Topic square root of 5 in radical form: Discover the fascinating world of mathematics with our comprehensive guide on the square root of 5 in radical form. Learn the definition, methods to calculate it, and why it is an irrational number. Dive into the intriguing aspects of square roots and their significance in various mathematical concepts.
Table of Content
Square Root of 5 in Radical Form
The square root of 5 in its simplest radical form is represented as:
\[\sqrt{5}\]
Steps to Find the Square Root of 5
- Recognize that 5 is not a perfect square, meaning its square root will be an irrational number.
- In its simplest form, the square root of 5 remains as \(\sqrt{5}\).
- If you need the decimal form, \(\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236\).
Examples and Applications
- To approximate the square root of 5 using the long division method, you repeatedly divide and average to achieve closer decimal values.
- In exponent form, the square root of 5 can be written as \(5^{1/2}\).
- The square root of 5 is often used in various mathematical problems and applications, such as solving quadratic equations and geometry.
Important Notes
- The square root of a number that is not a perfect square is always an irrational number.
- For computational purposes, the value can be approximated as \(\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236067977\).
- The square root of negative 5 is an imaginary number, expressed as \(i\sqrt{5}\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit \(\sqrt{-1}\).
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
| What is the simplest radical form of the square root of 5? | \(\sqrt{5}\) |
| Why is the square root of 5 irrational? | Because 5 is a prime number and cannot be expressed as a product of two equal integers. |
| What is the decimal approximation of \(\sqrt{5}\)? | Approximately 2.236. |
| Can the square root of 5 be simplified further? | No, \(\sqrt{5}\) is already in its simplest form. |

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 5, denoted as \( \sqrt{5} \), is a mathematical expression that represents a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 5. This number is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Understanding the properties and methods to calculate the square root of 5 is essential for various mathematical applications. In this section, we will explore the definition, properties, and calculation methods of the square root of 5 in its radical form.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Definition of the Square Root of 5
Calculating the Square Root of 5
- Using a Calculator
- Using Long Division Method
Simplest Radical Form
Decimal Approximation
Properties of the Square Root of 5
- Irrational Nature
- Exponent Form
Applications and Examples
- Example Problems
- Real-World Applications
Conclusion
Definition and Representation
The square root of 5 in radical form is represented as \( \sqrt{5} \). This radical expression denotes the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 5. The square root function provides a means to express this in a simplified and universally recognized form.
To understand the concept better, let’s break it down step by step:
- Start with the number 5, which is the radicand in this context.
- Applying the square root operation involves finding a number (let's call it \( q \)) such that \( q^2 = 5 \).
- In mathematical notation, this is written as \( \sqrt{5} \), and the value of \( \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 2.236.
It's important to note that 5 is not a perfect square, which means \( \sqrt{5} \) is an irrational number. This indicates that it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating.
For practical calculations, we often use approximations:
- \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.24 \) (rounded to two decimal places)
- \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \) (rounded to three decimal places)
In its simplest radical form, \( \sqrt{5} \) remains \( \sqrt{5} \) as it cannot be simplified further due to the absence of any perfect square factors other than 1 within the number 5.
This fundamental understanding of radicals and irrational numbers aids in various mathematical computations and concepts, providing a base for more complex algebraic operations.
Methods of Calculation
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 5, each varying in complexity and precision. Below, we explore three common methods: the Long Division Method, the Calculator Method, and the Computer Method.
