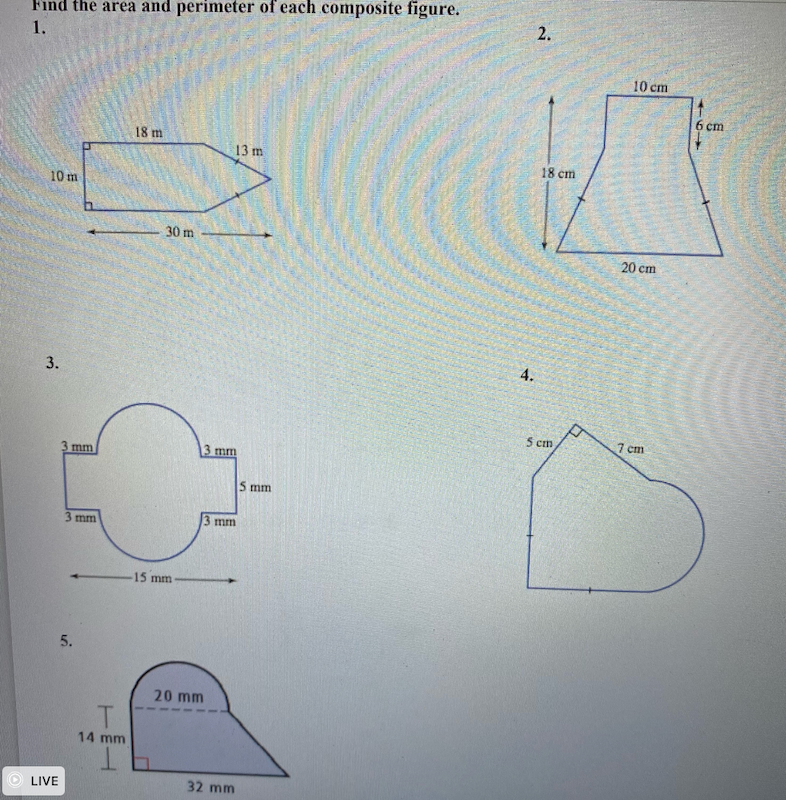
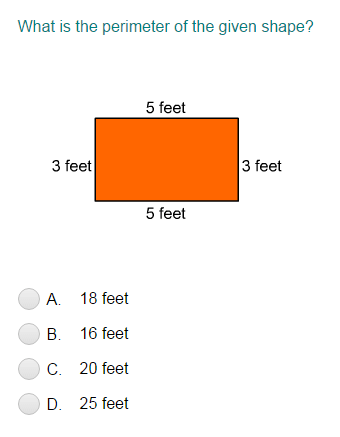
Topic what is the perimeter of triangle jeg: Understanding the perimeter of triangle JEG involves adding the lengths of its three sides. Whether it's an equilateral, isosceles, or scalene triangle, knowing how to calculate the perimeter is crucial for various applications in geometry and real-life situations. This article explores the different methods and formulas to find the perimeter of any triangle effectively.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction
- Definition and Basic Formula
- Methods to Calculate Perimeter
- Special Types of Triangles
- Example Calculations
- Applications of Triangle Perimeter
- FAQs
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của tam giác đều, bao gồm công thức và ví dụ minh họa, phù hợp với nội dung về tính chu vi của tam giác JEG.
Perimeter of a Triangle
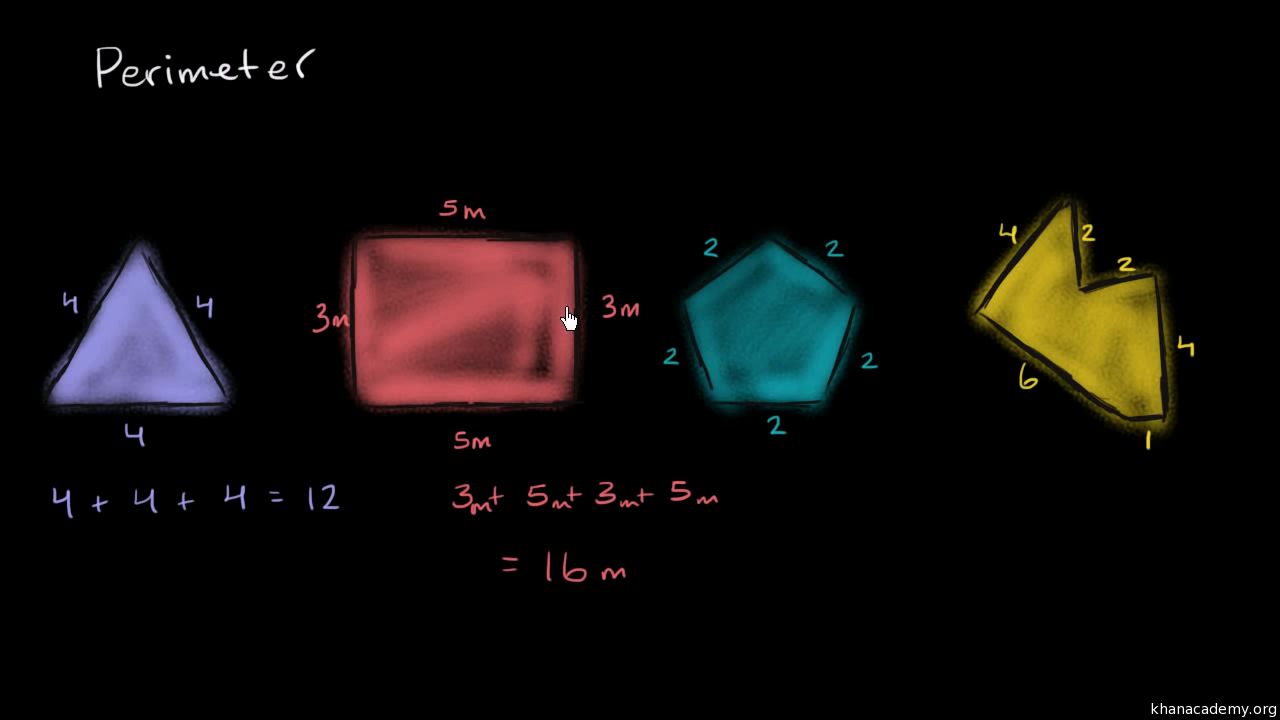
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length around the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its sides. The basic formula to find the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Examples of Calculating Perimeter
-
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal. If each side is \( s \), the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3s \]Example: If each side of an equilateral triangle is 6 units, then:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 \times 6 = 18 \text{ units} \] -
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides equal. If the equal sides are \( a \) and the base is \( b \), the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2a + b \]Example: If the equal sides are 5 units each and the base is 8 units, then:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times 5 + 8 = 18 \text{ units} \] -
Right Triangle
A right triangle can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse if needed. Given sides \( a \) and \( b \), and hypotenuse \( c \), the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]Example: For a right triangle with sides 3 units and 4 units, the hypotenuse is 5 units (since \( \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = 5 \)). Thus, the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
Special Triangle Formulas
For other types of triangles, such as those calculated using coordinates or more complex methods, different formulas may apply, but the general approach remains the same: summing the lengths of all sides.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. Whether the triangle is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene, calculating the perimeter involves adding the side lengths. This simple yet fundamental concept is essential in various fields, including geometry, construction, and navigation. In this article, we will explore the different methods to find the perimeter of various types of triangles and their practical applications.
Definition and Basic Formula
The perimeter of a triangle is defined as the total length of its boundary. To find the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. The formula is expressed as:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
In cases where not all sides are given, you can use trigonometric identities to find the missing sides. For example:
