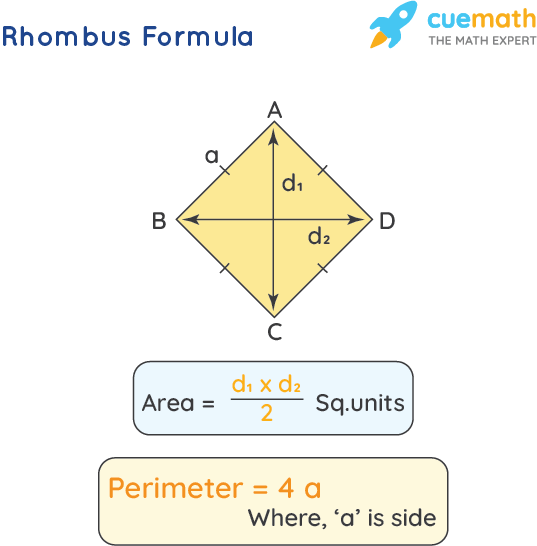
Topic how do you spell perimeter: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to spell perimeter correctly. Spelling can sometimes be tricky, but with our easy tips and clear explanations, you'll never misspell perimeter again. Whether you're a student, teacher, or just curious, this guide will help you master the spelling and understanding of perimeter.
Table of Content
- How to Spell Perimeter
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Correct Spelling of Perimeter
- Common Spelling Mistakes
- Understanding the Concept of Perimeter
- Perimeter in Geometry
- Practical Applications of Perimeter
- How to Calculate Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Tips for Remembering the Spelling
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
How to Spell Perimeter
The word perimeter is spelled as follows:
- P
- E
- R
- I
- M
- T
Definition of Perimeter
The term perimeter refers to the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
Mathematical Formula for Perimeter
The formula to calculate the perimeter varies depending on the shape:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): \( P = 2\pi r \)
Examples
- For a rectangle with length \( l = 5 \) and width \( w = 3 \), the perimeter \( P = 2(5 + 3) = 16 \).
- For a square with side length \( s = 4 \), the perimeter \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
- For a triangle with sides \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), and \( c = 5 \), the perimeter \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \).
- For a circle with radius \( r = 7 \), the circumference \( P = 2 \pi \times 7 = 14\pi \).

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It's an essential measurement used in various practical applications, from construction to everyday problem-solving.
To understand perimeter, let's break it down step by step:
- Definition: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides of a polygon. For simple shapes, like rectangles and squares, it's straightforward to calculate by adding the lengths of each side.
- Units of Measurement: Perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), inches (in), and feet (ft).
- Formula Application:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference, \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Examples:
- A square with each side measuring 5 cm has a perimeter of \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm.
- A rectangle with a length of 8 m and a width of 3 m has a perimeter of \( 2(8 + 3) = 22 \) m.
- Practical Applications: Calculating the perimeter is useful in various real-life situations, such as determining the amount of material needed to fence a garden or outline a field.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial for solving many geometric problems and is a foundational skill in mathematics.
Correct Spelling of Perimeter
The correct spelling of the word is perimeter. It is derived from the Greek words peri (meaning "around") and metron (meaning "measure"). Here is a breakdown of the spelling and common misspellings:
- Correct Spelling: perimeter
- Common Misspellings:
- perimete
- parimiter
- peremeters
- perimater
- permiter
- periemeter
- perimetr
- primater
- parimeter
- perimeeter
- perimiter
- primeter
- perimaters
- peremeter
- permieter
- permeter
- periameters
- periemeters
- perimitier
To help remember the correct spelling, note that "perimeter" starts with "peri-", which is a common prefix in English for words related to surrounding or enclosing. The suffix "-meter" indicates measurement. So, perimeter essentially means measuring around a boundary.
In pronunciation, "perimeter" is pronounced as puh-RIM-i-ter:
- Phonetic Spelling: [pəˈrɪmɪtər]
By focusing on the prefix "peri-" and the suffix "-meter", you can more easily remember the correct spelling and avoid common mistakes.
