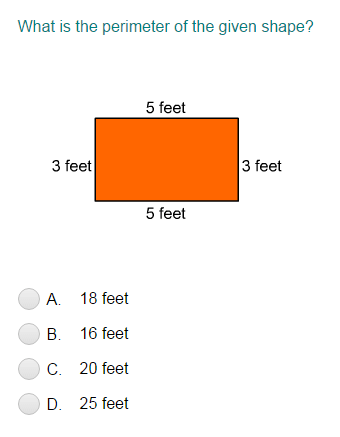
Topic what is the perimeter of this red polygon: Understanding the perimeter of polygons is essential for various mathematical applications. In this article, we will explore the concept of the perimeter, how to calculate it for different polygons, and provide examples to illustrate these calculations. Whether you're dealing with regular or irregular polygons, we've got you covered.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Polygon
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Polygon
- Formulas to Calculate the Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
- Special Cases: Polygons on a Coordinate Plane
- Difference Between Area and Perimeter
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Polygon
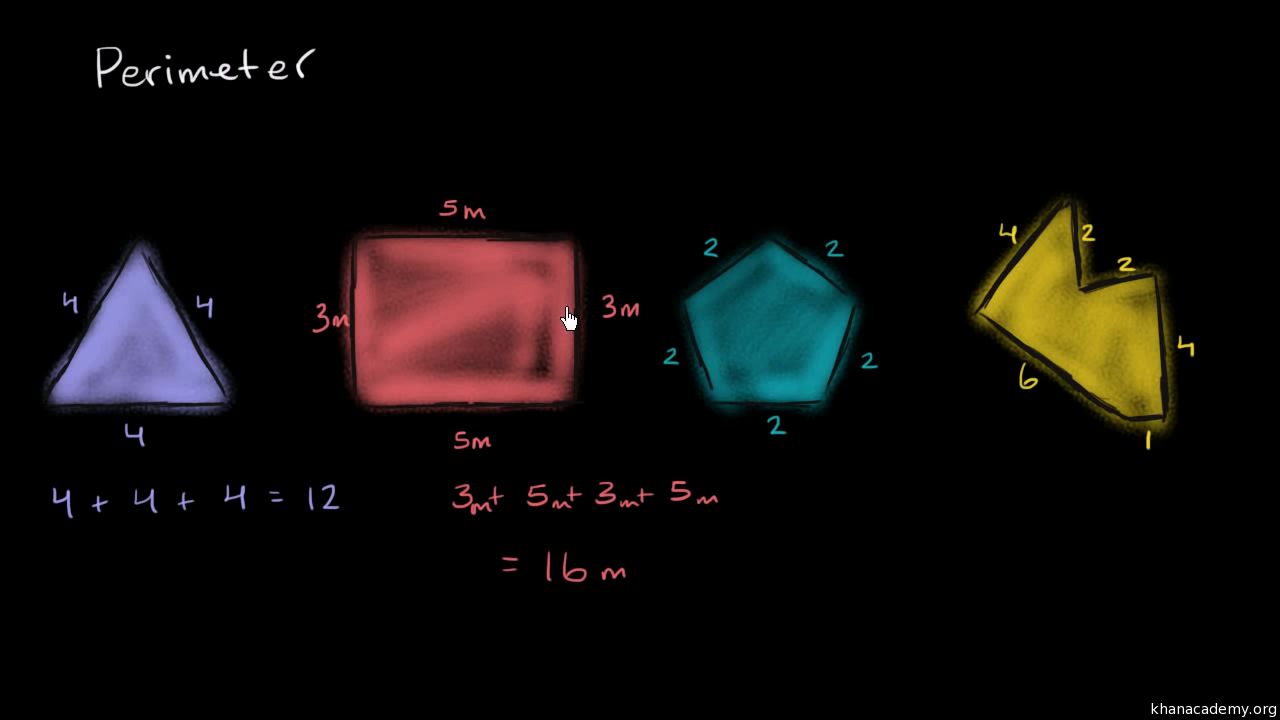
The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the boundary of the polygon. To calculate the perimeter, you need to add the lengths of all its sides.
Perimeter Formula
The general formula for the perimeter (P) of any polygon is:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i \]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( a_i \) is the length of the \( i \)-th side.
