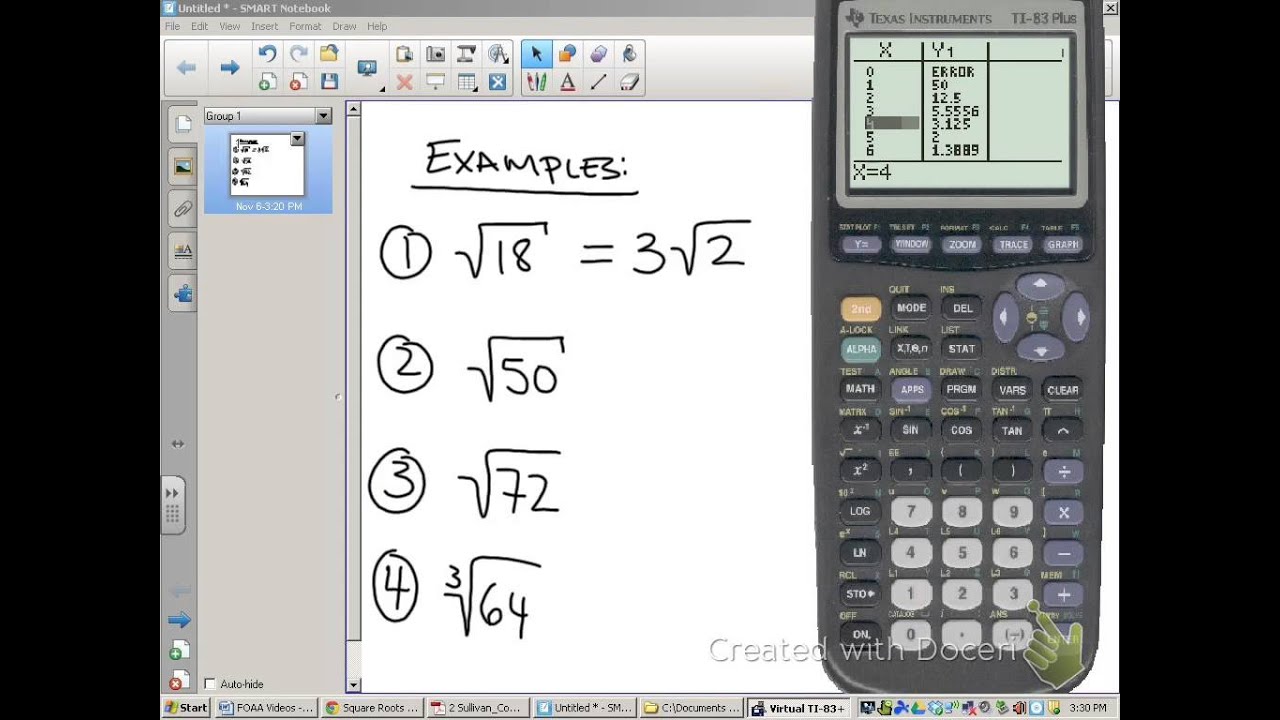
Advanced Techniques for Complex Expressions
When dealing with complex algebraic square roots, it's crucial to apply advanced techniques to simplify the expressions effectively. Here are some advanced methods:
1. Using the Product Rule
The product rule states that the square root of a product is the product of the square roots:
\(\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\)
- Identify and factor out perfect squares from the radicand.
- Separate the expression into the product of square roots.
- Simplify each square root individually.
2. Using the Quotient Rule
The quotient rule allows you to simplify the square root of a fraction by separating the numerator and the denominator:
\(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
- Apply the rule to rewrite the radical as a fraction of square roots.
- Simplify the numerator and the denominator separately.
3. Rationalizing the Denominator
To eliminate radicals from the denominator, multiply the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator:
- If you have \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{a}}\), multiply by \(\frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{a}}\).
- For more complex denominators, use the conjugate (e.g., for \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}}\), multiply by \(\frac{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{b}}{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{b}}\)).
4. Simplifying Nested Radicals
Nested radicals can be simplified by expressing them in a single radical expression:
- Use the product rule to combine the nested radicals.
- Simplify the resulting expression.
5. Handling Higher-Order Roots
For higher-order roots, express the radical as a fractional exponent:
\(\sqrt[n]{a} = a^{\frac{1}{n}}\)
- Convert the expression to exponential form.
- Simplify using the laws of exponents.
Examples
| \(\sqrt{50x^2y^3z}\) | \(\sqrt{25 \cdot 2x^2y^2 \cdot y \cdot z}\) | \(5xy\sqrt{2yz}\) |
| \(\sqrt[3]{8x^6}\) | \((8x^6)^{\frac{1}{3}}\) | \(2x^2\) |
By applying these techniques, you can simplify even the most complex algebraic square root expressions efficiently.
