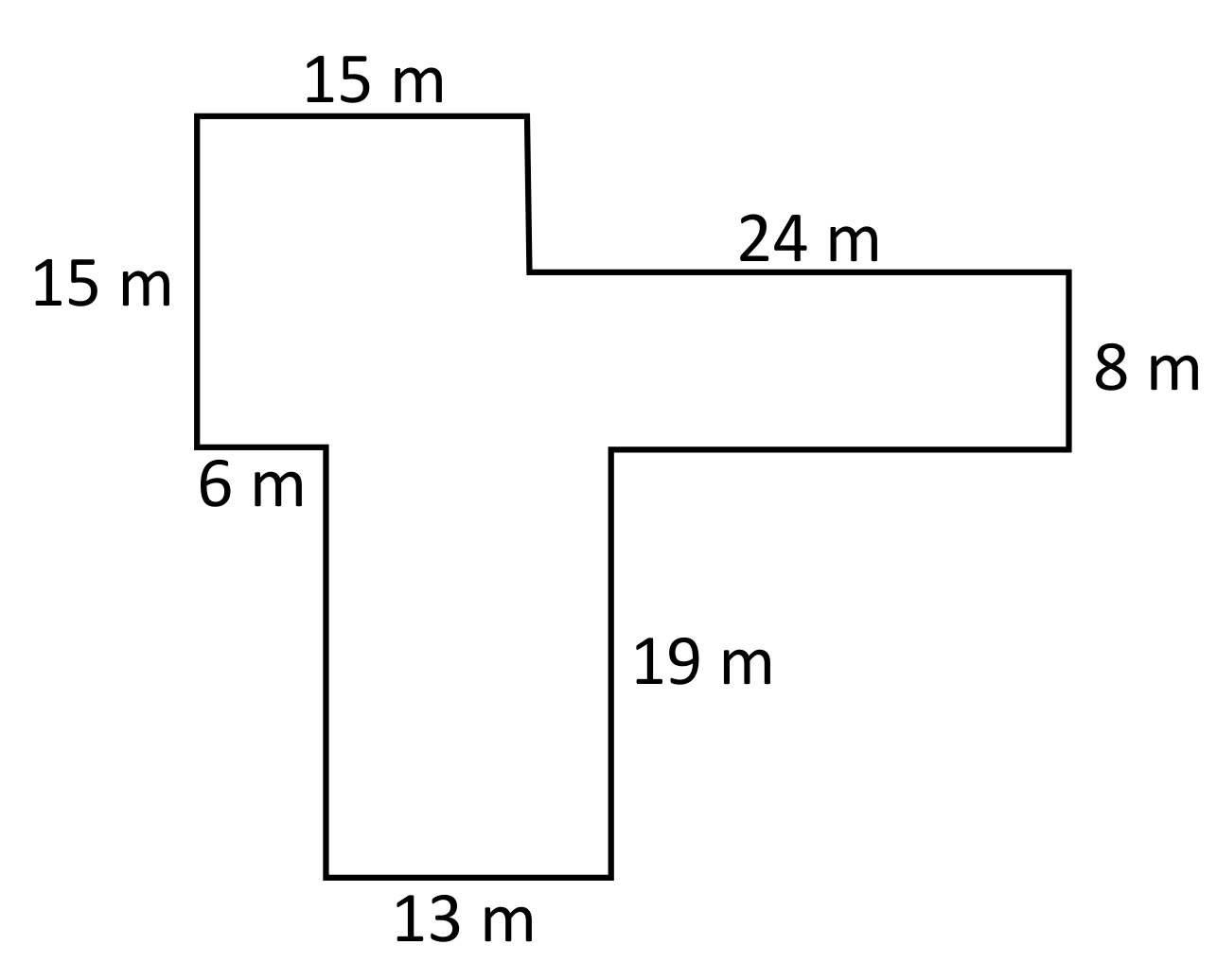
Topic how to find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices: Discover how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle when you have the coordinates of its vertices. This guide will walk you through the process step-by-step, making it easy to understand and apply the necessary formulas. Whether you're a student or just curious, you'll find this information helpful.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle Given Its Vertices
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Triangle
- Basic Formula for Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Using Coordinates to Find Side Lengths
- Calculating Perimeter Using Distance Formula
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter from Vertices
- Special Cases: Equilateral, Isosceles, and Scalene Triangles
- Applications of Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Using Online Calculators for Triangle Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Advanced Methods: Trigonometry and Vectors
- Additional Resources and Tools
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của tam giác dựa trên các đỉnh đã cho (0,0), (0, 5), (-7, 0).
