Topic perimeter graph calculator: The Perimeter Graph Calculator is your go-to tool for precise and efficient perimeter calculations. Whether you’re tackling simple shapes or complex polygons, this calculator simplifies the process, making it ideal for students, teachers, and professionals. Discover how this tool can enhance your geometry tasks and ensure accuracy every time.
Table of Content
Perimeter Graph Calculator
Calculating the perimeter of various geometric shapes can be simplified using graphing calculators and specialized online tools. Below is a comprehensive overview of different methods and tools available for calculating perimeters.
1. Perimeter of Basic Shapes
For basic shapes like rectangles and triangles, the perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all sides. The formulas are straightforward:
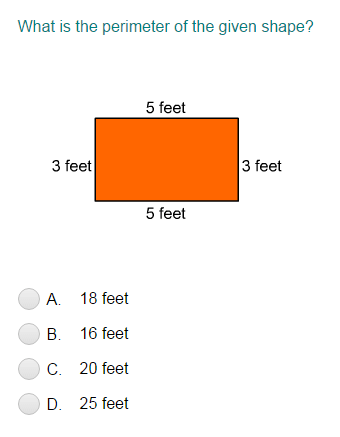
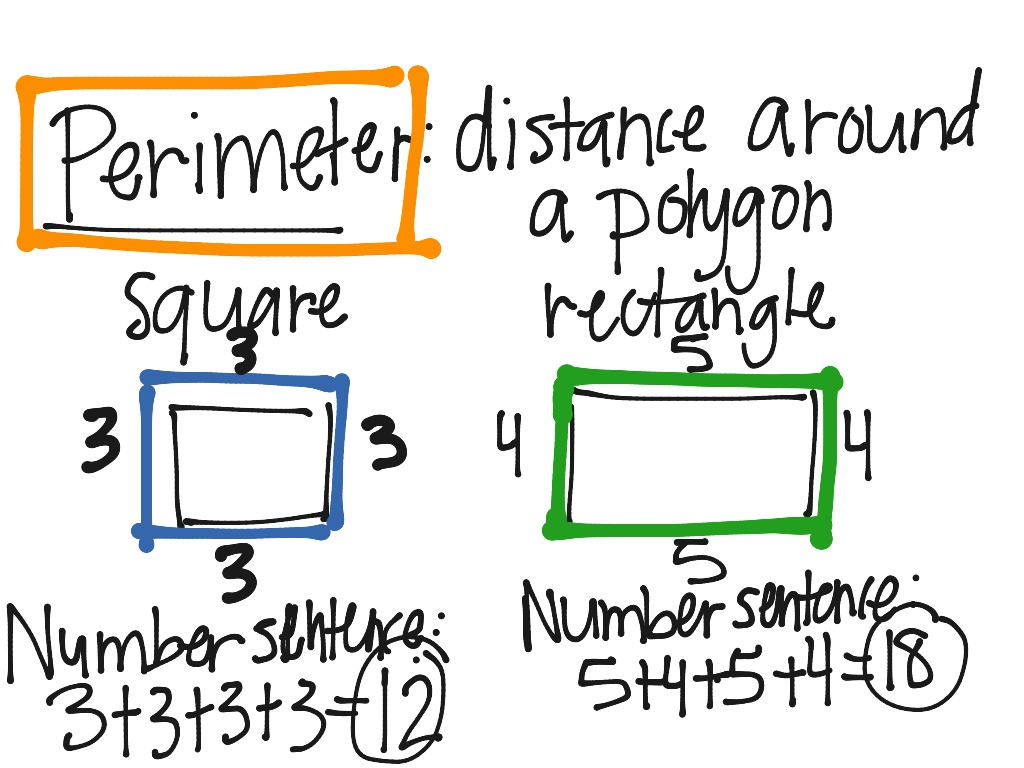
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
Where \( l \) is the length, \( w \) is the width, and \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the sides of the triangle.
2. Using Graphing Calculators
Graphing calculators, such as those provided by and , offer interactive ways to calculate and visualize perimeters.
- Desmos allows you to plot points and visualize the shape's perimeter by connecting the dots and calculating the sum of the lengths.
- GeoGebra provides tools to create custom shapes and automatically calculate their perimeter and area.
3. Online Perimeter Calculators
Several online calculators provide easy-to-use interfaces for calculating perimeters of various shapes:
- : Supports calculations for rectangles and other shapes using different input parameters like side lengths, area, and diagonals.
- : Offers formulas and explanations for a wide range of shapes, including circles and ellipses.
- : Specializes in polygon calculations using vertex coordinates.