Regular Polygons
For regular polygons, where all sides are equal, the formula simplifies to:
\[ P = n \times s \]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Equilateral Triangle: \( P = 3 \times \text{side} \)
- Square: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \)
- Regular Pentagon: \( P = 5 \times \text{side} \)
- Regular Hexagon: \( P = 6 \times \text{side} \)
Irregular Polygons
For irregular polygons, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides.
Example:
If a polygon has sides of lengths 7, 9, 6, and 5, then:
\[ P = 7 + 9 + 6 + 5 = 27 \text{ units} \]
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify if the polygon is regular or irregular.
- For regular polygons, use the formula \( P = n \times s \).
- For irregular polygons, sum the lengths of all sides.
- Ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before summing.
Examples
- Regular Hexagon: If each side is 7 units, \( P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \) units.
- Irregular Polygon: Sides are 3, 4, 6, 2, 1.5 units with a missing side \( x \). Given perimeter is 18.5 units:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 1.5 + x = 18.5 \]
Solve for \( x \):
\[ x = 18.5 - (3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 1.5) = 2 \text{ units} \]

READ MORE:
Understanding the Perimeter of a Polygon
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its edges. To understand how to calculate the perimeter, it's essential to grasp the basics of polygons and their properties.
A polygon is a 2-dimensional shape made up of straight line segments connected end to end. These segments are called the sides or edges of the polygon, and the points where two sides meet are called vertices. Polygons can be regular, with all sides and angles equal, or irregular, with sides and angles of different lengths and measures.
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, follow these steps:
- Identify all the sides: Count and measure the length of each side of the polygon.
- Add the lengths together: Sum all the side lengths to get the total perimeter.
Let's look at the formula for the perimeter of different types of polygons:
- Regular Polygons: For a regular polygon with n sides of length s, the formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = n \times s \]
- Irregular Polygons: For an irregular polygon, the perimeter is the sum of all its side lengths:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + \ldots + s_n \]
For example, consider a polygon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm. The perimeter is calculated as:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3\, \text{cm} + 4\, \text{cm} + 5\, \text{cm} + 6\, \text{cm} = 18\, \text{cm} \]
It's crucial to ensure that all side lengths are measured in the same unit to avoid errors in the calculation. By following these steps, you can easily determine the perimeter of any polygon, whether regular or irregular.
Formulas to Calculate the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. The formula used depends on whether the polygon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary).
Regular Polygons
For a regular polygon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter (\(P\)) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = n \times s \]
Where:
- n is the number of sides.
- s is the length of each side.
Example:
If you have a regular hexagon (6-sided polygon) with each side measuring 5 units, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Irregular Polygons
For an irregular polygon, where the sides can have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + \cdots + z \]
Where:
- a, b, c, ... , z are the lengths of the sides.
Example:
If you have a polygon with sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, 5 units, and 6 units, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 18 \text{ units} \]
Polygons on a Coordinate Plane
For polygons with vertices at known coordinates, you can use the distance formula to calculate the length of each side. The distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is given by:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
After calculating the lengths of all sides, sum them to find the perimeter.
Example:
For a polygon with vertices at (0,0), (0,3), (4,3), and (4,0), calculate the lengths of each side:
- Side 1: \( \sqrt{(0-0)^2 + (3-0)^2} = 3 \text{ units} \)
- Side 2: \( \sqrt{(4-0)^2 + (3-3)^2} = 4 \text{ units} \)
- Side 3: \( \sqrt{(4-4)^2 + (0-3)^2} = 3 \text{ units} \)
- Side 4: \( \sqrt{(0-4)^2 + (0-0)^2} = 4 \text{ units} \)
Then, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 3 + 4 = 14 \text{ units} \]
Special Cases
In some cases, you might need to find the perimeter of polygons with missing side lengths or with special properties (like being inscribed in a circle). The general approach involves using given data and known geometric properties to derive the missing information.
Understanding these formulas and applying them correctly allows you to find the perimeter of any polygon, whether it's a simple triangle or a complex multi-sided shape.
