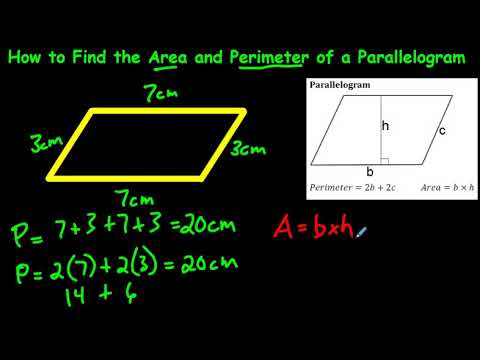
Topic formula perimeter of rhombus: The formula for the perimeter of a rhombus is a fundamental concept in geometry. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about calculating the perimeter, from basic properties to practical examples. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this article will provide clear and concise information to enhance your understanding.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of a Rhombus
- Introduction to the Rhombus
- Basic Properties of a Rhombus
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
- Practical Examples of Perimeter Calculation
- Visualizing the Rhombus and its Perimeter
- Applications of the Perimeter Formula
- Comparing the Rhombus with Other Quadrilaterals
- FAQs about the Rhombus and its Perimeter
- Summary and Key Takeaways
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi hình thoi một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn. Tham khảo video này để nắm vững công thức tính chu vi hình thoi.
Perimeter of a Rhombus
A rhombus is a type of polygon that is a quadrilateral with all four sides having equal length. Here we discuss how to calculate its perimeter.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Rhombus
The perimeter of a rhombus is calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides. Since all sides are equal in length, the formula simplifies to:
\[
P = 4 \times s
\]
where \( P \) is the perimeter, and \( s \) is the length of one side of the rhombus.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the rhombus.
- Multiply the length of the side by 4.
Example Calculation
Suppose each side of a rhombus measures 5 cm. To find the perimeter:
- Using the formula \( P = 4 \times s \), we substitute \( s = 5 \):
- \[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{cm} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the rhombus is 20 cm.
Other Related Properties of Rhombus
- All sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
- The diagonals of a rhombus are not necessarily equal in length.
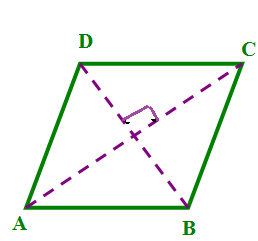
Visual Representation
Consider the following diagram where each side of the rhombus is labeled as \( s \):
READ MORE:
Introduction to the Rhombus
A rhombus is a type of quadrilateral with all four sides having equal length. It is a special case of a parallelogram where opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles are equal. Here are some key characteristics of a rhombus:
- All sides are of equal length.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
- Each diagonal divides the rhombus into two congruent triangles.
The perimeter of a rhombus can be calculated using the formula:
, where s is the length of one side of the rhombus.
Let's delve deeper into its properties and applications to understand how to calculate the perimeter effectively.
Basic Properties of a Rhombus
A rhombus is a fascinating geometric shape with several distinctive properties. Here, we explore these properties in detail:
- Equal Sides: All four sides of a rhombus are of equal length. If each side is denoted as s, then all sides measure s.
- Opposite Angles: Opposite angles of a rhombus are equal. If one angle is , then the opposite angle is also .
- Adjacent Angles: The adjacent angles of a rhombus are supplementary. This means that the sum of any two adjacent angles is .
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (90 degrees). This means they cut each other into equal halves and form four right-angled triangles within the rhombus.
- Perpendicular Diagonals: The diagonals are not only perpendicular but also bisect the angles of the rhombus.
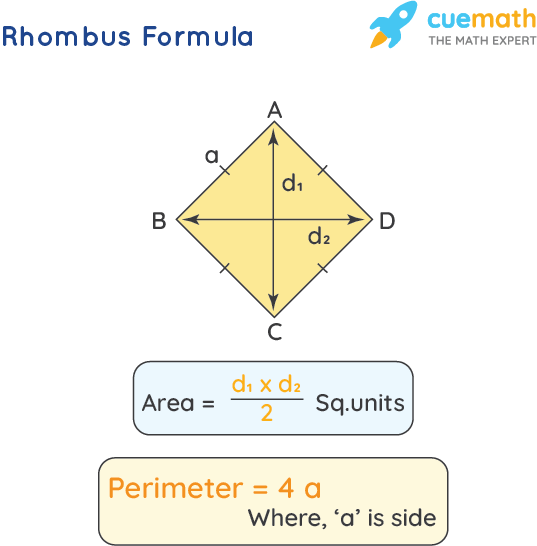
- Area: The area of a rhombus can be calculated using the lengths of the diagonals. If the diagonals are d1 and d2, then the area is given by:
Understanding these properties is crucial for accurately calculating the perimeter and other aspects of a rhombus.
