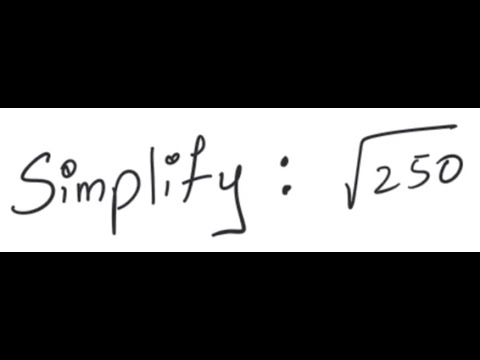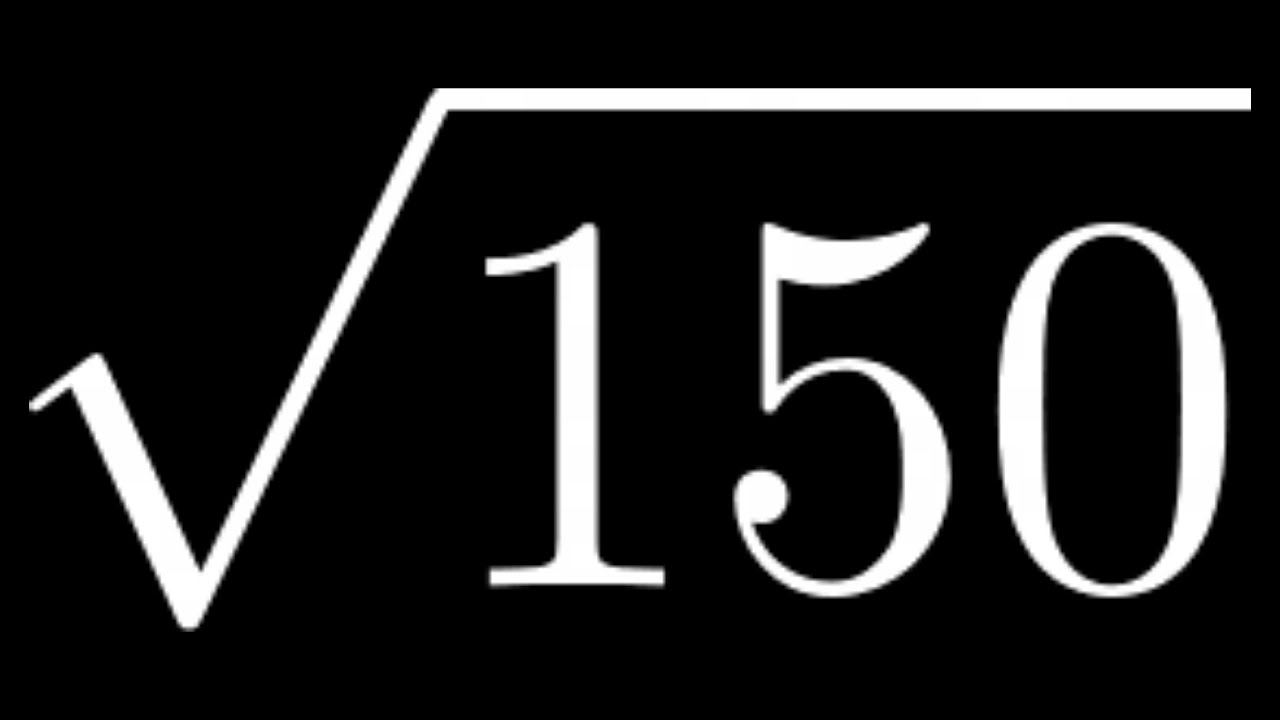Topic simplify 50 square root: Discover how to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) effortlessly with our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student tackling math problems or simply curious about mathematical techniques, this article provides clear steps and explanations to help you grasp the concept quickly. Learn the prime factorization method and other useful tips for simplifying square roots effectively.
Table of Content
- Search Results: Simplify 50 Square Root
- Introduction
- Methods to Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \)
- Step-by-Step Guide
- Prime Factorization Approach
- Simplification Techniques
- Mathematical Explanation
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 50. Xem ngay để hiểu rõ hơn về phương pháp tính sqrt(50)!
Search Results: Simplify 50 Square Root
When simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \), we can break it down as follows:
| Step 1: | Factorize 50 into prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \) |
| Step 2: | Take the square root of each factor: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{25} \) |
| Step 3: | Further simplify: \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \), hence \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \) |
Therefore, \( \sqrt{50} \) simplifies to \( 5\sqrt{2} \).