4. Detailed Example: Perimeter of a Polygon
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon using coordinates, follow these steps:
- List the coordinates of each vertex in order.
- Calculate the distance between each pair of consecutive vertices using the distance formula: \[ \text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- Sum all the distances to get the perimeter.
For example, a polygon with vertices A(1, 2), B(4, 5), and C(6, 1) would have a perimeter calculated as:
Which simplifies to:
\[
P \approx 4.24 + 4.47 + 5.10 \approx 13.81 \text{ units}
\]
5. Conclusion
Whether you're a student, teacher, or hobbyist, using these tools can significantly simplify the process of calculating perimeters for various shapes. By leveraging graphing calculators and online resources, you can quickly and accurately determine the perimeter, enhancing both learning and practical application.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various geometric shapes is essential for students, teachers, and professionals alike. The Perimeter Graph Calculator simplifies this task by providing precise calculations for shapes ranging from simple rectangles to complex polygons. This tool supports a wide array of geometric figures, allowing users to input dimensions or coordinates and receive accurate perimeter measurements. In this section, we'll explore different methods and tools for calculating perimeters, offering step-by-step guidance to enhance your mathematical proficiency.
- Basic Shapes Perimeter Calculation
- Graphing Calculators for Perimeter
- Online Perimeter Calculators
- Methods for Specific Shapes
- Examples and Practical Applications
Perimeter of Basic Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of basic geometric shapes is foundational in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the edges of a shape. Here’s a detailed guide to understanding and calculating the perimeter of various basic shapes:
- Rectangle
- Square
- Triangle
- Circle
- Ellipse
- Parallelogram
- Trapezoid
- Polygon
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Given the length \( l \) and width \( w \), the formula is:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
A square is a special case of a rectangle where all sides are equal. If each side length is \( s \), the perimeter is:
\[ P = 4s \]
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides. If the sides are \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the formula is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
For a circle, the perimeter is referred to as the circumference. Given the radius \( r \), the formula is:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
Calculating the perimeter of an ellipse is more complex. An approximation formula by Ramanujan is:
\[ P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \]
where \( a \) is the semi-major axis and \( b \) is the semi-minor axis.
The perimeter of a parallelogram is calculated by adding the lengths of its opposite sides. If the sides are \( a \) and \( b \), the formula is:
\[ P = 2(a + b) \]
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of all its sides. If the sides are \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \), the formula is:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
For any polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. If the polygon has \( n \) sides with lengths \( l_1, l_2, \ldots, l_n \), the formula is:
\[ P = l_1 + l_2 + \cdots + l_n \]
Understanding these formulas and how to apply them is essential for solving geometry problems involving perimeters. Using tools like graphing calculators can simplify these calculations, especially for more complex shapes.
Graphing Calculators
Graphing calculators are powerful tools for visualizing and calculating geometric properties, including the perimeter of various shapes. These calculators allow users to input equations, plot points, and dynamically interact with graphs to gain a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Here are some popular graphing calculators and how they can be used to calculate perimeters:
- Desmos Graphing Calculator
- Plot the vertices of the shape on the graph.
- Use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides.
- Sum the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter.
- GeoGebra Graphing Calculator
- Use the line segment tool to draw the shape on the coordinate plane.
- Label each vertex and use the software to measure the side lengths.
- Sum the measured lengths to calculate the perimeter.
- Symbolab Graphing Calculator
- Input the equations or coordinates of the shape's sides.
- Utilize the calculator's tools to determine the lengths of the sides.
- Add the side lengths to find the perimeter.
Desmos offers a free, user-friendly graphing calculator that supports a wide range of mathematical functions. To calculate the perimeter of a shape:
Desmos also provides specific tools for calculating perimeters of common shapes like polygons, circles, and more.
GeoGebra is another versatile graphing calculator that allows users to create and manipulate geometric figures. To find the perimeter:
GeoGebra includes features for calculating the perimeter of polygons, ellipses, and other shapes, making it a comprehensive tool for geometry.
Symbolab provides an online graphing calculator with step-by-step solutions for various geometric problems. To use Symbolab for perimeter calculations:
Symbolab's detailed solutions and explanations help users understand the process of calculating perimeters.
Graphing calculators like Desmos, GeoGebra, and Symbolab are invaluable resources for students and professionals alike. They simplify complex calculations, provide visual aids, and enhance the learning experience by making abstract concepts more tangible.
