Topic how to find the perimeter of a pentagon: Learn how to find the perimeter of a pentagon with our comprehensive guide. Whether it's a regular or irregular pentagon, our step-by-step instructions and examples will make the calculation simple and straightforward. Perfect for students, teachers, and geometry enthusiasts, this guide ensures you understand and master the concept effortlessly.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Introduction
- Understanding Pentagons
- Types of Pentagons
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- Formula for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Pentagon
- Examples of Regular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Formula for Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
- Examples of Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Comparing Perimeters of Regular and Irregular Pentagons
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của một ngũ giác, bao gồm các ví dụ minh họa và công thức cần thiết. Phù hợp cho học sinh và những người yêu thích hình học.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length around the five sides of the shape. The formula and methods to calculate the perimeter depend on whether the pentagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not necessarily equal).
Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
In a regular pentagon, all sides are of equal length. The perimeter (P) can be calculated using the following formula:
where s is the length of one side.
Example
If each side of a regular pentagon is 6 cm, the perimeter is:
Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all five sides. The formula is:
Example
If the side lengths of an irregular pentagon are 5 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm, the perimeter is:
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Identify if the pentagon is regular or irregular.
- If it is regular, measure one side length and use the formula \( P = 5 \times s \).
- If it is irregular, measure the lengths of all five sides.
- Sum the side lengths to find the perimeter.
Practice Problems
Try calculating the perimeter of these pentagons:
- A regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 cm.
- An irregular pentagon with sides measuring 3 cm, 5 cm, 7 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm.
Conclusion
Finding the perimeter of a pentagon is straightforward whether it is regular or irregular. For regular pentagons, simply multiply the side length by 5. For irregular pentagons, sum the lengths of all sides. Understanding these methods will help in solving various geometry problems involving pentagons.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Finding the perimeter of a pentagon is a fundamental concept in geometry that is essential for various practical applications. A pentagon is a five-sided polygon, and calculating its perimeter involves understanding whether it is regular or irregular.
In this guide, we will explore the methods to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons, ensuring you have a clear and comprehensive understanding of the process.
For a regular pentagon, where all sides and angles are equal, the calculation is straightforward. For an irregular pentagon, the process requires summing the lengths of all its sides. Let's dive into the details:
- Identify the type of pentagon: regular or irregular.
- Measure the length of the sides.
- Apply the appropriate formula based on the type.
This step-by-step guide will provide you with the knowledge and confidence to calculate the perimeter of any pentagon you encounter. Whether you are a student, teacher, or simply interested in geometry, this guide will be a valuable resource.
Understanding Pentagons
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon with five angles. It can be classified into two types: regular and irregular pentagons.
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal. Each interior angle measures 108 degrees, and the exterior angle is 72 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: The sides and angles are not equal.
Understanding the properties of pentagons is essential for calculating their perimeter and area. The perimeter of a pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. For a regular pentagon with side length \(a\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by the formula:
\[ P = 5a \]
In the case of an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is simply the sum of the lengths of its five sides:
\[ P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + a_4 + a_5 \]
Where \(a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, a_5\) are the lengths of the sides.
By understanding these basic principles, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any pentagon, whether it is regular or irregular.
Types of Pentagons
Pentagons can be categorized based on the equality of their sides and angles. Here are the main types of pentagons:
-
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has all five sides and angles equal. The formula to find the perimeter of a regular pentagon is given by:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( s \) is the length of a side. This symmetry makes calculations straightforward and is often used in geometric problems. -
Irregular Pentagon: An irregular pentagon has sides and angles that are not equal. To find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, you must measure and add up the lengths of all five sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides. This type of pentagon requires individual side measurements for perimeter calculations.
Understanding the type of pentagon you are dealing with is crucial for accurately calculating its perimeter. Regular pentagons have a simple, consistent formula, while irregular pentagons require a more detailed approach.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. It is a fundamental concept in geometry and is used to determine the boundary length of various shapes, including polygons like pentagons. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for solving many real-world problems and mathematical tasks.
