Topic perimeter khan academy: Discover the comprehensive resources Khan Academy offers for mastering the concept of perimeter. From introductory lessons and interactive exercises to advanced problems and real-world applications, learn how to calculate and apply perimeter in various contexts with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
- Perimeter Khan Academy Overview
- Perimeter and Area Basics
- Calculating Perimeter of Various Shapes
- Perimeter in 3D Geometry
- Practical Applications of Perimeter
- Interactive Exercises and Practice Problems
- Perimeter Word Problems
- Comparing Area and Perimeter
- Advanced Topics: Koch Snowflake and Fractals
- Video Tutorials and Visual Guides
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Perimeter
- Additional Resources and Quizzes
- YOUTUBE: Video này giới thiệu những khái niệm cơ bản về chu vi và diện tích trong hình học, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về các khái niệm quan trọng này.
Perimeter Khan Academy Overview
Khan Academy provides comprehensive resources for learning about perimeter, including instructional videos, practice exercises, and quizzes. Below is a detailed overview of the content available on the Khan Academy platform related to perimeter.
Introduction to Perimeter
Understanding the perimeter is fundamental in geometry. The perimeter is the total length of all sides of a polygon. It's a basic yet essential concept used in various real-life applications, such as fencing a yard or framing a picture.
Learning Resources
- Introduction to Perimeter: Basic explanations and introductory videos about what perimeter is and how to calculate it for different shapes.
- Finding Perimeter: Videos and articles explaining how to find the perimeter of polygons, including those with missing side lengths.
- Perimeter Word Problems: Practical word problems that apply perimeter calculations to real-world scenarios.
- Comparing Area and Perimeter: Lessons that compare and contrast the concepts of area and perimeter, providing a deeper understanding of their differences and applications.
Practice Exercises
Khan Academy offers a range of practice exercises to reinforce the understanding of perimeter. These exercises are designed to help students apply their knowledge in various contexts:
- Calculating the perimeter by counting unit squares.
- Finding missing side lengths when given the perimeter.
- Solving word problems involving perimeter.
Quizzes and Mastery Points
To ensure mastery of the topic, Khan Academy provides quizzes that students can take to test their understanding. Successfully completing these quizzes earns students mastery points, helping them track their progress:
- Quiz 1: Basic perimeter calculations and word problems.
- Quiz 2: Advanced perimeter problems involving missing side lengths.
- Quiz 3: Comparing and contrasting area and perimeter through various problems.
Interactive Videos
Interactive videos are an integral part of Khan Academy's teaching method. These videos not only explain the concepts but also involve interactive elements where students can participate and practice what they've learned directly within the video environment:
Real-Life Applications
Learning about perimeter is not just for academic purposes. It has various practical applications:
- Building and construction: Knowing the perimeter is essential for planning layouts and materials.
- Interior design: Calculating the perimeter helps in placing furniture and decorations.
- Gardening and landscaping: Designing garden beds and pathways requires perimeter measurements.
Conclusion
Khan Academy's resources on perimeter provide a solid foundation for students to understand and apply this essential geometric concept. With a mix of videos, articles, practice exercises, and quizzes, learners can gain confidence and mastery in calculating and using perimeter in various contexts.