Online Perimeter Calculators
Online perimeter calculators are versatile tools designed to simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of various geometric shapes. These calculators allow users to input dimensions or coordinates, providing instant and accurate results. Below is an overview of some popular online perimeter calculators and how to use them:
- Omni Calculator
- Select the shape you want to calculate the perimeter for.
- Input the necessary dimensions (e.g., radius for a circle, side lengths for a polygon).
- Click 'Calculate' to get the perimeter.
- Giga Calculator
- Choose the shape from the provided options (e.g., triangle, trapezoid, ellipse).
- Enter the known dimensions, such as side lengths or angles.
- Press 'Calculate' to see the perimeter and other relevant properties.
- Free Online Calc
- Enter the number of vertices for the polygon.
- Input the x and y coordinates for each vertex.
- The calculator will compute the distances between consecutive vertices and sum them to find the perimeter.
- Calculator Soup
- Select the desired shape calculator.
- Enter the required dimensions, such as side lengths or angles.
- Click 'Calculate' to obtain the perimeter.
Omni Calculator provides a comprehensive tool for calculating the perimeter of multiple shapes, including rectangles, circles, ellipses, and polygons. To use the Omni Calculator:
The calculator also offers detailed explanations and formulas used in the calculations.
Giga Calculator is another user-friendly option that supports a wide range of shapes. Here's how to use it:
Giga Calculator also includes visual aids and step-by-step instructions for each shape.
This calculator focuses on polygons and requires users to input the coordinates of the vertices. To use this tool:
This method is particularly useful for irregular polygons where traditional formulas do not apply.
Calculator Soup offers calculators for regular polygons, parallelograms, and more. To find the perimeter:
These calculators provide quick and accurate results, making them ideal for both educational and practical applications.
Online perimeter calculators like Omni Calculator, Giga Calculator, Free Online Calc, and Calculator Soup are invaluable resources for students, educators, and professionals. They simplify complex perimeter calculations and enhance understanding through detailed explanations and visual aids.
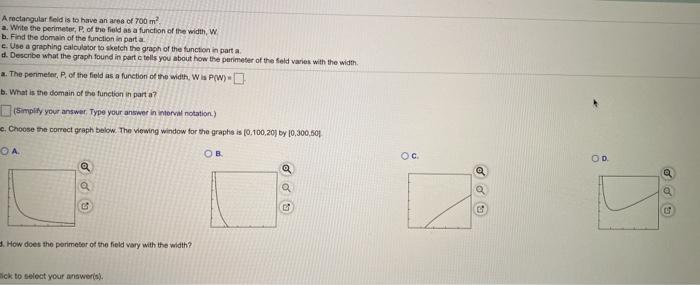
Specific Shape Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of specific shapes involves understanding their unique properties and applying appropriate formulas. Here are detailed steps for various shapes:
- Rectangle
- Square
- Triangle
- Circle
- Ellipse
- Trapezoid
- Parallelogram
- Polygon
For a rectangle, the perimeter is calculated by adding twice the length and twice the width:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
Where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
A square, being a special case of a rectangle where all sides are equal, has its perimeter calculated as:
\[ P = 4s \]
Where \( s \) is the length of one side.
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
For a circle, the perimeter, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius \( r \):
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex and often approximated using Ramanujan's formula:
\[ P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right] \]
Where \( a \) is the semi-major axis and \( b \) is the semi-minor axis.
The perimeter of a trapezoid is found by summing the lengths of all four sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
Where \( a \) and \( b \) are the bases, and \( c \) and \( d \) are the other two sides.
For a parallelogram, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of the opposite sides:
\[ P = 2(a + b) \]
Where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the sides.
The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. For a polygon with \( n \) sides of lengths \( l_1, l_2, \ldots, l_n \), the formula is:
\[ P = l_1 + l_2 + \cdots + l_n \]
For example, for a quadrilateral with vertices at \( (x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), (x_3, y_3), (x_4, y_4) \), the distances between consecutive vertices are calculated using the distance formula:
\[ \text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
The perimeter is then the sum of these distances.
Understanding these formulas and methods is crucial for accurately calculating the perimeter of various shapes. Using graphing calculators and online tools can further simplify these calculations by providing visual aids and automated computations.
Calculation Methods
There are various methods to calculate the perimeter of geometric shapes. Below are detailed steps and formulas for different methods:
Using Distance Formula
The distance formula is a fundamental tool for calculating the perimeter of shapes when their vertex coordinates are known. The formula to find the distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is:
\[
\text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Steps to calculate the perimeter using the distance formula:
- Identify the coordinates of all vertices of the shape.
- Use the distance formula to calculate the length of each side.
- Add all the calculated side lengths to find the total perimeter.
