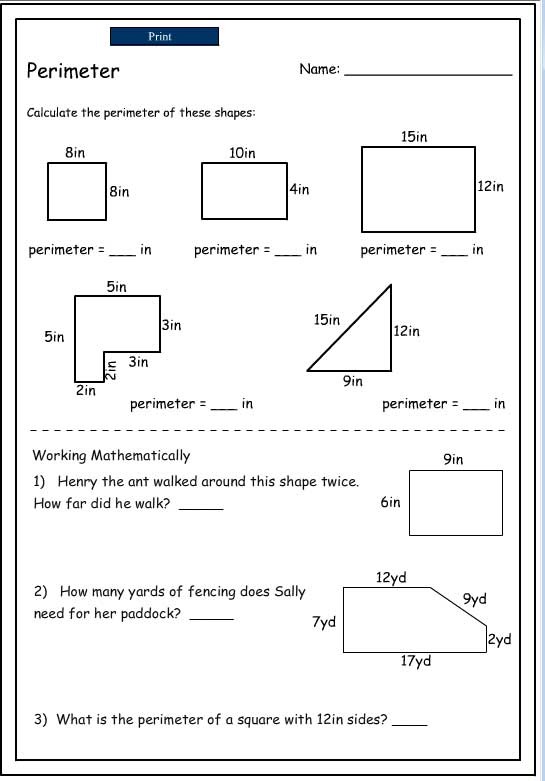
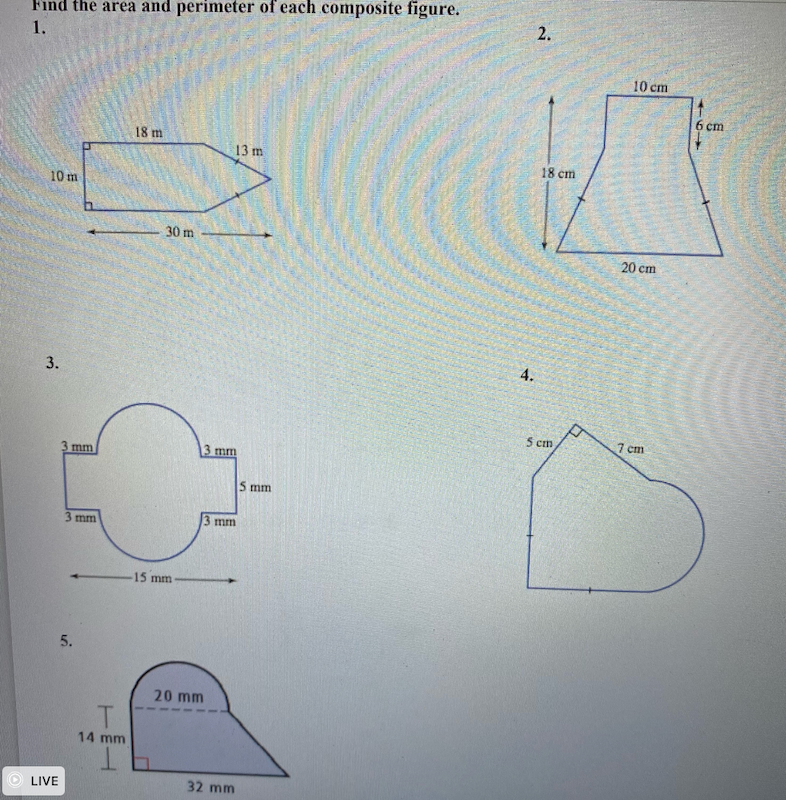
Topic what is the perimeter for a triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry, representing the total distance around the triangle. To find the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all three sides. This article will guide you through different types of triangles and the specific formulas used to calculate their perimeters, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for all learners.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction to Triangle Perimeters
- Basic Perimeter Formula
- Calculating the Perimeter of Different Types of Triangles
- Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle
- Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
- Perimeter of a Scalene Triangle
- Perimeter of a Right Triangle
- Practice Questions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Triangle
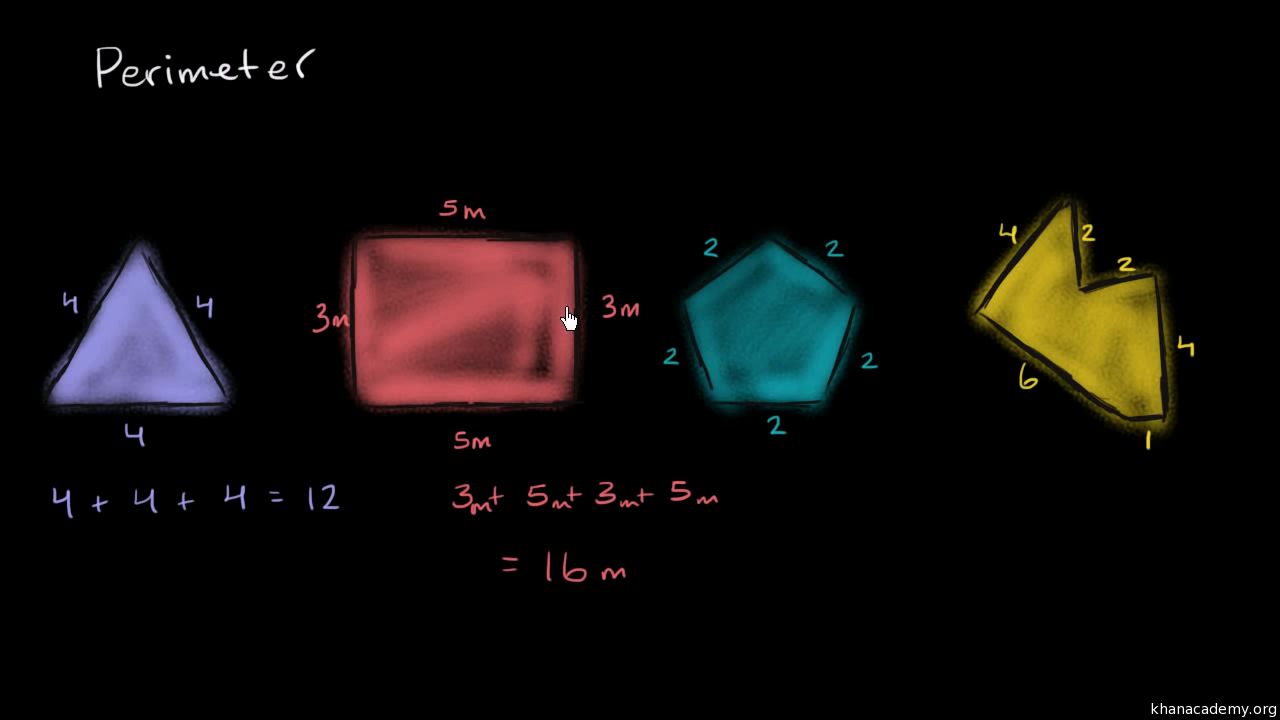
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. This measurement represents the total distance around the triangle.
General Formula
The general formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
Types of Triangles and Their Perimeters
- Equilateral Triangle: A triangle where all three sides are equal.
Formula: \( P = 3a \)
- Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with two equal sides.
Formula: \( P = 2a + b \)
- Scalene Triangle: A triangle with all sides of different lengths.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Right Triangle: A triangle with one 90-degree angle.
If the legs are \( a \) and \( b \), and the hypotenuse is \( c \), then using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\]
The perimeter is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
Example Problems
