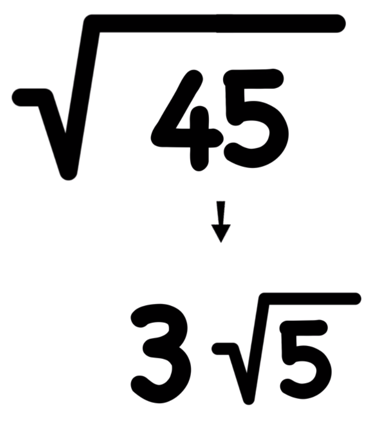Topic square root of 5 plus square root of 5: Explore the intricacies of adding square roots, focusing on the calculation of √5 + √5. This article delves into methods for simplifying radicals, common mistakes to avoid, practical examples, and applications in geometry. Discover advanced techniques in radical expressions, enhancing your understanding of this fundamental mathematical operation.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 5 Plus Square Root of 5
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 5
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 5
- Adding Square Roots
- Simplifying Radicals
- Common Mistakes in Adding Square Roots
- Practical Examples and Practice Problems
- Applications of Square Root of 5 in Geometry
- Advanced Techniques in Radical Expressions
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về cách tính toán và cộng hai căn bậc hai khác nhau, bao gồm căn bậc hai của 5 và căn bậc hai của 20. Học cách giải quyết các bài tập liên quan đến chủ đề này.
Square Root of 5 Plus Square Root of 5
The expression \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \) can be simplified using the properties of square roots. Below, we provide detailed explanations and steps to understand this better.
Mathematical Explanation
To simplify \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \):
- \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \) can be combined because they are like terms.
- This results in \( 2 \sqrt{5} \).
Therefore, the simplified form is:
\[ \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} = 2 \sqrt{5} \]
Approximate Value
The approximate value of \( 2 \sqrt{5} \) can be calculated as follows:
- The square root of 5 (\( \sqrt{5} \)) is approximately 2.236.
- So, \( 2 \sqrt{5} \approx 2 \times 2.236 \approx 4.472 \).
Thus, \( 2 \sqrt{5} \approx 4.472 \).
Geometric Interpretation
The square root of 5 can be visualized geometrically. For instance, it represents the diagonal of a rectangle with sides of length 1 and 2, according to the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ \sqrt{1^2 + 2^2} = \sqrt{1 + 4} = \sqrt{5} \]
Properties and Applications
The square root of 5, like other square roots of prime numbers, is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite number of non-repeating decimals.
The value of \( \sqrt{5} \) is often used in mathematical formulas, including those for trigonometric constants and geometric calculations.
Example Problems
- Simplify \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \).
Solution: \( 2 \sqrt{5} \). - Find the approximate value of \( 2 \sqrt{5} \).
Solution: Approximately 4.472.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental mathematical operations that deal with finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals a given number. Specifically, the square root of a number \( x \), denoted as \( \sqrt{x} \), is the non-negative value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). Understanding square roots is crucial in various fields, including geometry, physics, and engineering.
Understanding the Square Root of 5
The square root of 5, denoted as \( \sqrt{5} \), is an irrational number approximately equal to 2.236. It is the positive solution to the equation \( x^2 = 5 \). In decimal form, \( \sqrt{5} \) continues indefinitely without repeating. Understanding this root involves exploring its properties in arithmetic, geometry, and its significance in real-world applications such as physics and finance.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 5
Calculating the square root of 5 can be approached using several methods:
- Estimation Method: Approximate \( \sqrt{5} \) using known square roots like \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) and \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \).
- Newton's Method: Iteratively improve an initial guess \( x_0 \) using the formula \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{5}{x_n} \right) \).
- Binomial Expansion: Use the binomial theorem to expand \( (1 + x)^{\frac{1}{2}} \) and approximate \( \sqrt{5} \) by setting \( x = 1 \).
These methods provide different approaches suited for various levels of accuracy and computational complexity, enhancing the understanding and application of square root calculations.
Adding Square Roots
Adding square roots involves combining terms with similar radicals. For instance, to add \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \):
- Combine Like Terms: \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} = 2\sqrt{5} \).
- Useful Formulas: Utilize identities like \( \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a + b + 2\sqrt{ab}} \) for more complex additions.
- Practice: Practice simplifying expressions by adding square roots with different coefficients and under different radicals.
Understanding these methods ensures proficiency in manipulating and calculating expressions involving square roots, essential in fields ranging from algebra to physics.