Here are the key points to understand about perimeter:
- Definition: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides of a shape.
- Units: The perimeter is measured in linear units, such as meters, centimeters, or inches.
- Formula for Regular Polygons: For a regular polygon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter (P) can be calculated using the formula:
where n is the number of sides and s is the length of one side. - Formula for Irregular Polygons: For an irregular polygon, where sides may have different lengths, the perimeter is found by adding the length of each side together:
Calculating the perimeter is straightforward once you know the lengths of all sides. This basic understanding of perimeter is crucial for more complex geometrical calculations and practical applications.

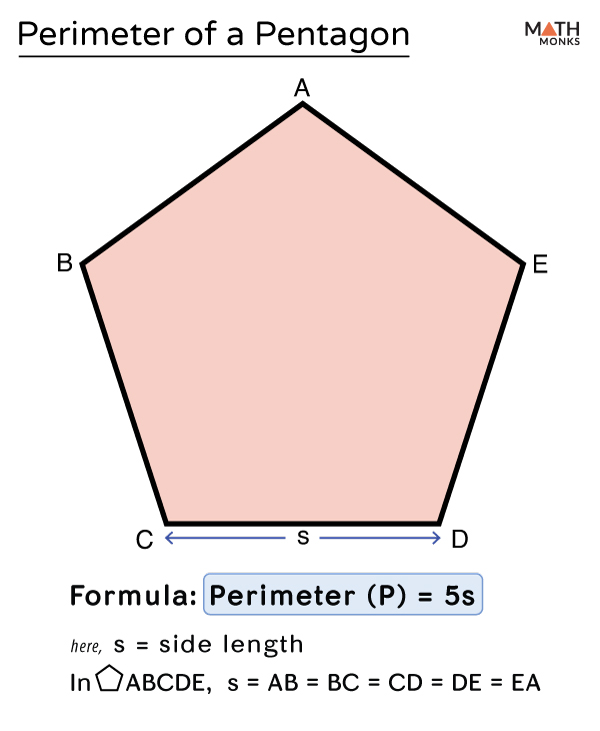
Formula for Regular Pentagon Perimeter
The perimeter of a regular pentagon is the total distance around its boundary. In a regular pentagon, all five sides are of equal length. To find the perimeter, you can use the following formula:
- Formula: \( P = 5s \)
- Where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the length of one side of the pentagon.
Here is a step-by-step process to calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon:
- Measure the side length: Determine the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply by five: Since all sides are equal in length, multiply the length of one side by five to get the total perimeter.
- Apply the formula: Substitute the measured side length into the formula \( P = 5s \).
For example, if each side of the pentagon is 6 cm long, the perimeter would be:
- Calculation: \( P = 5 \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 30 \, \text{cm} \)
This straightforward method allows you to quickly find the perimeter of any regular pentagon, ensuring you have accurate measurements for your geometric calculations.
Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon involves a straightforward process since all sides are of equal length. Follow these steps to determine the perimeter of a regular pentagon:
- Identify the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon: \( P = 5s \), where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the side length.
- Multiply the side length by 5 to get the perimeter.
For example, if the side length of a regular pentagon is 8 units:
- Identify the side length: \( s = 8 \) units.
- Apply the formula: \( P = 5 \times 8 \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 40 \) units.
The perimeter of a regular pentagon with a side length of 8 units is 40 units.
Examples of Regular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is straightforward since all its sides are equal. The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon with side length \( s \) is:
\[ P = 5s \]
Here are detailed examples to illustrate the calculation:
Example 1
Find the perimeter of a regular pentagon where each side is 7 cm long.
- Identify the side length \( s \) of the pentagon.
- Since all sides are equal, use the formula \( P = 5s \).