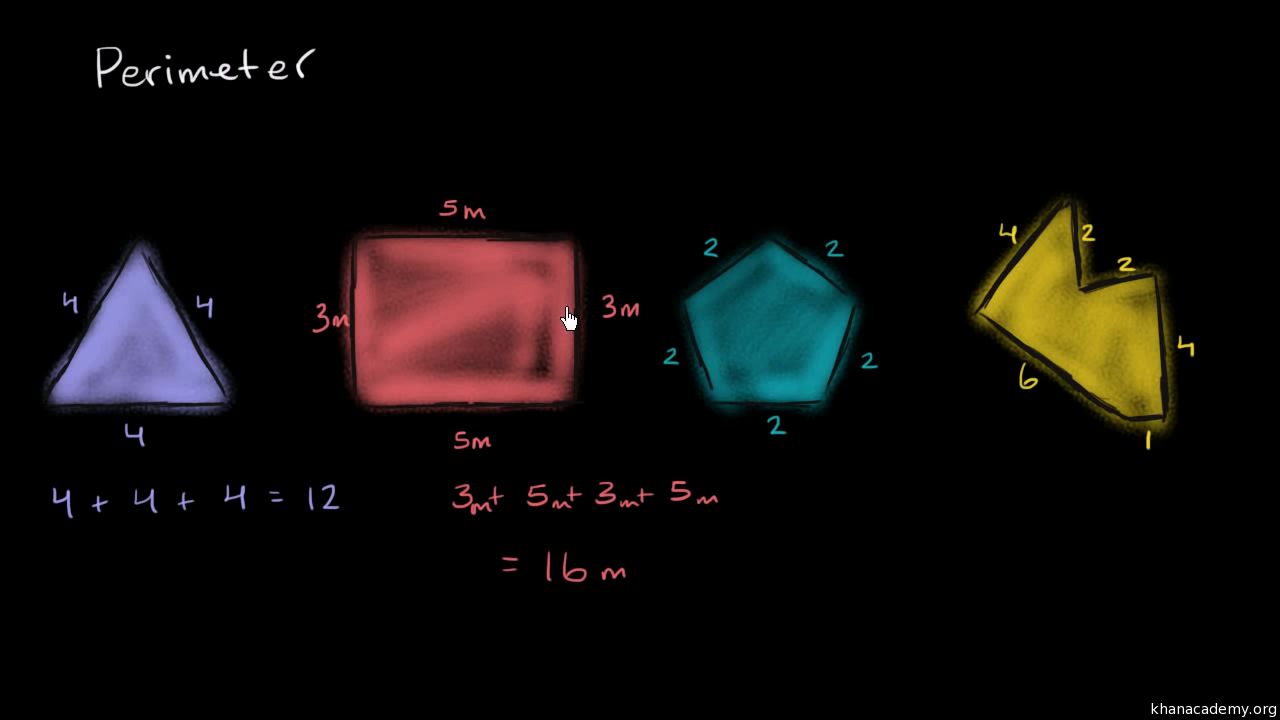
Perimeter and Area Basics
Understanding the basics of perimeter and area is crucial for solving various geometry problems. Here, we'll break down the fundamental concepts and provide step-by-step methods for calculating the perimeter and area of different shapes.
Definitions
- Perimeter: The total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all sides.
- Area: The amount of space enclosed within a shape. It is measured in square units.
Perimeter Formulas
- Rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4 \times s \) where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: \( P = 2 \pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius (also known as the circumference).
Area Formulas
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Square: \( A = s^2 \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \) where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Examples
Let's apply these formulas to some examples:
- Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle with length 8 units and width 5 units.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (8 + 5) = 26 \) units
- Area: \( A = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) square units
- Find the perimeter and area of a circle with radius 3 units.
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( P = 2 \pi \times 3 \approx 18.85 \) units
- Area: \( A = \pi \times 3^2 \approx 28.27 \) square units
Visualizing Perimeter and Area
Using grids can help visualize and calculate the area. For instance, the area of a rectangle can be visualized by counting unit squares within the shape.

Practice Problems
Practice calculating the perimeter and area of various shapes to solidify your understanding:
- A square with a side length of 7 units.
- A triangle with sides measuring 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units.
- A rectangle with a length of 10 units and a width of 4 units.
Further Learning
Explore more exercises and visual guides on .