Common Spelling Mistakes
While the word "perimeter" might seem straightforward, it is often misspelled in various ways. Here are some of the most common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
- Perameter: This is a frequent misspelling. Remember, "perimeter" is derived from the Greek words "peri" (around) and "metron" (measure), so it includes the "i" after "per".
- Perimeter: Some might mistakenly add an extra "i" making it "perimetre" or "perimiter". Stick to "perimeter" to avoid errors.
- Parameter: This word is related but distinct from "perimeter". While "parameter" refers to a defining or limiting factor, "perimeter" specifically means the boundary around a shape.
To avoid these mistakes, follow these steps:
- Break down the word into syllables: per-i-me-ter. Pronouncing each syllable can help reinforce the correct spelling in your memory.
- Remember the meaning: Relate "perimeter" to its definition of measuring around an object. This can help differentiate it from similar words.
- Practice with examples: Use "perimeter" in sentences to get comfortable with its spelling and context.
By understanding these common pitfalls and actively practicing, you can confidently spell "perimeter" correctly every time.
Understanding the Concept of Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is the length of the boundary that encloses a geometric figure. Understanding how to calculate and apply the perimeter is essential for solving various mathematical problems and practical applications.
Here is a step-by-step explanation to understand the concept of the perimeter:
-
Definition:
The perimeter is defined as the sum of the lengths of all sides of a polygon. For a closed figure, the perimeter is the total distance around the shape.
-
Basic Formula:
The general formula for calculating the perimeter of a polygon is:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s_i \) represents the length of each side \( i \) of the polygon.
-
Specific Formulas for Common Shapes:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference, calculated by \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
-
Visualization:
Visualizing the perimeter involves imagining walking along the edge of the shape from one vertex back to the starting point. This helps in comprehending the concept more clearly.
-
Applications:
The concept of the perimeter is used in various real-life situations, such as determining the amount of fencing required to enclose a yard, the length of trim needed for a border, or the distance around a track.
Understanding and calculating the perimeter is a crucial skill in geometry that enhances spatial reasoning and problem-solving abilities.

Perimeter in Geometry
In geometry, the perimeter is an essential measurement that represents the total distance around a two-dimensional shape. It is a key concept used to understand the properties and dimensions of various geometric figures. Here’s a detailed step-by-step explanation of the perimeter in geometry:
-
Definition:
The perimeter of a geometric figure is the total length of its outer boundary. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of the figure.
-
Perimeter of Common Shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is given by the formula: \[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) of a square is given by: \[ P = 4s \] where \(s\) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the side lengths.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference \(C\), is calculated by: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \(r\) is the radius.
-
Irregular Shapes:
For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by measuring and summing the lengths of all the sides.
-
Measurement Units:
Perimeter is measured in linear units, such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet, depending on the units used for the side lengths.
-
Visualization:
To visualize the perimeter, imagine tracing the outline of the shape with a string. The length of the string when fully stretched out is the perimeter of the shape.
-
Applications:
The concept of perimeter is used in various practical applications, such as determining the length of fencing required to enclose a garden, the amount of trim needed for a room, or the distance around a walking path.
Understanding the perimeter in geometry helps in comprehending the dimensions and properties of shapes, which is crucial for solving geometric problems and real-world tasks.
Practical Applications of Perimeter
The concept of perimeter is not only fundamental in geometry but also has numerous practical applications in everyday life. Here are detailed examples and explanations of how perimeter is used in various real-world scenarios:
-
Fencing a Property:
One of the most common uses of perimeter is in determining the length of fencing required to enclose a property. By calculating the perimeter of the land, one can purchase the appropriate amount of fencing material.
- Example: To fence a rectangular yard measuring 50 meters in length and 30 meters in width: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) = 2(50 + 30) = 160 \text{ meters} \]
-
Construction and Carpentry:
In construction, the perimeter is used to determine the amount of materials needed for framing, molding, and other finishing tasks. Knowing the perimeter helps in ordering the correct lengths of materials.