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides 5, 6, and 3.
Solution:
\[
P = 5 + 6 + 3 = 14
\] - An equilateral triangle has a perimeter of 81 cm. Find the length of each side.
Solution:
\[
81 = 3a \implies a = 27 \text{ cm}
\]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Note down the lengths of all three sides of the given triangle.
- Ensure that all lengths are in the same unit.
- Add the lengths of the three sides.
- The sum represents the perimeter of the triangle.
Common Mistakes
- Confusing perimeter with area. Remember, perimeter is the distance around the shape, not the space inside it.
- Adding sides with different units. Convert all side lengths to the same unit before adding.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Triangle Perimeters
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its boundary, which is calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides. This is a fundamental concept in geometry that applies to all types of triangles, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for solving various geometric problems and can be easily done using the basic perimeter formula.
-
For any triangle with side lengths \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
-
For an equilateral triangle, where all three sides are equal with length \(s\):
\[ P = 3s \]
-
For an isosceles triangle, with two equal sides of length \(a\) and base \(b\):
\[ P = 2a + b \]
-
For a right triangle, where \(a\) and \(b\) are the legs and \(c\) is the hypotenuse:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Calculating the perimeter helps in understanding the properties and measures of different types of triangles. It is also crucial in various real-life applications, such as construction and design, where knowing the boundaries is necessary.