1. Long Division Method
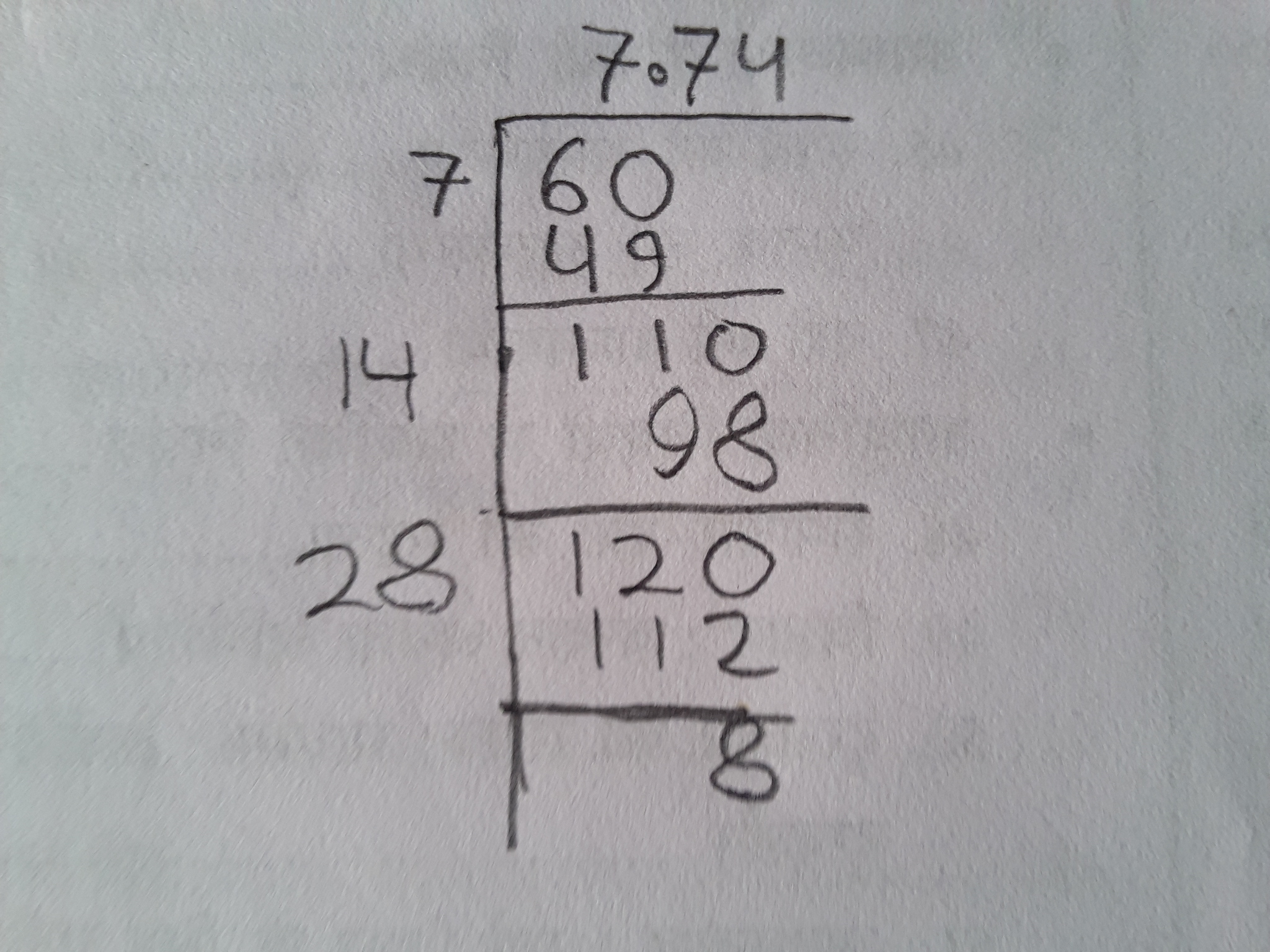
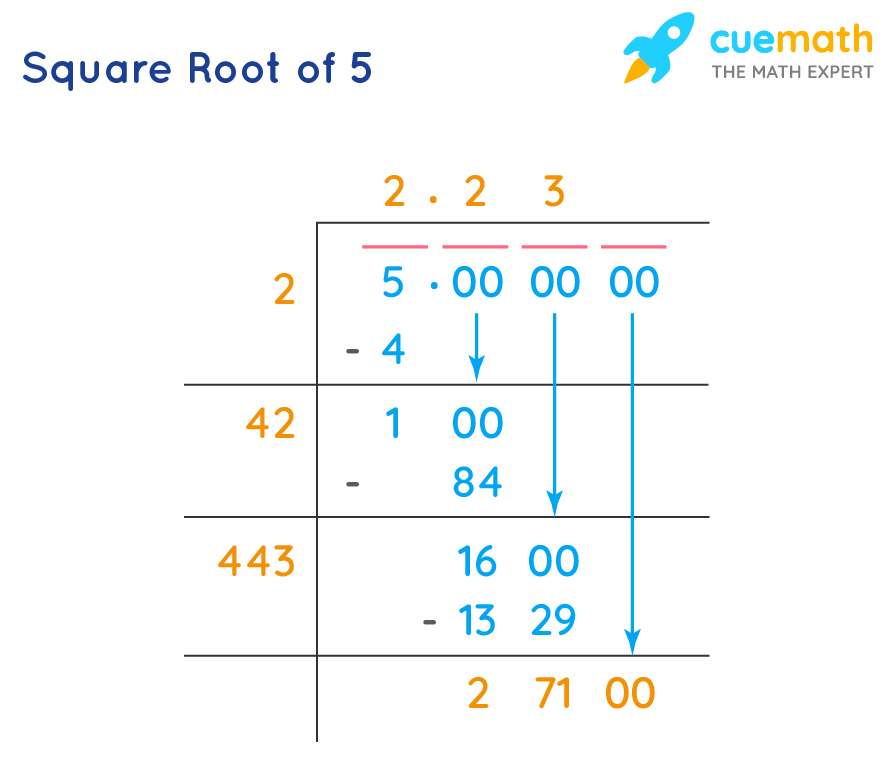
The long division method is a manual technique to find the square root of a number. Follow these steps to find the square root of 5 using this method:
- Start by grouping the digits of the number in pairs from the decimal point. For 5, write it as 5.000000.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair. For 5, the largest number is 2, because \(2^2 = 4\).
- Subtract the square of this number from the first pair. \(5 - 4 = 1\).
- Bring down the next pair of zeros, making it 100.
- Double the current quotient (which is 2), and find a digit that, when added to the quotient and multiplied by the new digit, gives a product less than or equal to 100. The suitable digit is 2, because \(42 \times 2 = 84\).
- Subtract 84 from 100, getting 16, and bring down the next pair of zeros to make it 1600.
- Repeat the process to get more decimal places as needed.
The approximate value of √5 using the long division method is 2.236.
2. Calculator Method
Using a calculator is a straightforward way to find the square root of 5. Most scientific calculators have a square root function:
- Turn on the calculator and enter the number 5.
- Press the square root button (√).
- The display will show the result, which is approximately 2.236.
3. Computer Method
Various software and programming languages can be used to compute the square root of 5. Below are examples using Python, Excel, and Google Sheets:
Python
In Python, you can use the `math` module to calculate the square root:
import math
result = math.sqrt(5)
print(result) # Output: 2.23606797749979
Excel
In Excel, you can use the SQRT function to find the square root of 5:
- Open Excel and click on a cell.
- Type
=SQRT(5)and press Enter. - The cell will display the result, 2.236.
Google Sheets
In Google Sheets, the process is similar to Excel:
- Open Google Sheets and click on a cell.
- Type
=SQRT(5)and press Enter. - The cell will display the result, 2.236.

Properties of the Square Root of 5
The square root of 5, represented as √5, has several interesting properties that are important in mathematics. Here, we explore whether 5 is a perfect square, the rationality of √5, and how to simplify it.
- Is 5 a Perfect Square?
- Rational or Irrational Number?
