Topic how to find the perimeter of a room: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on finding the perimeter of a room! Whether you're a DIY enthusiast, a homeowner, or a professional contractor, understanding how to accurately calculate the perimeter of a room is essential. In this article, we'll explore various methods, formulas, and tips to help you measure and calculate room perimeters with ease and precision.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Room
- Examples
- Tips for Measuring
- Examples
- Tips for Measuring
- Tips for Measuring
- Table of Contents
- Introduction to Finding the Perimeter
- Basic Methods for Calculating Perimeter
- Considering Room Shape and Complexity
- Taking Accurate Measurements
- Common Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Tools and Instruments for Measuring Perimeter
- Useful Tips and Tricks for Efficient Measurement
- Summary and Recap
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính diện tích và chu vi phòng của bạn một cách chính xác và dễ dàng trong video này.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Room
The perimeter of a room is the total distance around its edges. Calculating the perimeter depends on the shape of the room. Here are the steps and formulas for different room shapes:
Square Room
- Measure the length of one wall.
- Multiply this length by 4, as all sides of a square are equal.
Formula: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \)
Rectangular Room
- Measure the length and width of the room.
- Double the length and the width.
- Add these doubled values together.
Formula: \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
Triangular Room
- Measure the length of all three walls.
- Add these lengths together.
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
Circular Room
- Measure the diameter of the room.
- Multiply this measurement by \(\pi\) (approximately 3.14159).
Formula: \( P = \pi \times \text{diameter} \)
Irregular Shaped Room
- Measure the length of each wall.
- Add all these lengths together.
Formula: \( P = \sum \text{side lengths} \)
READ MORE:
Examples
Example 1: Rectangular Room
For a room with a length of 18 feet and a width of 14 feet:
\( P = 2 \times (18 + 14) = 2 \times 32 = 64 \) feet
Example 2: Square Room
For a room with each side measuring 20 feet:
\( P = 4 \times 20 = 80 \) feet
Example 3: Triangular Room
For a room with sides measuring 15 feet, 20 feet, and 20 feet:
\( P = 15 + 20 + 20 = 55 \) feet
Example 4: Circular Room
For a room with a diameter of 10 feet:
\( P = \pi \times 10 \approx 31.42 \) feet
Tips for Measuring
- Use a measuring tape for accurate measurements.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (convert if necessary).
- Mark your starting point to ensure you measure the entire perimeter accurately.
Examples
Example 1: Rectangular Room
For a room with a length of 18 feet and a width of 14 feet:
\( P = 2 \times (18 + 14) = 2 \times 32 = 64 \) feet
Example 2: Square Room
For a room with each side measuring 20 feet:
\( P = 4 \times 20 = 80 \) feet
Example 3: Triangular Room
For a room with sides measuring 15 feet, 20 feet, and 20 feet:
\( P = 15 + 20 + 20 = 55 \) feet
Example 4: Circular Room
For a room with a diameter of 10 feet:
\( P = \pi \times 10 \approx 31.42 \) feet
Tips for Measuring
- Use a measuring tape for accurate measurements.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (convert if necessary).
- Mark your starting point to ensure you measure the entire perimeter accurately.
Tips for Measuring
- Use a measuring tape for accurate measurements.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (convert if necessary).
- Mark your starting point to ensure you measure the entire perimeter accurately.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Finding the Perimeter of a Room
Understanding the Basics: Methods for Calculating Perimeter
Considering Room Shape and Complexity
Taking Accurate Measurements for Perimeter Calculation
Exploring Common Perimeter Formulas for Different Room Shapes
Practical Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Utilizing Tools and Instruments for Precise Perimeter Measurement
Effective Tips and Tricks for Efficient Perimeter Determination
Summary and Recap: Mastering Perimeter Calculations for Any Room
Introduction to Finding the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a room is an essential skill for various purposes, from home renovation projects to construction planning. Understanding how to find the perimeter ensures accurate measurements, leading to efficient use of materials and resources. In this section, we'll delve into the fundamentals of perimeter calculation, providing you with the knowledge and tools necessary to tackle any room measurement task.
