Topic what is the perimeter of polygon xydb: The perimeter of polygon XYDB is a fundamental concept in geometry, involving the sum of all its sides. Understanding how to calculate this measurement is crucial for various applications in mathematics and beyond. This article delves into the methods and formulas used to determine the perimeter, providing examples and practical insights to enhance your comprehension.
Table of Content
Perimeter of Polygon XYDB
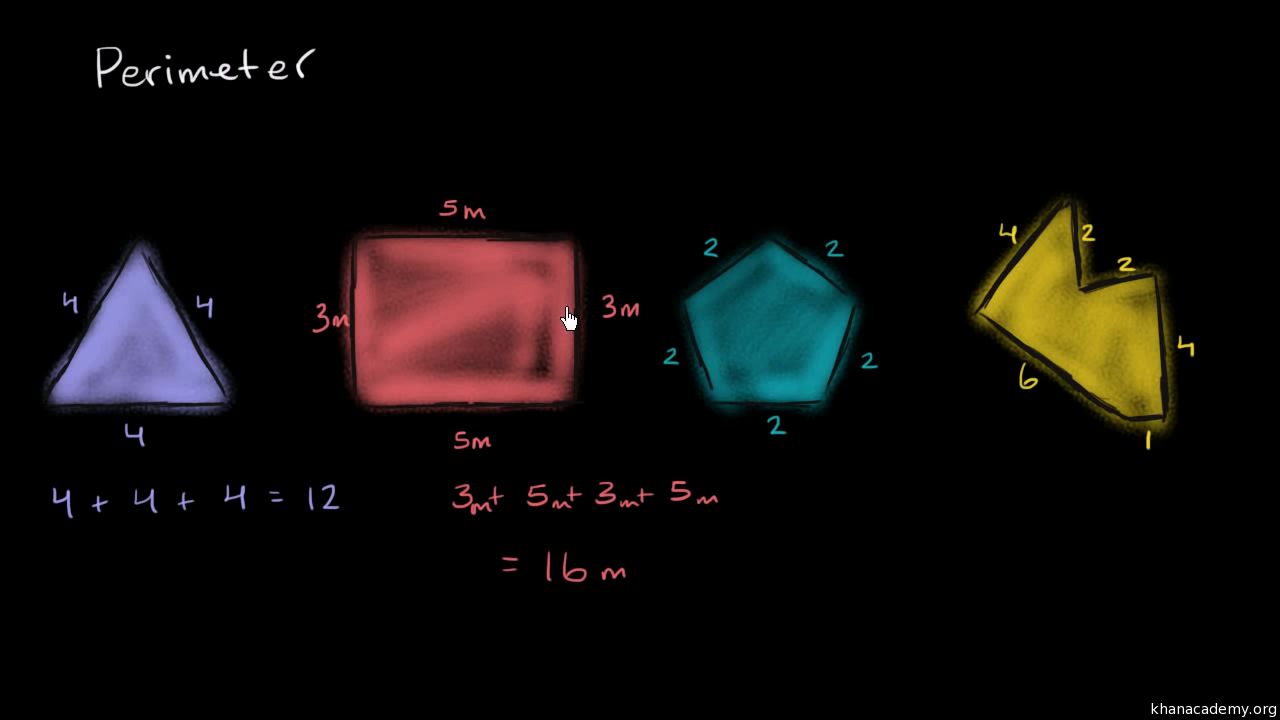
The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the outer edges of the polygon. It can be calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. Below are steps and examples for calculating the perimeter of both regular and irregular polygons.
Formula
For any polygon, the perimeter (P) is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
$$ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i $$
Where \( s_i \) represents the length of each side.
Steps to Find Perimeter
- Identify if the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal).
