Topic questions on perimeter: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on perimeter! This article covers essential questions on perimeter, providing formulas, examples, and practice problems to help you understand and master this fundamental concept. Whether you're a student, teacher, or simply curious, you'll find valuable information and resources here.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Basic Concepts and Definitions
- Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
- How to Calculate Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
- Perimeter and Its Relation to Area and Volume
- Advanced Perimeter Topics
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Frequently Asked Questions about Perimeter
- Additional Resources and Tools
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp lớn, ví dụ với hình chữ L trong hình học, do thầy J giảng dạy.
Understanding Perimeter
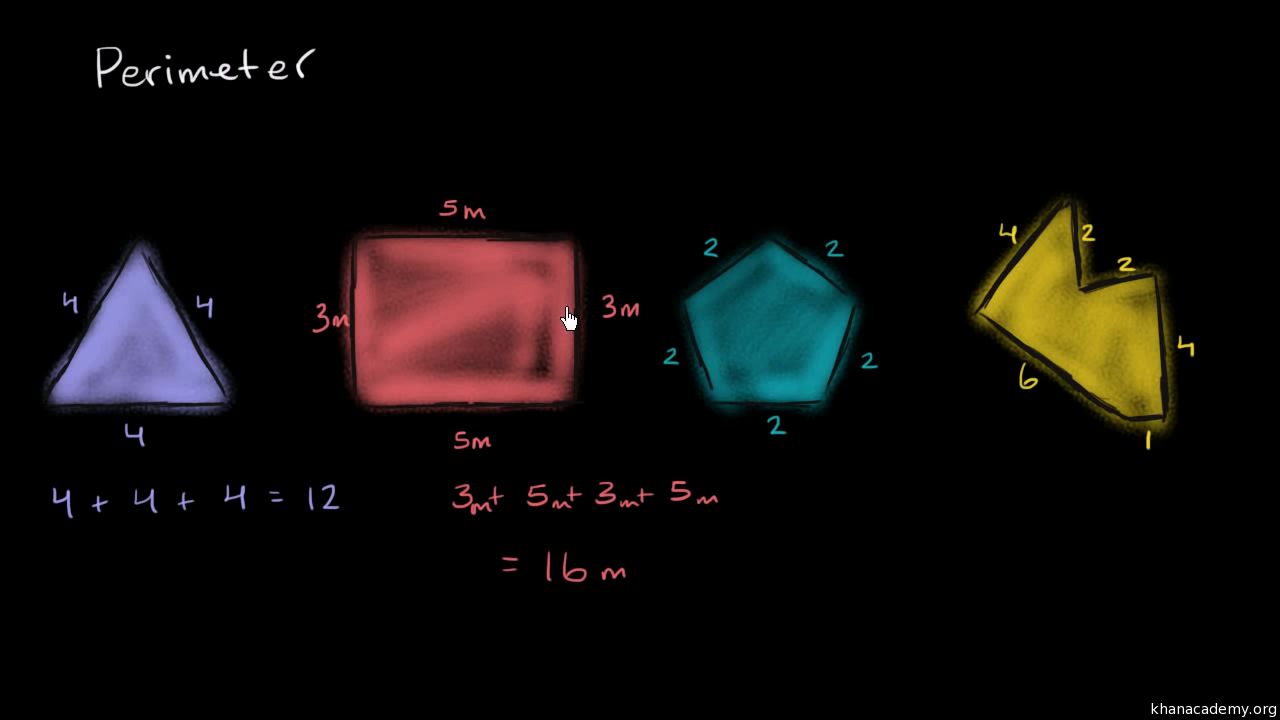
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. It's a fundamental concept in geometry, often used in various real-life situations, from fencing a garden to framing a picture.
Perimeter Formulas
To calculate the perimeter, you add up the lengths of all the sides of a shape. Here are some common formulas:
- Square: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the side length.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Regular Polygon: \( P = n \times a \), where \( n \) is the number of sides, and \( a \) is the side length.