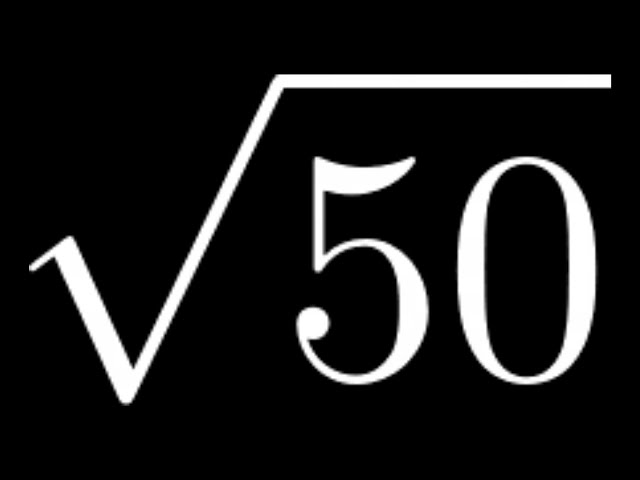
READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding how to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) involves breaking down the square root into simpler terms. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Start by identifying any perfect square factors of 50. In this case, 25 is a perfect square because \( 25 = 5^2 \).
- Express 50 as a product of its prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Apply the square root property to simplify: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{25} \).
- Calculate \( \sqrt{25} \) which equals 5, hence \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
By following these steps, you can simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) efficiently and accurately.
Methods to Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \)
There are several methods to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) effectively:
- Prime Factorization: Break down 50 into its prime factors \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \). Then, simplify each factor under the square root.
- Estimation Method: Approximate \( \sqrt{50} \) by finding square roots of nearby perfect squares (e.g., \( \sqrt{49} \approx 7 \) and \( \sqrt{64} \approx 8 \)).
- Using a Calculator: Utilize a scientific calculator to directly compute \( \sqrt{50} \).
Each method offers a different approach to simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \), catering to various preferences and situations.
Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these clear steps to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) smoothly:
- Identify the factors of 50: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Split the square root into separate terms: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} \).
- Apply the square root property to simplify: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{25} \).
- Calculate \( \sqrt{25} \), which equals 5, hence \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
By following these steps, you can confidently simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) step-by-step.
Prime Factorization Approach
The prime factorization approach is a reliable and straightforward method to simplify the square root of a number. In this section, we will break down the process of simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \) step by step using prime factorization.
-
First, find the prime factors of 50:
- 50 is an even number, so it is divisible by 2.
- Divide 50 by 2 to get 25.
- 25 is not divisible by 2. The next prime number is 3, but 25 is not divisible by 3 either.
- 25 is divisible by 5. Divide 25 by 5 to get 5.
- 5 is a prime number, so the prime factorization of 50 is:
50 = 2 × 5 × 5 -
Express \( \sqrt{50} \) using the prime factors:
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} \)
-
Group the prime factors into pairs:
\( \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} = \sqrt{2 \times (5 \times 5)} \)
-
Simplify the expression by taking the square root of the paired factors:
\( \sqrt{2 \times (5 \times 5)} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5^2} \)
-
Since the square root of \( 5^2 \) is 5, the expression simplifies to:
\( \sqrt{2} \times 5 \)
-
Finally, write the simplified form:
\( 5\sqrt{2} \)
Therefore, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{50} \) using the prime factorization approach is \( 5\sqrt{2} \).

Simplification Techniques
To simplify the square root of 50, we can use several techniques that make the process straightforward and easy to understand. Here are the detailed steps:
Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down the number under the square root into its prime factors and simplifying accordingly.
- First, factorize 50 into its prime factors:
\( 50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5 \)
- Rewrite the square root of 50 using these factors:
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} \)
- Since the square root of a product is the product of the square roots, simplify by taking the square root of the perfect square (25):
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5^2} \)
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2} \times 5 \)
- Therefore, the simplified form is:
\( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Using the Properties of Square Roots
The properties of square roots can also be useful in simplification. Specifically, the property \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \) helps to break down complex radicals.
- For example, \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} \)
- Applying the property:
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} \)
- Since \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \):
\( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Decimal Form and Estimation
Although the exact simplified form of \( \sqrt{50} \) is \( 5\sqrt{2} \), it can also be useful to know its approximate decimal value, especially for practical applications.
