Topic khan academy perimeter: Explore the comprehensive lessons on perimeter offered by Khan Academy. Dive into various topics including calculating perimeter for different shapes, solving perimeter word problems, and understanding the relationship between perimeter and area. Whether you are a student or a teacher, these resources will help you achieve mastery in geometry.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter with Khan Academy
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Perimeter of Basic Shapes
- Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
- Perimeter Word Problems
- Comparing Area and Perimeter
- Advanced Perimeter Concepts
- Practice and Quizzes on Perimeter
- Unit Tests and Mastery Points
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để học cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình cơ bản như hình vuông, hình chữ nhật và tam giác.
Understanding Perimeter with Khan Academy
Khan Academy provides a comprehensive resource for learning about the perimeter. The lessons cover various aspects of perimeter calculations, practice exercises, and quizzes to help reinforce the concepts.
Learning Resources
Practice Exercises
Khan Academy offers a variety of practice problems to help students master the concept of perimeter:
- Find perimeter by counting units
- Find perimeter when given side lengths
- Perimeter word problems
Quizzes
After learning and practicing, students can take quizzes to test their understanding and track their progress:
Additional Topics
In addition to perimeter, Khan Academy covers related topics to provide a well-rounded understanding:
For more detailed lessons and practice exercises, visit the website.
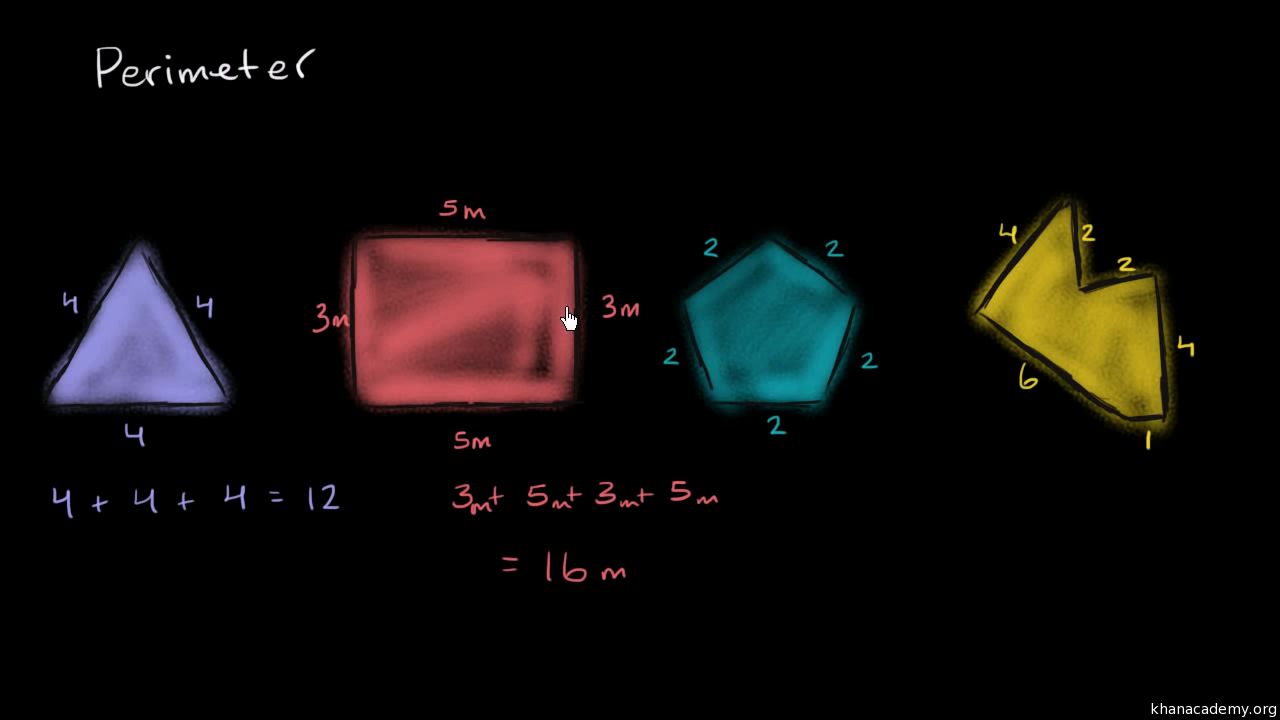
Introduction to Perimeter
Perimeter is the distance around the outer edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is an important concept in geometry and is often used in various real-world applications, such as determining the length of fencing needed to enclose a yard or the trim required to go around a room.