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
| Shape | Formula | Example Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4a \) | If \( a = 5 \) cm, then \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2(l + w) \) | If \( l = 6 \) cm and \( w = 4 \) cm, then \( P = 2(6 + 4) = 20 \) cm |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) | If \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 4 \) cm, and \( c = 5 \) cm, then \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm |
| Circle | \( C = 2\pi r \) | If \( r = 7 \) cm, then \( C = 2 \pi \times 7 \approx 44 \) cm |
Sample Questions on Perimeter
- What is the perimeter of a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm?
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm.
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 3 cm.
- If one side of a square is 12 cm, what is its perimeter?
- A regular hexagon has a side length of 4 cm. What is its perimeter?
Answers
- The perimeter of the rectangle is \( P = 2(8 + 5) = 26 \) cm.
- The perimeter of the triangle is \( P = 5 + 7 + 10 = 22 \) cm.
- The circumference of the circle is \( C = 2 \pi \times 3 \approx 18.85 \) cm.
- The perimeter of the square is \( P = 4 \times 12 = 48 \) cm.
- The perimeter of the hexagon is \( P = 6 \times 4 = 24 \) cm.
Practical Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is useful in various fields such as architecture, landscaping, and any project involving space management. Whether you’re measuring the length of a fence required to enclose a garden or determining the amount of trim needed for a picture frame, perimeter calculations are invaluable.
Interactive Perimeter Exercises
Try solving these problems to test your understanding:
- Design a rectangular pool with a given perimeter and find possible dimensions.
- Calculate the amount of fencing needed to enclose a triangular plot of land.
- Determine the perimeter of different polygons given in a coordinate plane.
For more practice, explore online resources that offer interactive exercises and games to enhance your perimeter calculation skills.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. It's a fundamental concept in geometry that helps in understanding the boundaries of various shapes. Whether you're calculating the perimeter of simple polygons like squares and rectangles, or more complex shapes like circles and irregular polygons, the perimeter provides crucial information for both academic studies and real-world applications.
To better understand perimeter, let's explore some basic examples and formulas:
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square with side length \( s \) is given by \( P = 4s \).
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) is given by \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is given by \( P = a + b + c \).
- Circle: The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle with radius \( r \) is given by \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Polygons: The perimeter of a regular polygon with \( n \) sides, each of length \( s \), is \( P = ns \).
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter using these formulas is essential for solving many geometric problems. For instance, in real-life applications, knowing the perimeter is crucial for tasks such as fencing a yard, framing a picture, or designing a garden layout.
Let's delve deeper into the specific methods for calculating perimeter in different scenarios in the sections below.
Basic Concepts and Definitions
Understanding the basic concepts and definitions related to perimeter is essential for solving geometric problems accurately. Below are key terms and ideas that form the foundation of perimeter calculations:
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. It is measured in linear units such as meters, feet, or inches.
- Polygon: A polygon is a closed plane figure with three or more straight sides. Examples include triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons.
- Regular Polygon: A polygon with all sides and angles equal. Examples include equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Polygon: A polygon with sides and/or angles of different lengths and degrees.
- Circle: A round plane figure whose boundary (the circumference) is equidistant from its center.
- Formula: A mathematical expression used to calculate the perimeter of a shape. Each shape has a specific formula based on its properties.
To calculate the perimeter, you need to follow these steps:
- Identify the shape of the object.
- Determine the necessary measurements (side lengths, radius, etc.).
- Apply the appropriate formula.
Let's explore these concepts with specific examples:
| Shape | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4s \) | If \( s = 5 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{m} \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2l + 2w \) | If \( l = 8 \, \text{m} \) and \( w = 3 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 = 22 \, \text{m} \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) | If \( a = 3 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 4 \, \text{m} \), and \( c = 5 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{m} \) |
| Circle | \( C = 2\pi r \) | If \( r = 7 \, \text{m} \), then \( C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 44 \, \text{m} \) |
With these basics in mind, you can approach perimeter problems with confidence and precision. The next sections will provide more detailed examples and practice problems to reinforce these concepts.
Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes involves using specific formulas tailored to each geometric figure. Below, we outline the formulas for common shapes, along with detailed explanations and examples.
- Square: A square has four equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 4s \)
Example: If each side \( s = 5 \, \text{m} \), then the perimeter \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{m} \).
- Rectangle: A rectangle has opposite sides that are equal.
Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
Example: If length \( l = 8 \, \text{m} \) and width \( w = 3 \, \text{m} \), then the perimeter \( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 = 22 \, \text{m} \).
- Triangle: A triangle has three sides, and the perimeter is the sum of all sides.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
Example: If the sides are \( a = 3 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 4 \, \text{m} \), and \( c = 5 \, \text{m} \), then the perimeter \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{m} \).
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference.
Formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
Example: If the radius \( r = 7 \, \text{m} \), then the circumference \( C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 44 \, \text{m} \).
- Regular Polygon: A regular polygon has all sides and angles equal.
Formula: \( P = ns \)
Example: For a regular pentagon (5 sides) with each side \( s = 6 \, \text{m} \), the perimeter \( P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \, \text{m} \).
- Irregular Polygon: An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths.
Formula: \( P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \) (sum of all side lengths)
Example: For a polygon with side lengths \( s_1 = 3 \, \text{m} \), \( s_2 = 4 \, \text{m} \), \( s_3 = 5 \, \text{m} \), and \( s_4 = 6 \, \text{m} \), the perimeter \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 18 \, \text{m} \).
Understanding and using these formulas allows you to accurately calculate the perimeter of various shapes. Practice these calculations with different values to master the concept of perimeter.
How to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing the lengths of its sides. Below are the detailed steps and methods for calculating the perimeter of various shapes:
- Using Side Lengths:
- Square: Add the lengths of all four sides, or use the formula \( P = 4s \).
Example: If each side \( s = 6 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \, \text{m} \).
- Rectangle: Add the lengths of all four sides, or use the formula \( P = 2l + 2w \).
Example: If length \( l = 8 \, \text{m} \) and width \( w = 4 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 4 = 24 \, \text{m} \).
- Triangle: Add the lengths of the three sides.
Example: If the sides are \( a = 5 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 7 \, \text{m} \), and \( c = 10 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 5 + 7 + 10 = 22 \, \text{m} \).
- Polygon: Sum the lengths of all sides.
Example: For a pentagon with sides \( 3 \, \text{m} \), \( 4 \, \text{m} \), \( 5 \, \text{m} \), \( 6 \, \text{m} \), and \( 7 \, \text{m} \), the perimeter \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \, \text{m} \).
- Square: Add the lengths of all four sides, or use the formula \( P = 4s \).
- Using Formulas:
- Circle: Use the formula for circumference \( C = 2\pi r \).
Example: If the radius \( r = 5 \, \text{m} \), then \( C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 5 \approx 31.4 \, \text{m} \).
- Regular Polygon: Use the formula \( P = ns \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side.
Example: For a hexagon (6 sides) with each side \( s = 4 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 6 \times 4 = 24 \, \text{m} \).
- Circle: Use the formula for circumference \( C = 2\pi r \).
- Using Coordinates:
- For shapes on a coordinate plane, use the distance formula to find the length of each side, then sum these lengths.
Distance formula between points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\):
\[
\text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]Example: For a triangle with vertices at \((0,0)\), \((4,0)\), and \((4,3)\):
\[
\text{Side 1} = \sqrt{(4-0)^2 + (0-0)^2} = 4
\]\[
\text{Side 2} = \sqrt{(4-4)^2 + (3-0)^2} = 3
\]\[
\text{Side 3} = \sqrt{(4-0)^2 + (3-0)^2} = 5
\]Then the perimeter \( P = 4 + 3 + 5 = 12 \, \text{units} \).
- For shapes on a coordinate plane, use the distance formula to find the length of each side, then sum these lengths.
By following these methods, you can accurately determine the perimeter of various shapes, whether using simple side lengths, formulas, or coordinates.

Examples and Practice Problems
Practicing perimeter problems is essential to mastering the concept. Below are various examples and practice problems for different shapes. Work through these step-by-step to improve your understanding and skills.
Example Problems for Common Shapes
- Square:
Given a square with side length \( s = 5 \, \text{m} \), calculate the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 4s = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{m} \).
- Rectangle:
Given a rectangle with length \( l = 8 \, \text{m} \) and width \( w = 3 \, \text{m} \), calculate the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 2l + 2w = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 = 22 \, \text{m} \).
