Topic perimeter given coordinates calculator: Unlock the simplicity of geometry with our "Perimeter Given Coordinates Calculator." This tool effortlessly calculates the perimeter of polygons using their vertex coordinates. Ideal for students, teachers, and professionals, it ensures accurate and quick results, making geometry problems a breeze. Start using it today to enhance your mathematical efficiency and precision.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Calculation Using Coordinates
- Introduction
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Polygon
- Using Online Calculators
- Formulas and Examples
- Applications and Use Cases
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của các hình dạng khác nhau dựa trên tọa độ các điểm đỉnh.
Perimeter Calculation Using Coordinates
This guide explains how to calculate the perimeter of different geometric shapes when given the coordinates of their vertices. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape, and using coordinates allows precise calculations.
1. Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
To find the perimeter of a quadrilateral given its vertices, follow these steps:
- Use the distance formula to find the length of each side.
- Sum the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter.
The distance formula between two points \( (x_1, y_1) \) and \( (x_2, y_2) \) is:
\[
D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Example:
Given vertices of quadrilateral DEFG at (5, 7), (8, 7), (1, 3), and (9, 3), calculate the perimeter:
- Calculate \( DE \): \[ DE = \sqrt{(8 - 5)^2 + (7 - 7)^2} = 3 \]
- Calculate \( FG \): \[ FG = \sqrt{(9 - 1)^2 + (3 - 3)^2} = 8 \]
- Calculate \( EG \): \[ EG = \sqrt{(8 - 9)^2 + (7 - 3)^2} = 4.1 \]
- Calculate \( FD \): \[ FD = \sqrt{(5 - 1)^2 + (7 - 3)^2} = 5.7 \]
Sum the lengths to get the perimeter:
\[
Perimeter = 3 + 8 + 4.1 + 5.7 = 20.8
\]
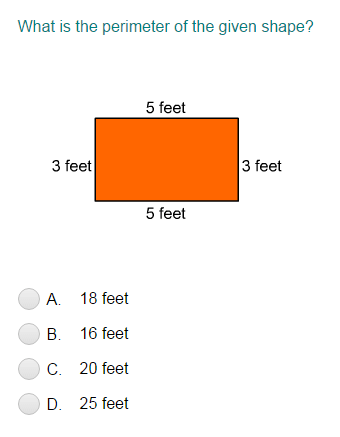
2. Perimeter of a Rectangle
To find the perimeter of a rectangle given its vertices, identify the lengths of its sides using the distance formula, then use the perimeter formula:
Perimeter formula:
\[
Perimeter = 2 \times (width + height)
\]
Example:
Given vertices of a rectangle at (0, 0), (-7, 0), (-7, -4), and (0, -4), calculate the perimeter:
- Calculate the width: \[ Width = \sqrt{(-7 - 0)^2 + (0 - 0)^2} = 7 \]
- Calculate the height: \[ Height = \sqrt{(0 - 0)^2 + (-4 - 0)^2} = 4 \]
Sum the lengths to get the perimeter:
\[
Perimeter = 2 \times (7 + 4) = 22
\]
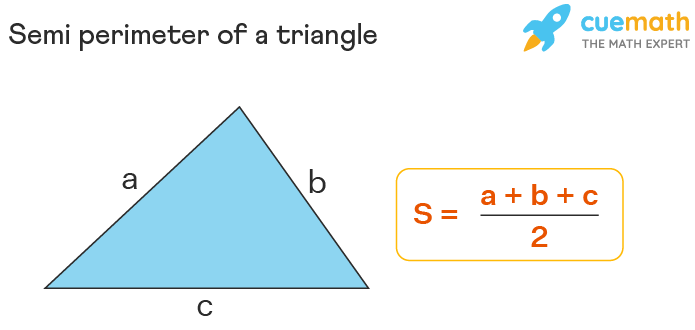
3. Perimeter of a Triangle
To find the perimeter of a triangle, use the distance formula to calculate each side length, then sum these lengths:
Example:
Given vertices of triangle ABC at (1, 7), (-5, 1), and (5, -11), calculate the perimeter:
- Calculate \( AB \): \[ AB = \sqrt{((-5 - 1)^2 + (1 - 7)^2)} = \sqrt{36 + 36} = 8.49 \]
- Calculate \( BC \): \[ BC = \sqrt{((5 + 5)^2 + (-11 - 1)^2)} = \sqrt{100 + 144} = 12.81 \]
- Calculate \( AC \): \[ AC = \sqrt{((5 - 1)^2 + (-11 - 7)^2)} = \sqrt{16 + 324} = 18.44 \]
Sum the lengths to get the perimeter:
\[
Perimeter = 8.49 + 12.81 + 18.44 = 39.74
\]
Using these steps, you can calculate the perimeter of various shapes accurately given their coordinates.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Calculating the perimeter of a shape given its coordinates is a fundamental task in geometry, useful in various fields such as surveying, navigation, and computer graphics. This process involves determining the distances between consecutive points using the Euclidean distance formula and summing these distances. This article will guide you through the step-by-step procedure of calculating the perimeter for different types of polygons using their vertex coordinates.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
Calculating the perimeter of a quadrilateral involves finding the sum of the lengths of all its sides. This can be done using the coordinates of the vertices. Here is a detailed, step-by-step process:
Identify the coordinates of each vertex: Each vertex is represented by a pair of coordinates \((x, y)\) in a two-dimensional Cartesian plane.