To find the perimeter of a shape, you simply add up the lengths of all its sides. For regular polygons (shapes with all sides and angles equal), you can multiply the length of one side by the number of sides.
For example, the perimeter of a rectangle can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
Let's explore the concept of perimeter through different shapes and examples:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
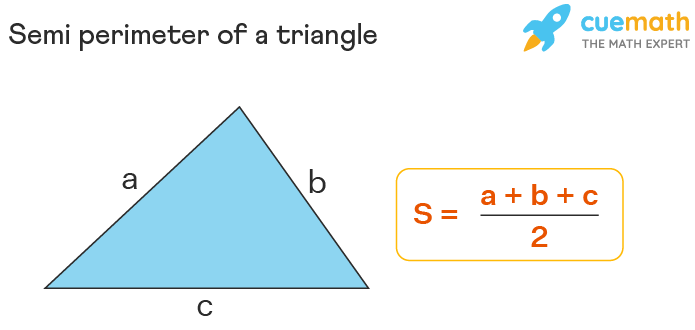
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
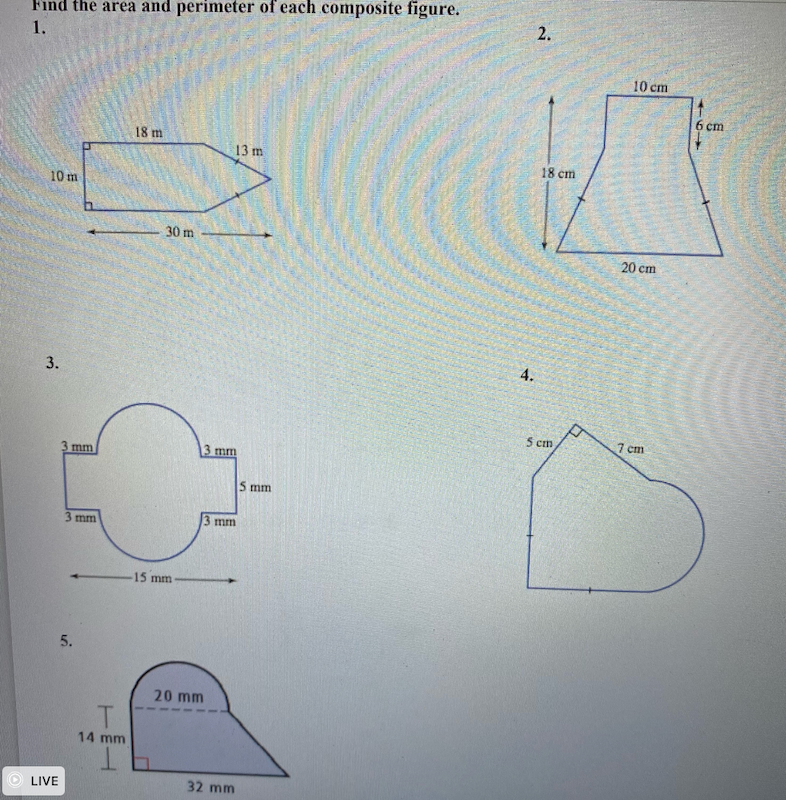
For more complex shapes, you might need to break them down into simpler components, calculate the perimeter of each component, and then sum those perimeters.
Understanding perimeter is foundational for advancing in geometry and for practical problem-solving in everyday life.
Perimeter of Basic Shapes
Understanding the perimeter of basic shapes is essential in geometry. The perimeter is the total length around a shape. Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter for some common shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides are equal, the formula is:
\[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Square: Since all four sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is simply four times the length of one side:
\[ P = 4 \times side \]
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference. It is calculated using the radius (r) or the diameter (d). The formulas are:
\[ C = 2 \times \pi \times r \] or \[ C = \pi \times d \]
These formulas provide a foundation for calculating the perimeter of various shapes. Practice these calculations to strengthen your understanding of geometry.
Calculating Perimeter with Missing Sides
When calculating the perimeter of a shape with one or more missing side lengths, we need to use the information we have to determine the missing values. Here’s a step-by-step method to approach this:
- Identify the Known Sides:
First, identify all the side lengths that are given. Write them down and keep track of which sides are known and which are missing.
- Use Shape Properties:
Use the properties of the shape to find the missing sides. For example:
- For a rectangle, opposite sides are equal.
- For a square, all sides are equal.
- For a triangle, you may use the perimeter formula and the lengths of the other sides to find the missing length.