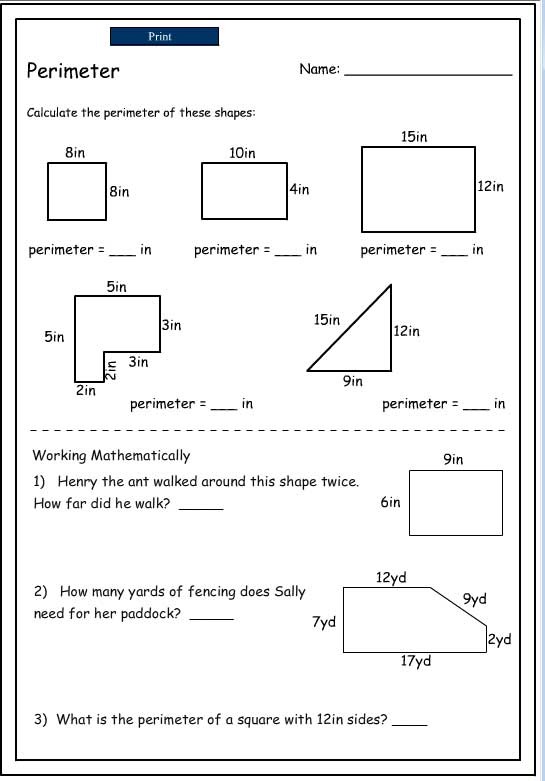
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Here are some detailed examples demonstrating how to calculate the perimeter of various types of polygons.
Example 1: Square
For a square with each side of length \( s \):
Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 4s \)
If \( s = 5 \) units:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units}
\]
Example 2: Rectangle
For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \):
Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) \)
If \( l = 6 \) units and \( w = 3 \) units:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2(6 + 3) = 2 \times 9 = 18 \text{ units}
\]
Example 3: Irregular Polygon
Consider an irregular polygon with sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, 6 units, 2 units, and 1.5 units:
To find the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 1.5 = 16.5 \text{ units}
\]
Example 4: Equilateral Triangle
For an equilateral triangle where all sides are equal, and each side \( s \):
Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 3s \)
If \( s = 7 \) units:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 \times 7 = 21 \text{ units}
\]
Example 5: Polygon on a Coordinate Plane
Consider a quadrilateral with vertices at coordinates (0, 0), (0, 3), (3, 3), and (3, 0):
First, calculate the length of each side using the distance formula:
\[
\text{Length of side} \, AB = \sqrt{(0-0)^2 + (3-0)^2} = 3 \text{ units}
\]
\[
\text{Length of side} \, BC = \sqrt{(3-0)^2 + (3-3)^2} = 3 \text{ units}
\]
\[
\text{Length of side} \, CD = \sqrt{(3-3)^2 + (3-0)^2} = 3 \text{ units}
\]
\[
\text{Length of side} \, DA = \sqrt{(3-0)^2 + (0-0)^2} = 3 \text{ units}
\]
Summing these lengths gives the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12 \text{ units}
\]
Regular vs. Irregular Polygons
Polygons are classified into two main categories based on the equality of their sides and angles: regular polygons and irregular polygons.
Regular Polygons
A regular polygon is a polygon where all sides are of equal length and all interior angles are of equal measure. This uniformity gives regular polygons a symmetrical appearance. Common examples of regular polygons include:
- Equilateral Triangle: A triangle with three equal sides and three equal angles (each measuring 60 degrees).
- Square: A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four equal angles (each measuring 90 degrees).
- Regular Pentagon: A five-sided polygon with all sides and angles equal.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular polygon is:
Where:
- P = Perimeter
- n = Number of sides
- s = Length of one side
Irregular Polygons
An irregular polygon is a polygon where not all sides are of equal length and not all interior angles are of equal measure. Irregular polygons do not have a symmetrical appearance and can take various shapes. Examples include:
- Scalene Triangle: A triangle with all sides and angles of different measures.
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with opposite sides equal and all angles equal (each measuring 90 degrees), but not all sides are of equal length.
- Irregular Quadrilateral: A four-sided polygon with sides and angles of different measures.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon is:
Where:
- P = Perimeter
- si = Length of the i-th side
Examples
Let's look at some examples to understand the calculation of the perimeter for both types of polygons:
Example 1: Regular Polygon (Square)
Consider a square with each side of length 4 units. Since a square is a regular polygon, we use the formula for regular polygons:
Example 2: Irregular Polygon
Consider an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 3 units, 4 units, 5 units, 4 units, and 3 units. The perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all sides:

Special Cases: Polygons on a Coordinate Plane
Polygons on a coordinate plane present unique opportunities to calculate the perimeter using the coordinates of their vertices. This process involves the application of the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides.