- We know that \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \).
- Multiplying this by 5 gives the decimal approximation:
\( \sqrt{50} \approx 5 \times 1.414 = 7.07 \)
Summary
In summary, the square root of 50 can be simplified using the prime factorization method or properties of square roots to get \( 5\sqrt{2} \). For practical purposes, the decimal approximation is approximately 7.07.
Mathematical Explanation
The square root of a number \( n \) is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives \( n \). For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \). This is expressed as \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \). The number 50 is not a perfect square, so its square root is not an integer.
To simplify \( \sqrt{50} \), we use the properties of square roots and factorization:
- First, factor the number 50 into its prime factors:
- \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \)
- Next, apply the product rule for radicals, which states \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \):
- \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{5^2} \)
- Since \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \), we can simplify further:
- \( \sqrt{50} = 5 \cdot \sqrt{2} \)
Therefore, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{50} \) is \( 5\sqrt{2} \).
To verify, we can approximate the values:
- \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071 \)
- \( 5\sqrt{2} \approx 5 \times 1.414 = 7.07 \)
The simplified radical form is particularly useful in various mathematical applications, as it often makes further calculations easier and more precise.
Conclusion
The simplification of the square root of 50 to \(5\sqrt{2}\) is a useful mathematical exercise that enhances our understanding of prime factorization and radical expressions. Through the prime factorization method, we decompose 50 into its prime factors, allowing us to simplify the square root by extracting the perfect square factors.
We explored different techniques, including the prime factorization and long division methods, to simplify and approximate the square root of 50. The prime factorization approach involves breaking down 50 into \(2 \times 5^2\) and then simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \) to \( 5\sqrt{2} \). This method illustrates how breaking down numbers into their prime components can simplify the process of finding square roots.
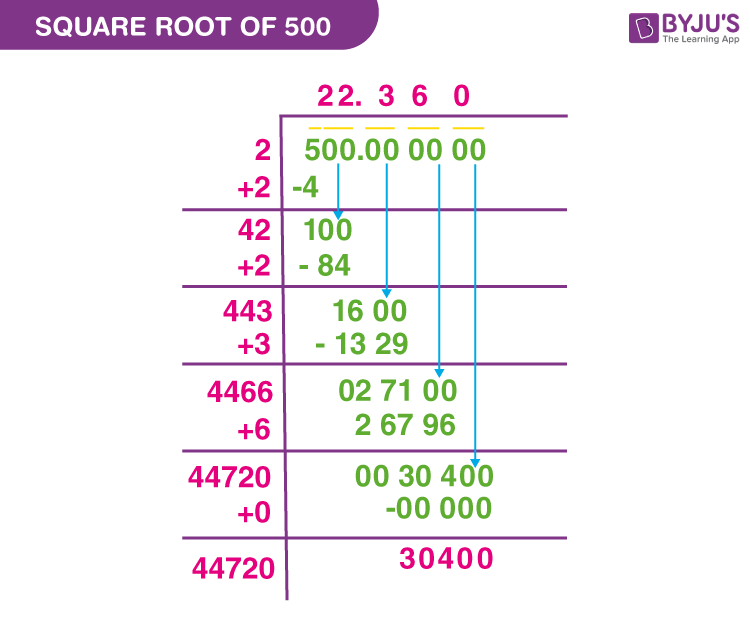
The long division method provides a more precise decimal approximation of the square root of 50, demonstrating the iterative process of refining the value to achieve greater accuracy. This method is particularly useful for non-perfect squares and offers a systematic approach to obtaining decimal values.
Understanding these techniques not only helps in simplifying square roots but also strengthens foundational mathematical skills that are applicable in various advanced topics. By mastering the simplification of square roots, students can build a solid base for tackling more complex mathematical problems and concepts.
In summary, the simplification of \( \sqrt{50} \) to \( 5\sqrt{2} \) exemplifies the power of prime factorization in simplifying radical expressions. This process, combined with the precise long division method, provides a comprehensive understanding of both the exact and approximate values of square roots, reinforcing essential mathematical principles and problem-solving skills.
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 50. Xem ngay để hiểu rõ hơn về phương pháp tính sqrt(50)!
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 50: Sqrt(50)
READ MORE:
Giản đồ căn bậc hai của số | Giản đồ toán học, Căn bậc hai của 50
Giản đồ căn bậc hai của số | Giản đồ toán học, Căn bậc hai của 50