Topic pythagorean theorem calculator perimeter: Explore the power of the Pythagorean theorem calculator for perimeter in this comprehensive guide. Learn how to effortlessly calculate the perimeter of right triangles using this essential tool. Master the fundamentals of geometry and enhance your problem-solving skills with step-by-step instructions and practical examples. Start your journey to geometric mastery today!
Table of Content
- Pythagorean Theorem Calculator for Perimeter
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem
- 2. Understanding Right Triangles
- 3. Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
- 4. Pythagorean Theorem Calculator Overview
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
- 6. Practical Examples of Pythagorean Theorem Calculations
- 7. Importance of Perimeter Calculation in Geometry
- 8. Conclusion: Enhancing Geometry Skills with Pythagorean Theorem Calculators
- YOUTUBE:
Pythagorean Theorem Calculator for Perimeter
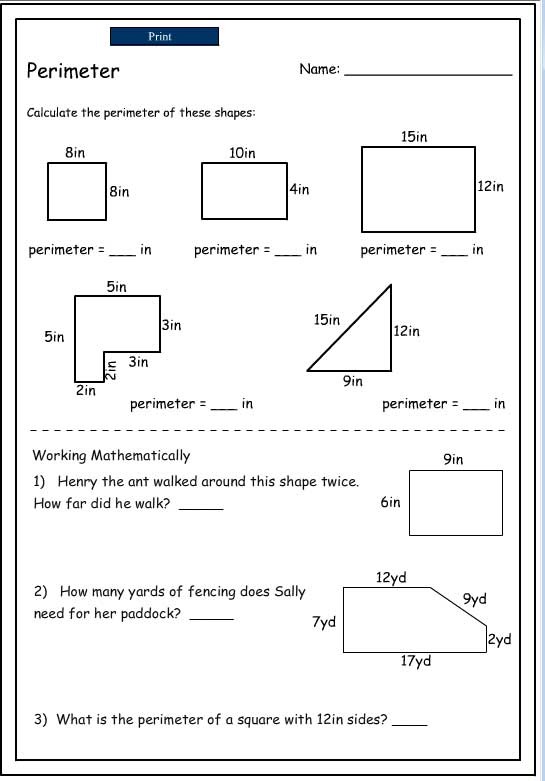
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry used to calculate the length of the sides of a right triangle. It states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
To calculate the perimeter of a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem, you can use the formula:
Perimeter = a + b + c
Where:
- a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides (legs) of the right triangle.
- c is the length of the hypotenuse.
Using a Pythagorean theorem calculator, you can input the lengths of two sides of the right triangle, and the calculator will compute the length of the third side and then calculate the perimeter using the formula mentioned above.
Example:
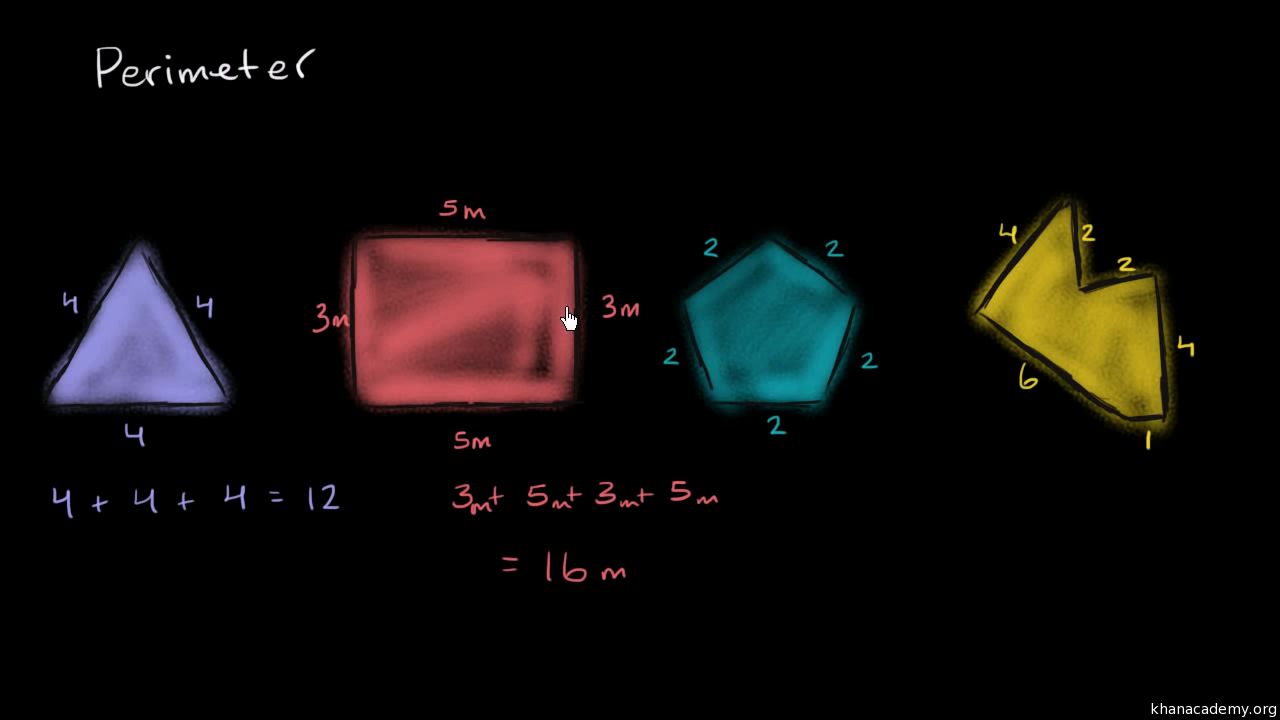
Suppose you have a right triangle with side lengths of 3 and 4 units. Using the Pythagorean theorem, you can find the length of the hypotenuse (c):
c = √(3^2 + 4^2) = √(9 + 16) = √25 = 5 units
Now, you can calculate the perimeter:
Perimeter = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 units
So, the perimeter of the right triangle is 12 units.