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle Given Its Vertices
To calculate the perimeter of a triangle when the coordinates of its vertices are given, you can use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides and then sum these lengths. Below are the steps and formulas involved:
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle: A(\(x_1, y_1\)), B(\(x_2, y_2\)), and C(\(x_3, y_3\)).
- Use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of each side of the triangle.
- Sum the lengths of the three sides to get the perimeter.
Distance Formula
The distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is given by:
\[
d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Calculating the Sides
- Side \(AB\): \[ d_{AB} = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- Side \(BC\): \[ d_{BC} = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2} \]
- Side \(CA\): \[ d_{CA} = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_1)^2 + (y_3 - y_1)^2} \]
Perimeter Formula
The perimeter \(P\) of the triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\[
P = d_{AB} + d_{BC} + d_{CA}
\]
Example
Let's calculate the perimeter of a triangle with vertices A(1, 2), B(4, 6), and C(7, 1).
- Calculate \(d_{AB}\): \[ d_{AB} = \sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (6 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
- Calculate \(d_{BC}\): \[ d_{BC} = \sqrt{(7 - 4)^2 + (1 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + (-5)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 25} = \sqrt{34} \approx 5.83 \]
- Calculate \(d_{CA}\): \[ d_{CA} = \sqrt{(7 - 1)^2 + (1 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{6^2 + (-1)^2} = \sqrt{36 + 1} = \sqrt{37} \approx 6.08 \]
- Sum the lengths to find the perimeter: \[ P = 5 + 5.83 + 6.08 \approx 16.91 \]

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length around the triangle, calculated by summing the lengths of its sides. Given the vertices of a triangle in a coordinate system, the lengths of the sides can be determined using the distance formula, and subsequently, the perimeter can be calculated. This method is essential in various applications, including geometry problems, real-life measurements, and more.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle: \( A(x_1, y_1) \), \( B(x_2, y_2) \), and \( C(x_3, y_3) \).
- Calculate the length of each side using the distance formula:
- \( AB = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \)
- \( BC = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2} \)
- \( CA = \sqrt{(x_1 - x_3)^2 + (y_1 - y_3)^2} \)
- Add the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter: \( P = AB + BC + CA \).
Example Calculation
Consider a triangle with vertices at \( A(2, 3) \), \( B(4, 7) \), and \( C(6, 3) \).
| Calculate the length of \( AB \): | \( AB = \sqrt{(4 - 2)^2 + (7 - 3)^2} = \sqrt{4 + 16} = \sqrt{20} \approx 4.47 \) |
| Calculate the length of \( BC \): | \( BC = \sqrt{(6 - 4)^2 + (3 - 7)^2} = \sqrt{4 + 16} = \sqrt{20} \approx 4.47 \) |
| Calculate the length of \( CA \): | \( CA = \sqrt{(6 - 2)^2 + (3 - 3)^2} = \sqrt{16} = 4 \) |
| Perimeter: | \( P = 4.47 + 4.47 + 4 = 12.94 \) |
Thus, the perimeter of the triangle is approximately 12.94 units.
Basic Formula for Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its sides. The basic formula to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is straightforward and is given by:
\[\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c\]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the lengths of the three sides of the triangle. Let's denote these sides as \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\).