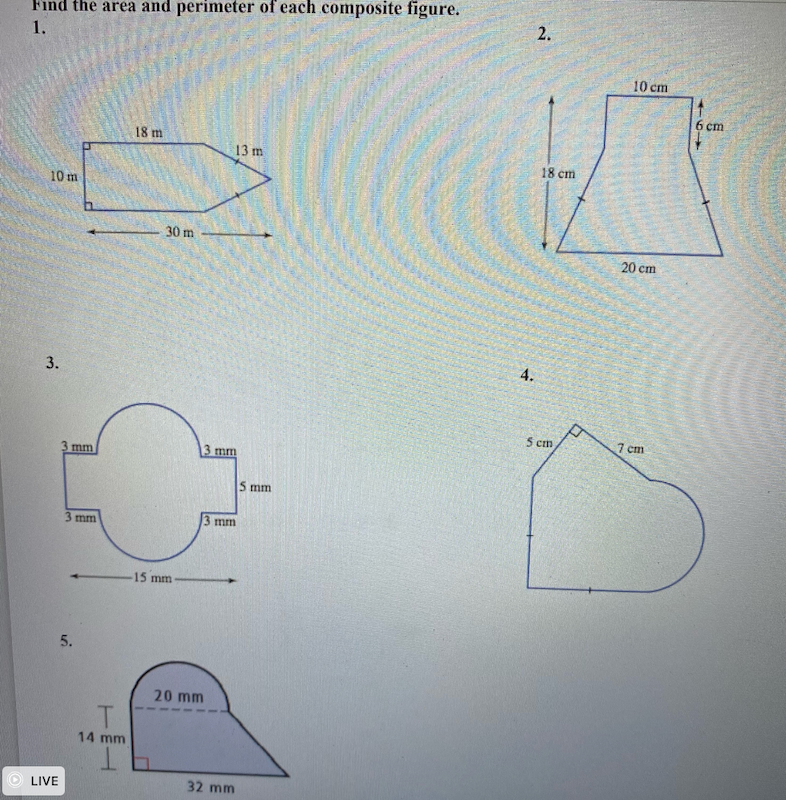
Calculating Perimeter of Various Shapes
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is crucial in geometry. The perimeter is the total length around a shape. Here are the methods to calculate the perimeter for different geometric shapes:
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding together the lengths of all four sides. The formula is:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter, \(l\) is the length, and \(w\) is the width.
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is four times the length of one side. The formula is:
\[
P = 4s
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter and \(s\) is the length of a side.
Perimeter of a Triangle
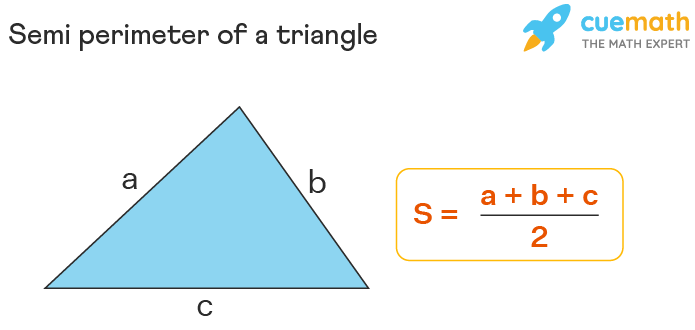
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. The formula is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter, and \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference)
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius or diameter. The formula is:
\[
C = 2\pi r \quad \text{or} \quad C = \pi d
\]
where \(C\) is the circumference, \(r\) is the radius, and \(d\) is the diameter.
Perimeter of a Parallelogram
The perimeter of a parallelogram is the sum of the lengths of all sides. The formula is:
\[
P = 2(a + b)
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter, \(a\) is the length of one pair of opposite sides, and \(b\) is the length of the other pair of opposite sides.
Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. The formula is:
\[
P = a + b + c + d
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter, and \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\) are the lengths of the sides.
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
The perimeter of a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal) is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides. The formula is:
\[
P = n \cdot s
\]
where \(P\) is the perimeter, \(n\) is the number of sides, and \(s\) is the length of one side.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are a few examples and practice problems to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter:
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm.
- Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 4 m.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 7 cm, 8 cm, and 9 cm.
- Compute the circumference of a circle with a radius of 6 cm.
- Find the perimeter of a parallelogram with sides 8 cm and 5 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a trapezoid with sides measuring 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm.
- Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with a side length of 2 cm.
By practicing these problems, you will improve your ability to calculate the perimeter of various shapes accurately.
Perimeter in 3D Geometry
While perimeter is traditionally associated with 2D shapes, understanding its application in 3D geometry can be useful for various mathematical and practical purposes. In 3D geometry, the concept of perimeter can be extended to the edges of polyhedra and other 3D shapes.
Here are some key points to understand how perimeter works in 3D geometry:
1. Perimeter of the Base Shapes
Many 3D shapes have bases that are 2D polygons. To find the perimeter of these bases:
- Cubes and Rectangular Prisms: The base is a square or rectangle. Calculate the perimeter by summing all the sides.