- Triangle:
Given a triangle with sides \( a = 3 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 4 \, \text{m} \), and \( c = 5 \, \text{m} \), calculate the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = a + b + c = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{m} \).
- Circle:
Given a circle with radius \( r = 7 \, \text{m} \), calculate the circumference.
Solution: \( C = 2\pi r = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 44 \, \text{m} \).
Word Problems Involving Perimeter
A farmer wants to build a fence around a rectangular field with a length of 150 meters and a width of 100 meters. What is the total length of the fence needed?
Solution: Use the perimeter formula for a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
\( P = 2 \times 150 + 2 \times 100 = 300 + 200 = 500 \, \text{m} \)
A triangular garden has sides measuring 12 meters, 16 meters, and 20 meters. What is the perimeter of the garden?
Solution: Use the perimeter formula for a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
\( P = 12 + 16 + 20 = 48 \, \text{m} \)
Interactive Exercises
Try solving these problems on your own:
- Find the perimeter of a hexagon with each side measuring 6 meters.
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 10 meters.
- A rectangular pool has a length of 25 meters and a width of 10 meters. How much tile is needed to go around the pool?
- Determine the perimeter of an irregular polygon with sides measuring 3m, 4m, 5m, 6m, and 7m.
By working through these examples and problems, you'll enhance your understanding of perimeter and become more proficient in calculating it for various shapes and scenarios.
Applications of Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of perimeter is widely used in various real-life applications, ranging from everyday activities to specialized professional tasks. Understanding how to calculate perimeter can be beneficial in numerous scenarios:
- Fencing and Bordering:
When installing a fence around a property, garden, or any enclosed area, the perimeter measurement helps determine the total length of fencing material required. For instance, if you need to fence a rectangular yard measuring 30 meters by 20 meters, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\( P = 2l + 2w = 2 \times 30 + 2 \times 20 = 60 + 40 = 100 \, \text{m} \)
- Design and Architecture:
Architects and designers use perimeter calculations to plan the layout of buildings and structures. Knowing the perimeter of rooms or buildings helps in planning for materials such as baseboards, moldings, and other finishing elements.
- Landscaping and Gardening:
Perimeter measurements are essential in landscaping to determine the amount of materials needed for borders, paths, and garden beds. For example, to outline a circular flower bed with a radius of 5 meters, the circumference (perimeter) is calculated as:
\( C = 2\pi r = 2 \times 3.14 \times 5 \approx 31.4 \, \text{m} \)
- Sports and Recreation:
In sports, knowing the perimeter of fields and courts is important for setting up boundaries and planning activities. For instance, the perimeter of a standard soccer field (90 meters by 120 meters) can be calculated as:
\( P = 2l + 2w = 2 \times 90 + 2 \times 120 = 180 + 240 = 420 \, \text{m} \)
- Fashion and Sewing:
Fashion designers and tailors use perimeter measurements to determine the lengths of fabrics needed for creating garments, trims, and accessories.
- Construction and Carpentry:
In construction, calculating the perimeter of a plot or structure is crucial for estimating materials like siding, framing, and insulation. For instance, to determine the perimeter of a rectangular plot measuring 50 meters by 40 meters:
\( P = 2l + 2w = 2 \times 50 + 2 \times 40 = 100 + 80 = 180 \, \text{m} \)
By understanding and applying perimeter calculations, you can efficiently plan and execute a variety of tasks in daily life and professional settings. Practice these calculations to enhance your skills and accuracy.
Perimeter and Its Relation to Area and Volume
The concepts of perimeter, area, and volume are fundamental in geometry and have various applications in real life. Understanding their relationships helps in solving complex problems and making practical decisions.
