Topic how to find perimeter of hexagon: Discover the simplest methods to calculate the perimeter of a hexagon, whether regular or irregular. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential formulas and step-by-step instructions, ensuring you can determine the perimeter with confidence. Perfect for students, educators, and geometry enthusiasts looking to enhance their mathematical skills.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Hexagon
- Introduction to Hexagon Perimeter
- Formula for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
- Example Calculation for Regular Hexagon
- Formula for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
- Example Calculation for Irregular Hexagon
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculation
- Summary and Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết và hấp dẫn về cách tính chu vi của một lục giác đều. Khám phá cách tính toán chính xác và các ứng dụng thực tế của nó.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Hexagon
The perimeter of a hexagon can be determined using simple formulas depending on whether the hexagon is regular or irregular. Below are the methods to calculate the perimeter of both types of hexagons.
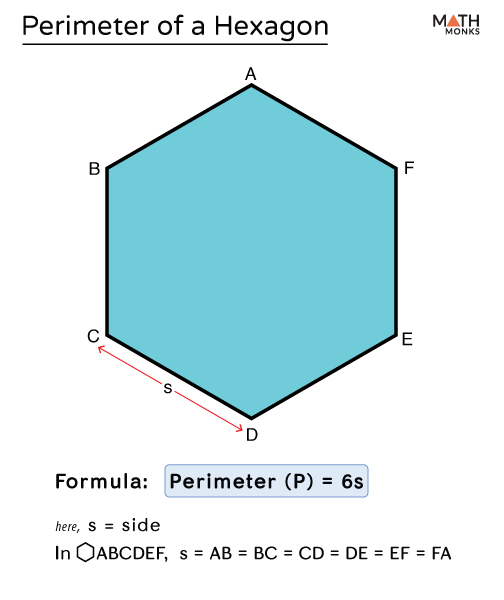
Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has all six sides of equal length. The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a regular hexagon is:
\[ P = 6 \times s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the hexagon.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
- Measure the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Multiply the length by 6.
- The result is the perimeter of the hexagon.
Example
If the side length \( s \) of a regular hexagon is 5 units:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter \( P \) of an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all its sides:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \]
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon
- Measure the lengths of all six sides of the hexagon.
- Add the lengths together.
- The sum is the perimeter of the hexagon.
Example
If the side lengths of an irregular hexagon are 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 units:
\[ P = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 = 39 \text{ units} \]

READ MORE:
Introduction to Hexagon Perimeter
The perimeter of a hexagon is the total length around the shape, which can be calculated easily with the right approach. Hexagons can be either regular, with all sides of equal length, or irregular, with sides of different lengths. Understanding how to find the perimeter of both types is crucial for various mathematical and practical applications.
To calculate the perimeter of a hexagon, you need to know the length of its sides. The process differs slightly depending on whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- Regular Hexagon: All six sides are of equal length.
- Irregular Hexagon: Sides have different lengths.
Below are the methods for calculating the perimeter for each type of hexagon:
- For a regular hexagon, use the formula: \[ P = 6s \] where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- For an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all six sides: \[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \] where \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5, \) and \( s_6 \) are the lengths of the sides.
In the following sections, we will explore these methods in more detail, providing step-by-step instructions and examples to ensure a thorough understanding of how to find the perimeter of any hexagon.
Formula for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
To find the perimeter of a regular hexagon, you can use a straightforward formula. A regular hexagon is defined by having all six sides of equal length. The perimeter \( P \) is the total distance around the hexagon, which can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side \( s \) by the number of sides, which is 6.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a regular hexagon is:
\[ P = 6s \]
Here's how you can apply the formula step-by-step:
- Identify the length of one side of the regular hexagon. This length is denoted as \( s \).
- Multiply the length of the side \( s \) by the number of sides, which is 6.
- The resulting product is the perimeter \( P \) of the hexagon.
For example, if each side of the hexagon is 5 units long, you can calculate the perimeter as follows:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
This means that the perimeter of the hexagon is 30 units.
The simplicity of this formula makes it easy to quickly determine the perimeter of any regular hexagon, which is useful in a variety of practical and academic applications, such as in tiling patterns, engineering designs, and more.
Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a regular hexagon is a simple process. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to ensure you get accurate results.
- Identify the Length of One Side:
- First, measure or identify the length of one side of the hexagon. Let's denote this length as \( s \).
- Apply the Perimeter Formula:
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon: \[ P = 6s \]
- Perform the Multiplication:
- Multiply the length of one side \( s \) by 6. This step involves simple multiplication to find the total perimeter.