- For a square base with side length \( s \):
- For a rectangular base with length \( l \) and width \( w \):
\[ P = 4s \]
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
- Cylinders: The base is a circle. Calculate the circumference (perimeter) using the radius \( r \):
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
2. Perimeter of Polyhedra
For polyhedra such as cubes, pyramids, and prisms, the perimeter can refer to the total length of all the edges.
- Cubes: Each edge length is \( s \), and there are 12 edges:
\[ P = 12s \]
- Rectangular Prisms: For a prism with dimensions \( l \), \( w \), and \( h \):
\[ P = 4(l + w + h) \]
- Regular Polyhedra: If all edges are equal, multiply the number of edges by the edge length.
3. Perimeter in 3D Space Applications
Understanding the perimeter in 3D shapes is crucial in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and computer graphics. For example, calculating the total edge length of a framework can help in estimating material requirements.
4. Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to reinforce the concept:
- Calculate the perimeter of the base of a rectangular prism with dimensions \( 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( 3 \, \text{cm} \), and \( 2 \, \text{cm} \).
- Find the total edge length of a cube with each side measuring \( 4 \, \text{cm} \).
- Determine the circumference of the base of a cylinder with a radius of \( 7 \, \text{cm} \).
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter in 3D geometry helps bridge the concepts from 2D shapes and enhances problem-solving skills in more complex geometrical contexts.
Practical Applications of Perimeter
Understanding the perimeter of shapes is essential in various real-world contexts. Here are some practical applications where calculating perimeter is useful:
-
Fencing and Landscaping
When planning to build a fence around a yard or garden, calculating the perimeter helps determine the length of the fence needed.
Example: If you have a rectangular garden that is 30 meters long and 20 meters wide, the perimeter (P) is calculated as:
P = 2(l + w)
P = 2(30 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m}) = 100 \, \text{m} -
Building and Construction
In construction, the perimeter of a plot of land helps in planning the boundary walls and layout of buildings.
Example: A rectangular plot of land measures 50 meters by 40 meters. The perimeter (P) is:
P = 2(l + w)
P = 2(50 \, \text{m} + 40 \, \text{m}) = 180 \, \text{m} -
Interior Design
When installing baseboards, crown molding, or wallpaper, knowing the perimeter of the room is crucial for purchasing the correct amount of materials.
Example: A room has four walls with the following lengths: 10 meters, 15 meters, 10 meters, and 15 meters. The perimeter (P) is:
P = 10 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m} = 50 \, \text{m} -
Sports Fields
For designing sports fields, such as a soccer field or a running track, calculating the perimeter helps in setting the boundary lines and lanes.
Example: A standard soccer field measures 100 meters by 70 meters. The perimeter (P) is:
P = 2(l + w)
P = 2(100 \, \text{m} + 70 \, \text{m}) = 340 \, \text{m}
Understanding and calculating perimeter is not only a fundamental mathematical skill but also a practical tool for everyday problem-solving and planning in various fields.

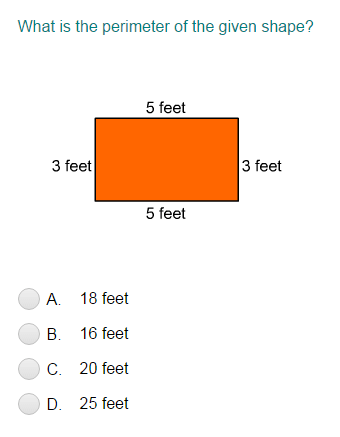
Interactive Exercises and Practice Problems
Engaging with interactive exercises and practice problems is essential for mastering the concept of perimeter. Below are various activities and problems designed to enhance your understanding and skills.
Basic Perimeter Exercises
These exercises will help you get started with calculating the perimeter of simple shapes.
- Find the perimeter by counting unit squares:
- Draw a shape on graph paper and count the unit squares along its edges.
- Example: For a rectangle with length 4 units and width 3 units, count all the unit squares along the edges to find the perimeter.
- Find the perimeter when given side lengths:
- Add up the lengths of all sides of the shape.
- Example: A triangle with sides of 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units has a perimeter of \(3 + 4 + 5 = 12\) units.