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter of a rhombus is the total length around the shape. Since all four sides of a rhombus are of equal length, calculating the perimeter is straightforward. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
- Identify the length of one side of the rhombus, denoted as s.
- Recall that a rhombus has four sides of equal length.
- Multiply the length of one side by four to find the perimeter.
The formula for the perimeter of a rhombus is:
Where:
- is the length of one side of the rhombus.
For example, if each side of the rhombus measures 5 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
Thus, understanding the perimeter of a rhombus involves recognizing its equal sides and applying a simple multiplication to find the total length around the shape.
Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a rhombus is straightforward if you follow these steps. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you understand the process:
- Measure the Length of One Side:
Begin by measuring the length of one side of the rhombus. Denote this length as s.
- Understand the Perimeter Formula:
The formula for the perimeter of a rhombus is:
- Multiply by Four:
To find the perimeter, multiply the length of one side by four. This step is crucial as it accounts for all four equal sides of the rhombus.
- Example Calculation:
For instance, if each side of the rhombus measures 6 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
- Verification:
To ensure accuracy, verify the measurement of one side and the multiplication. Mistakes in either can lead to incorrect results.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any rhombus, ensuring precision in your mathematical work.
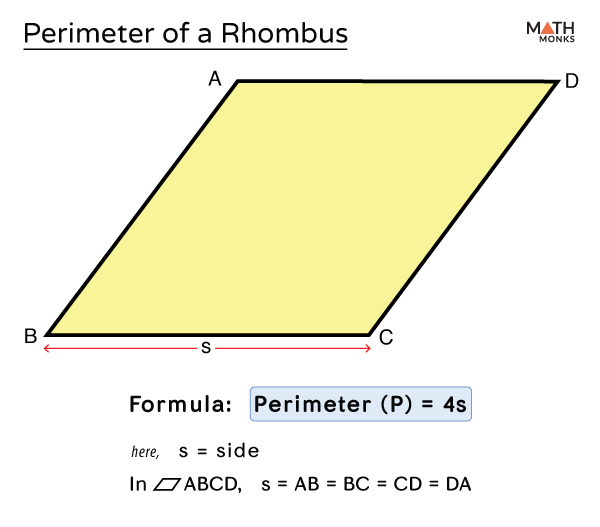
Practical Examples of Perimeter Calculation
To understand the calculation of the perimeter of a rhombus, let's go through a few practical examples using different known values.
Example 1: Using the Side Length
Find the perimeter of a rhombus where each side is 5 cm.
- Identify the formula for the perimeter when the side length is known: \( P = 4s \).
- Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 5 \).
- Calculate the result: \( P = 20 \) cm.
The perimeter of the rhombus is 20 cm.
Example 2: Using the Lengths of Diagonals
Find the perimeter of a rhombus with diagonals of 6 cm and 8 cm.
- Identify the formula for the perimeter when the diagonals are known: \( P = 2\sqrt{d_1^2 + d_2^2} \).
- Substitute the diagonal lengths into the formula: \( P = 2\sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 2\sqrt{36 + 64} \).
- Further simplify: \( P = 2\sqrt{100} \).
- Calculate the result: \( P = 2 \times 10 = 20 \) cm.
The perimeter of the rhombus is 20 cm.
Example 3: Using One Diagonal and One Angle
Find the perimeter of a rhombus with one diagonal of 10 cm and an internal angle of 60°.
- Recall that the diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
- Use the given angle to find half of the diagonal segment: \( d_1/2 \).
- Apply trigonometric identities to find the side length: \( \sin(60°) = \frac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}} \).
- Find the length of the side: \( \text{side} = \frac{10}{2 \sin(60°)} = \frac{10}{2 \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}} = \frac{10}{\sqrt{3}} \approx 5.77 \) cm.
- Use the side length to find the perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 5.77 \approx 23.08 \) cm.
The perimeter of the rhombus is approximately 23.08 cm.
By working through these examples, you can see how the perimeter of a rhombus can be calculated using different given values and formulas.
Visualizing the Rhombus and its Perimeter
Understanding the perimeter of a rhombus becomes easier when we can visualize the shape and its properties. A rhombus is a type of quadrilateral where all four sides have equal length, and opposite angles are equal. It looks like a tilted square or a diamond shape.