- **Given Two Sides and the Included Angle (SAS)**: Use the law of cosines to find the third side: \[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cdot \cos(\gamma)} \] Then, calculate the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
- **Given Two Angles and One Side (ASA)**: Use the law of sines to find the remaining sides: \[ \frac{a}{\sin(\alpha)} = \frac{b}{\sin(\beta)} = \frac{c}{\sin(\gamma)} \] Then, calculate the perimeter by adding the lengths of all three sides.
By understanding and applying these formulas, you can determine the perimeter of any triangle, even if not all sides are directly provided.
Methods to Calculate Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its boundary, calculated by adding the lengths of its sides. Here are detailed methods to calculate the perimeter of various types of triangles:
1. General Method
For any triangle with side lengths \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
2. Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. If each side length is \(a\), the perimeter is:
\[ P = 3a \]
3. Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. If the equal sides are \(a\) and the base is \(b\), the perimeter is:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
4. Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. The perimeter is simply the sum of the side lengths:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
5. Right Triangle
For a right triangle, where one angle is \(90^\circ\), the sides are typically denoted as the base (\(b\)), the height (\(h\)), and the hypotenuse (\(c\)). Using the Pythagorean theorem, if \(b\) and \(h\) are known, the hypotenuse \(c\) is calculated as:
\[ c = \sqrt{b^2 + h^2} \]
Then the perimeter is:
\[ P = b + h + c \]
or substituting \(c\):
\[ P = b + h + \sqrt{b^2 + h^2} \]
Step-by-Step Example
- Note down the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit.
- Add the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter.
- Express the perimeter with the appropriate unit.
For example, to find the perimeter of a triangle with sides 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm:
\[ P = 5 + 4 + 3 = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
Applications
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is useful in various real-world scenarios, such as determining the amount of fencing needed to enclose a triangular garden or the length of trim required to frame a triangular section of a room.
Special Types of Triangles
Triangles come in various forms, each with unique properties. Understanding these special types of triangles can help in calculating their perimeter and solving related problems. Here are some of the primary types:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides and angles are equal. The formula for the perimeter is \( P = 3a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Isosceles Triangle: Has two equal sides and two equal angles. The perimeter formula is \( P = 2a + b \), where \( a \) is the length of the equal sides and \( b \) is the base.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides and angles are different. The perimeter is simply the sum of all three sides, \( P = a + b + c \).
- Right Triangle: Has one 90-degree angle. The perimeter can be found using the formula \( P = a + b + c \), where \( c \) is the hypotenuse, calculated using the Pythagorean theorem \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \).