- For a regular polygon, multiply the length of one side by the number of sides:
$$ P = n \times s $$
- \( n \) = number of sides
- \( s \) = length of one side
- For an irregular polygon, sum the lengths of all sides:
$$ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + \ldots + s_n $$
Example Calculations
| Polygon Type | Formula | Example |
| Regular Hexagon | $$ P = 6 \times s $$ | If each side is 7 feet: $$ P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \text{ feet} $$ |
| Irregular Quadrilateral | $$ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 $$ | If sides are 7, 9, 6, and 5 feet: $$ P = 7 + 9 + 6 + 5 = 27 \text{ feet} $$ |
Common Regular Polygon Formulas
- Equilateral Triangle: $$ P = 3 \times s $$
- Square: $$ P = 4 \times s $$
- Regular Pentagon: $$ P = 5 \times s $$
- Regular Hexagon: $$ P = 6 \times s $$
Conclusion
To find the perimeter of polygon XYDB, sum the lengths of all its sides. Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before summing.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Polygons
Polygons are fundamental shapes in geometry, defined as flat, two-dimensional figures bounded by straight sides. They can range from simple triangles and rectangles to more complex shapes with multiple sides. Understanding the basic properties and types of polygons is essential in various fields of mathematics and its applications.
There are two main types of polygons:
- Regular Polygons: These have all sides and angles equal, like equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Polygons: These have sides and angles that are not necessarily equal, such as scalene triangles and rectangles.
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundary, calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. For regular polygons, the formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = n \times s \]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side. For irregular polygons, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \]
Understanding the perimeter helps in various practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed to build a fence around a plot of land.
| Type of Polygon | Formula for Perimeter |
|---|---|
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) |
| Square | \( P = 4a \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2(l + w) \) |
For more complex polygons, you can use coordinate geometry and the distance formula to calculate the perimeter. For instance, given vertices \((x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), \ldots, (x_n, y_n)\), the perimeter is:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2} + \sqrt{(x_n - x_1)^2 + (y_n - y_1)^2} \]
This comprehensive understanding of polygons and their perimeters is crucial for solving geometric problems efficiently.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundary. In other words, it is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental aspect of geometry, which helps in understanding the dimensions and scale of various shapes.
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Identify the lengths of all sides of the polygon.
- Ensure that all side lengths are in the same unit. If they are not, convert them to the same unit.
- Add the lengths of all sides to get the total perimeter.
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a polygon is given by:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i
\]
where \( a_i \) represents the length of each side of the polygon and \( n \) is the number of sides.
For example, if we have a quadrilateral with side lengths of 5, 7, 3, and 6 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
P = 5 + 7 + 3 + 6 = 21 \, \text{units}
\]
In the case of regular polygons, where all sides are of equal length, the perimeter can be simplified to:
\[
P = n \times a
\]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( a \) is the length of one side.
Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundary. Calculating the perimeter varies based on whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal). Here are the steps and formulas to calculate the perimeter of various types of polygons:
1. Regular Polygons
For a regular polygon, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = n \times s
\]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Equilateral Triangle: For a triangle with all sides equal, the perimeter is \( 3 \times s \).
- Square: For a square, the perimeter is \( 4 \times s \).
2. Irregular Polygons
For an irregular polygon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. The formula is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]
where \( s_i \) represents the length of each side of the polygon.
3. Polygons with Given Vertices
To find the perimeter of a polygon with known vertex coordinates, use the distance formula to calculate the length of each side:
\[
D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Sum the lengths of all sides to get the perimeter.
- Calculate the distance between each pair of consecutive vertices using the distance formula.
- Add all these distances to obtain the total perimeter.
