Topic how is perimeter measured: Discover the essential methods and formulas for measuring the perimeter of various shapes. This comprehensive guide explains how to accurately calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular figures, using simple tools and techniques. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone interested in geometry, this article will enhance your understanding of perimeter measurement.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter Measurement
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Basic Definition of Perimeter
- Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
- Perimeter of Regular Shapes
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
- Methods to Measure Perimeter
- Tools for Measuring Perimeter
- Applications of Perimeter Measurement
- Common Mistakes in Perimeter Calculation
- Tips for Accurate Perimeter Measurement
- Advanced Perimeter Concepts
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Học cách tính chu vi qua video bài học toán học dành cho trẻ em. Giải thích dễ hiểu và thú vị để thu hút sự chú ý của các em nhỏ.
Understanding Perimeter Measurement
The perimeter of a geometric shape is the total distance around the edges of the shape. It is a measure of the boundary length of a two-dimensional figure.
Perimeter of Common Shapes
1. Rectangle
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, you need to add up the lengths of all four sides. The formula is:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
2. Square
Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is calculated by:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
3. Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
4. Circle (Circumference)
The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, and it is calculated using the formula:
\[ C = 2 \pi r \]
\[ C = \pi d \]
where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
Measuring Perimeter in Irregular Shapes
For irregular shapes, the perimeter can be measured by adding the lengths of all the sides. If the shape is complex, it can be divided into simpler shapes, and the perimeter of each part can be calculated and then summed.
Applications of Perimeter
- Construction: Calculating the amount of materials needed for borders or fences.
- Landscaping: Planning the layout and boundaries of gardens or lawns.
- Sports: Determining the dimensions of fields and courts.
- Art and Design: Creating frames and borders for artwork.
Perimeter Calculation Tools
Various tools and methods can be used to measure the perimeter, including:
- Ruler or Measuring Tape: For simple and small shapes.
- GPS Devices: For larger and outdoor shapes.
- Digital Software: CAD programs for precise and complex shapes.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary. It is an important concept in geometry and is used to measure the distance around various two-dimensional figures. Understanding perimeter helps in various practical applications such as construction, landscaping, and design.
Here are some key points to understand about perimeter:
- Definition: The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
- Unit of Measurement: Perimeter is measured in linear units, such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet.
- Applications: Perimeter measurements are used in real life for fencing properties, framing pictures, and more.
Let's explore the step-by-step methods to calculate the perimeter for different shapes:
- Perimeter of Regular Shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four.
\[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding twice the length and twice the width.
\[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Equilateral Triangle: The perimeter is three times the length of one side.
\[ P = 3a \] where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four.
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes:
- Sum the lengths of all sides to find the total perimeter.
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference):
- The circumference of a circle is calculated using the radius or the diameter.
\[ C = 2 \pi r \] or \[ C = \pi d \] where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
- The circumference of a circle is calculated using the radius or the diameter.
By understanding these basic principles and formulas, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any two-dimensional shape.
Basic Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is the measure of the distance around the outside of a figure. Understanding the perimeter is crucial for various practical applications, such as construction, landscaping, and design.
Here is a detailed breakdown of the basic definition of perimeter:
- Perimeter of Regular Shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four.
\[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding twice the length and twice the width.
\[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Equilateral Triangle: The perimeter is three times the length of one side.
\[ P = 3a \] where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four.
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes:
- For irregular shapes, the perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all the sides. This method is applicable to any polygon regardless of the number of sides or their lengths.
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference):
- The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius or diameter.
\[ C = 2 \pi r \] or \[ C = \pi d \] where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
- The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius or diameter.
In summary, the perimeter is a measure of the total distance around a shape. Whether the shape is regular, irregular, or circular, specific formulas can be used to calculate the perimeter accurately. This measurement is essential for a variety of real-world applications, making it a valuable concept in geometry.
Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a shape involves summing the lengths of its sides. Different geometric shapes have specific formulas to simplify this process. Here, we will explore the formulas for calculating the perimeter of various regular and irregular shapes.
- Perimeter of Regular Shapes:
- Square:
The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four:
\[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle:
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding twice the length and twice the width:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Equilateral Triangle:
The perimeter is three times the length of one side:
\[ P = 3a \] where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Square:
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes:
- For irregular shapes, the perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all sides:
- This method applies to polygons with any number of sides and varying side lengths.
\[ P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + \ldots + a_n \]
- Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference):
- The circumference of a circle is calculated using the radius or the diameter:
\[ C = 2 \pi r \] or \[ C = \pi d \] where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
- Perimeter of a Regular Polygon:
- For regular polygons with \( n \) sides of equal length \( a \), the perimeter is:
\[ P = n \times a \]
These formulas provide a straightforward way to calculate the perimeter for various shapes, ensuring accuracy and ease in measurement. Understanding these formulas is essential for solving geometric problems and practical applications in fields like construction, design, and landscaping.