- Add the lengths of the three sides together using the formula:
- For example, if the sides of the triangle are 5, 7, and 9 units, then:
\[\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c\]
\[\text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 \text{ units}\]
Using Coordinates to Find Side Lengths
If the vertices of the triangle are given as coordinates in a plane, the side lengths can be calculated using the distance formula. For vertices \(A(x_1, y_1)\), \(B(x_2, y_2)\), and \(C(x_3, y_3)\):
- The length of side \(AB\) is:
- The length of side \(BC\) is:
- The length of side \(CA\) is:
\[AB = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\]
\[BC = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2}\]
\[CA = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_1)^2 + (y_3 - y_1)^2}\]
Once the lengths of all sides are calculated, they can be summed up to find the perimeter using the basic formula:
\[\text{Perimeter} = AB + BC + CA\]

Calculating Perimeter Using Distance Formula
To calculate the perimeter of a triangle given its vertices, we need to determine the lengths of its sides using the distance formula. Follow these steps:
- Identify the coordinates of the vertices. Let the vertices be A(\(x_1, y_1\)), B(\(x_2, y_2\)), and C(\(x_3, y_3\)).
- Calculate the length of each side using the distance formula:
- For side AB: \[ AB = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- For side BC: \[ BC = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2} \]
- For side CA: \[ CA = \sqrt{(x_1 - x_3)^2 + (y_1 - y_3)^2} \]
- Sum the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = AB + BC + CA \]
Let's consider an example:
- Vertices: A(1, 2), B(4, 6), C(7, 8)
- Calculate the lengths:
- AB: \[ AB = \sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (6 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
- BC: \[ BC = \sqrt{(7 - 4)^2 + (8 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 2^2} = \sqrt{9 + 4} = \sqrt{13} \approx 3.6 \]
- CA: \[ CA = \sqrt{(7 - 1)^2 + (8 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{6^2 + 6^2} = \sqrt{36 + 36} = \sqrt{72} \approx 8.5 \]
- Calculate the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 3.6 + 8.5 = 17.1 \]
This method ensures accurate calculation of the perimeter for any triangle given its vertex coordinates.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter from Vertices
To find the perimeter of a triangle when the coordinates of its vertices are given, follow these steps:
-
Label the vertices of the triangle as \( A(x_1, y_1) \), \( B(x_2, y_2) \), and \( C(x_3, y_3) \).
-
Calculate the length of side AB using the distance formula:
\[ AB = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \] -
Calculate the length of side BC using the distance formula:
\[ BC = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2} \] -
Calculate the length of side CA using the distance formula:
\[ CA = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_1)^2 + (y_3 - y_1)^2} \] -
Sum the lengths of all three sides to find the perimeter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = AB + BC + CA \]
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any triangle given its vertices.
Special Cases: Equilateral, Isosceles, and Scalene Triangles
In the study of triangles, there are three special cases to consider: equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles. Each type has unique properties that affect how you calculate the perimeter.
Equilateral Triangles
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. This simplifies the perimeter calculation significantly.
- Identify the length of one side, \( a \).
- Since all sides are equal, the perimeter \( P \) is given by: \[ P = 3a \]
Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and one side of a different length.
- Identify the lengths of the equal sides, \( a \), and the base, \( b \).
- The perimeter \( P \) is calculated as: \[ P = 2a + b \]
Scalene Triangles
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths.
- Identify the lengths of all three sides, \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- The perimeter \( P \) is simply the sum of the lengths of the sides: \[ P = a + b + c \]
By understanding these special cases, you can quickly determine the perimeter of any triangle based on its classification and given side lengths.
Applications of Triangle Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a triangle using its vertices has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Construction: In construction and engineering, calculating the perimeter of a triangle is essential for determining material requirements, such as fencing or framing.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors often use triangle perimeter calculations to measure and map out land boundaries accurately.
- Architecture: Architects utilize triangle perimeter calculations in designing structures, ensuring precise dimensions and layouts.
- Geometry and Mathematics: Studying triangle perimeters helps students grasp fundamental geometric concepts and develop problem-solving skills.