Compute the distance between consecutive vertices using the distance formula:
\[
\text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]Repeat this for all pairs of consecutive vertices.
Add up the distances: Sum the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter.
For example, consider a quadrilateral with vertices A(1, 2), B(4, 6), C(7, 2), and D(4, -2). To calculate its perimeter:
Distance AB: \(\sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (6 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
Distance BC: \(\sqrt{(7 - 4)^2 + (2 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
Distance CD: \(\sqrt{(7 - 4)^2 + (2 - (-2))^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
Distance DA: \(\sqrt{(1 - 4)^2 + (2 - (-2))^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
The perimeter is the sum of these distances: \(5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20\) units.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of a quadrilateral using the coordinates of its vertices.
Calculating the Perimeter of a Polygon
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon given its coordinates, follow these steps:
- Identify the Coordinates: List the coordinates of all vertices in order.
- Compute the Distances: Use the distance formula to find the length of each side:
$$ \text{distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} $$
- Sum the Distances: Add the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter.
For example, given a polygon with vertices \( A(2, 4) \), \( B(5, 7) \), \( C(8, 4) \), and \( D(5, 1) \):
- Distance \( AB \): $$ \sqrt{(5 - 2)^2 + (7 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 $$
- Distance \( BC \): $$ \sqrt{(8 - 5)^2 + (4 - 7)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 $$
- Distance \( CD \): $$ \sqrt{(5 - 8)^2 + (1 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 $$
- Distance \( DA \): $$ \sqrt{(2 - 5)^2 + (4 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 $$
The perimeter is calculated by summing these distances:
$$ \text{Perimeter} = AB + BC + CD + DA = 4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 = 16.96 $$
Therefore, the perimeter of the polygon is approximately 16.96 units.
Using Online Calculators
Online calculators for calculating the perimeter given coordinates are incredibly useful tools that simplify complex mathematical processes. These calculators help users determine the perimeter of various geometric shapes by inputting the coordinates of their vertices. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use these calculators effectively:
-
Identify the coordinates of each vertex of the shape you are working with. These should be in a two-dimensional Cartesian plane and represented as (x, y).
-
Input the coordinates into the calculator. Most online tools have a simple interface where you can enter each coordinate pair.
-
The calculator uses the distance formula to compute the length of each side of the shape. The distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is calculated as:
$$\text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2}$$
-
After computing the lengths of all sides, the calculator sums these distances to find the perimeter. For a polygon with vertices (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn), the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
$$P = \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2} + \sqrt{(x_1 - x_n)^2 + (y_1 - y_n)^2}$$
-
Review the results provided by the calculator. These tools often also show the intermediate steps, allowing users to understand how the final result was obtained.
Using these online calculators saves time and reduces the potential for errors in manual calculations, making them essential for students, professionals, and anyone working with geometric figures.

Formulas and Examples
When calculating the perimeter of a polygon, it is essential to know the coordinates of each vertex. This section provides formulas and examples to help you understand the process.