- Substitute the side length into the formula:
- \( s = 7 \) cm
- \( P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \) cm
- The perimeter of the pentagon is 35 cm.
Example 2
Calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 inches.
- Note the side length \( s \) of the pentagon.
- Apply the formula \( P = 5s \).
- Plug in the side length:
- \( s = 10 \) inches
- \( P = 5 \times 10 = 50 \) inches
- The perimeter of the pentagon is 50 inches.
Example 3
Determine the perimeter of a regular pentagon with a side length of 4.5 meters.
- Recognize the side length \( s \).
- Use the perimeter formula \( P = 5s \).
- Insert the side length into the formula:
- \( s = 4.5 \) meters
- \( P = 5 \times 4.5 = 22.5 \) meters
- The perimeter of the pentagon is 22.5 meters.
By following these examples, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any regular pentagon as long as you know the length of its sides.
Formula for Irregular Pentagon Perimeter
To find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, you simply need to sum the lengths of all five sides. Unlike a regular pentagon, where each side is of equal length, an irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. The general formula for the perimeter (P) of an irregular pentagon is:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
Here, \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) represent the lengths of the five sides of the pentagon.
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, follow these steps:
- Measure the length of each side of the pentagon.
- Sum the lengths of all five sides.
Let's go through an example calculation:
- Side \( a = 5 \) cm
- Side \( b = 7 \) cm
- Side \( c = 6 \) cm
- Side \( d = 4 \) cm
- Side \( e = 8 \) cm
Using the formula:
\[ P = 5 + 7 + 6 + 4 + 8 \]
\[ P = 30 \, \text{cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of this irregular pentagon is 30 cm.

Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon involves adding the lengths of all five sides. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
-
Identify and Measure All Sides: First, measure the length of each side of the pentagon. Label these sides as \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), \( d \), and \( e \).
- For example, let \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 7 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 6 \, \text{cm} \), \( d = 8 \, \text{cm} \), and \( e = 9 \, \text{cm} \).
-
Sum the Lengths of All Sides: Add the lengths of the five sides to find the perimeter.
Using the example values:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e
\]Substituting the values:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm}
\]Calculate the sum:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 35 \, \text{cm}
\] -
Verify Your Calculation: Double-check each measurement and the addition to ensure accuracy. Errors in measurement or arithmetic can lead to incorrect results.
If any side lengths are not directly measurable, consider using geometric properties or tools like the Pythagorean theorem to calculate unknown side lengths based on available information.
In conclusion, the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is simply the total length of its sides. Make sure to measure accurately and verify your calculations to obtain the correct perimeter.
Examples of Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Below are two examples illustrating this process:
Example 1:
Consider an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths:
- Side 1: 5 cm
- Side 2: 7 cm
- Side 3: 4 cm
- Side 4: 6 cm
- Side 5: 8 cm
To find the perimeter, sum all the side lengths:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5\,\text{cm} + 7\,\text{cm} + 4\,\text{cm} + 6\,\text{cm} + 8\,\text{cm} \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 30\,\text{cm} \]
Example 2:
Consider another irregular pentagon with these side lengths:
- Side 1: 3.5 m
- Side 2: 4.2 m
- Side 3: 5.1 m
- Side 4: 2.8 m
- Side 5: 3.9 m
To calculate the perimeter, sum all the side lengths:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3.5\,\text{m} + 4.2\,\text{m} + 5.1\,\text{m} + 2.8\,\text{m} + 3.9\,\text{m} \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 19.5\,\text{m} \]
Steps for Calculation:
- List the lengths of all sides of the pentagon.
- Add the lengths together to find the total perimeter.
These examples demonstrate the straightforward method of summing side lengths to determine the perimeter of an irregular pentagon.
Comparing Perimeters of Regular and Irregular Pentagons
Understanding the differences between the perimeters of regular and irregular pentagons is crucial for various applications in geometry and real-life scenarios. Below is a detailed comparison:
- Regular Pentagon
- All sides are of equal length.