Practical Applications of Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is a crucial mathematical skill with a wide range of practical applications. Here are some examples of how this concept is used in various fields:
-
Geometry and Architecture:
In geometry, square roots are used to calculate the lengths of sides in right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem. Architects use square roots to determine distances and structural integrity in building designs. For example, the length of the diagonal of a square with side length \( a \) is \( \sqrt{2}a \).
-
Physics:
Square roots are often used in physics to solve for variables in equations involving speed, velocity, and acceleration. For example, the time \( t \) it takes for an object to fall from a height \( h \) is given by \( t = \sqrt{\frac{h}{4}} \).
-
Finance:
In finance, square roots are used to calculate the volatility of stock prices. Volatility, which measures how much the price of a stock varies, is found by taking the square root of the variance of the stock's returns.
-
Statistics:
Square roots are used to compute the standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance. This helps in understanding the dispersion of a data set and is fundamental in statistical analysis.
-
Engineering:
Square roots are used in engineering to calculate the stress and strain on materials, as well as in the analysis of electrical circuits to determine power and voltage relationships.
-
Computer Science:
In computer graphics, square roots are used to calculate distances between points in space, which is essential for rendering images and animations accurately.
-
Navigation:
Pilots and navigators use square roots to calculate distances and bearings between locations on a map. This is crucial for plotting courses and ensuring accurate travel routes.
-
Accident Investigation:
Police officers use square roots to determine the speed of vehicles before a collision based on the length of skid marks. The formula \( v = \sqrt{24d} \), where \( d \) is the skid distance, helps in reconstructing accidents.
Understanding and simplifying square roots is essential not just in academic settings but also in solving real-world problems efficiently and accurately.
Using Online Calculators for Simplification
Online calculators can be incredibly useful tools for simplifying algebraic square roots. These calculators not only provide quick and accurate results but also offer step-by-step explanations that help users understand the process. Here's how you can use an online calculator to simplify algebraic square roots:
- Identify the Expression: Start by clearly identifying the square root expression you need to simplify. For example, consider the expression \( \sqrt{50x^2 y} \).
- Access a Reliable Calculator: Visit a reliable online calculator website such as CalculatorSoup or MathCracker. These websites provide dedicated tools for simplifying radical expressions.
- Enter the Expression: Input the expression into the calculator. Most calculators will have fields where you can enter the radicand (the number or expression inside the square root) and any coefficients or variables. For example, you might enter \( 50x^2 y \) as the radicand.
- Select Simplification Method: Some calculators offer options to choose the method of simplification, such as prime factorization or using common algebraic rules. Select the appropriate method based on your needs.
- Calculate: Click the 'Calculate' button to process the expression. The calculator will apply the chosen method to simplify the square root. For example, \( \sqrt{50x^2 y} \) simplifies to \( 5x \sqrt{2y} \).
- Review the Steps: Many calculators will display the steps taken to arrive at the simplified result. Review these steps to understand how the simplification was performed. This can include breaking down the radicand into its prime factors and simplifying any perfect squares.
- Practice with Different Expressions: To become proficient in simplifying square roots, practice with various expressions. Use the calculator to check your work and ensure you understand the simplification process.
Using online calculators not only saves time but also enhances your understanding of the simplification process. These tools are especially useful for complex expressions that may be challenging to simplify manually. By following the steps provided by the calculator, you can learn to simplify square roots more efficiently and accurately.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you master the simplification of algebraic square roots. Each example includes a detailed solution to guide you through the process.
Example 1: Simplify \(\sqrt{12x^2}\)
- Factor the number and the variable inside the square root:
\[\sqrt{12x^2} = \sqrt{4 \cdot 3 \cdot x^2}\]
- Separate the factors:
\[\sqrt{4} \cdot \sqrt{3} \cdot \sqrt{x^2}\]
- Simplify each square root:
\[2 \cdot \sqrt{3} \cdot x = 2x\sqrt{3}\]
Example 2: Simplify \(\sqrt{50y^3}\)
- Factor the number and the variable inside the square root:
\[\sqrt{50y^3} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2 \cdot y^2 \cdot y}\]
- Separate the factors:
\[\sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{y^2} \cdot \sqrt{y}\]
- Simplify each square root:
\[5 \cdot \sqrt{2} \cdot y \cdot \sqrt{y} = 5y\sqrt{2y}\]
Practice Problems
Try simplifying the following square root expressions on your own. Solutions are provided below each problem for you to check your work.