- Identify the coordinates of each vertex of the polygon. Each vertex is represented by a set of coordinates (x, y) in a two-dimensional Cartesian plane.
- Compute the distance between consecutive vertices using the distance formula:
\( \text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \) - Add up the distances of all sides to find the perimeter:
\( \text{Perimeter} = \sum \text{Distance} \)
For example, consider a polygon with vertices at A(2, 4), B(5, 7), C(8, 4), and D(5, 1). The perimeter can be calculated as follows:
| Distance AB: | \( \sqrt{(5 - 2)^2 + (7 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 \) |
| Distance BC: | \( \sqrt{(8 - 5)^2 + (4 - 7)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + (-3)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 \) |
| Distance CD: | \( \sqrt{(5 - 8)^2 + (1 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{(-3)^2 + (-3)^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 \) |
| Distance DA: | \( \sqrt{(2 - 5)^2 + (4 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{(-3)^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{18} \approx 4.24 \) |
| Perimeter: | \( 4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 + 4.24 = 16.96 \) |
Following these steps ensures accurate calculation of the perimeter of any polygon using the coordinates of its vertices.
Applications and Use Cases
Online calculators for calculating the perimeter of polygons based on coordinates are extremely useful tools in various fields. These calculators simplify complex mathematical processes, making it easier for users to obtain accurate results quickly. Here are some common applications and use cases:
- Engineering and Architecture: Engineers and architects use these calculators to determine the perimeter of land plots, building layouts, and other structural designs. This helps in planning and ensuring precise measurements.
- Geography and Cartography: Geographers and cartographers utilize these tools to measure the perimeter of geographical features such as lakes, forests, and urban areas based on their coordinates. This is essential for map-making and spatial analysis.
- Land Surveying: Land surveyors rely on perimeter calculators to measure property boundaries accurately. This information is crucial for legal documentation and land division.
- Education: In educational settings, these calculators serve as excellent teaching aids for students learning about geometry, trigonometry, and coordinate systems. They provide a practical way to understand theoretical concepts.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use these tools to measure the perimeter of various urban features such as parks, residential areas, and commercial zones. This assists in effective city planning and resource allocation.
- Agriculture: Farmers and agricultural planners utilize perimeter calculators to measure fields and plots for crop planning, irrigation systems, and fencing requirements.
These applications highlight the versatility and importance of perimeter calculators in various professional and academic fields. By simplifying calculations and ensuring accuracy, these tools contribute significantly to efficient planning and decision-making processes.
Additional Resources
Here are some useful online calculators and tools that can help you calculate the perimeter of various geometric shapes given their coordinates:
-
GeoGebra:
GeoGebra offers a comprehensive suite of tools for geometry, algebra, and calculus, including the ability to calculate perimeters of polygons by inputting vertex coordinates. Visit:
-
Desmos Geometry Tool:
Desmos provides an intuitive interface for creating and analyzing geometric shapes. Use its geometry tool to calculate the perimeter by entering the coordinates of each vertex. Visit:
-
CalcTool Perimeter Calculator:
CalcTool offers a straightforward online perimeter calculator for polygons. Simply enter the coordinates of the vertices, and it calculates the perimeter automatically. Visit:
-
OnlineMSchool Perimeter Calculator:
OnlineMSchool provides a detailed polygon perimeter calculator, allowing users to input coordinates and obtain results with visual representations. Visit:
-
MathIsFun Polygon Calculator:
MathIsFun features a polygon calculator that helps in calculating the perimeter and area by entering the coordinates of vertices. Visit:
For those who prefer manual calculations or need to understand the underlying mathematics, the following resources provide detailed explanations and step-by-step guides:
-
Khan Academy Geometry:
Khan Academy offers free, high-quality lessons on geometry, including methods for calculating the perimeter of various shapes using coordinates. Visit:
-
Wolfram Alpha:
Wolfram Alpha allows users to enter specific geometric problems, including finding the perimeter given coordinates, and provides detailed solutions. Visit:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của các hình dạng khác nhau dựa trên tọa độ các điểm đỉnh.
Tìm Chu Vi
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách xác định chu vi của tứ giác bằng cách sử dụng công thức khoảng cách cho bốn điểm.
Cách xác định chu vi của tứ giác bằng công thức khoảng cách của bốn điểm