- Example: To install baseboards around a room measuring 4 meters by 5 meters: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(4 + 5) = 18 \text{ meters} \]
-
Gardening and Landscaping:
Gardeners and landscapers use the perimeter to design flower beds, lawns, and other garden features. It helps in calculating the amount of edging, borders, or fencing required.
- Example: To create a circular flower bed with a radius of 3 meters: \[ \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r = 2 \times 3.14 \times 3 = 18.84 \text{ meters} \]
-
Sports Fields and Tracks:
Perimeter measurements are crucial in designing sports fields and running tracks. It ensures that the dimensions meet official regulations and helps in planning the layout of the facility.
- Example: To determine the perimeter of a standard 400-meter running track: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 400 \text{ meters} \]
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers use the perimeter to plan the layout of furniture, rugs, and other elements within a room. It helps in ensuring that items fit perfectly within the space.
- Example: To find the perimeter of a rectangular room for placing a carpet: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) \] For a room of 6 meters by 4 meters: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(6 + 4) = 20 \text{ meters} \]
-
Clothing and Fashion:
In fashion design, perimeter measurements are used to calculate the lengths of fabric, trims, and hems required for garments. It ensures a proper fit and finish for the clothing items.
The perimeter is a versatile measurement that plays a crucial role in various fields, from construction and landscaping to sports and fashion. Understanding how to calculate and apply the perimeter helps in making precise and efficient decisions in these practical applications.
How to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing the lengths of all its sides. Different geometric shapes have specific formulas for calculating the perimeter. Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter for various shapes:
-
Rectangle:
For a rectangle, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Example: If a rectangle has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters: \[ P = 2(8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \text{ meters} \]
-
Square:
For a square, the perimeter \( P \) is given by:
\[
P = 4s
\]where \( s \) is the side length.
- Example: If each side of a square is 6 meters: \[ P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ meters} \]
-
Triangle:
For a triangle, the perimeter \( P \) is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Example: For a triangle with sides of 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters: \[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ meters} \]
-
Circle:
For a circle, the perimeter is known as the circumference \( C \) and is calculated by:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]where \( r \) is the radius.
- Example: If a circle has a radius of 7 meters: \[ C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 = 43.96 \text{ meters} \]
-
Irregular Shapes:
For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by measuring and summing the lengths of all the sides. Each side is measured individually and then added together.
By following these formulas and steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any geometric shape, enhancing your understanding and application of this fundamental geometric concept.
Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a geometric shape involves using specific formulas tailored to each shape. Here are the detailed formulas for calculating the perimeter of common geometric shapes:
-
Rectangle:
The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
-
Square:
The perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by:
\[
P = 4s
\]where \( s \) is the side length.
-
Triangle:
The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
-
Circle (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference \( C \), is calculated by:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]where \( r \) is the radius.
-
Regular Polygon:
The perimeter \( P \) of a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal) with \( n \) sides, each of length \( s \), is given by:
\[
P = n \times s
\] -
Irregular Polygon:
For an irregular polygon, the perimeter \( P \) is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]where \( s_i \) represents the length of each side \( i \).
By applying these formulas, you can calculate the perimeter of various geometric shapes accurately, aiding in solving both theoretical and practical problems involving perimeter.

Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of different shapes can be enhanced through specific examples. Below are detailed examples of perimeter calculations for various geometric shapes:
-
Rectangle:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 10 meters and a width of 4 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
P = 2(l + w)
\]Substitute \( l = 10 \) meters and \( w = 4 \) meters:
\[
P = 2(10 + 4) = 2 \times 14 = 28 \text{ meters}
\] -
Square:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 5 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
P = 4s
\]Substitute \( s = 5 \) meters:
\[
P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ meters}
\] -
Triangle:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides of 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]Substitute \( a = 3 \) meters, \( b = 4 \) meters, and \( c = 5 \) meters:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ meters}
\] -
Circle (Circumference):
Example: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a radius of 7 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
C = 2\pi r
\]Substitute \( r = 7 \) meters:
\[
C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 = 43.96 \text{ meters}
\] -
Regular Pentagon:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
P = n \times s
\]Substitute \( n = 5 \) and \( s = 6 \) meters:
\[
P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \text{ meters}
\] -
Irregular Polygon:
Example: Calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon with side lengths of 4 meters, 7 meters, 3 meters, and 6 meters.