Perimeter and Area
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary, while the area is the measure of the space enclosed within that boundary. The relationship between perimeter and area can vary depending on the shape:
- Square:
Given a square with side length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) and area \( A \) are calculated as:
\( P = 4s \)
\( A = s^2 \)
Example: If \( s = 4 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \, \text{m} \) and \( A = 4^2 = 16 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Rectangle:
For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \):
\( P = 2l + 2w \)
\( A = lw \)
Example: If \( l = 5 \, \text{m} \) and \( w = 3 \, \text{m} \), then \( P = 2 \times 5 + 2 \times 3 = 16 \, \text{m} \) and \( A = 5 \times 3 = 15 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Circle:
For a circle with radius \( r \):
\( C = 2\pi r \) (Circumference, which is the perimeter of a circle)
\( A = \pi r^2 \)
Example: If \( r = 7 \, \text{m} \), then \( C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \approx 44 \, \text{m} \) and \( A = 3.14 \times 7^2 \approx 154 \, \text{m}^2 \).
Perimeter and Volume
Volume measures the space occupied by a 3-dimensional object, whereas perimeter applies to 2-dimensional shapes. However, understanding the perimeter can be useful in calculating surface area, which is related to volume:
- Cube:
For a cube with side length \( s \):
Perimeter of one face (square): \( P = 4s \)
Surface area: \( SA = 6s^2 \)
Volume: \( V = s^3 \)