Advanced Perimeter Exercises
These exercises will challenge you to apply your knowledge of perimeter in more complex situations.
- Find a missing side length when given the perimeter:
- Use the known perimeter to solve for the unknown side length.
- Example: If a rectangle has a perimeter of 20 units and three sides are known to be 5 units each, find the fourth side.
- Perimeter word problems:
- Apply perimeter calculations to real-world scenarios.
- Example: If you need to put fencing around a rectangular garden that is 10 units long and 6 units wide, calculate the total length of fencing required.
Interactive Practice Problems
Test your skills with these interactive problems:
- Interactive problem sets on Khan Academy:
- Find perimeter by counting units: Get 3 out of 4 questions correct to level up!
- Find perimeter when given side lengths: Get 5 out of 7 questions correct to level up!
- Find a missing side length when given perimeter: Get 3 out of 4 questions correct to level up!
- Perimeter word problems: Get 3 out of 4 questions correct to level up!
- Perimeter quizzes:
- Level up on all the above skills and collect up to 400 Mastery points on Khan Academy quizzes.
Resources
For more detailed interactive exercises and practice problems, visit the Khan Academy's perimeter section where you can find a variety of resources and quizzes to test your knowledge.
Perimeter Word Problems
Solving word problems involving perimeter can help deepen your understanding of how perimeter works in practical scenarios. Here are some examples and steps to solve these types of problems:
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle
Problem: A rectangle has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. What is the perimeter?
- Identify the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \)
- Substitute the given values: \( l = 8 \) meters, \( w = 5 \) meters
- Calculate: \( P = 2 \times (8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \) meters
Example 2: Finding a Missing Side Length
Problem: The perimeter of a rectangular garden is 60 meters. If the length of the garden is 20 meters, what is the width?
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \)
- Rearrange to solve for the width: \( w = \frac{P}{2} - l \)
- Substitute the known values: \( P = 60 \) meters, \( l = 20 \) meters
- Calculate: \( w = \frac{60}{2} - 20 = 30 - 20 = 10 \) meters
Example 3: Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
Problem: A regular hexagon (a six-sided polygon with equal sides) has a side length of 7 meters. What is the perimeter?
- Identify the formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon: \( P = n \times s \)
- Substitute the given values: \( n = 6 \) (number of sides), \( s = 7 \) meters
- Calculate: \( P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \) meters
Practice Problems
- Problem 1: A square playground has a perimeter of 48 meters. What is the length of one side?
- Problem 2: The perimeter of a triangle is 24 meters. If two sides are 8 meters each, what is the length of the third side?
- Problem 3: A rectangular field is twice as long as it is wide. If the perimeter is 90 meters, what are the dimensions of the field?
Interactive Exercises
Practice solving perimeter word problems with interactive exercises on Khan Academy:
Comparing Area and Perimeter
Understanding the difference between area and perimeter is crucial for solving various mathematical problems and applying these concepts in real-world situations. Below, we explore the key differences and provide examples to illustrate how these measurements are used.
Definitions
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the outside of the shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides.
- Area: The area of a shape is the amount of space inside the shape. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square centimeters).
Formulas for Common Shapes
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( P = 2(l + w) \) | \( A = l \times w \) |
| Square | \( P = 4s \) | \( A = s^2 \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \) |
| Circle | \( P = 2\pi r \) (Circumference) | \( A = \pi r^2 \) |
Examples
Here are some practical examples to help understand how to calculate and compare area and perimeter:
Example 1: Rectangle
Consider a rectangle with a length of 10 units and a width of 5 units:
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(10 + 5) = 30 \) units
- Area: \( A = 10 \times 5 = 50 \) square units
Example 2: Square
Consider a square with a side length of 4 units:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \) units
- Area: \( A = 4^2 = 16 \) square units
Example 3: Triangle
Consider a triangle with sides of 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units, and a height corresponding to the 4-unit base:
- Perimeter: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) units
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 3 = 6 \) square units
Example 4: Circle
Consider a circle with a radius of 7 units:
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( P = 2\pi \times 7 \approx 43.98 \) units
- Area: \( A = \pi \times 7^2 \approx 153.94 \) square units
Comparison in Real-World Situations
In practical applications, understanding the relationship between area and perimeter can be crucial. For example, when fencing a garden (perimeter) versus planting crops (area), knowing how these measurements affect the outcome helps in planning and resource allocation.