- For example, if \( s = 7 \) units: \[ P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \text{ units} \]
- State the Result:
- The final result is the perimeter of the hexagon. For our example, the perimeter is 42 units.
By following these steps, you can easily and accurately calculate the perimeter of any regular hexagon. This method is useful for various applications in mathematics, engineering, and design where precise measurements are essential.
Example Calculation for Regular Hexagon
To find the perimeter of a regular hexagon, you need to know the length of one of its sides. A regular hexagon has six equal sides. The perimeter \( P \) of a regular hexagon can be calculated using the formula:
\( P = 6 \times \text{side length} \)
Let's go through an example to illustrate how this works.
- First, determine the length of one side of the hexagon. For this example, let's assume the side length is 5 units.
- Using the formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon:
- Substitute the given side length into the formula:
- Multiply to find the perimeter:
\( P = 6 \times \text{side length} \)
\( P = 6 \times 5 \)
\( P = 30 \, \text{units} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular hexagon with a side length of 5 units is 30 units.
| Side Length (units) | Perimeter (units) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 30 |
This straightforward method can be applied to any regular hexagon by simply changing the side length. Just remember to multiply the side length by 6 to find the perimeter.

Formula for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
An irregular hexagon has six sides of varying lengths. To find the perimeter of an irregular hexagon, you need to sum the lengths of all its sides. The formula for calculating the perimeter \( P \) is straightforward and can be expressed as:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e + f \)
where \( a, b, c, d, e, \) and \( f \) are the lengths of the six sides of the hexagon.
Let's break down how you can apply this formula step by step:
- Measure or obtain the lengths of all six sides of the hexagon. Ensure you have accurate measurements for each side.
- List the lengths of the sides. For example, if the sides have the following lengths:
- Side 1 (\( a \)) = 3.5 units
- Side 2 (\( b \)) = 4.2 units
- Side 3 (\( c \)) = 5.1 units
- Side 4 (\( d \)) = 4.8 units
- Side 5 (\( e \)) = 6.3 units
- Side 6 (\( f \)) = 2.9 units
- Apply the perimeter formula by adding all the side lengths together:
- Perform the addition to find the perimeter:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e + f \)
Substitute the given side lengths into the formula:
\( P = 3.5 + 4.2 + 5.1 + 4.8 + 6.3 + 2.9 \)
\( P = 26.8 \, \text{units} \)
Thus, the perimeter of this irregular hexagon is 26.8 units.
| Side Number | Side Length (units) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 4.2 |
| 3 | 5.1 |
| 4 | 4.8 |
| 5 | 6.3 |
| 6 | 2.9 |
| Total Perimeter = 26.8 units | |
This formula can be used for any irregular hexagon by summing the lengths of its sides, making it easy to calculate the perimeter regardless of the side lengths.
Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
The perimeter of an irregular hexagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Measure Each Side:
- Using a ruler or measuring tape, measure the length of each of the six sides of the hexagon.
- Ensure that the measurements are in the same unit (e.g., all in centimeters or all in inches).
- List the Side Lengths:
- Record each side length. For example, let's say the side lengths are \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), \(e\), and \(f\).
- Add the Side Lengths:
- Sum the lengths of all six sides using the formula: \[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e + f \]
- Example Calculation:
- Assume the side lengths are:
Side \(a\) = 5 cm Side \(b\) = 7 cm Side \(c\) = 6 cm Side \(d\) = 8 cm Side \(e\) = 5 cm Side \(f\) = 7 cm - Calculate the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 5 + 7 = 38 \text{ cm} \]
- Assume the side lengths are:
By following these steps, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any irregular hexagon by summing the lengths of all its sides.
Example Calculation for Irregular Hexagon
Let's consider an example of calculating the perimeter of an irregular hexagon with sides of varying lengths. The sides of the hexagon are as follows:
- Side AB = 4.2 cm
- Side BC = 5.1 cm
- Side CD = 3.8 cm
- Side DE = 6.0 cm
- Side EF = 4.7 cm
- Side FA = 5.4 cm
To find the perimeter of the irregular hexagon, we simply add the lengths of all its sides:
- First, list the lengths of each side:
- \(AB = 4.2 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(BC = 5.1 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(CD = 3.8 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(DE = 6.0 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(EF = 4.7 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(FA = 5.4 \, \text{cm}\)
- Add the lengths together:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = AB + BC + CD + DE + EF + FA
\]
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4.2 + 5.1 + 3.8 + 6.0 + 4.7 + 5.4
\] - Perform the addition:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4.2 + 5.1 + 3.8 + 6.0 + 4.7 + 5.4 = 29.2 \, \text{cm}
\]
Therefore, the perimeter of the given irregular hexagon is 29.2 cm.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a hexagon, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Misidentifying the Type of Hexagon: Ensure you correctly identify whether the hexagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal). The method for finding the perimeter differs based on this identification.