Example: If \( s = 3 \, \text{m} \), then perimeter of one face \( P = 4 \times 3 = 12 \, \text{m} \), surface area \( SA = 6 \times 3^2 = 54 \, \text{m}^2 \), and volume \( V = 3^3 = 27 \, \text{m}^3 \).
- Rectangular Prism:
For a rectangular prism with length \( l \), width \( w \), and height \( h \):
Perimeter of the base (rectangle): \( P = 2l + 2w \)
Surface area: \( SA = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh \)
Volume: \( V = lwh \)
Example: If \( l = 4 \, \text{m} \), \( w = 3 \, \text{m} \), and \( h = 2 \, \text{m} \), then perimeter of the base \( P = 2 \times 4 + 2 \times 3 = 14 \, \text{m} \), surface area \( SA = 2 \times 4 \times 3 + 2 \times 4 \times 2 + 2 \times 3 \times 2 = 52 \, \text{m}^2 \), and volume \( V = 4 \times 3 \times 2 = 24 \, \text{m}^3 \).
By understanding the relationships between perimeter, area, and volume, you can better analyze and solve various geometric problems, enhancing your mathematical skills and practical applications.
Advanced Perimeter Topics
Advanced perimeter topics delve into more complex shapes and mathematical techniques. This section covers the perimeter of irregular shapes, perimeter in coordinate geometry, and using trigonometry for perimeter calculations.
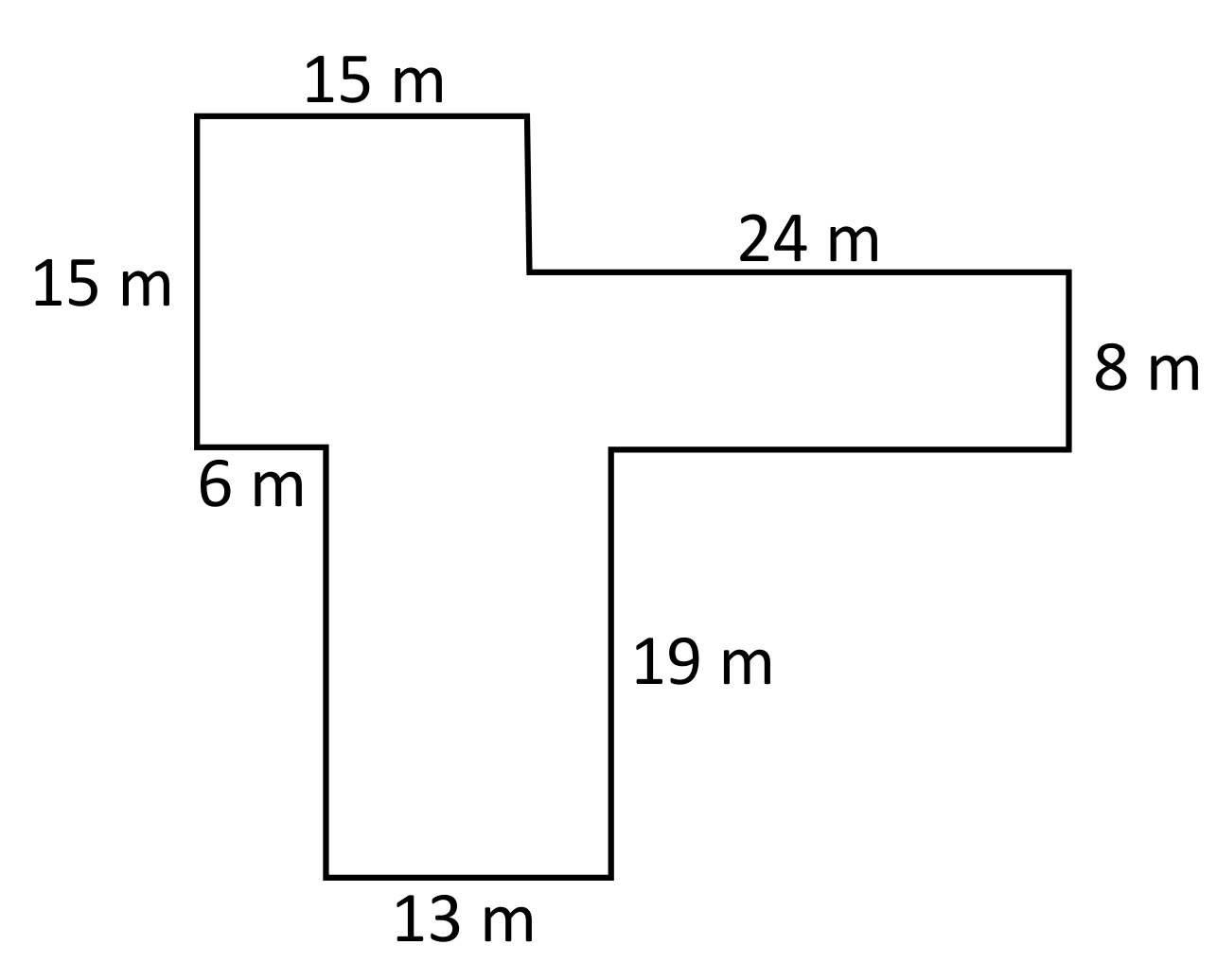
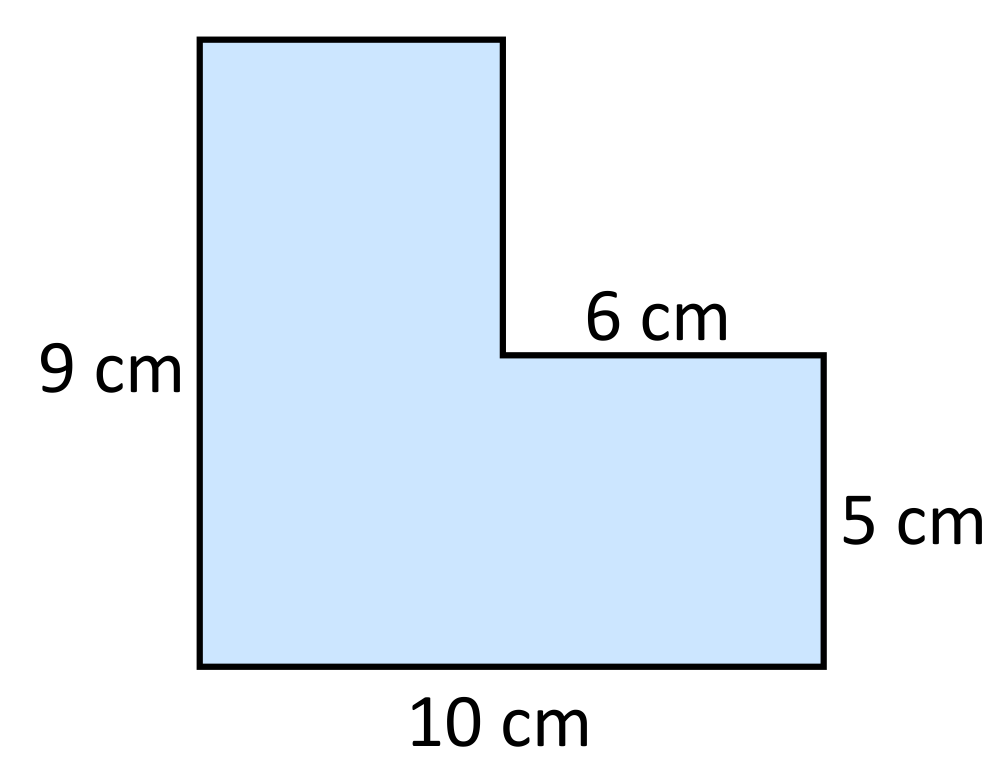
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes involves summing the lengths of all the sides. This can be more challenging than regular shapes but follows the same principle:
- Example: An irregular pentagon with sides measuring 5m, 7m, 3m, 6m, and 4m.