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem
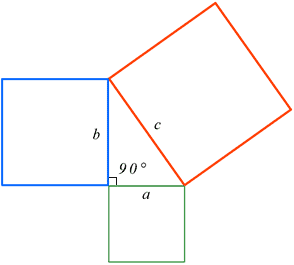
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in mathematics, named after the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras. It establishes a relationship between the sides of a right triangle, specifically stating that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
This theorem is expressed mathematically as:
a² + b² = c²
where:
- a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides (legs) of the right triangle,
- c is the length of the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean Theorem has wide-ranging applications in various fields, including geometry, physics, engineering, and even computer graphics. Understanding this theorem is crucial for solving problems related to right triangles and their properties.
2. Understanding Right Triangles
A right triangle is a geometric shape that has one angle measuring 90 degrees, known as a right angle. It is one of the most fundamental shapes in geometry and plays a crucial role in various mathematical concepts.
Key features of a right triangle include:
- Right Angle: One of the angles in the triangle measures exactly 90 degrees.
- Hypotenuse: The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse. It is the longest side of the triangle.
- Legs: The other two sides of the triangle that form the right angle are called legs. They can vary in length and are typically labeled as 'a' and 'b'.
Properties of right triangles are extensively studied and applied in mathematics and real-world scenarios. Understanding the characteristics and relationships within right triangles is essential for solving problems in geometry, trigonometry, and other branches of mathematics.
3. Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is not only a fundamental concept in geometry but also a practical tool for solving real-world problems involving right triangles. One common application is calculating distances, especially in situations where direct measurement is not feasible.
Here are some scenarios where the Pythagorean Theorem can be applied:
- Distance Calculation: Given two points in a coordinate plane, the distance between them can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem. This is particularly useful in navigation, surveying, and engineering.
- Perimeter Calculation: In geometry, the perimeter of a right triangle can be determined by summing the lengths of its three sides. The Pythagorean Theorem provides a method for finding the missing side when the lengths of the other two sides are known.
- Construction: The Pythagorean Theorem is utilized in construction projects to ensure accuracy and precision when laying out foundations, building structures, and designing architectural elements.
By understanding how to apply the Pythagorean Theorem in various contexts, individuals can solve a wide range of problems efficiently and accurately.
4. Pythagorean Theorem Calculator Overview
A Pythagorean Theorem calculator is a valuable tool for quickly and accurately computing the length of a missing side in a right triangle or solving related problems. These calculators typically provide a user-friendly interface where users can input known values and obtain the result effortlessly.
Key features and functionalities of a Pythagorean Theorem calculator include:
- Input Fields: Users can enter the known values, such as the lengths of the two legs or the hypotenuse, into designated input fields.
- Calculation: The calculator applies the Pythagorean Theorem formula to compute the length of the missing side or the desired parameter, such as the perimeter or area of the triangle.
- Instant Results: Upon entering the required information, the calculator instantly displays the calculated result, allowing users to quickly verify their calculations.
- Additional Functions: Some Pythagorean Theorem calculators may offer additional features, such as the ability to solve for angles, perform unit conversions, or generate step-by-step solutions.
Whether used in educational settings to reinforce understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem or in practical applications for solving real-world problems, Pythagorean Theorem calculators serve as invaluable tools for students, professionals, and enthusiasts alike.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
- Open the Calculator: Start by accessing the Pythagorean Theorem calculator either through a web browser or a dedicated application on your device.
- Input Known Values: Identify the known values of the right triangle, which typically include the lengths of two sides (legs) or the hypotenuse.
- Enter Values: Input the known values into the corresponding fields provided by the calculator. Ensure accuracy when entering numerical values.
- Initiate Calculation: Once all the necessary information is entered, initiate the calculation process by clicking on the "Calculate" button or similar action.
- Review Results: After the calculation is complete, review the results displayed by the calculator. Verify that the computed value aligns with your expectations based on the given inputs.
- Interpret Output: Interpret the output provided by the calculator. Depending on the application, the result may represent the length of a missing side, the perimeter of the triangle, or other relevant parameters.
- Optional Steps: Depending on the features of the calculator, you may have the option to perform additional functions, such as solving for angles, converting units, or generating step-by-step solutions.