- Apply the Perimeter Formula:
For rectangles and squares, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as follows:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
For triangles, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths:
\( P = a + b + c \)
- Solve for the Missing Length:
Rearrange the perimeter formula to solve for the missing side length. For example, if the perimeter of a rectangle and the length of three sides are known, you can find the fourth side.
Example:
- Given a rectangle with sides \( l = 10 \) cm and \( w = 5 \) cm, and one width missing:
- \( P = 2(10 + 5) = 30 \) cm
- If one side is unknown: \( 30 = 2(10 + x) \)
- Solve for \( x \): \( x = 5 \) cm
By following these steps, you can effectively calculate the perimeter of various shapes even when some side lengths are missing.
Perimeter Word Problems
Word problems involving the perimeter require careful reading and problem-solving skills. Here are some steps to tackle them effectively:
- Read the problem carefully: Identify the shape and the given side lengths.
- Identify missing sides: Determine which sides are missing and need to be calculated.
- Use known formulas: Apply the perimeter formulas for the relevant shapes.
- Perform calculations: Add up all the sides to find the total perimeter.
Here are a few examples of perimeter word problems:
-
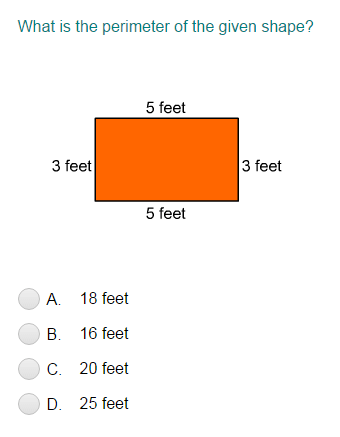
A rectangle has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. What is the perimeter?
Solution: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) = 2 \times (8 + 5) = 26 \) meters.
-
A square garden has a side length of 10 meters. Find the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = 4 \times s = 4 \times 10 = 40 \) meters.
-
A triangle has sides of 7 meters, 8 meters, and 9 meters. Calculate the perimeter.
Solution: \( P = a + b + c = 7 + 8 + 9 = 24 \) meters.
When solving these problems, ensure all units are consistent and double-check calculations for accuracy. Word problems can vary greatly, so practice is key to mastering perimeter calculations.

Comparing Area and Perimeter
Understanding the distinction between area and perimeter is crucial in geometry. While both concepts are related to the shape and size of figures, they measure different properties.
The perimeter of a shape is the total length around the figure, calculated by adding up the lengths of all its sides. It is measured in units of length such as meters, centimeters, or feet.
On the other hand, the area is the measure of the space inside the shape, expressed in square units such as square meters or square centimeters. The formulas to calculate area vary depending on the shape.
- For a rectangle, the area is calculated as \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \).
- For a triangle, the area is \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- For a circle, the area is \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \) where \( r \) is the radius.
Let’s compare area and perimeter through an example:
| Shape | Dimensions | Perimeter | Area |
| Rectangle | Length = 5 units, Width = 3 units | \( 2 \times (5 + 3) = 16 \) units | \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) square units |
| Square | Side = 4 units | \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \) units | \( 4^2 = 16 \) square units |
From the examples above, we can see that even if the perimeter values are similar, the area can vary significantly. Understanding these differences is essential for solving geometric problems accurately.
Advanced Perimeter Concepts
In this section, we delve into more intricate aspects of perimeter, exploring advanced concepts that build upon the fundamental understanding gained from previous sections.
- Composite Shapes: Learn how to calculate the perimeter of complex figures composed of multiple basic shapes.
- Irregular Polygons: Understand how to find the perimeter of irregular polygons by breaking them down into simpler shapes or utilizing advanced formulas.
- Perimeter of Circles: Discover methods for determining the perimeter of circles, including circumference, and explore the relationship between perimeter and diameter.
- Perimeter in Real-Life Scenarios: Explore applications of perimeter in various real-world contexts, such as fencing, landscaping, and architecture.
- Perimeter Ratios and Proportions: Investigate how perimeter ratios and proportions are used to solve advanced problems involving scaling and similarity.
- Perimeter Extension Problems: Challenge yourself with extension problems that require applying advanced perimeter concepts to solve complex geometric puzzles.
Practice and Quizzes on Perimeter
Test your understanding and reinforce your knowledge of perimeter with a variety of practice exercises and interactive quizzes available on Khan Academy:
- Perimeter of Basic Shapes: Practice finding the perimeter of squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles through interactive exercises.