Using the formula:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} s_i
\]Substitute the side lengths:
\[
P = 4 + 7 + 3 + 6 = 20 \text{ meters}
\]
These examples illustrate how to apply the formulas for calculating the perimeter of different geometric shapes. Practicing with various examples helps solidify the understanding of perimeter calculations.
Tips for Remembering the Spelling
Remembering the correct spelling of "perimeter" can be challenging, but with a few helpful tips and tricks, you can master it easily. Here are some detailed strategies to help you remember how to spell "perimeter":
-
Break it Down:
Divide the word into smaller parts: "peri" + "meter". This helps in visualizing the word and recalling the correct sequence of letters.
-
Mnemonic Devices:
Create a mnemonic to remember the spelling. For example:
- "Peri" can remind you of the prefix meaning "around" or "surrounding".
- "Meter" can remind you of measurement, as a perimeter measures the distance around a shape.
- Combine them into a phrase: "A meter measures the peri (around) the shape."
-
Visual Cues:
Write the word down multiple times while saying it aloud. Visual and auditory repetition can reinforce memory.
-
Use in Sentences:
Practice using the word "perimeter" in different sentences. For example:
- "The perimeter of the garden is 30 meters."
- "We need to calculate the perimeter of the rectangle."
-
Flashcards:
Create flashcards with the word "perimeter" on one side and its definition on the other. Review these regularly to reinforce the spelling in your memory.
-
Word Associations:
Associate "perimeter" with other words you know. For example, think of "periscope" (which looks around) or "peripheral" (related to the edge). These associations can help reinforce the spelling of "perimeter".
-
Quiz Yourself:
Take spelling quizzes or ask someone to quiz you on the spelling of "perimeter". Testing yourself can help solidify your knowledge.
By employing these tips and regularly practicing, you can confidently remember and correctly spell the word "perimeter". Consistent practice and the use of mnemonic devices are especially effective in reinforcing the correct spelling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how to spell and calculate the perimeter is a fundamental skill in both everyday life and various fields of study, especially geometry. By mastering the correct spelling and comprehending the concept, you can confidently apply perimeter calculations in various practical situations.
To summarize:
- Correct Spelling: The word "perimeter" is spelled P-E-R-I-M-E-T-E-R.
- Definition: The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape.
- Common Mistakes: Be cautious of common misspellings such as "perimiter" or "peremeter."
- Concept: Understanding the perimeter involves recognizing it as a measure of the boundary length of shapes.
- Applications: Perimeter calculations are essential in various real-life scenarios, including construction, crafting, and land measurement.
- Calculation: Calculating the perimeter typically involves summing the lengths of all sides of the shape.
For example:
- Square: Perimeter = 4 × side length
- Rectangle: Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
- Triangle: Perimeter = sum of all three side lengths
Remember these formulas and tips to make calculating and spelling the perimeter easier:
- Double-check your spelling: P-E-R-I-M-E-T-E-R.
- Review the shape's properties: Ensure you understand the shape you are working with.
- Use the appropriate formula: Apply the correct perimeter formula based on the shape.
- Practice regularly: Regular practice will help reinforce your understanding and accuracy.
By following these steps, you can confidently tackle perimeter-related tasks and avoid common pitfalls. Keep practicing, and soon you'll find calculating and spelling the perimeter becomes second nature.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical tips for mastering the concept of perimeter. Thank you for reading, and happy calculating!
Chu vi là gì? - Hình học cho trẻ em
READ MORE:
Chu vi của các hình dạng phổ biến