Basic Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its boundary, calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides. The basic formula for the perimeter of a triangle is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Where:
- \(a\) is the length of the first side
- \(b\) is the length of the second side
- \(c\) is the length of the third side
To find the perimeter of any triangle, follow these steps:
- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit.
- Use the formula by adding the lengths of the three sides.
- Write down the calculated perimeter with the appropriate unit.
Here is an example:
| Example: | Given a triangle with side lengths \(a = 5\) cm, \(b = 7\) cm, and \(c = 9\) cm, the perimeter is calculated as: |
| Step 1: | Identify the side lengths: \(a = 5\) cm, \(b = 7\) cm, \(c = 9\) cm. |
| Step 2: | Use the perimeter formula: \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Step 3: | Calculate the sum: \( P = 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 \) cm. |
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 21 cm.
Calculating the Perimeter of Different Types of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its boundary, which is the sum of all its sides. Different types of triangles have specific characteristics, and the methods to calculate their perimeters vary accordingly. Below are the detailed steps to calculate the perimeters for equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles:
1. Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides equal. If the length of each side is a, then the perimeter (P) can be calculated as:
\[ P = 3a \]
For example, if each side of an equilateral triangle is 7 cm, then:
\[ P = 3 \times 7 = 21 \text{ cm} \]
2. Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. If the lengths of the equal sides are a and the base is b, then the perimeter (P) can be calculated as:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
For example, if the equal sides are 5 cm each and the base is 7 cm, then:
\[ P = 2 \times 5 + 7 = 17 \text{ cm} \]
3. Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. If the lengths of the sides are a, b, and c, then the perimeter (P) is simply the sum of these lengths:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
For example, if the sides of a scalene triangle are 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, then:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ cm} \]
4. Right Triangle
For a right triangle, where one of the angles is 90 degrees, the perimeter can be calculated if you know the lengths of the two legs (a and b) and the hypotenuse (c). Using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
Once you have all three sides, the perimeter (P) can be calculated as:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
For example, if the legs of the right triangle are 3 cm and 4 cm, the hypotenuse will be 5 cm (since \[ \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = 5 \]). Hence, the perimeter will be:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ cm} \]
Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are of equal length. This geometric property makes calculating the perimeter straightforward and simple. The formula for the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is:
Perimeter \( P \) = \( 3a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side of the triangle.
To understand this better, let's break it down step by step:
- Identify the length of one side of the equilateral triangle. Let's denote this length as \( a \).
- Since all sides of an equilateral triangle are equal, multiply the length of one side by 3.
- This gives you the total perimeter of the triangle.
For example, if the side length of an equilateral triangle is 5 cm, the perimeter would be:
Perimeter \( P \) = \( 3 \times 5 = 15 \) cm.
Using this simple formula, you can quickly determine the perimeter of any equilateral triangle, ensuring accurate and efficient calculations.
This formula is extremely useful in various fields, including geometry, construction, and design, where precise measurements are crucial.

Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides of equal length. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be calculated using the lengths of its sides. If the two equal sides are denoted as \( a \) and the base (the unequal side) as \( b \), the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the following formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
To calculate the perimeter step by step:
- Identify the lengths of the two equal sides (denoted as \( a \)).
- Identify the length of the base (denoted as \( b \)).
- Substitute these values into the perimeter formula \( P = 2a + b \).
- Perform the arithmetic operation to find the perimeter.
For example, if the lengths of the equal sides are 5 cm each, and the base is 6 cm, the perimeter calculation would be:
\[ P = 2 \times 5\, \text{cm} + 6\, \text{cm} = 10\, \text{cm} + 6\, \text{cm} = 16\, \text{cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the isosceles triangle is 16 cm.
Perimeter of a Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle is a type of triangle where all three sides have different lengths. To find the perimeter of a scalene triangle, you simply add up the lengths of all its sides. Here is a detailed guide on how to calculate the perimeter of a scalene triangle:
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the scalene triangle. Let's denote these sides as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a triangle: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( P \) is the perimeter, and \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the three sides.
- Sum the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter.
For example, if the sides of a scalene triangle are 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 4 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 15 \, \text{cm}
\]
If you only know two sides of the triangle and the included angle, you can use the Law of Cosines to find the third side. The Law of Cosines states:
\[
c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(C)
\]
where \( C \) is the angle opposite side \( c \).