- Solution: \( P = 5 + 7 + 3 + 6 + 4 = 25 \, \text{m} \)
Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, you can calculate the perimeter of polygons by using the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides. For a polygon with vertices \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), ..., \((x_n, y_n)\), the distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is given by:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
Example: Find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices at \((1, 1)\), \((4, 5)\), and \((1, 5)\).
- Calculate the distance between \((1, 1)\) and \((4, 5)\): \[ d_1 = \sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (5 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = 5 \, \text{units} \]
- Calculate the distance between \((4, 5)\) and \((1, 5)\): \[ d_2 = \sqrt{(1 - 4)^2 + (5 - 5)^2} = \sqrt{(-3)^2 + 0} = 3 \, \text{units} \]
- Calculate the distance between \((1, 5)\) and \((1, 1)\): \[ d_3 = \sqrt{(1 - 1)^2 + (1 - 5)^2} = \sqrt{0 + (-4)^2} = 4 \, \text{units} \]
- Sum the distances to find the perimeter: \[ P = d_1 + d_2 + d_3 = 5 + 3 + 4 = 12 \, \text{units} \]
Using Trigonometry for Perimeter
Trigonometry can be useful for finding the perimeter of shapes when angles and some side lengths are known. For example, in a triangle where two sides and the included angle are known, you can use the Law of Cosines to find the third side:
\[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(C) \]
Example: Given a triangle with sides \( a = 5 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 7 \, \text{m} \), and the included angle \( C = 60^\circ \), find the perimeter.
- Use the Law of Cosines to find side \( c \): \[ c^2 = 5^2 + 7^2 - 2 \times 5 \times 7 \times \cos(60^\circ) \] \[ c^2 = 25 + 49 - 70 \times 0.5 \] \[ c^2 = 74 - 35 \] \[ c^2 = 39 \] \[ c = \sqrt{39} \approx 6.24 \, \text{m} \]
- Sum the sides to find the perimeter: \[ P = 5 + 7 + 6.24 = 18.24 \, \text{m} \]
Mastering these advanced perimeter topics will enhance your problem-solving skills and prepare you for more complex mathematical challenges.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When calculating perimeter, certain common mistakes can lead to incorrect results. By being aware of these mistakes and understanding how to avoid them, you can improve your accuracy and confidence in solving perimeter problems.
Common Mistakes
- Forgetting to Sum All Sides:
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting to include all sides of the shape in the calculation. This often happens with irregular shapes or polygons with many sides.
- Mixing Up Units:
Using different units for different sides or not converting them to a common unit can lead to errors. Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before calculating the perimeter.
- Incorrectly Applying Formulas:
Using the wrong formula for the given shape is another frequent error. For example, applying the rectangle perimeter formula to a triangle will yield incorrect results.
- Errors in Coordinate Geometry:
When using coordinates, mistakes in applying the distance formula or arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect perimeter values.
- Ignoring Decimal Precision:
Rounding off values too early or not maintaining sufficient decimal places can lead to inaccuracies, especially in more precise calculations.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
- Double-Check All Sides:
Always ensure that you have included every side in your perimeter calculation. For irregular shapes, carefully trace and add each side length.
- Consistent Units:
Verify that all measurements are in the same unit before beginning your calculations. Convert units if necessary to maintain consistency.
- Use Correct Formulas:
Ensure that you are using the appropriate formula for the shape in question. Review geometric properties and formulas for different shapes regularly.
- Careful with Coordinates:
When calculating perimeter using coordinates, apply the distance formula accurately for each pair of points. Double-check your arithmetic to avoid errors.