To calculate the perimeter of a polygon on a coordinate plane, follow these steps:
- Identify the vertices: Note down the coordinates of all the vertices of the polygon. For example, consider a polygon with vertices A(1,2), B(4,5), C(7,8), and D(1,6).
- Calculate the distance between each pair of vertices: Use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides between consecutive vertices.
The distance formula between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
Let's apply this to our example:
- Length of AB: \[ \sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (5 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} = \sqrt{18} = 4.24 \] units
- Length of BC: \[ \sqrt{(7 - 4)^2 + (8 - 5)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 9} = \sqrt{18} = 4.24 \] units
- Length of CD: \[ \sqrt{(1 - 7)^2 + (6 - 8)^2} = \sqrt{36 + 4} = \sqrt{40} = 6.32 \] units
- Length of DA: \[ \sqrt{(1 - 1)^2 + (2 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{0 + 16} = \sqrt{16} = 4 \] units
Sum the lengths: Add up the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter of the polygon.
In our example:
\[ P = 4.24 + 4.24 + 6.32 + 4 = 18.8 \] units
This method ensures accurate perimeter calculations for any polygon plotted on a coordinate plane.
Difference Between Area and Perimeter
Understanding the difference between area and perimeter is crucial for solving many geometric problems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Perimeter:
- The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its boundary.
- It is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, etc.
- To calculate the perimeter, add the lengths of all the sides of the polygon.
- Area:
- The area of a polygon is the amount of space enclosed within its boundary.
- It is measured in square units such as square meters, square centimeters, square inches, etc.
- To calculate the area, use the appropriate formula depending on the shape of the polygon.
Formulas
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \( P = 4s \) | \( A = s^2 \) |
| Rectangle | \( P = 2(l + w) \) | \( A = lw \) |
| Triangle | \( P = a + b + c \) | \( A = \frac{1}{2}bh \) |
| Regular Polygon | \( P = ns \) | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times Perimeter \times Apothem \) |
Examples
- Square: For a square with a side length of 5 units:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units
- Area: \( A = 5^2 = 25 \) square units
- Rectangle: For a rectangle with a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units:
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(6 + 4) = 20 \) units
- Area: \( A = 6 \times 4 = 24 \) square units
In summary, while the perimeter is concerned with the boundary lengths of the polygon, the area focuses on the space enclosed by the polygon. Understanding and applying these concepts appropriately is key to solving various geometric problems efficiently.
Practice Problems and Solutions
To help you master the concept of calculating the perimeter of polygons, here are some practice problems along with their solutions. Try to solve them on your own before looking at the solutions.
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has each side of length 5 cm. Calculate the perimeter.
- Step 1: Identify the number of sides (n) and the length of one side (s).
- Step 2: Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular polygon: \( P = n \times s \).
- Step 3: Substitute the values into the formula: \( P = 5 \times 5 = 25 \) cm.
Solution: The perimeter of the pentagon is 25 cm.
Problem 2: Perimeter of an Irregular Quadrilateral
An irregular quadrilateral has side lengths of 7 m, 8 m, 5 m, and 6 m. Calculate the perimeter.
- Step 1: List the side lengths.
- Step 2: Sum the lengths of all the sides: \( P = 7 + 8 + 5 + 6 \).
- Step 3: Perform the addition: \( P = 26 \) m.
Solution: The perimeter of the quadrilateral is 26 m.
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Triangle on a Coordinate Plane
Find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (3, 0), and (3, 4) on a coordinate plane.
- Step 1: Use the distance formula to find the lengths of each side:
- Distance between (0, 0) and (3, 0): \( \sqrt{(3-0)^2 + (0-0)^2} = 3 \) units.
- Distance between (3, 0) and (3, 4): \( \sqrt{(3-3)^2 + (4-0)^2} = 4 \) units.
- Distance between (0, 0) and (3, 4): \( \sqrt{(3-0)^2 + (4-0)^2} = 5 \) units.
- Step 2: Sum the lengths of all the sides: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 \).
- Step 3: Perform the addition: \( P = 12 \) units.
Solution: The perimeter of the triangle is 12 units.
Problem 4: Perimeter of a Hexagon with Mixed Units
A hexagon has side lengths given as 3 cm, 3 cm, 30 mm, 3 cm, 0.03 m, and 3 cm. Calculate the perimeter in centimeters.