Each of these triangles has distinct characteristics that can be utilized in various geometric calculations and practical applications. For example, the simplicity of an equilateral triangle makes it easy to calculate its perimeter, while the properties of a right triangle are essential in trigonometry.

Example Calculations
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is essential for solving various geometric problems. Here, we will go through some example calculations to illustrate different methods.
Example 1: Scalene Triangle
Given a triangle ABC with sides AB = 6 inches, BC = 8 inches, and AC = 10 inches, the perimeter is calculated as:
- Check if all sides are known: AB = 6 inches, BC = 8 inches, AC = 10 inches.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a triangle, \( P = a + b + c \).
- Calculate: \( P = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 \) inches.
Example 2: Right Triangle
For a right triangle PQR with sides PQ = 4 inches and QR = 3 inches, find the perimeter:
- Calculate the hypotenuse PR using the Pythagorean theorem: \( PR^2 = PQ^2 + QR^2 \).
- \( PR = \sqrt{4^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{16 + 9} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \) inches.
- Find the perimeter: \( P = PQ + QR + PR = 4 + 3 + 5 = 12 \) inches.
Example 3: Equilateral Triangle
Given a rectangular wire bent into an equilateral triangle with a perimeter of 297 inches, find the length of each side:
- The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is given by \( P = 3a \), where \( a \) is the side length.
- Solve for \( a \): \( 297 = 3a \) which gives \( a = 99 \) inches.
Example 4: Isosceles Triangle
Given an isosceles triangle with two equal sides of 17 inches each and a total perimeter of 48 inches, find the length of the base:
- Let the base be \( b \). The perimeter formula for an isosceles triangle is \( P = 2l + b \).
- Given \( P = 48 \) inches and \( l = 17 \) inches, solve for \( b \): \( 48 = 2(17) + b \) which simplifies to \( b = 14 \) inches.
Applications of Triangle Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle finds its use in various real-life scenarios. Below are some key applications where calculating the perimeter of a triangle is essential:
-
Fencing a Triangular Garden
If you have a triangular-shaped garden and you want to install a fence around it, knowing the perimeter is crucial. By measuring the lengths of all three sides of the garden and summing them up, you get the total length of fencing material required.
For example, if the sides of the garden are 10 meters, 15 meters, and 20 meters, the total perimeter (and hence the length of the fence needed) would be \( 10 + 15 + 20 = 45 \) meters.
-
Tying a Triangular Box
When packaging a triangular-shaped box, calculating the perimeter helps determine the length of the string or ribbon needed to wrap around the box. This ensures that the packaging material completely covers the box without falling short.
For a box with sides measuring 8 cm, 12 cm, and 15 cm, the total length of the ribbon needed to wrap around it is \( 8 + 12 + 15 = 35 \) cm.
-
Constructing Triangular Structures
In construction, knowing the perimeter of triangular sections is essential for estimating the amount of materials required. This is particularly important in the construction of roofs, bridges, and other architectural elements that incorporate triangular shapes.
For instance, if a triangular roof section has sides of 25 feet, 30 feet, and 35 feet, the perimeter helps in determining the length of the roof edge, which is \( 25 + 30 + 35 = 90 \) feet.
-
Surveying and Mapping
In land surveying, triangles are often used to divide the land into manageable sections. Knowing the perimeter of these triangular sections allows for accurate calculations of distances and areas, which is crucial for mapping and planning purposes.
For a triangular plot with sides 50 meters, 70 meters, and 90 meters, the perimeter is \( 50 + 70 + 90 = 210 \) meters, aiding in the estimation of boundary lengths.
-
Crafts and Design
In various crafts and design projects, the perimeter of triangles can be used to determine the amount of material needed, such as fabric, wire, or beads. This ensures efficient use of resources without wastage.
For example, if you are making a triangular patchwork quilt with side lengths of 30 cm, 40 cm, and 50 cm, the total length of the edges that you need to cover or decorate is \( 30 + 40 + 50 = 120 \) cm.
FAQs
- What is the perimeter of a triangle?
- What is the formula for a triangle's perimeter?
- How to calculate the perimeter of a right triangle?
- How to find the third side and the perimeter of a triangle with given sides?
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its three sides. It's calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides together.
The formula to find the perimeter of a triangle depends on the given information. For example, if you have the lengths of all three sides, you simply add them together. If you have two sides and an included angle, you add those two sides together and then add the third side. If you have two angles and the included side, you would use the Law of Sines or Cosines to find the length of the third side and then add all three sides together.
In a right triangle, one of the angles is a right angle (90 degrees). To calculate the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse. You simply add the lengths of all three sides together.
If you are given the lengths of two sides of a triangle, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the third side (in the case of a right triangle) or the Law of Cosines (for any triangle). Once you have all three side lengths, you add them together to find the perimeter.
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của tam giác đều, bao gồm công thức và ví dụ minh họa, phù hợp với nội dung về tính chu vi của tam giác JEG.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi của Tam Giác Đều | Hình học | Toán