Once you have all three sides, you can then calculate the perimeter using the formula mentioned above.
Perimeter of a Right Triangle
The perimeter of a right triangle can be calculated using the lengths of its three sides. A right triangle has one angle of 90 degrees, with the side opposite this angle being the hypotenuse. The other two sides are referred to as the legs of the triangle.
The formula for the perimeter (P) of a right triangle is:
Where:
- a is one leg of the triangle
- b is the other leg of the triangle
- c is the hypotenuse of the triangle
To find the hypotenuse c, you can use the Pythagorean theorem:
Simplifying this gives:
Once you have calculated the hypotenuse, you can substitute a, b, and c into the perimeter formula.
Example Problem
Suppose you have a right triangle with legs of lengths 3 cm and 4 cm. To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Calculate the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
- Find the perimeter:
Therefore, the perimeter of the right triangle is 12 cm.
Practice Questions
Here are some practice questions to help you understand and calculate the perimeter of different types of triangles. Work through each problem step by step to reinforce your understanding.
-
Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides of length 7 cm, 10 cm, and 5 cm.
Solution:
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c = 7 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} = 22 \, \text{cm}
\] -
Calculate the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 9 inches.
Solution:
For an equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal. The formula for the perimeter is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 \times \text{side} = 3 \times 9 \, \text{inches} = 27 \, \text{inches}
\] -
Determine the perimeter of an isosceles triangle with equal sides of 8 meters each and a base of 6 meters.
Solution:
The formula for the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times \text{side} + \text{base} = 2 \times 8 \, \text{meters} + 6 \, \text{meters} = 22 \, \text{meters}
\] -
Find the perimeter of a right triangle with legs of 6 cm and 8 cm.
Solution:
First, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = \sqrt{100} = 10 \, \text{cm}
\]Then, calculate the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c = 6 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm}
\] -
A triangular garden has two sides of 12 ft and 9 ft, with an included angle of 60 degrees. Calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
Use the law of cosines to find the third side:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma)} = \sqrt{12^2 + 9^2 - 2 \cdot 12 \cdot 9 \cdot \cos(60^\circ)} = \sqrt{144 + 81 - 108} = \sqrt{117} \approx 10.82 \, \text{ft}
\]Then, calculate the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c = 12 \, \text{ft} + 9 \, \text{ft} + 10.82 \, \text{ft} \approx 31.82 \, \text{ft}
\]
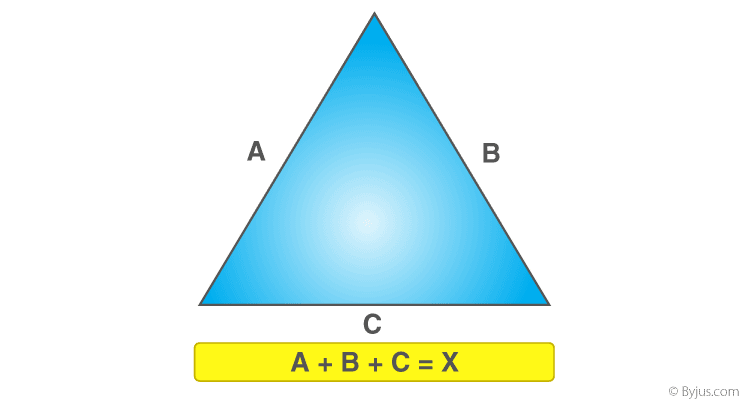
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the Perimeter of a Triangle?
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its boundary. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
-
What is the Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle?
The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle. -
How to Find the Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle?
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3a
\]
where \(a\) is the length of one side. -
Can a Triangle Have the Same Perimeter and Area?
Yes, a triangle can have the same perimeter and area in special cases. Such triangles are known as equable triangles.
-
How to Find the Third Side and Perimeter of a Right Triangle Given Two Sides?
In a right triangle, you can find the third side using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c^2 = a^2 + b^2
\]
where \(c\) is the hypotenuse, and \(a\) and \(b\) are the other two sides. Once you have all three sides, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\] -
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle With Coordinates?
If the vertices of a triangle are given in coordinate form, the lengths of the sides can be calculated using the distance formula. Once the lengths of all sides are known, the perimeter is the sum of these lengths.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi của Tam Giác | Toán Học với Thầy J