Basic Methods for Calculating Perimeter
When it comes to calculating the perimeter of a room, there are several straightforward methods you can employ:
Linear Addition: Measure each side of the room using a tape measure and then add all the measurements together to find the total perimeter.
Counting Steps: For larger rooms or irregular shapes, count the number of steps it takes to walk around the room's perimeter, each step representing a standard measurement unit.
String Method: Attach a string or rope along the walls of the room, following the perimeter, and then measure the length of the string to determine the perimeter.
Using a Laser Distance Measurer: Utilize modern technology with a laser distance measurer to accurately measure each side of the room and calculate the perimeter automatically.

Considering Room Shape and Complexity
When determining the perimeter of a room, the shape and complexity of the room's layout significantly influence the calculation method. Here’s a step-by-step guide to consider various shapes and complexities:
1. Rectangular and Square Rooms
For rooms that are rectangular or square, calculating the perimeter is straightforward:
- Identify the length (\(l\)) and width (\(w\)) of the room.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \[ P = 2l + 2w \] For a square room, since all sides are equal (\(s\)): \[ P = 4s \]
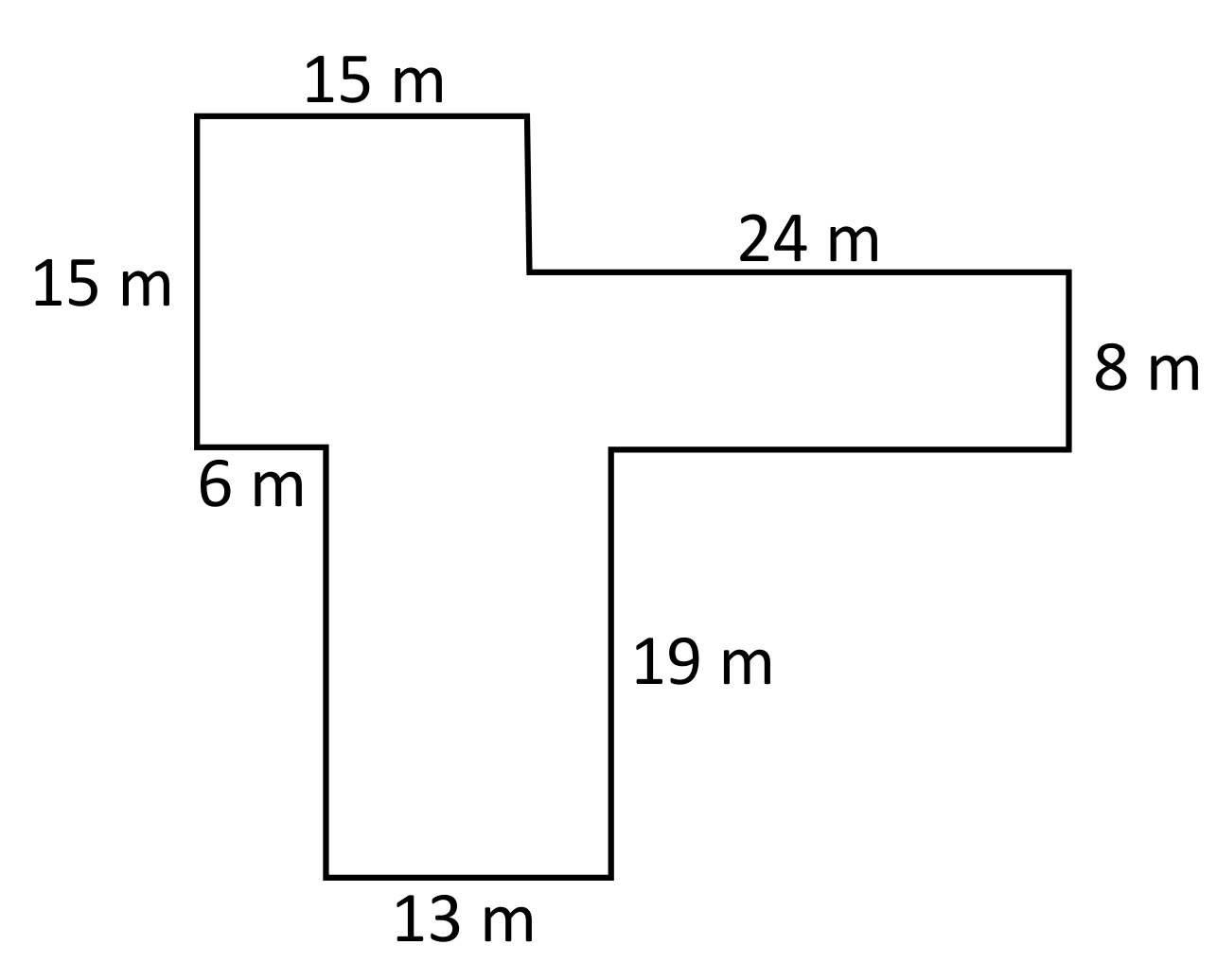
2. L-Shaped and Irregular Rooms
L-shaped or irregular rooms require a more detailed approach:
- Divide the room into regular shapes (rectangles or squares).
- Calculate the perimeter of each section separately.
- Add the perimeters of the individual sections, ensuring shared walls are not double-counted.
3. Circular and Semi-Circular Rooms
For rooms with curved walls, such as circular or semi-circular sections:
- Identify the radius (\(r\)) of the circular section.
- For a full circle, use the formula: \[ P = 2\pi r \]
- For a semi-circle, calculate the curved part and add the diameter: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
4. Multi-Sided (Polygonal) Rooms
For rooms that have multiple sides (polygonal shapes):
- Identify and measure the length of each side of the polygon.
- Add all the side lengths together to find the perimeter: \[ P = \text{sum of all side lengths} \]
Practical Tips
- Use a measuring tape for accuracy and measure each side carefully.