- Computer Graphics: Triangle perimeter calculations are foundational in computer graphics for rendering images and modeling objects.
- Navigation: Triangle perimeters play a role in navigation, particularly in determining distances between points on maps or GPS systems.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers may use triangle perimeters in creating geometric patterns or compositions.
These are just a few examples of how understanding triangle perimeter calculation can be applied across various disciplines, demonstrating its versatility and importance in practical contexts.

Using Online Calculators for Triangle Perimeter
Online calculators can be incredibly useful tools for quickly and accurately finding the perimeter of a triangle when you have the coordinates of its vertices. These calculators typically utilize mathematical formulas and algorithms to compute the perimeter based on the input provided.
Here's how you can use online calculators to find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices:
- Search for a reliable online calculator designed for calculating the perimeter of a triangle using vertex coordinates. You can use search engines like Google or Bing to find these calculators.
- Once you've found a suitable calculator, open it in your web browser.
- Look for input fields where you can enter the coordinates of the vertices of your triangle. Depending on the calculator, you may need to input the coordinates in different formats (e.g., Cartesian coordinates or polar coordinates).
- Enter the coordinates of the vertices of your triangle into the corresponding input fields. Make sure to input the coordinates accurately to ensure correct results.
- After entering the coordinates, some calculators may require you to specify the type of triangle (e.g., equilateral, isosceles, scalene) to apply the appropriate perimeter formula.
- Once all necessary information has been entered, initiate the calculation process. This may involve clicking a "Calculate" button or similar action.
- Wait for the calculator to process the input data and compute the perimeter of the triangle.
- Once the calculation is complete, the online calculator will typically display the perimeter of the triangle either directly on the webpage or in a separate output section.
- You can then use the calculated perimeter for further analysis or in any applicable problem-solving scenarios.
Using online calculators for finding the perimeter of a triangle with vertices can save you time and effort compared to manually performing the calculations. Additionally, these calculators often provide accurate results, making them valuable tools for both educational and practical purposes.
Examples and Practice Problems
Exploring examples and practice problems is an effective way to reinforce your understanding of finding the perimeter of a triangle with vertices. Let's delve into some scenarios:
- Example 1: Given the vertices A(2, 3), B(5, 7), and C(8, 4), calculate the perimeter of the triangle ABC.
- Example 2: Consider a triangle with vertices D(-1, -2), E(3, 4), and F(7, -2). Determine the perimeter of triangle DEF.
- Practice Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a triangle with vertices G(-3, 1), H(2, -4), and I(4, 5).
- Practice Problem 2: Given the coordinates J(0, 0), K(6, 0), and L(3, 5), determine the perimeter of triangle JKL.
- Practice Problem 3: Suppose you have a triangle with vertices M(4, 2), N(1, 6), and O(-3, 2). Calculate the perimeter of triangle MNO.
These examples and practice problems offer a hands-on approach to applying the concepts of triangle perimeter calculation. Work through each scenario step by step, utilizing the distance formula or online calculators to verify your solutions. By practicing these problems, you'll enhance your skills and confidence in finding the perimeter of triangles with vertices.
Common Mistakes and Tips
When calculating the perimeter of a triangle using its vertices, there are some common mistakes to avoid and helpful tips to ensure accuracy:
- Incorrect Distance Calculation: One common mistake is miscalculating the distance between vertices. Ensure you are using the correct formula, such as the distance formula in coordinate geometry, to find the lengths of the sides.
- Missing Side Lengths: Another error is forgetting to include all side lengths when calculating the perimeter. Double-check that you have accounted for each side of the triangle.
- Order of Vertices: The order in which you consider the vertices matters. Make sure you consistently follow either clockwise or counterclockwise order when determining the lengths of the sides.
- Incorrect Units: Pay attention to the units of measurement to avoid errors in the final perimeter calculation. Ensure that all side lengths are in the same units before summing them up.
