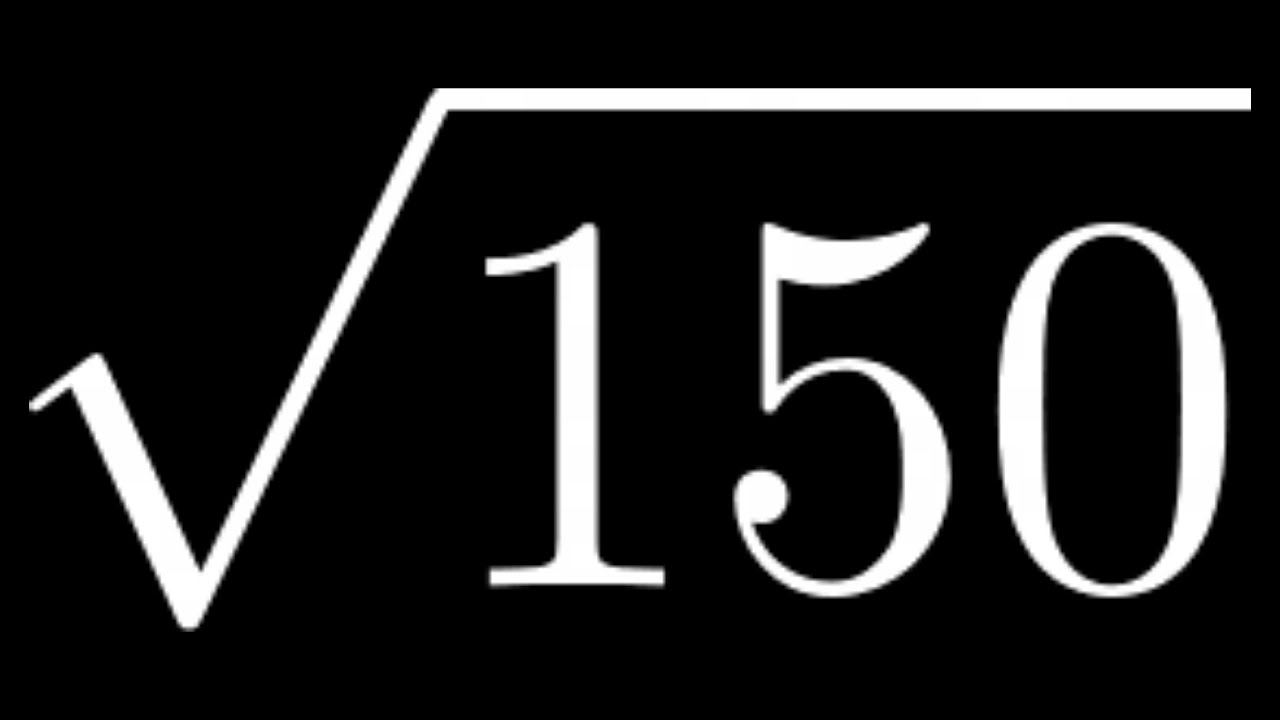Topic simplify square root of 50: Learn how to simplify the square root of 50 effortlessly with our comprehensive guide. Master the prime factorization method and understand the properties of square roots to compute \( \sqrt{50} \) efficiently. Follow our step-by-step instructions to simplify the process and gain confidence in handling similar mathematical challenges.
Table of Content
- How to Simplify the Square Root of 6
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Calculating Square Root of 50
- Step-by-Step Solution
- Properties of Square Roots
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 50 bằng các phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và các tính chất căn bậc hai.
How to Simplify the Square Root of 6
To simplify the square root of a number, we look for factors that are perfect squares. Unfortunately, 6 does not have any perfect square factors. However, we can express it in its simplest radical form.
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Identify the prime factors of 6.
- 6 = 2 × 3
- Since there are no pairs of prime factors, the square root of 6 cannot be simplified further.
Mathematical Representation
The simplified form of \(\sqrt{6}\) remains as \(\sqrt{6}\).