- Double-check measurements, especially for irregular shapes, to ensure no sides are missed or double-counted.
- When dealing with complex shapes, sketch the layout and label each side to keep track of measurements.
Understanding the shape and complexity of a room is essential for accurate perimeter calculation. By breaking down the room into manageable sections and applying the appropriate formulas, you can determine the perimeter effectively.
Taking Accurate Measurements
Accurate measurements are crucial for determining the perimeter of a room. Follow these steps to ensure precision:
Tools Needed
- Measuring tape
- Laser distance measurer (optional for larger rooms)
- Pencil and paper or a digital device for recording measurements
- Carpenter's square for checking right angles
Steps for Accurate Measurement
-
Measure Wall Lengths:
- Position the measuring tape along the bottom edge of the wall. Ensure it is straight and tight.
- Note the starting point and endpoint, and record the measurement.
- Repeat the measurement at the top of the wall if walls are not square, and average the two measurements.
-
Measure Wall Heights:
- Use a step ladder to measure from floor to ceiling, holding the tape vertically.
- Repeat at several points along each wall and average the measurements.
-
Account for Irregular Spaces:
- Break the room into smaller, regular shapes if it has bay windows or nooks.
- Measure each shape separately and calculate its area or perimeter.
- Add the measurements to get the total for the room.
-
Include Doorways and Windows:
- Measure the height and width of doors and windows, including trim.
- Measure the distance from the nearest corner to ensure precise placement.
Tips for Accuracy
- Always double-check measurements for accuracy.
- Ensure the measuring tape is not worn or stretched.
- Use a helper for holding the tape in place, especially in larger rooms.
- Record measurements clearly and organize them systematically, either on paper or using digital tools.
- Consider using a laser distance measurer for more accurate readings in large or complex spaces.
Accurate measurements are fundamental for various projects, from estimating materials for flooring and trim to planning furniture layouts and renovations. Following these steps will help you achieve precise results, ensuring your project is completed efficiently and effectively.