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- Maintain Decimal Precision:
Carry out calculations with sufficient decimal precision and avoid rounding off intermediate results too early. This helps in achieving more accurate final results.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and following the tips to avoid them, you can enhance your ability to calculate perimeter accurately and efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions about Perimeter
Below are some common questions and detailed answers about perimeter:
- What is the perimeter?
The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is the distance around the shape.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a rectangle?
To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, use the formula:
\( P = 2(l + w) \)
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width of the rectangle.
- What is the perimeter formula for a square?
The perimeter of a square is calculated using the formula:
\( P = 4a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
- How can you find the perimeter of a triangle?
For a triangle, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all three sides:
\( P = a + b + c \)
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- What is the perimeter of a circle (circumference)?
The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is found using the formula:
\( C = 2\pi r \)
where \( r \) is the radius of the circle and \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a polygon?
The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\( P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \)
where \( s_i \) is the length of side \( i \) and \( n \) is the number of sides.
- What is the formula for the perimeter of an irregular shape?
For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by adding up the lengths of all the sides. There is no specific formula; you simply measure each side and sum them.
- How do you find the perimeter of a shape using coordinates?
If you have the vertices of a shape on a coordinate plane, you can calculate the perimeter by finding the distance between each pair of consecutive vertices and then summing these distances. The distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is calculated using the distance formula:
\( d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \)
- Can the perimeter and area of a shape be the same number?
Yes, it is possible for the perimeter and area of a shape to have the same numerical value, although it is relatively rare and depends on the specific dimensions of the shape.
- How is perimeter used in real life?
Perimeter is used in various real-life applications such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or installing baseboard around a room. It is essential for any task that involves measuring the boundary of a physical space.
Additional Resources and Tools
To further enhance your understanding of perimeter, the following resources and tools are highly recommended:
- Online Perimeter Calculators
These calculators can help you quickly determine the perimeter of various shapes. Simply input the required dimensions, and the calculator will do the rest.
- Educational Videos
Watching videos can provide visual and auditory learners with a better grasp of perimeter concepts. Here are some useful video resources:
- Printable Worksheets
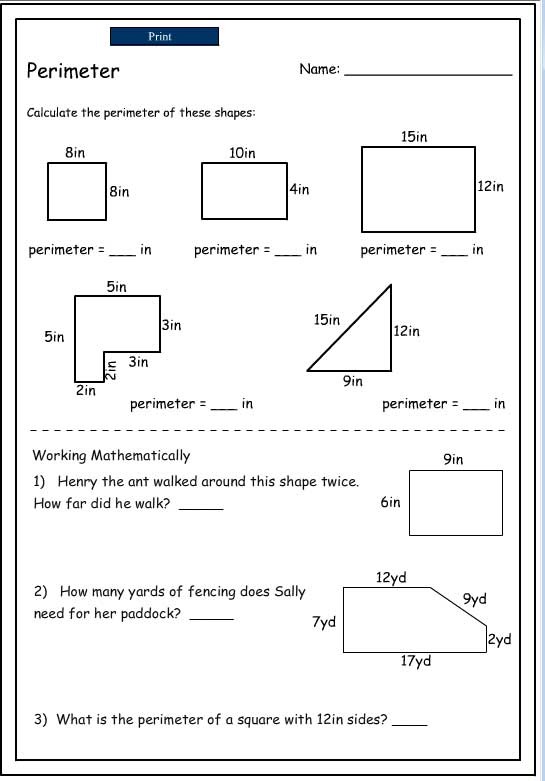
Practice makes perfect! Use these printable worksheets to test your knowledge and improve your skills in calculating perimeter:
These resources will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of perimeter and its applications, helping you to master this essential geometry concept.
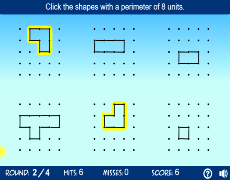
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp lớn, ví dụ với hình chữ L trong hình học, do thầy J giảng dạy.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp Lớn | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi trong toán học, do thầy J giảng dạy.
Tìm Chu Vi | Toán Học với Thầy J