- Utilize Additional Features: Explore any additional features or functionalities offered by the calculator to enhance your understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem and its applications.
By following these step-by-step instructions, users can effectively utilize a Pythagorean Theorem calculator to solve problems involving right triangles and enhance their mathematical skills.
6. Practical Examples of Pythagorean Theorem Calculations
The Pythagorean Theorem finds numerous applications in real-world scenarios, enabling individuals to solve practical problems involving distances, measurements, and geometric relationships. Here are some practical examples of how the Pythagorean Theorem can be applied:
- Surveying: Surveyors use the Pythagorean Theorem to measure distances between points on land accurately. By employing triangulation techniques, they can determine the lengths of inaccessible or irregularly shaped areas.
- Construction: Architects and engineers utilize the Pythagorean Theorem in construction projects to ensure structural stability and proper alignment. For example, they may use it to calculate the diagonal measurements of rectangular structures or to determine the lengths of roof rafters.
- Navigation: Navigators and pilots rely on the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate distances between waypoints or landmarks. This is particularly crucial in aviation, maritime navigation, and outdoor activities such as hiking or orienteering.
- Physics: Physicists use the Pythagorean Theorem to analyze the motion of objects in two-dimensional space. It plays a fundamental role in determining displacement, velocity, and acceleration, especially in projectile motion and vector analysis.
- Technology: Pythagorean Theorem calculations are embedded in various technological applications, including GPS systems, computer graphics, and image processing algorithms. They enable precise positioning, mapping, and rendering of visual elements.
These examples illustrate the versatility and importance of the Pythagorean Theorem in diverse fields, showcasing its practical relevance beyond theoretical mathematics.
7. Importance of Perimeter Calculation in Geometry
Perimeter calculation is a fundamental aspect of geometry that plays a crucial role in various mathematical and real-world contexts. Understanding the importance of perimeter calculation contributes to a deeper comprehension of geometric shapes and their properties.
Here are some reasons why perimeter calculation is essential in geometry:
- Shape Identification: Calculating the perimeter helps identify and distinguish different geometric shapes. The perimeter provides valuable information about the boundaries and outlines of shapes, aiding in their classification and analysis.
- Measurement: Perimeter calculation enables precise measurement of the total length of a shape's boundary. This is particularly useful in scenarios where accurate measurements are required for construction, design, or analysis purposes.
- Area Computation: In many cases, the perimeter of a shape is directly related to its area. Understanding the perimeter allows for the computation of the area of polygons, circles, and other geometric figures using appropriate formulas.
- Problem Solving: Perimeter calculation is often an essential step in solving geometry problems and real-world applications. Whether determining fencing requirements for a garden or estimating material quantities for a construction project, perimeter calculation provides valuable insights.
- Conceptual Understanding: Mastery of perimeter calculation enhances conceptual understanding of geometric concepts such as congruence, similarity, and proportionality. It reinforces the relationship between linear measurements and geometric shapes.
Overall, the ability to calculate perimeter is essential for both theoretical exploration and practical application in geometry, facilitating accurate measurements, problem-solving, and geometric analysis.
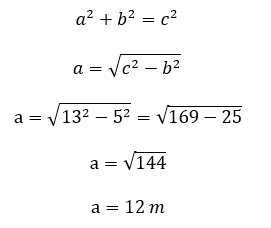
8. Conclusion: Enhancing Geometry Skills with Pythagorean Theorem Calculators
In conclusion, leveraging Pythagorean Theorem calculators significantly enhances one's geometry skills. These calculators not only simplify complex calculations but also provide a practical understanding of the theorem's applications in real-world scenarios. Here are some key benefits and steps for effectively using these calculators:
- Simplification of Calculations: Pythagorean Theorem calculators automate the process of finding the lengths of sides in right triangles, reducing the likelihood of manual errors.
- Time Efficiency: These tools save time, allowing students and professionals to focus on understanding concepts rather than getting bogged down by lengthy computations.
- Enhanced Learning: By visualizing the steps and results, users can better grasp how the Pythagorean Theorem works, reinforcing their learning through practice.
- Versatile Applications: These calculators can be used in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and physics, demonstrating the theorem's broad relevance.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: Regular use of Pythagorean Theorem calculators helps in developing strategic approaches to solving geometric problems, fostering critical thinking.
To effectively use a Pythagorean Theorem calculator for perimeter calculations, follow these steps:
- Input the Known Values: Enter the lengths of the two sides of the right triangle (legs) into the calculator.
- Calculate the Hypotenuse: The calculator will use the Pythagorean Theorem formula \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \) to find the hypotenuse.
- Find the Perimeter: Add the lengths of all three sides (two legs and the hypotenuse) to determine the perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \).
- Verify Results: Double-check the calculated values to ensure accuracy, particularly in practical applications.
Incorporating Pythagorean Theorem calculators into your study routine can transform your approach to geometry, making learning more interactive and effective. As you continue to explore geometric concepts, these calculators will serve as valuable tools, deepening your comprehension and boosting your confidence in tackling complex problems.
Sử dụng Định lý Pythagoras để tìm Diện tích & Chu vi
READ MORE:
Định lý Pythagoras | MathHelp.com