Perimeter of Regular Shapes
The perimeter of regular shapes can be easily calculated using specific formulas tailored to each type of shape. Regular shapes have sides of equal length, simplifying the calculation process. Here, we will discuss the perimeter formulas for some common regular shapes.
- Square:
A square has four equal sides. The perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by four:
\[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle:
A rectangle has opposite sides of equal length. The perimeter is found by adding twice the length and twice the width:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Equilateral Triangle:
An equilateral triangle has three equal sides. The perimeter is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by three:
\[ P = 3a \] where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Regular Polygon:
A regular polygon has \( n \) sides of equal length. The perimeter is calculated by multiplying the number of sides by the length of one side:
\[ P = n \times a \] where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( a \) is the length of a side.
Let's summarize these formulas in a table for quick reference:
| Shape | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | \[ P = 4s \] |
| Rectangle | \[ P = 2(l + w) \] |
| Equilateral Triangle | \[ P = 3a \] |
| Regular Polygon | \[ P = n \times a \] |
Understanding these formulas makes it easier to calculate the perimeter of regular shapes accurately. These calculations are fundamental in various practical fields, including construction, design, and engineering.
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes can be more challenging than for regular shapes, as the sides are not necessarily equal in length. However, the basic principle remains the same: summing the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of irregular shapes.
- Identify All Sides:
Begin by identifying and measuring the length of each side of the irregular shape. This can be done using a ruler, tape measure, or any appropriate measuring tool.
- Sum the Lengths:
Add the lengths of all the sides together. The sum will give you the total perimeter of the shape. The formula for this is:
\[ P = a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + \ldots + a_n \]
where \( a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots, a_n \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Complex Irregular Shapes:
For more complex shapes, you might need to break the shape down into simpler parts, calculate the perimeter of each part, and then sum these perimeters.
- Divide the shape into smaller, regular shapes such as rectangles, triangles, or circles.