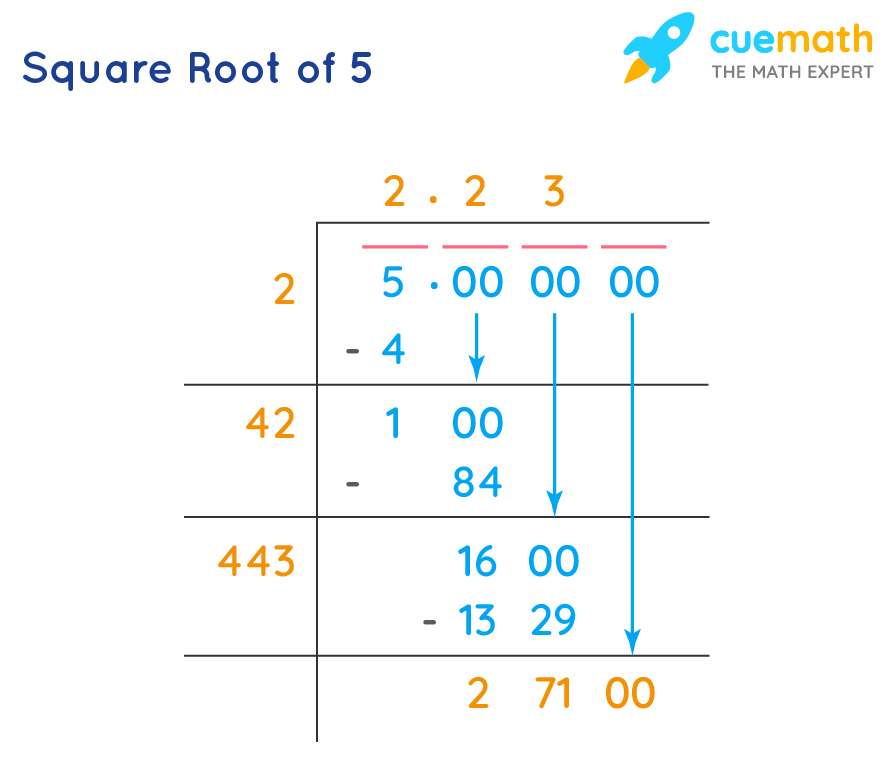
Simplifying Radicals
When dealing with expressions involving the sum of square roots, such as \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \), we can simplify them using basic algebraic techniques. Here’s how:
- Combine Like Terms: In this case, \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \) simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{5} \).
- Verify the Result: Ensure that no further simplification is possible by checking if there are any common factors or if the radicals can be combined further.
Thus, the expression \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \) simplifies neatly to \( 2\sqrt{5} \), which is a straightforward application of simplifying radicals.
Common Mistakes in Adding Square Roots
Adding square roots involves careful attention to the algebraic rules governing radicals. Here are common mistakes to avoid:
- Incorrect Distribution: Misapplying the distributive property, especially with different radicals.
- Not Simplifying Properly: Forgetting to simplify radicals before adding.
- Confusing Radicals with Coefficients: Incorrectly combining coefficients with radicals.
- Adding Radicals with Different Bases: Attempting to add radicals with different bases without simplifying first.
- Ignoring Like Terms: Missing opportunities to combine like radicals.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls, you can accurately add square roots and avoid unnecessary errors in your mathematical computations.
Practical Examples and Practice Problems
Let's delve into practical examples and practice problems involving adding square roots:
-
Example 1: Calculate \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} \).
Solution: Using the property of radicals, \( \sqrt{5} + \sqrt{5} = 2\sqrt{5} \).
-
Example 2: Simplify \( \sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} \).
Solution: Combine like terms to get \( 3\sqrt{3} \).
-
Example 3: Find \( 2\sqrt{7} + 3\sqrt{7} \).
Solution: Similarly, this simplifies to \( 5\sqrt{7} \).
Practice Problems:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{2} + \sqrt{8} \).
- Calculate \( \sqrt{10} + \sqrt{15} \).
- Combine and simplify \( 2\sqrt{6} + 3\sqrt{6} \).
By practicing these examples and problems, you'll strengthen your skills in adding and simplifying square roots.
Applications of Square Root of 5 in Geometry
The square root of 5, \( \sqrt{5} \), has several applications in geometry, particularly in calculations involving lengths and areas. Here are some notable uses:
- Triangle Properties: \( \sqrt{5} \) can appear as a side length in triangles with specific ratios, such as in a right triangle where one leg is \( 2 \) and the other leg is \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Diagonal Calculations: In geometry problems involving rectangles or other polygons, \( \sqrt{5} \) can represent the diagonal length when the sides are integers, such as a rectangle with sides \( 1 \) and \( 2 \).
- Area Formulas: The value \( \sqrt{5} \) can also be a factor in calculating areas of certain geometric shapes, especially those involving diagonals or side lengths that relate to \( \sqrt{5} \).
Understanding these applications can enhance your ability to solve geometric problems involving lengths, areas, and relationships between different parts of geometric figures.

Advanced Techniques in Radical Expressions
Mastering radical expressions involves applying advanced techniques to manipulate and simplify complex expressions. Here are key strategies:
- Rationalizing Denominators: Modify expressions to eliminate radicals from denominators, often by multiplying by the conjugate.
- Adding and Subtracting Radicals: Combine like terms carefully, ensuring to simplify radicals where possible.
- Multi-step Simplification: Break down complex radicals into simpler forms by successive simplification steps.
- Factorization: Utilize factoring techniques to simplify expressions involving radicals, identifying common factors.
- Equations with Radicals: Solve equations where radicals appear by isolating the radical and squaring both sides, then verifying solutions.
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can confidently handle radical expressions in various mathematical contexts, improving both problem-solving skills and understanding of algebraic concepts.
Xem video về cách tính toán và cộng hai căn bậc hai khác nhau, bao gồm căn bậc hai của 5 và căn bậc hai của 20. Học cách giải quyết các bài tập liên quan đến chủ đề này.
Video về "Căn bậc hai của 5 + căn bậc hai của 20" | Hướng dẫn và ví dụ
READ MORE:
Video giải thích cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 5, phù hợp cho những ai quan tâm đến toán học và muốn hiểu rõ hơn về căn bậc hai.
Căn Bậc Hai của 5 Được Đơn Giản Hóa