Common Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of a room involves understanding the shape of the room and applying the appropriate mathematical formulas. Below are some common shapes and their perimeter formulas:
Square
For a square, all four sides are of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) is:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Rectangle
For a rectangle, opposite sides are equal in length. The formula for the perimeter (P) is:
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
or
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
Triangle
For a triangle, the perimeter (P) is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) is:
\[ P = 3s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Circle
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference (C). The formula is:
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
where \( r \) is the radius.
Parallelogram
For a parallelogram, the perimeter (P) is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\[ P = 2(a + b) \]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
Trapezoid
For a trapezoid (or trapezium), the perimeter (P) is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
Understanding these formulas allows for accurate calculation of the perimeter for various room shapes, helping in tasks such as flooring, molding, and other projects that require precise measurements.
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a room can vary depending on the shape of the room. Below are some examples demonstrating how to find the perimeter for different room shapes.
Example 1: Rectangle
To find the perimeter of a rectangular room, you add together the lengths of all four sides. Alternatively, you can use the perimeter formula for a rectangle:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width})
\]
For a room with a length of 5.1 meters and a width of 9.4 meters, the calculation would be:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (5.1 + 9.4) = 2 \times 14.5 = 29 \text{ meters}
\]
Example 2: Square
A square room has equal side lengths. The perimeter can be calculated by adding all four sides or using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{Side Length}
\]
For a room with each side measuring 3.7 meters, the calculation would be:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 3.7 = 14.8 \text{ meters}
\]
Example 3: Irregular Room
For an irregularly shaped room, you need to measure and add the lengths of all sides. Suppose a room has sides of 3 meters, 4.5 meters, 2.5 meters, and 6 meters. The perimeter calculation is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4.5 + 2.5 + 6 = 16 \text{ meters}
\]
Example 4: Regular Hexagon
For a regular hexagonal room, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is calculated by multiplying the side length by six:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 6 \times \text{Side Length}
\]
For a hexagonal room with each side measuring 8.2 meters, the calculation is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 6 \times 8.2 = 49.2 \text{ meters}
\]
Example 5: L-Shaped Room
To calculate the perimeter of an L-shaped room, you need to measure each segment of the boundary and add them together. Suppose the sides are 5 meters, 7 meters, 3 meters, 4 meters, and 6 meters. The perimeter calculation is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 3 + 4 + 6 = 25 \text{ meters}
\]
By following these examples, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of rooms with various shapes.

Tools and Instruments for Measuring Perimeter
Accurate perimeter measurement of a room requires a variety of tools and instruments. Here's a detailed look at some of the most useful tools for this task:
- Measuring Tape:
A measuring tape is a fundamental tool for measuring perimeter. It is flexible, allowing it to measure around corners and irregular shapes. Most measuring tapes are marked in both inches and centimeters, making them versatile for any measurement system.
- Laser Measure:
Laser measures are advanced tools that use laser technology to provide precise distance measurements. They are particularly useful for long distances and high ceilings. Simply point the laser at the opposite wall, and the device will give an accurate reading almost instantly.
- Ruler and Yardstick:
For smaller or more precise measurements, rulers and yardsticks are indispensable. They are typically used to measure short distances and are especially useful in tight spaces where a measuring tape might be cumbersome.
- Square and Level:
These tools help ensure that measurements are straight and accurate. A square is used to measure right angles and ensure that corners are perfect, while a level ensures that lines are perfectly horizontal or vertical, which is crucial for accurate measurements.
- Protractor:
For rooms with non-standard angles, a protractor can be used to measure and verify angles accurately. This is particularly useful in rooms with angled walls or ceilings.
- Notebook and Pencil:
Always have a notebook and pencil on hand to jot down measurements as you go. This helps keep track of each wall's length and any other relevant details.
- Digital Measuring Tools:
Advanced digital tools like digital micrometers and calipers can measure very small distances with high precision, which is useful for detailed and intricate measurements in complex spaces.