- Calculate the perimeter of each smaller shape using the appropriate formulas.
- Sum the perimeters of the smaller shapes to find the total perimeter.
- Use of Coordinates:
If the shape’s vertices are defined by coordinates on a plane, the distance formula can be used to calculate the length of each side:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
where \( (x_1, y_1) \) and \( (x_2, y_2) \) are the coordinates of two consecutive vertices. Sum the distances of all sides to get the perimeter.
Here is a practical example:
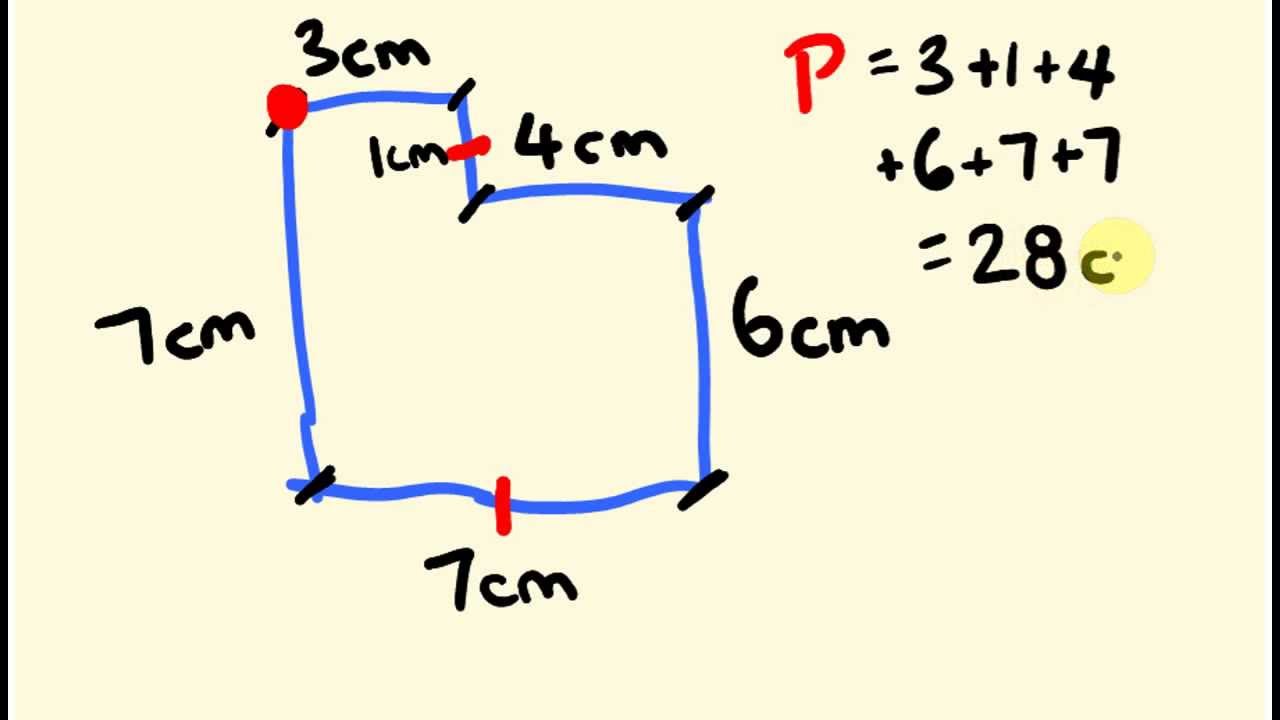
Suppose you have an irregular quadrilateral with side lengths of 5 cm, 7 cm, 9 cm, and 6 cm.
The perimeter would be calculated as follows:
\[ P = 5 + 7 + 9 + 6 = 27 \, \text{cm} \]
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any irregular shape, ensuring precise measurements for various practical applications.
Methods to Measure Perimeter
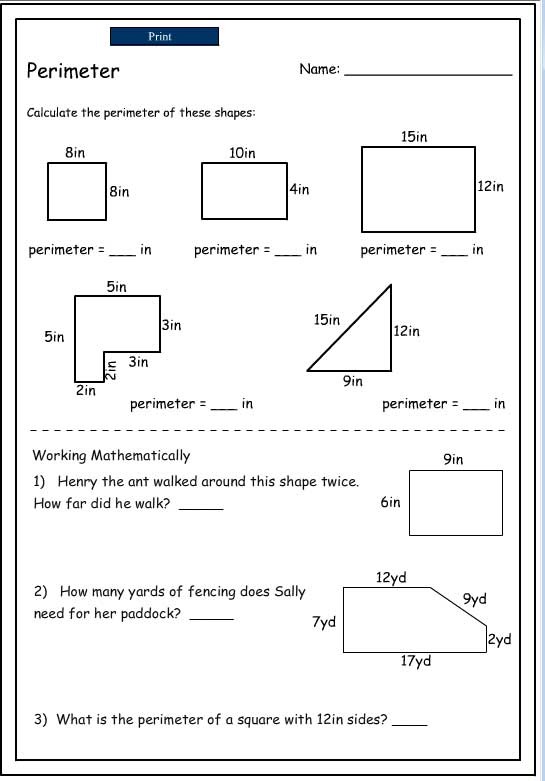
Measuring the perimeter of a shape involves different methods depending on whether the shape is regular or irregular. Here are detailed steps and methods for measuring the perimeter:
1. Using a Measuring Tool
This is the most straightforward method where you use a ruler, measuring tape, or a similar tool to measure each side of the shape. Here’s how to do it:
- Place the measuring tool along one side of the shape and note the length.
- Repeat for all sides of the shape.
- Add the lengths of all sides together to get the perimeter.
2. Using a String for Irregular Shapes
For shapes with curved or irregular boundaries, a string can be used:
- Carefully place the string along the edge of the shape, following all the contours.
- Mark or cut the string where it completes the boundary.
- Lay the string straight and measure its length using a ruler or measuring tape.
3. Grid Method for Irregular Shapes
This method is useful for shapes drawn on graph paper:
- Place the shape on a piece of graph paper and trace its outline.
- Count the number of grid units along the boundary of the shape.
- Multiply the number of units by the length of each unit to get the perimeter.
4. Formula-Based Calculation for Regular Shapes
For regular shapes, use specific formulas to calculate the perimeter:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4a \) where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \) where \( r \) is the radius.
5. Using Software and Perimeter Calculators
There are various online tools and software that can calculate the perimeter based on input values. These tools are particularly useful for complex shapes:
- Enter the required dimensions into the perimeter calculator.
- The software processes the input and provides the perimeter value.