Examples
| Example 1: | Find the perimeter of a square with side length 5 units. |
| Solution: | Perimeter = \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units |
| Example 2: | Find the perimeter of a polygon with sides 3, 4, 5, and 6 units. |
| Solution: | Perimeter = \( 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 18 \) units |
| Example 3: | Find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices at (0,0), (0,3), and (4,0). |
| Solution: |
|
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of polygons involves summing the lengths of all sides. Here are some detailed examples:
-
Example 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle
Consider a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \). The perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
For a rectangle with \( l = 8 \) units and \( w = 5 \) units:
\[ P = 2(8) + 2(5) = 16 + 10 = 26 \text{ units} \]
-
Example 2: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length. If each side is \( s \) units, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 5s \]
For a pentagon with \( s = 4 \) units:
\[ P = 5(4) = 20 \text{ units} \]
-
Example 3: Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
For an irregular polygon, sum the lengths of all its sides. Consider a polygon with side lengths of 3, 5, 7, and 9 units:
\[ P = 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 = 24 \text{ units} \]
-
Example 4: Perimeter of a Triangle
For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
For a triangle with \( a = 5 \) units, \( b = 6 \) units, and \( c = 7 \) units:
\[ P = 5 + 6 + 7 = 18 \text{ units} \]
-
Example 5: Perimeter of a Square
A square has four equal sides. If each side is \( s \) units, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 4s \]
For a square with \( s = 3 \) units:
\[ P = 4(3) = 12 \text{ units} \]

Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
Polygons are classified into two main categories: regular and irregular polygons. Understanding the differences between these two types is essential for various geometric calculations, including finding the perimeter.
Regular Polygons
A regular polygon is a polygon with all sides and all interior angles equal. Examples include equilateral triangles, squares, and regular pentagons. Because of their symmetry, the formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular polygon is straightforward:
- Determine the number of sides (n).
- Measure the length of one side (s).
- Use the formula: Perimeter = n × s.
For instance, for a regular hexagon (six sides) with each side measuring 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as:
Perimeter = 6 × 5 = 30 units.
Irregular Polygons
Irregular polygons have sides and angles of different lengths and measures. To find the perimeter of an irregular polygon, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of each side individually.
- Add up all the side lengths to get the total perimeter.
For example, consider a polygon with side lengths of 3 units, 4 units, 5 units, 6 units, and 7 units. The perimeter is calculated as:
Perimeter = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 units.
Key Differences
- Symmetry: Regular polygons are symmetrical, while irregular polygons lack symmetry.
- Formula: The perimeter of regular polygons can be found using a simple multiplication formula, whereas the perimeter of irregular polygons requires adding each side length.
- Ease of Calculation: Regular polygons are easier to work with due to their uniform side lengths and angles.
Understanding whether a polygon is regular or irregular is crucial for accurately calculating its perimeter and other properties. Regular polygons simplify many geometric computations, while irregular polygons, though more complex, can be approached methodically by measuring and summing individual side lengths.
Types of Polygons
Polygons are two-dimensional shapes with straight sides. They are classified based on the number of sides and whether their sides and angles are equal. Understanding the types of polygons is essential for various geometric calculations, including perimeter, area, and more.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Triangle | A polygon with three sides and three angles. Examples include equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles. |
| Quadrilateral | A four-sided polygon. Common quadrilaterals include squares, rectangles, and trapezoids. |
| Pentagon | A five-sided polygon. It can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular. |
| Hexagon | A six-sided polygon, which can also be regular or irregular. |
| Heptagon | A seven-sided polygon, less common but still significant in geometry. |
| Octagon | An eight-sided polygon, famously seen in stop signs. |
Polygons can be further divided into regular and irregular types:
- Regular Polygons: All sides and angles are equal. Examples include equilateral triangles and squares.
- Irregular Polygons: Sides and angles are not equal. Examples include scalene triangles and irregular pentagons.
Understanding the types and properties of polygons is crucial for calculating their perimeter. Each type has specific methods to find the perimeter based on its sides.
Common Shapes and Their Perimeters
The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the outside of the shape, calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. Below are some common polygons and the methods to find their perimeters:
Square
A square is a regular polygon with four equal sides.
- Formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Example: If each side of the square is 5 cm, then the perimeter \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a polygon with opposite sides equal and all angles right angles.
- Formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Example: If the length \( l = 8 \) cm and the width \( w = 5 \) cm, then the perimeter \( P = 2(8 + 5) = 26 \) cm.
Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three sides. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its sides.
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Example: If the sides of the triangle are 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, then the perimeter \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm.