Through these examples and explanations, students can better grasp the concepts of area and perimeter, making it easier to apply them in both academic and real-life scenarios.
Advanced Topics: Koch Snowflake and Fractals
The Koch snowflake is a classic example of a fractal, a shape that exhibits self-similarity at different scales. This means that no matter how much you zoom in on the shape, you'll always see the same pattern. The construction of the Koch snowflake begins with an equilateral triangle. Here is a step-by-step process to understand its formation and properties:
- Start with an equilateral triangle.
- Divide each side of the triangle into three equal parts.
- Construct an equilateral triangle on the middle segment of each side.
- Remove the base of the constructed triangle, leaving a star shape.
- Repeat steps 2-4 for each of the new segments indefinitely.
Despite the seemingly simple construction process, the Koch snowflake has some intriguing properties:
- Infinite Perimeter: As you add more triangles, the perimeter of the snowflake increases without bound. Mathematically, the perimeter approaches infinity.
- Finite Area: Although the perimeter is infinite, the area enclosed by the Koch snowflake is finite. This paradoxical property is a hallmark of fractals.
The formula for the perimeter \(P_n\) and area \(A_n\) after \(n\) iterations can be expressed as:
- \(P_n = P_0 \left(\frac{4}{3}\right)^n\), where \(P_0\) is the initial perimeter of the equilateral triangle.
- \(A_n = \frac{2 \sqrt{3}}{5} s^2\), where \(s\) is the side length of the initial equilateral triangle.
The Koch snowflake illustrates important concepts in fractal geometry, showing how a figure can have an infinite boundary while enclosing a finite area. Fractals like the Koch snowflake are used in various fields, from computer graphics to nature modeling, due to their unique properties of self-similarity and infinite complexity.
Here is a visual representation of the first few iterations of the Koch snowflake:
| Iteration | Shape | Perimeter | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |  |
\(3s\) | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}s^2\) |
| 1 |  |
\(4s\) | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}s^2 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{12}s^2\) |
| 2 |  |
\(4 \cdot \frac{4}{3}s\) | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}s^2 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{12}s^2 + \frac{\sqrt{3}}{36}s^2\) |
For further exploration of the Koch snowflake and other fascinating fractals, you can watch detailed videos and tutorials on .
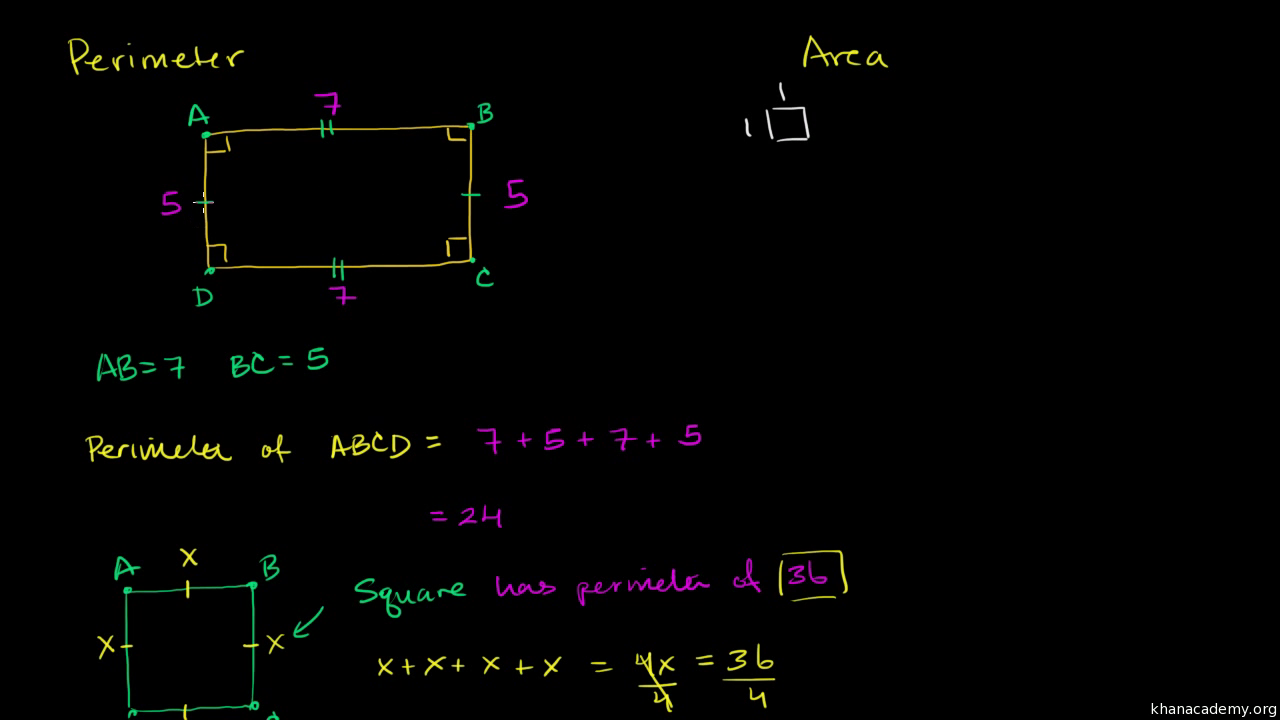
Video Tutorials and Visual Guides
Understanding perimeter is made easier with visual aids and step-by-step tutorials. Below is a curated list of video tutorials and guides available on Khan Academy to help you master the concept of perimeter.
- Perimeter Introduction
This video introduces the concept of perimeter, explaining how to measure the distance around different shapes.
- Calculating Perimeter
Learn how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes, including polygons and irregular figures.
- Finding Perimeter with Missing Sides
This tutorial teaches you how to determine the perimeter when some side lengths are missing, using logical reasoning and arithmetic.
- Perimeter Word Problems