- Incorrectly Adding Side Lengths: For irregular hexagons, carefully add the lengths of all six sides. Missing or duplicating a side length can result in an incorrect perimeter.
- Mixing Up Units: Always ensure that all side lengths are in the same unit before adding them together. Mixing units (e.g., meters and centimeters) without proper conversion will lead to incorrect results.
- Incorrect Application of Formulas: For regular hexagons, use the formula \( P = 6a \) where \( a \) is the side length. For irregular hexagons, the perimeter is simply the sum of all the side lengths.
- Neglecting to Measure Accurately: When measuring side lengths, use precise tools and methods to ensure accuracy. Small errors in measurement can significantly affect the final perimeter calculation.
- Forgetting to Verify Calculations: Always double-check your work. Recalculate the perimeter to verify that your initial result is accurate. This helps catch any arithmetic mistakes.
- Misinterpreting Coordinate Geometry: When using the distance formula to calculate side lengths from coordinates, ensure you correctly apply the formula \( \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \) for each side. Misapplication can lead to errors in side length determination.
By keeping these common mistakes in mind and double-checking your work, you can ensure an accurate calculation of the hexagon's perimeter.
Practical Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a hexagon is useful in various real-world applications. Here are some practical uses:
- Architecture and Design: Hexagonal shapes are frequently used in architectural designs, such as floor tiles, pavements, and building layouts. Knowing the perimeter helps in material estimation and cost calculation.
- Beekeeping: The honeycomb structure in beehives is a perfect example of hexagons in nature. Beekeepers use perimeter calculations to estimate the amount of wax needed for artificial hives or to gauge the honey production capacity.
- Chemistry: Hexagonal patterns are common in the molecular structures of many compounds, such as graphene. Scientists calculate the perimeter to understand bond lengths and molecular stability.
- Game Design: Board games and digital games often use hexagonal grids to create complex playing fields. Knowing the perimeter helps in designing balanced and engaging game mechanics.
- Engineering: The hexagon is used in engineering projects, such as bolts and nuts, for its strength and ease of use. Engineers calculate the perimeter for sizing tools and components accurately.
- Fabric Design: Hexagonal patterns in fabrics are used for their aesthetic appeal. Designers calculate the perimeter of these shapes to create harmonious and balanced patterns in textiles.
These applications demonstrate the importance of understanding hexagon perimeter calculations in various fields, highlighting its relevance beyond theoretical mathematics.
Summary and Conclusion
In this article, we have explored various aspects of finding the perimeter of a hexagon, both regular and irregular. A hexagon, being a six-sided polygon, has a perimeter calculated by summing the lengths of its sides. For a regular hexagon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is simply six times the length of one side. On the other hand, for an irregular hexagon, the perimeter is the sum of all six different side lengths.
Key points covered include:
- Introduction to Hexagon Perimeter: Understanding the basic concept and significance of perimeter in hexagons.
- Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon: Using the simple formula \( P = 6s \) where \( s \) is the side length.
- Formula for Regular Hexagon Perimeter: Reinforcing the mathematical approach to finding the perimeter.
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Hexagon Perimeter: Providing a detailed method for calculating the perimeter with example calculations.
- Example Calculation for Regular Hexagon: Demonstrating a practical example to illustrate the calculation.
- Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon: Discussing the approach for finding the perimeter of hexagons with unequal sides.
- Formula for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter: Explaining the need to sum all different side lengths.
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter: Offering a methodical process for calculating the perimeter of an irregular hexagon with an example.
- Example Calculation for Irregular Hexagon: Presenting a detailed example to solidify understanding.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Highlighting frequent errors in calculation and ways to avoid them.
- Practical Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculation: Exploring real-world uses of hexagon perimeter calculations, such as in construction, design, and nature.
Understanding the perimeter of hexagons, both regular and irregular, is essential for various mathematical and practical applications. By mastering the calculations and being aware of common mistakes, one can efficiently apply these concepts in different scenarios.
We hope this comprehensive guide has enhanced your knowledge and confidence in calculating the perimeter of hexagons. Keep practicing with different examples to become proficient in these calculations.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết và hấp dẫn về cách tính chu vi của một lục giác đều. Khám phá cách tính toán chính xác và các ứng dụng thực tế của nó.
Chu vi của một lục giác đều: Vấn đề của ngày
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi hình lục giác dành cho học sinh lớp 7. Video giải thích chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
CÁCH TÌM CHU VI HÌNH LỤC GIÁC: LỚP 7