Each of these tools plays a crucial role in ensuring that the perimeter measurements of a room are accurate and efficient. Combining these tools allows for the flexibility and precision needed to tackle any measurement challenge.
Useful Tips and Tricks for Efficient Measurement
Accurate and efficient measurement is essential for calculating the perimeter of a room. Here are some useful tips and tricks to help you achieve precise measurements:
-
Use the Right Tools:
Ensure you have the proper measuring tools such as a tape measure, laser distance measurer, or measuring wheel. These tools are designed to provide accurate readings and make the process easier.
-
Double-Check Your Measurements:
Always measure twice to ensure accuracy. Taking a second measurement can help catch any mistakes and verify the correctness of your initial measurement.
-
Measure from Multiple Points:
For more complex rooms, measure from different points to account for any irregularities in wall shape or length. This will help ensure a more accurate overall measurement.
-
Minimize Human Error:
Hold the measuring tape steady and ensure it is properly aligned with the walls. Using a laser distance measurer can also help reduce errors caused by unsteady hands.
-
Take Advantage of Tape Measure Features:
Most tape measures have additional markings and features that can assist in more precise measurement. For example, use the tape measure’s hook to anchor it at the start point or utilize built-in measurement markings for quick calculations.
-
Use a Helper:
If possible, have someone assist you with holding the tape measure or reading the measurements. This can help ensure the tape is straight and properly positioned.
-
Calibrate Your Tools:
Regularly check and calibrate your measuring tools to ensure they are providing accurate readings. Over time, tools can become misaligned, leading to inaccurate measurements.
-
Perform Math Calculations:
Use a calculator or a measuring tool with built-in calculation features to easily find midpoints or convert measurements. This can help when you need to split a distance or work with different units.
-
Measure in Clear Conditions:
Avoid measuring in low light or cluttered conditions. Clear any obstacles and ensure there is adequate lighting to read the measurements accurately.
By following these tips, you can improve the accuracy and efficiency of your perimeter measurements, ensuring reliable results for your projects.
Summary and Recap
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a room involves several key steps and considerations. In this guide, we've covered various aspects to ensure accurate and efficient measurement. Let's summarize the main points:
- Introduction to Finding the Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the edges of a room. It's essential for tasks like installing baseboards or estimating materials for renovation projects.
- Basic Methods for Calculating Perimeter: For standard shapes like rectangles and squares, the perimeter can be easily calculated by adding the lengths of all sides. For a rectangle, use the formula \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Considering Room Shape and Complexity: Irregularly shaped rooms require more detailed measurement. Break the room into simpler geometric shapes, calculate the perimeter for each, and then sum these values.
- Taking Accurate Measurements: Use precise tools like laser measures or tape measures. Ensure measurements are taken at the same height along walls and avoid obstacles that could distort the measurements.
- Common Perimeter Formulas for Different Shapes: Understand and use the appropriate formulas for different shapes:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations: Practical examples help solidify understanding. For instance, a rectangular room measuring 12 feet by 10 feet has a perimeter of \( 2 \times (12 + 10) = 44 \) feet.
- Tools and Instruments for Measuring Perimeter: Various tools can enhance accuracy, including:
- Tape Measure: Flexible and suitable for most basic measurements.
- Laser Measure: Provides precise digital readings and is excellent for large or irregular spaces.
- Measuring Wheel: Ideal for very large areas, especially outdoors.
- Useful Tips and Tricks for Efficient Measurement:
- Double-check Measurements: Always measure twice to ensure accuracy.
- Measure in Sections: For complex shapes, break the room into manageable sections.
- Record Measurements Clearly: Write down measurements immediately to avoid confusion.
By following these guidelines and using the right tools, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any room, regardless of its shape or complexity. Whether for DIY projects or professional tasks, understanding perimeter calculation is a valuable skill.
Khám phá cách tính diện tích và chu vi phòng của bạn một cách chính xác và dễ dàng trong video này.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi Phòng của Tôi
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một phòng trong video này.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích Của Một Phòng