Solve real-world problems involving perimeter to enhance your understanding and application of the concept.
- Comparing Area and Perimeter
Explore the differences between area and perimeter and how to compare them effectively through visual examples.
These resources are designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of perimeter, making learning interactive and engaging.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Perimeter
Here are some common questions and detailed answers about the concept of perimeter:
- What is perimeter?
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
- How do you calculate the perimeter of a rectangle?
To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, use the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
For example, if the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter is:
\[ 2 \times (5 + 3) = 16 \text{ units} \]
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a triangle?
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If the sides are denoted as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- How can I find the perimeter of a circle?
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference. It can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r \]
where \( r \) is the radius of the circle and \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Is there a difference between perimeter and area?
Yes, the perimeter is the distance around a shape, while the area is the measure of the space inside the shape. They are different concepts and are calculated differently.
- Can perimeter be applied to 3D shapes?
Perimeter typically applies to 2D shapes. For 3D shapes, we often refer to the edge length or surface area instead.
- Why is understanding perimeter important?
Understanding perimeter is important in various real-life applications such as fencing a yard, framing a picture, or planning the layout of a garden. It helps in measuring boundaries and understanding the dimensions of different shapes.
- Are there interactive exercises to practice perimeter calculations?
Yes, there are many interactive exercises available on Khan Academy and other educational websites that help reinforce the concept of perimeter through practice problems and real-life applications.
Additional Resources and Quizzes
To further enhance your understanding of perimeter, Khan Academy offers a variety of additional resources and quizzes. These materials provide comprehensive learning tools and practice exercises to solidify your knowledge. Below are some key resources and quizzes available:
-
Learning Resources
-
-
Practice Quizzes
-
Each quiz and resource is designed to guide you step-by-step through the concepts, offering practice problems and explanations to ensure you grasp the fundamentals of perimeter. Utilize these tools to master perimeter calculations and related geometry concepts.
Video này giới thiệu những khái niệm cơ bản về chu vi và diện tích trong hình học, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về các khái niệm quan trọng này.
Chu vi và diện tích: những điều cơ bản | Chu vi, diện tích và thể tích | Hình học | Khan Academy
READ MORE:
Video này giới thiệu về khái niệm chu vi trong đo lường, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức cơ bản trong môn Tiền Đại số.
Giới thiệu về chu vi | Đo lường | Tiền Đại số | Khan Academy