Here are some key properties to visualize:
- All four sides are of equal length.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals bisect each other at right angles (90 degrees).
Diagram of a Rhombus
Consider the following diagram of a rhombus with side length \( s \):

In the above diagram:
- The side length is denoted as \( s \).
- The diagonals intersect at right angles.
- The intersection point of the diagonals is the center of the rhombus.
Calculating the Perimeter
The perimeter of a rhombus can be calculated using the simple formula:
\( P = 4s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the rhombus.
Example Calculation
Let's calculate the perimeter of a rhombus with a side length of 5 cm:
- Identify the side length: \( s = 5 \) cm.
- Use the perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \).
- Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 5 \) cm.
- Calculate the result: \( P = 20 \) cm.
So, the perimeter of the rhombus is 20 cm.
Visualizing with Diagonals
The diagonals of a rhombus are also useful in visualizing and calculating its properties. The diagonals bisect each other at right angles, and you can use the lengths of the diagonals to calculate the perimeter if the side length is unknown.
The relationship between the side length and the diagonals \( d_1 \) and \( d_2 \) is given by the formula:
\( s = \sqrt{\left(\frac{d_1}{2}\right)^2 + \left(\frac{d_2}{2}\right)^2} \)
Once the side length is found, you can calculate the perimeter using the perimeter formula.
Interactive Visualization
For an interactive experience, you can use online tools that allow you to drag and resize the rhombus, observing how the perimeter changes dynamically. These tools help in understanding the geometric properties of the rhombus better.
Visualizing the rhombus with its equal sides and diagonal properties helps in grasping the concept of its perimeter effectively.
Applications of the Perimeter Formula
The perimeter formula for a rhombus, \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side, is widely applicable in various fields. Understanding these applications can help in both academic contexts and practical real-world situations.
1. Engineering and Construction
In engineering and construction, precise calculations are crucial. Rhombus shapes are often used in design elements such as tiles, windows, and certain structural components. For example:
- Tile Design: Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the amount of material needed for borders or frames.
- Structural Components: When rhombus-shaped trusses or panels are used, knowing the perimeter helps in material estimation and cutting processes.
2. Manufacturing and Industrial Design
In manufacturing, the perimeter formula is useful for quality control and material efficiency:
- Packaging: Rhombus-shaped packaging requires accurate perimeter measurements to ensure proper material use and to avoid wastage.
- Product Design: Items such as jewelry, specifically diamond cuts, utilize rhombus shapes where the perimeter helps in detailing and finishing processes.
3. Art and Architecture
Artists and architects often incorporate geometric shapes, including rhombuses, into their work:
- Mosaic Art: Rhombus tiles in mosaics require precise perimeter calculations for fitting and aesthetic alignment.
- Architectural Elements: Decorative elements like windows or latticework often use rhombus shapes, necessitating perimeter calculations for design accuracy.
4. Agriculture and Land Measurement
In agriculture, understanding the perimeter of a rhombus-shaped plot is essential for fencing and irrigation planning:
- Fencing: Determining the total length of fencing needed around a rhombus-shaped field ensures proper enclosure and security.
- Irrigation: Knowing the perimeter aids in the design of efficient irrigation systems that follow the plot's boundaries.
5. Sports and Recreation
Sports fields and recreational areas sometimes adopt rhombus shapes for various reasons:
- Field Marking: Calculating the perimeter is necessary for marking boundaries and setting up game areas.
- Track Design: Perimeter measurements ensure accurate track layout for sports that utilize rhombus-shaped tracks.
Overall, the formula for the perimeter of a rhombus is not only a fundamental mathematical concept but also a practical tool in numerous fields ranging from engineering to agriculture. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and precision in various applications.
Comparing the Rhombus with Other Quadrilaterals
The rhombus is a unique quadrilateral with distinct properties that set it apart from other types of quadrilaterals. Below, we will compare the rhombus to other common quadrilaterals such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids.
1. Rhombus vs. Square
- Sides: Both rhombuses and squares have four sides of equal length.
- Angles: All angles in a square are 90 degrees, whereas the angles in a rhombus are not necessarily right angles.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of both shapes bisect each other at right angles. However, the diagonals of a square are equal in length, whereas those of a rhombus are not.
2. Rhombus vs. Rectangle
- Sides: A rhombus has four sides of equal length, while a rectangle has opposite sides of equal length.