- Simplification of √5
- Decimal Representation
- Multiplication Property
- Radical Expressions
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer. For example, 4 is a perfect square because it is 22. However, 5 cannot be expressed as the square of any integer. Therefore, 5 is not a perfect square.
A rational number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. An irrational number cannot be written as a simple fraction. The square root of 5 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a fraction. Its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating, approximately equal to 2.23606797749979.
Simplifying a square root involves expressing it in its simplest radical form. Since 5 is a prime number, it does not have any perfect square factors other than 1. Therefore, √5 is already in its simplest form and cannot be simplified further.
While the radical form of the square root of 5 is √5, its decimal representation is useful in many calculations. The approximate value of √5 is 2.23606797749979. This value is often rounded to 2.24 for practical purposes.
When multiplying radicals, the product of the square roots of two numbers is equal to the square root of the product of those numbers. For example:
√5 * √5 = √(5 * 5) = √25 = 5
Radical expressions can often be simplified or combined if they share the same radicand. For instance, when combining like radicals:
3√5 + 2√5 = (3 + 2)√5 = 5√5
Applications and Examples
The square root of 5, represented as \( \sqrt{5} \), has various applications in mathematics and the real world. Understanding these applications helps in appreciating its significance and utility. Here are some detailed examples:
- Mathematical Calculations
- Geometry
- Physics and Engineering
- Real-World Examples
- Architecture and Design
- Nature
- Financial Models
In mathematics, \( \sqrt{5} \) is used in various algebraic and geometric calculations. It appears in the solutions of quadratic equations and in the computations involving irrational numbers. For example, in solving the equation \( x^2 - 5 = 0 \), the solutions are \( x = \pm\sqrt{5} \).
The square root of 5 is significant in geometry, especially in relation to the golden ratio. The golden ratio \( \phi \) can be expressed as \( \phi = \frac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} \). This ratio is often found in the proportions of geometric shapes and is widely used in design and architecture.
In physics and engineering, \( \sqrt{5} \) appears in formulas involving wave equations, resonance frequencies, and in the calculation of certain physical constants. For instance, in the context of wave mechanics, the relationship between frequency and wavelength may involve irrational numbers like \( \sqrt{5} \).
The golden ratio, involving \( \sqrt{5} \), is used in designing aesthetically pleasing structures. Famous examples include the Parthenon in Greece and the pyramids of Egypt.
The arrangement of leaves around a stem, the branching of trees, and other natural patterns often follow the golden ratio, thus involving \( \sqrt{5} \).
In financial models, especially those involving growth rates and risk assessment, the golden ratio and its components, such as \( \sqrt{5} \), are used to predict and analyze market trends.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of the square root of 5 in various fields. Its presence in both theoretical and practical contexts underscores its fundamental role in mathematics and beyond.
FAQs on the Square Root of 5
This section addresses some common questions about the square root of 5, providing detailed answers and explanations.
-
What is the value of √5?
The square root of 5 is approximately 2.236. In radical form, it is written as \( \sqrt{5} \).
-
Why is √5 an irrational number?
The square root of 5 is considered an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. This is because there are no two integers whose quotient equals \( \sqrt{5} \). The decimal representation of \( \sqrt{5} \) is non-terminating and non-repeating.
-
Is 5 a perfect square?
No, 5 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. Since there is no integer \( n \) such that \( n^2 = 5 \), 5 is not a perfect square.
-
What is the simplest radical form of the square root of 5?
The simplest radical form of the square root of 5 is \( \sqrt{5} \). This form cannot be simplified further because 5 is a prime number and does not have any perfect square factors other than 1.
-
What is the square root of -5?
The square root of -5 involves imaginary numbers. It is expressed as \( \sqrt{-5} = \sqrt{5} \cdot i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit, defined as \( i^2 = -1 \).
Đơn Giản Biểu Thức Căn Bậc Hai: Căn Bậc Hai của x^5
READ MORE:
Cách tìm tích của căn bậc hai của hai số, căn(5) . căn(50)