- Formula for perimeter: \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Example: If each side of a regular pentagon is 6 units, the perimeter \( P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \) units.
- Irregular Pentagon
- Sides are of different lengths.
- Formula for perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \), where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the five sides.
- Example: If the side lengths are 3 units, 7 units, 8 units, 5 units, and 6 units, the perimeter \( P = 3 + 7 + 8 + 5 + 6 = 29 \) units.
The key differences can be summarized as follows:
| Aspect | Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
|---|---|---|
| Side Lengths | All equal | Different |
| Perimeter Formula | \( P = 5a \) | \( P = a + b + c + d + e \) |
| Example Calculation | If \( a = 6 \): \( P = 30 \) units | If \( a = 3 \), \( b = 7 \), \( c = 8 \), \( d = 5 \), \( e = 6 \): \( P = 29 \) units |
Regular pentagons are simpler to calculate due to their uniformity, while irregular pentagons require individual measurement of each side. Both types have their unique properties and uses in various fields such as architecture, design, and mathematics.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon can sometimes lead to errors if certain common pitfalls are not avoided. Here are some mistakes to watch out for:
- Not Differentiating Between Regular and Irregular Pentagons:
It's essential to use the correct formula based on whether the pentagon is regular or irregular. For a regular pentagon, use \( P = 5s \), where \( s \) is the side length. For an irregular pentagon, sum the lengths of all five sides: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Incorrect Measurement:
Ensure accurate measurement of all sides. Even a small error in measuring one side can significantly affect the total perimeter. Double-check measurements for precision.
- Mixing Units:
Always use the same unit of measurement for all sides. Mixing units (e.g., inches and centimeters) without proper conversion can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Calculation Errors:
Simple arithmetic mistakes can lead to wrong results. Use a calculator to ensure accuracy, especially when dealing with irregular pentagons.
- Forgetting to Add All Sides:
When calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, remember to include the lengths of all five sides. Missing even one side will result in an inaccurate perimeter.
- Rounding Off Too Early:
Perform calculations with exact numbers and round off only at the final step to maintain precision.
By being mindful of these common errors, you can ensure more accurate and reliable calculations of the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons.
Applications of Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon has various practical applications in different fields. Here are some examples:
-
Architecture and Construction:
In architectural design, particularly when creating polygonal structures, knowing the perimeter is essential for calculating material requirements. For instance, when designing pentagonal buildings or sections of buildings, the perimeter helps determine the amount of baseboard, fencing, or framing needed.
-
Landscaping:
Landscapers often use geometric shapes in garden designs. Calculating the perimeter of a pentagonal flower bed or pathway allows for accurate planning of borders, fencing, and the allocation of decorative elements.
-
Art and Design:
Artists and graphic designers may use pentagons in their work. Understanding the perimeter helps in scaling designs accurately and ensuring proportions are maintained when creating patterns or motifs.
-
Education:
Teaching students how to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon helps them understand geometric principles and apply mathematical concepts to real-world problems. It also improves their problem-solving skills.
-
Sports and Recreation:
In some sports, field or court designs incorporate polygonal shapes. Knowing the perimeter can assist in marking boundaries and planning the layout of the playing area, ensuring consistency and fairness in the game setup.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners use geometric calculations to design and layout city blocks, parks, and other infrastructure. Calculating the perimeter of various shapes, including pentagons, aids in efficient space utilization and resource allocation.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của một ngũ giác, bao gồm các ví dụ minh họa và công thức cần thiết. Phù hợp cho học sinh và những người yêu thích hình học.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Ngũ Giác
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác đều và không đều, bao gồm các công thức và ví dụ minh họa. Phù hợp cho học sinh và những người yêu thích hình học.
Chu Vi Ngũ Giác, Chu Vi cho Ngũ Giác Đều và Không Đều kèm Công Thức & Ví Dụ