- Angles: All angles in a rectangle are 90 degrees, while a rhombus typically has two pairs of equal opposite angles that are not 90 degrees.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other, but they do not intersect at right angles. In a rhombus, diagonals are unequal and intersect at right angles.
3. Rhombus vs. Parallelogram
- Sides: Both rhombuses and parallelograms have opposite sides that are equal in length, but all four sides of a rhombus are equal.
- Angles: Both shapes have opposite angles that are equal. However, a rhombus can be seen as a special type of parallelogram with all sides equal.
- Diagonals: Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other but do not necessarily intersect at right angles. In contrast, the diagonals of a rhombus always intersect at right angles.
4. Rhombus vs. Trapezoid
- Sides: A rhombus has four sides of equal length, while a trapezoid has only one pair of parallel sides.
- Angles: The angles in a rhombus are not necessarily right angles, whereas a trapezoid can have right angles, but it is not a requirement.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at right angles and bisect each other. In a trapezoid, the diagonals do not have any special properties in relation to angle or bisecting.
5. Summary
While the rhombus shares some properties with other quadrilaterals such as the square, rectangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid, its defining feature is that all four sides are of equal length, and its diagonals intersect at right angles and bisect each other. Understanding these distinctions helps in identifying and differentiating the rhombus from other quadrilaterals.

FAQs about the Rhombus and its Perimeter
-
What is a rhombus?
A rhombus is a type of quadrilateral where all four sides have equal length. It is also known as an equilateral quadrilateral. The opposite sides are parallel, and the opposite angles are equal.
-
How do you calculate the perimeter of a rhombus?
The perimeter of a rhombus can be calculated using the formula:
$$ P = 4 \times a $$
where \( a \) is the length of a side of the rhombus. If the side length is known, simply multiply it by 4.
-
Can you calculate the perimeter of a rhombus using the diagonals?
Yes, if the lengths of the diagonals are known, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula:
$$ P = 2 \sqrt{d_1^2 + d_2^2} $$
where \( d_1 \) and \( d_2 \) are the lengths of the diagonals. This formula is derived from the relationship between the sides and diagonals of a rhombus.
-
What are some properties of a rhombus?
Some key properties of a rhombus include:
- All sides are of equal length.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
- Each diagonal divides the rhombus into two congruent triangles.
-
Is a square a type of rhombus?
Yes, a square is a special type of rhombus where all the angles are right angles (90 degrees). Therefore, all squares are rhombuses, but not all rhombuses are squares.
-
How is a rhombus different from other quadrilaterals?
Unlike general quadrilaterals, all sides of a rhombus are equal. It differs from a rectangle in that a rectangle has equal opposite sides and right angles, whereas a rhombus has equal sides but does not necessarily have right angles. A parallelogram shares some properties with a rhombus, such as parallel opposite sides, but a parallelogram does not require all sides to be equal.
Summary and Key Takeaways
The rhombus is a special type of quadrilateral characterized by its equal sides and unique properties. Here are the key takeaways from our comprehensive guide:
- Definition and Properties:
- A rhombus is a four-sided polygon (quadrilateral) with all sides of equal length.
- Opposite sides are parallel, and opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles and are not equal.
- Perimeter Formula:
The perimeter of a rhombus can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times a
\]
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the rhombus.If the lengths of the diagonals are known, the perimeter can also be calculated using:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \sqrt{d_1^2 + d_2^2}
\]
where \( d_1 \) and \( d_2 \) are the lengths of the diagonals. - Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Identify the length of one side or the lengths of the diagonals.
- Apply the appropriate formula based on the known measurements.
- Calculate the perimeter using either \( 4 \times \text{side length} \) or \( 2 \sqrt{d_1^2 + d_2^2} \).
- Comparison with Other Quadrilaterals:
- Unlike squares, which also have equal sides and right angles, a rhombus does not generally have right angles.
- Parallelograms have opposite sides that are equal and parallel but do not necessarily have equal side lengths or bisecting diagonals at right angles.
- Kites have two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal, but their diagonals intersect at right angles and only one pair of opposite angles are equal.
- Applications:
The perimeter formula is essential in various practical applications, including architecture, design, and land measurement, where knowing the boundary length is crucial.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi hình thoi một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn. Tham khảo video này để nắm vững công thức tính chu vi hình thoi.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Thoi
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm diện tích và chu vi hình thoi một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn. Tham khảo video này để nắm vững công thức tính diện tích và chu vi hình thoi.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Hình Thoi