- Forgetting to Add Side Lengths: Some may mistakenly attempt to find the perimeter by summing up the coordinates of the vertices. Remember that you should be adding the lengths of the sides, not the coordinates themselves.
Here are some tips to enhance your accuracy and efficiency when finding the perimeter of a triangle with vertices:
- Organize Your Work: Keep your calculations neat and organized, labeling each side length and corresponding vertex to avoid confusion.
- Double-Check Formulas: Before proceeding with calculations, review the formulas you'll be using to ensure they're applied correctly.
- Use Technology Wisely: While manual calculations are valuable for understanding, consider utilizing online calculators or software to verify your results quickly.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, calculating triangle perimeters improves with practice. Work through various examples to reinforce your understanding and proficiency.
Advanced Methods: Trigonometry and Vectors
When it comes to finding the perimeter of a triangle using its vertices, advanced methods involving trigonometry and vectors can provide efficient and precise solutions. Here's how:
- Trigonometry: Utilizing trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, allows you to calculate side lengths and angles of triangles based on the given vertices. For example, you can use the Law of Cosines to find the length of a side when two sides and the included angle are known.
- Vector Addition: Vectors offer a powerful tool for analyzing geometric shapes, including triangles. By representing each side of the triangle as a vector, you can perform vector addition to find the resultant vector, which represents the perimeter of the triangle. This method is particularly useful when dealing with triangles in three-dimensional space.
- Angle Formulas: Trigonometric identities and angle formulas, such as the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines, provide alternative approaches to finding side lengths and angles of triangles. These formulas are especially helpful when dealing with non-right triangles or when the lengths of only a few sides are known.
- Coordinate Geometry: Combining trigonometry with coordinate geometry enables you to find the lengths of sides and angles of a triangle by considering the coordinates of its vertices. By applying trigonometric concepts within the framework of coordinate geometry, you can derive precise solutions for perimeter calculations.
While these advanced methods may involve more complex mathematical concepts, they offer a deeper understanding of the geometric properties of triangles and provide alternative approaches to solving perimeter problems.

Additional Resources and Tools
Exploring additional resources and utilizing specialized tools can further enhance your understanding and proficiency in finding the perimeter of a triangle with vertices. Here are some valuable resources and tools to consider:
- Mathematics Websites: Websites dedicated to mathematics education often offer detailed explanations, tutorials, and practice problems related to geometry, including the calculation of triangle perimeters. Explore platforms like Khan Academy, Math Is Fun, and Brilliant for comprehensive resources.
- Online Courses: Enrolling in online courses or tutorials specifically focusing on geometry and trigonometry can provide structured learning experiences tailored to your level of expertise. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer a variety of courses taught by experts in the field.
- Mathematical Software: Leveraging mathematical software programs can streamline complex calculations and facilitate visualization of geometric concepts. Consider using tools like GeoGebra, Mathematica, or MATLAB for geometric analysis and problem-solving.
- Community Forums: Engaging with online communities and forums dedicated to mathematics can provide valuable insights, support, and collaborative learning opportunities. Websites such as Math Stack Exchange and Reddit's r/mathematics are excellent platforms for seeking assistance and sharing knowledge.
- Textbooks and References: Referencing textbooks and academic resources on geometry and trigonometry can provide in-depth explanations and theoretical foundations for perimeter calculations. Explore titles like "Geometry: A Comprehensive Course" by Dan Pedoe or "Trigonometry" by I.M. Gelfand and Mark Saul for comprehensive coverage of relevant topics.
By exploring these additional resources and utilizing specialized tools, you can strengthen your mathematical skills and tackle perimeter problems with confidence and precision.
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của tam giác dựa trên các đỉnh đã cho (0,0), (0, 5), (-7, 0).
Tìm chu vi của tam giác có các đỉnh (0,0), (0, 5), (-7, 0)
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của tam giác dựa trên các đỉnh đã cho.
Tìm Chu Vi của Tam Giác với Các Đỉnh Cho Trước