- Missing Sides and Word Problems: Test your ability to calculate perimeter when some sides are missing or when presented with real-world scenarios.
- Advanced Perimeter Problems: Challenge yourself with complex perimeter problems involving composite shapes, irregular polygons, and circles.
- Interactive Quizzes: Engage in interactive quizzes to assess your understanding of perimeter concepts and receive instant feedback.
- Custom Practice: Customize your practice sessions to focus on specific areas of perimeter that you find challenging.
Unit Tests and Mastery Points
Track your progress and master perimeter concepts with unit tests and mastery points offered on Khan Academy:
- Unit Tests: Take comprehensive unit tests to assess your understanding of perimeter topics covered in the course.
- Immediate Feedback: Receive immediate feedback on your performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Mastery Challenges: Engage in mastery challenges to solidify your knowledge and earn mastery points.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor your progress as you complete unit tests and earn mastery points to gauge your proficiency.
- Personalized Learning: Benefit from personalized recommendations based on your performance to enhance your learning experience.
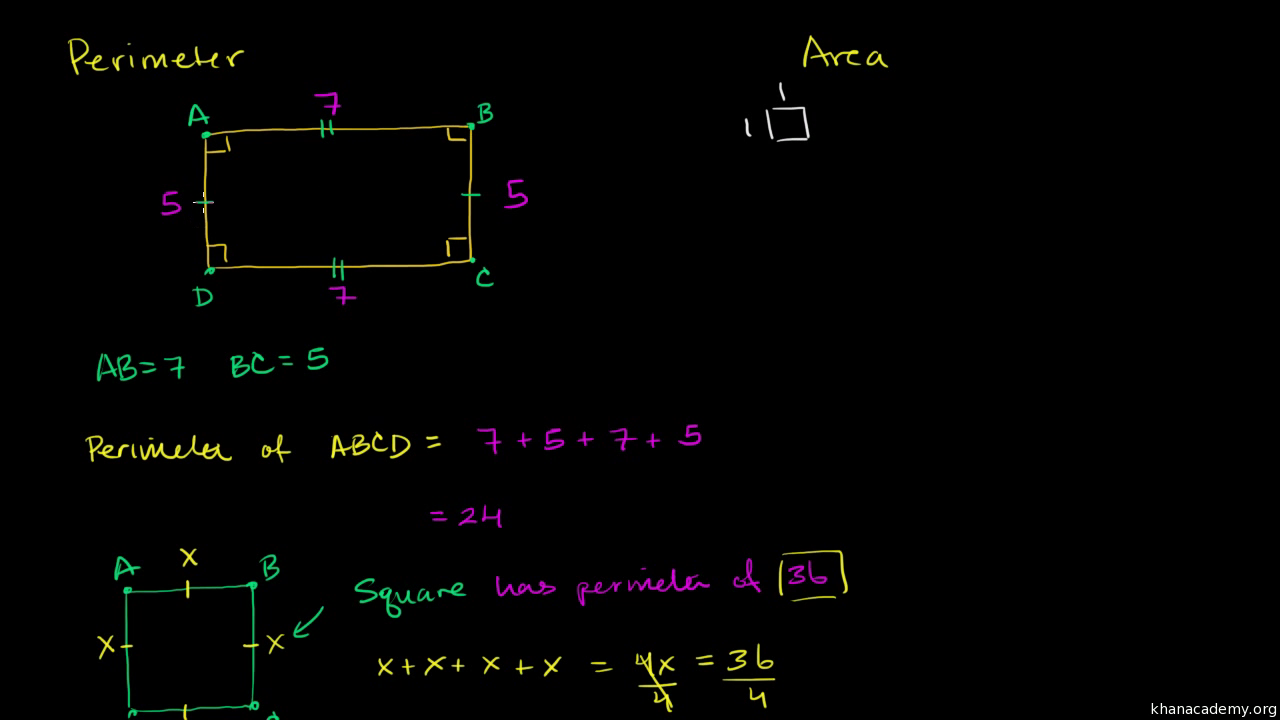
Xem video này để học cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình cơ bản như hình vuông, hình chữ nhật và tam giác.
Diện tích và chu vi: Cơ bản | Chu vi, diện tích và thể tích | Hình học | Khan Academy
READ MORE:
Xem video này để tìm hiểu về khái niệm chu vi và cách tính chu vi của các hình cơ bản như hình vuông và hình chữ nhật.
Giới thiệu về chu vi | Đo lường | Tiền Đại số | Khan Academy