Box Method for Irregular Shapes
The box method is useful for calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes by dividing them into smaller, manageable sections. Here’s how it works:
- Enclose the irregular shape within a bounding box or rectangle.
- Divide the shape into simpler geometric figures (triangles, rectangles, etc.).
- Calculate the perimeter of each simpler figure using known formulas.
- Add up the perimeters of the simpler figures, subtracting any internal shared boundaries.
Shoelace Formula for Polygons
The Shoelace formula (or Gauss's area formula) is a method to calculate the area of a polygon when the coordinates of its vertices are known, but it can also be adapted to find the perimeter. Here’s the adapted method for the perimeter:
- List the coordinates of the polygon’s vertices in a sequential order (either clockwise or counterclockwise).
- Apply the distance formula to each consecutive pair of vertices to find the length of each side.
- Add up all the side lengths to get the perimeter.
For example, for a polygon with vertices \((x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), ..., (x_n, y_n)\):
\[
\text{Perimeter} = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2}
\]
where \((x_{n+1}, y_{n+1})\) is the same as \((x_1, y_1)\) to close the polygon.
Example Calculations
Here are examples of using the methods described above:
Example: Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- Given vertices: \((2, 4), (5, 7), (8, 4), (5, 1)\)
- Calculate side lengths:
- AB: \(\sqrt{(5-2)^2 + (7-4)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} \approx 4.24\)
- BC: \(\sqrt{(8-5)^2 + (4-7)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} \approx 4.24\)
- CD: \(\sqrt{(5-8)^2 + (1-4)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} \approx 4.24\)
- DA: \(\sqrt{(2-5)^2 + (4-1)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} \approx 4.24\)
- Add the side lengths: \(4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 \approx 16.96\)
- The perimeter of the quadrilateral is approximately 16.96 units.
Examples and Practical Applications
Here are some step-by-step examples and practical applications of calculating perimeters using graph calculators and online resources.
Example 1: Calculating the Perimeter of a Triangle
Consider a triangle with vertices at A(1, 2), B(4, 6), and C(5, 2).
- Use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of each side:
- AB = \( \sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (6 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
- BC = \( \sqrt{(5 - 4)^2 + (2 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{1 + 16} = \sqrt{17} \approx 4.123 \)
- CA = \( \sqrt{(1 - 5)^2 + (2 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{16 + 0} = \sqrt{16} = 4 \)
- Add the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter:
Perimeter = 5 + 4.123 + 4 ≈ 13.123 units
Example 2: Calculating the Perimeter of a Polygon Using GeoGebra
Let's find the perimeter of a quadrilateral with vertices at A(2, 3), B(6, 7), C(8, 3), and D(4, 1) using GeoGebra.
- Input the vertices into GeoGebra to plot the quadrilateral.
- Use the distance tool to measure each side:
- AB = \( \sqrt{(6 - 2)^2 + (7 - 3)^2} = \sqrt{16 + 16} = \sqrt{32} \approx 5.657 \)
- BC = \( \sqrt{(8 - 6)^2 + (3 - 7)^2} = \sqrt{4 + 16} = \sqrt{20} \approx 4.472 \)
- CD = \( \sqrt{(8 - 4)^2 + (3 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{16 + 4} = \sqrt{20} \approx 4.472 \)
- DA = \( \sqrt{(4 - 2)^2 + (1 - 3)^2} = \sqrt{4 + 4} = \sqrt{8} \approx 2.828 \)
- Sum the lengths to find the perimeter:
Perimeter = 5.657 + 4.472 + 4.472 + 2.828 ≈ 17.429 units
Example 3: Real-World Application - Fencing a Garden
Suppose you need to fence a rectangular garden that is 10 meters long and 7 meters wide.
- Calculate the perimeter of the garden using the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle:
Perimeter = 2(length + width) = 2(10 + 7) = 2 × 17 = 34 meters
- Determine the amount of fencing material needed:
You will need 34 meters of fencing to enclose the garden.
Example 4: Using Omni Calculator for Complex Shapes
For more complex shapes like irregular polygons, use the Omni Calculator's perimeter calculator:
- Input the coordinates of each vertex of the polygon.
- Let the calculator compute the distances between consecutive vertices and sum them to find the perimeter.
- For example, a pentagon with vertices at (1, 1), (4, 1), (6, 3), (3, 5), and (1, 4) can have its perimeter calculated automatically.
Tìm Chu Vi
READ MORE:
Tính Chu Vi Của Hình Cho Trước | Độ dài các cạnh lần lượt là 9, 12 và 15