- Step 1: Convert all lengths to the same unit (cm):
- 30 mm = 3 cm
- 0.03 m = 3 cm
- Step 2: List the side lengths: 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm.
- Step 3: Sum the lengths of all the sides: \( P = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 \).
- Step 4: Perform the addition: \( P = 18 \) cm.
Solution: The perimeter of the hexagon is 18 cm.
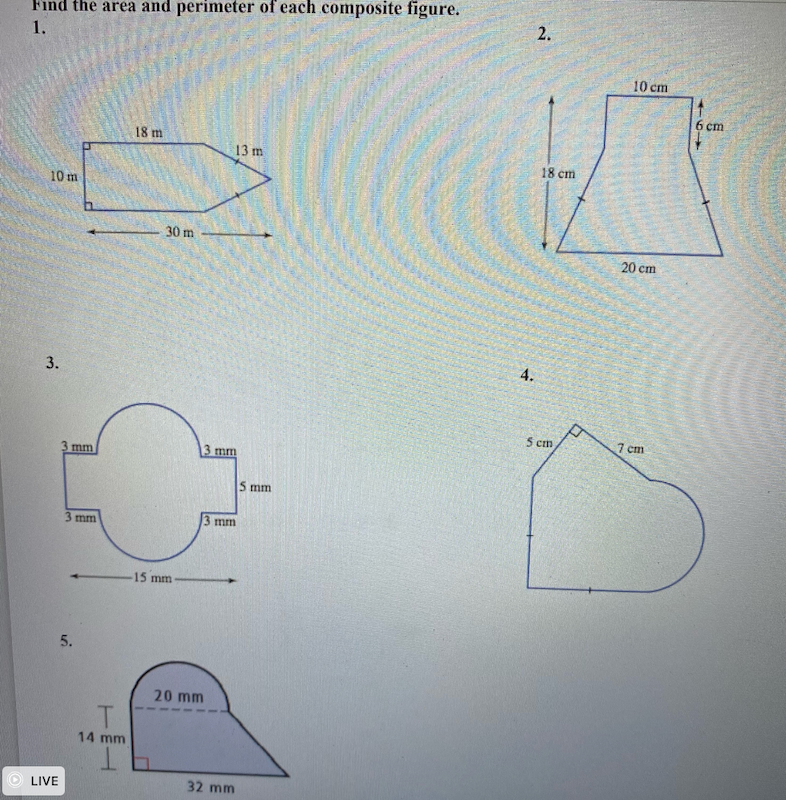
Problem 5: Composite Shape Perimeter
Calculate the perimeter of an L-shaped polygon with the following side lengths: 5 m, 3 m, 2 m, 3 m, 1 m, 6 m.
- Step 1: List all the side lengths.
- Step 2: Sum the lengths of all the sides: \( P = 5 + 3 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 6 \).
- Step 3: Perform the addition: \( P = 20 \) m.
Solution: The perimeter of the L-shaped polygon is 20 m.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What is the perimeter of a polygon?
A: The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the outside, which is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides.
-
Q: How do you find the perimeter of a regular polygon?
A: For a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), the perimeter can be found using the formula:
P = n \times s , wheren is the number of sides ands is the length of one side. -
Q: Can the perimeter of an irregular polygon be calculated?
A: Yes, for an irregular polygon, add up the lengths of all its sides. There is no specific formula, so each side must be measured and summed.
-
Q: How do you find the perimeter of a polygon on a coordinate plane?
A: Use the distance formula to find the length of each side between points
(x_1, y_1) and(x_2, y_2) :\sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} . Sum these distances to get the perimeter. -
Q: What units are used for perimeter?
A: Perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet, depending on the units used for the sides.
-
Q: Is there a difference between the perimeter and area?
A: Yes, the perimeter measures the distance around a shape, while the area measures the amount of space inside the shape.

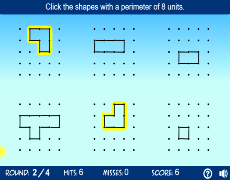
Chu vi của hình đa giác đỏ này là bao nhiêu? 27 in 22 in 22 in 8 in 2 in
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn tìm chu vi của các đa giác một cách dễ hiểu và chính xác.
Chu vi - Tìm chu vi của đa giác