Example Calculation:
For a rectangle with a length of 7 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter can be calculated as:
Formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
Calculation: \( P = 2(7 + 3) = 2 \times 10 = 20 \) units
These methods provide accurate and efficient ways to measure the perimeter of various shapes, ensuring that you can handle both simple and complex geometric figures.
Tools for Measuring Perimeter
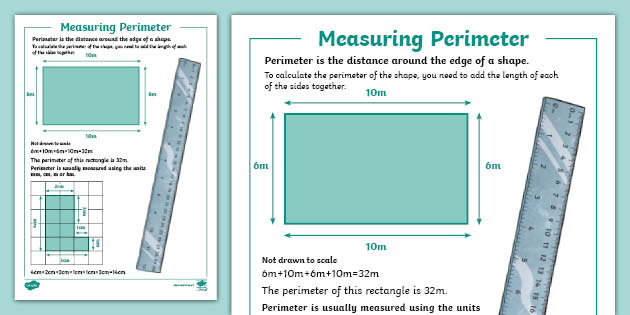
Measuring the perimeter of an object or shape accurately requires the use of various tools, each suited to different types of measurements. Here are some common tools used for measuring perimeter:
-
Ruler:
A ruler is ideal for measuring the perimeter of smaller objects. It can come in different units such as inches or centimeters, making it versatile for different scales of measurement.
-
Measuring Tape:
A flexible measuring tape is perfect for measuring the perimeter of larger or irregularly shaped objects. It allows for easy wrapping around curves and edges, providing an accurate measurement.
-
Meter Stick or Yardstick:
These are useful for measuring straight edges of larger objects. They are typically one meter or one yard in length and provide a sturdy and accurate measurement tool for larger dimensions.
-
Wheel Measure:
Also known as a measuring wheel, this tool is excellent for measuring the perimeter of large areas. It consists of a wheel attached to a handle that you roll along the boundary of the area being measured. The wheel's rotations are counted and converted into distance.
-
Laser Measure:
A laser measure provides a highly accurate and quick method to measure distances. By pointing the laser at a target and reading the distance on the digital display, you can measure the perimeter of both regular and irregular shapes without the need for physical contact.
-
Trundle Wheel:
Similar to a wheel measure, a trundle wheel is used for measuring longer distances. It is rolled along the perimeter of an area, and each click of the wheel represents a specific distance, allowing for easy measurement of long perimeters.
Each tool has its advantages, and the choice of tool depends on the size and shape of the object or area whose perimeter you are measuring. Using the right tool ensures precision and ease in obtaining accurate measurements.
Applications of Perimeter Measurement
Perimeter measurement is a fundamental concept in geometry that finds extensive applications in various fields. Here are some of the key areas where perimeter measurement is used:
-
Construction and Architecture:
In construction, perimeter measurements are crucial for determining the boundaries of a plot of land, laying out foundations, and designing structures. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure that buildings are constructed within the designated space and comply with zoning laws.
-
Landscaping and Agriculture:
Perimeter measurements are used to design and manage gardens, parks, and agricultural fields. Knowing the perimeter helps in planning the layout, fencing the area, and calculating the amount of materials needed for irrigation systems.
-
Sports and Recreation:
In sports, perimeter measurements are essential for designing fields, tracks, and courts. For example, the perimeter of a soccer field or a running track must be accurately measured to ensure standard dimensions and fair play.
-
Manufacturing and Industry:
In manufacturing, perimeter measurements are used to design components and ensure they fit together correctly. This is especially important in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is critical.
-
Home Improvement:
Homeowners use perimeter measurements for various projects such as installing fences, painting rooms, or laying flooring. Accurate measurements help in purchasing the right amount of materials and avoiding waste.
-
Urban Planning and Surveying:
Urban planners and surveyors use perimeter measurements to map out cities, design road networks, and allocate land for public and private use. This helps in efficient land use and infrastructure development.
-
Environmental Conservation:
In environmental conservation, perimeter measurements are used to define the boundaries of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves. This helps in monitoring and managing these areas effectively.
Overall, perimeter measurement is a versatile tool that plays a vital role in various aspects of our daily lives, from large-scale urban planning to small home improvement projects.
Common Mistakes in Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter accurately can sometimes be challenging. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Misidentifying Side Lengths: Incorrectly identifying the lengths of the sides, especially in irregular shapes, can lead to errors.
- Omitting Sides: Forgetting to include all sides in the calculation, particularly in composite shapes.
- Misreading Units: Confusing units (e.g., centimeters vs. meters) can result in incorrect calculations.
- Incorrect Use of Formulas: Applying the wrong formula for the given shape, such as using the formula for a rectangle on a parallelogram.