Pentagon
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon. If it is regular, all sides are of equal length.
- Formula for regular pentagon: \( P = 5s \)
- Example: If each side of a regular pentagon is 7 cm, then the perimeter \( P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \) cm.
Hexagon
A hexagon is a six-sided polygon. For a regular hexagon, all sides are equal.
- Formula for regular hexagon: \( P = 6s \)
- Example: If each side of a regular hexagon is 4 cm, then the perimeter \( P = 6 \times 4 = 24 \) cm.
Irregular Polygon
An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all its sides.
- Formula: \( P = \sum \text{side lengths} \)
- Example: For a polygon with sides measuring 3 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, and 4 cm, the perimeter \( P = 3 + 5 + 7 + 4 = 19 \) cm.
Special Cases
Sometimes, polygons have unique properties that simplify perimeter calculations. For example, a parallelogram has opposite sides that are equal, so its perimeter formula is similar to that of a rectangle:
- Formula for parallelogram: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Example: If a parallelogram has sides 6 cm and 8 cm, then the perimeter \( P = 2(6 + 8) = 28 \) cm.
Visualization with MathJax
We can also represent these formulas using MathJax for better visualization:
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Pentagon: \( P = 5s \)
- Hexagon: \( P = 6s \)
- Irregular Polygon: \( P = \sum \text{side lengths} \)
Understanding the perimeters of various polygons helps in geometry and practical applications. Practice with different shapes and their measurements to master the concept of perimeter.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practice solving perimeter problems with these examples. Detailed solutions are provided to help you understand the steps involved in finding the perimeter of different polygons.
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
Given the irregular polygon ABCDEF with side lengths:
- AB = 3 units
- BC = 4 units
- CD = 6 units
- DE = 2 units
- EF = 1.5 units
- FA = x units
If the total perimeter is 18.5 units, find the length of FA.
Solution:
- Calculate the sum of the known sides: \(3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 1.5 = 16.5\) units
- Subtract this sum from the total perimeter to find FA: \(18.5 - 16.5 = 2\) units
Therefore, the length of FA is 2 units.
Example 2: Perimeter of an Equilateral Triangle
Find the length of each side of an equilateral triangle if the perimeter is 27 units.
Solution:
- Let the length of each side be \(a\) units.
- The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is given by \(3 \times a\).
- Set up the equation: \(3a = 27\).
- Solve for \(a\): \(a = \frac{27}{3} = 9\) units.
Therefore, each side of the equilateral triangle is 9 units long.
Example 3: Perimeter of a Square with a Cut-Out Triangle
Consider a square with side length 5 units. A triangle with sides equal to 5 units is cut out from one side. Calculate the perimeter of the resulting shape.
Solution:
- Initially, the perimeter of the square is \(4 \times 5 = 20\) units.
- After cutting out the triangle, three sides of the square remain (each 5 units) and three sides of the triangle (each 5 units) form the perimeter of the new shape.
- Total perimeter: \(3 \times 5 + 3 \times 5 = 15 + 15 = 30\) units.
Therefore, the perimeter of the new shape is 30 units.

READ MORE:
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the perimeter of polygon XYDB?
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of all its sides. For polygon XYDB, if each side is given as 5 units, and it has four sides, the perimeter is calculated as:
Perimeter = 4 × 5 = 20 units
-
How do you calculate the perimeter of a polygon?
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, add the lengths of all its sides. For regular polygons, the formula is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = n \times s
\]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side. -
What is the difference between a regular and an irregular polygon?
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal, such as a square or an equilateral triangle. An irregular polygon does not have equal side lengths or equal angles, like a rectangle or a scalene triangle.
-
Can the perimeter of an irregular polygon be calculated in the same way?
Yes, the perimeter of an irregular polygon is also found by adding the lengths of all its sides, regardless of their differences in length.
-
What units are used to measure the perimeter of a polygon?
The perimeter of a polygon is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, feet, or inches, depending on the context and the measurements provided.