- Simplify \(\sqrt{18x^4}\)
Solution: \[3x^2\sqrt{2}\]
- Simplify \(\sqrt{72y^2}\)
Solution: \[6y\sqrt{2}\]
- Simplify \(\sqrt{45z^6}\)
Solution: \[3z^3\sqrt{5}\]
- Simplify \(\sqrt{27a^5b^3}\)
Solution: \[3a^2b\sqrt{3ab}\]
Advanced Practice Problem
Simplify the following complex expression:
\[\sqrt{50x^6y^3} \cdot \sqrt{18x^2y}\]
- Combine the expressions under one square root:
\[\sqrt{50x^6y^3 \cdot 18x^2y} = \sqrt{900x^8y^4}\]
- Simplify inside the square root:
\[900x^8y^4 = (30x^4y^2)^2\]
- Take the square root of the entire expression:
\[30x^4y^2\]
These examples and practice problems should help solidify your understanding of simplifying algebraic square roots. Remember to always look for perfect square factors and simplify step by step.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of an algebraic expression?
The square root of an algebraic expression involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original expression. For example, the square root of \(x^2\) is \(x\).
-
How do I simplify square roots with variables?
To simplify square roots with variables:
- Factor the radicand (the expression under the square root) into perfect squares.
- Rewrite the radicand as a product of square roots.
- Simplify each square root. For example, \(\sqrt{x^4} = x^2\).
-
What if the variable has an odd exponent?
For variables with odd exponents, separate the variable into a product of an even exponent and a single variable. For example, \(\sqrt{x^5} = \sqrt{x^4 \cdot x} = x^2 \sqrt{x}\).
-
Can all square roots be simplified?
Not all square roots can be simplified into rational numbers. Some remain in their radical form. For instance, \(\sqrt{2}\) is already in its simplest form because 2 is not a perfect square.
-
How do I simplify the square root of a fraction?
Use the quotient rule: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\). Simplify the numerator and denominator separately. For example, \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{2}{3}\).
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid?
- Forgetting to simplify completely.
- Incorrectly factoring the radicand.
- Neglecting to use absolute value for even-powered variables when necessary.
-
Are there online tools to help simplify square roots?
Yes, many online calculators are available that can help simplify algebraic square roots. These tools often provide step-by-step solutions to help you understand the process.
Conclusion
Simplifying algebraic square roots is an essential skill in algebra that helps in solving complex mathematical problems with ease. By mastering the basic properties and methods of simplification, you can handle more advanced expressions and apply these techniques in various practical scenarios.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Understanding Square Roots: Square roots represent the inverse operation of squaring a number. It's crucial to grasp this concept to simplify expressions effectively.
- Basic Properties: Familiarize yourself with properties such as the product and quotient rules, which are fundamental in breaking down complex square root expressions.
- Step-by-Step Simplification: Follow a structured approach to simplify square roots. Identify perfect squares, factorize expressions, and simplify the radicals step by step.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Be cautious of common errors such as incorrect factorization, misunderstanding properties, and misapplying rules. Practice to avoid these pitfalls.
- Advanced Techniques: Use advanced techniques like rationalizing the denominator and combining like terms to simplify more complex expressions.
- Practical Applications: Simplifying square roots is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world applications in engineering, physics, computer science, and various other fields.
- Online Calculators: Utilize online calculators to verify your work and gain a better understanding of the simplification process. These tools can provide step-by-step solutions and explanations.
By integrating these concepts and techniques into your practice, you will develop a strong foundation in algebraic simplification. Continue to explore and practice regularly to enhance your skills. Happy learning!
Additional Resources
Here are some useful resources to help you further understand and simplify algebraic square roots:
-
An online calculator that provides step-by-step solutions for simplifying square roots and other algebraic expressions.
-
Offers a comprehensive calculator for simplifying square roots, showing detailed steps for the solution process.
-
A powerful tool from WolframAlpha that can simplify square roots and provide visual explanations.
-
Free video tutorials and practice problems on simplifying square roots and related algebraic concepts.
-
In-depth explanations and examples on how to simplify square roots, including common mistakes to avoid.
-
Interactive lessons and quizzes to help reinforce your understanding of simplifying square roots.
These resources provide various tools, tutorials, and practice exercises to enhance your skills in simplifying algebraic square roots. Make sure to explore each one to find the methods and explanations that work best for you.
Video hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai trong đại số, giúp người xem hiểu rõ và sử dụng hiệu quả.
Hướng Dẫn Sử Dụng Máy Tính ClassWiz - Đại Số 4-1 Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính TI 84 Plus CE để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai và các căn khác, giúp người xem nắm bắt kỹ thuật và áp dụng hiệu quả.
TI 84 Plus CE Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai và Các Căn Khác