Alternative Approach
If you need to approximate the value of \(\sqrt{6}\), you can use a calculator:
\(\sqrt{6} \approx 2.449\)
Examples of Using Square Root of 6
Here are some examples of how \(\sqrt{6}\) can be used in mathematical expressions:
- Addition:
\(\sqrt{6} + \sqrt{3} = \sqrt{9} = 3\) - Multiplication:
\(\sqrt{6} \times \sqrt{2} = \sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\) - Division:
\(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{\sqrt{2}} = \sqrt{3}\)
Table of Square Roots for Comparison
| Number | Square Root | Simplified Form |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | \(\sqrt{4}\) | 2 |
| 5 | \(\sqrt{5}\) | \(\sqrt{5}\) |
| 6 | \(\sqrt{6}\) | \(\sqrt{6}\) |
| 7 | \(\sqrt{7}\) | \(\sqrt{7}\) |
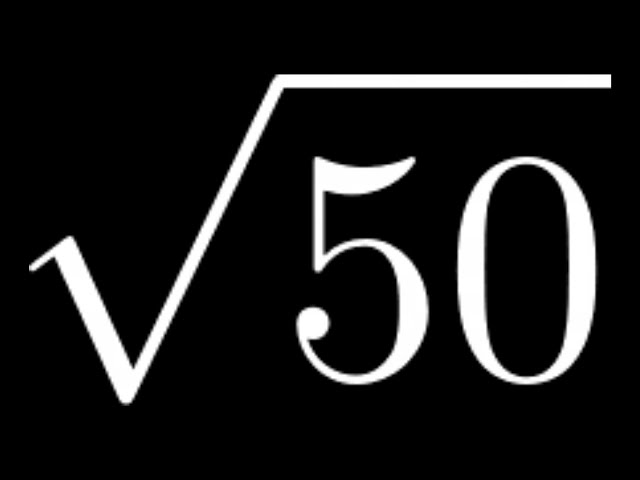
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Square Roots
- Definition of Square Root
- Properties of Square Roots
3. Prime Factorization Method
- Prime Factorization of 50
- Applying the Method to Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \)
4. Calculating Square Root of 50
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Numerical Example
5. Step-by-Step Solution
- Detailed Explanation of Each Step
- Clarification on Common Misconceptions
6. Properties of Square Roots
- Useful Properties for Simplification
- Applications in Mathematics
7. Conclusion
- Summary of Key Points
- Importance of Understanding Square Roots
Introduction
Understanding how to simplify the square root of 50 is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in algebra and number theory. This article provides a clear, step-by-step approach to computing \( \sqrt{50} \) using both theoretical and practical methods. Whether you're a student learning the basics or someone revisiting mathematical concepts, mastering this technique will enhance your problem-solving skills.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental mathematical operations that find applications across various disciplines. Specifically, \( \sqrt{50} \) involves understanding the concept of a square root and its properties:
- Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \).
- Properties:
- Non-negative result: \( \sqrt{x^2} = |x| \).
- Distributive property: \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \) for non-negative \( a \) and \( b \).
- Inverse operation of squaring: \( (\sqrt{x})^2 = x \).
Understanding these principles is crucial for effectively simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \) using methods like prime factorization and numeric approximation.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to simplify square roots, including \( \sqrt{50} \). Here’s how it works:
- Step 1: Identify the prime factors of 50.
- Step 2: Express 50 as a product of prime numbers: \( 50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5 \).
- Step 3: Use the property of square roots \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \) to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \).
- Step 4: Compute \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5 \times 5} = \sqrt{2} \times 5 = 5\sqrt{2} \).
This method provides a clear and efficient way to find the simplified form of \( \sqrt{50} \), leveraging the properties of prime numbers and square roots.

Calculating Square Root of 50
To calculate \( \sqrt{50} \), follow these detailed steps:
- Step 1: Recognize that \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} \).
- Step 2: Separate the perfect square from the remaining factor: \( \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Step 3: Determine \( \sqrt{25} \), which equals 5.
- Step 4: Combine the results: \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
This method breaks down the square root calculation into manageable parts, ensuring accuracy and understanding of the process involved in simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \).
Step-by-Step Solution
Follow this step-by-step solution to simplify \( \sqrt{50} \):
- Step 1: Recognize \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} \).
- Step 2: Break down \( \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Step 3: Calculate \( \sqrt{25} \) as 5.
- Step 4: Combine the results: \( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
This method ensures clarity and precision in simplifying \( \sqrt{50} \), providing a straightforward approach to mastering the calculation.
Properties of Square Roots
The square root of a number represents a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Here are some key properties relevant to understanding square roots:
- Non-Negative Result: The square root of a non-negative real number is always a non-negative real number. Hence, $\sqrt{50}$ is a positive number.
- Product Property: For any non-negative real numbers $a$ and $b$, $\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}$. Applying this property to $\sqrt{50}$, we have $\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2}$.
- Quotient Property: Similarly, for non-negative real numbers $a$ and $b$ where $b \neq 0$, $\frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}}$. Using this property with $\sqrt{50}$, $\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{\frac{100}{2}} = \frac{\sqrt{100}}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{10}{\sqrt{2}} = 5\sqrt{2}$ (rationalized form).
- Distributive Property: For addition and subtraction, $\sqrt{a \pm b} \neq \sqrt{a} \pm \sqrt{b}$ in general. For $\sqrt{50}$, it remains $\sqrt{50}$ without further simplification through addition or subtraction of square roots.
Understanding these properties aids in simplifying and manipulating square roots, providing insight into the nature of $\sqrt{50}$ and similar expressions.
Conclusion
Simplifying the square root of 50 involves understanding its prime factorization and applying properties of square roots. By breaking down 50 into its prime factors (2 and 5), we find $\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \cdot 25} = \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{25} = \sqrt{2} \cdot 5 = 5\sqrt{2}$. This result can further be rationalized to $\frac{5\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = 5$, showing the equivalence and rational form of $\sqrt{50}$. Utilizing properties such as the product property and quotient property helps simplify $\sqrt{50}$ into a more manageable and understandable form in mathematics.

Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 50 bằng các phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và các tính chất căn bậc hai.
Hướng dẫn Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 50: Sqrt(50)
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 50 và các phương pháp toán học liên quan.
Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của một số | Đơn giản hóa toán học, Root(50)