- Arithmetic Errors: Simple addition mistakes can throw off the entire calculation.
To avoid these mistakes, double-check each step, ensure all sides are accounted for, and use the correct formulas for each specific shape.
Tips for Accurate Perimeter Measurement
Accurate perimeter measurement is crucial for ensuring the success of various projects, from construction to landscaping. Here are some detailed tips to help you achieve precise measurements:
- Use the Right Tools: Select appropriate measuring instruments such as measuring tapes, laser distance meters, or rolling tape measures. Ensure your tools are in good condition and properly calibrated.
- Clear the Area: Remove any obstacles that might interfere with the measurement process. This ensures you get an uninterrupted and accurate reading of the perimeter.
- Take Multiple Measurements: Measure each side of the area multiple times to ensure consistency. Record all measurements and compare them to identify any discrepancies.
- Maintain Steady Hands: When using manual tools, hold them steadily to avoid errors due to shaking or movement.
- Consistent Contact Pressure: Apply equal pressure when measuring with manual instruments to maintain accuracy.
- Measure from Fixed Points: Use fixed points such as corners or marked spots to start and end your measurements. This reduces the chances of cumulative errors.
- Environmental Factors: Be mindful of environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the accuracy of some measuring tools. Try to measure under stable conditions.
- Document Measurements: Keep detailed records of all measurements, including the date and conditions under which they were taken. This helps in verifying and cross-checking measurements later.
- Regular Calibration: Ensure that all your measuring instruments are regularly calibrated to maintain their accuracy over time.
- Seek Professional Help: For complex projects requiring high precision, consider consulting with professionals who have experience and access to advanced measuring tools.
By following these tips, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter measurements, ensuring reliable and precise results for your projects.
Advanced Perimeter Concepts
Understanding advanced concepts of perimeter involves exploring its applications in various geometric contexts, including more complex shapes and real-world problems. Below are some detailed concepts and formulas to consider:
Perimeter in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of polygons can be calculated using the distance formula. For a polygon with vertices \((x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), \ldots, (x_n, y_n)\), the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2} + \sqrt{(x_1 - x_n)^2 + (y_1 - y_n)^2}
\]
Use of Calculus in Perimeter
For curves, calculus can be used to find the perimeter or arc length. The formula for the length \(L\) of a curve \(y = f(x)\) from \(x = a\) to \(x = b\) is:
\[
L = \int_{a}^{b} \sqrt{1 + \left(\frac{dy}{dx}\right)^2} \, dx
\]
This integral accounts for the continuous nature of the curve, providing an exact length.
Perimeter of Ellipses
Calculating the perimeter of an ellipse requires an approximation as there is no simple formula. The approximate perimeter \(P\) can be calculated using Ramanujan's formula:
\[
P \approx \pi \left[ 3(a + b) - \sqrt{(3a + b)(a + 3b)} \right]
\]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the ellipse.
Perimeter in Real-World Applications
In real-world scenarios, perimeter measurements are crucial in fields such as architecture, engineering, and land surveying. For instance, determining the fencing needed for a plot of land involves calculating the perimeter.
- Architecture: Ensuring that a structure fits within a plot requires precise perimeter calculations.
- Engineering: Road construction often involves calculating the perimeter of various sections to estimate materials needed.
- Land Surveying: Defining property boundaries involves measuring the perimeter of the land.
Advanced Theorems Related to Perimeter
- Triangle Inequality Theorem: In any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than the length of the remaining side. This theorem ensures that a valid triangle is formed.
- Pythagorean Theorem: In right-angled triangles, the perimeter can be derived by first calculating the hypotenuse using \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\) and then summing all sides.
Example Calculations
Let's calculate the perimeter of a polygon using coordinate geometry:
- Consider a triangle with vertices at \((1, 2)\), \((4, 6)\), and \((6, 2)\).
- Calculate the distance between each pair of vertices:
- \(\sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (6 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = 5\)
- \(\sqrt{(6 - 4)^2 + (2 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{4 + 16} = \sqrt{20} = 2\sqrt{5}\)
- \(\sqrt{(6 - 1)^2 + (2 - 2)^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
- Sum the distances to get the perimeter: \(5 + 2\sqrt{5} + 5 \approx 15.47\).
These advanced concepts and techniques highlight the versatility and importance of perimeter calculations in both theoretical and practical applications.
Conclusion
Understanding and accurately measuring the perimeter of various shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry that has practical applications in numerous fields such as construction, design, and everyday problem-solving. The basic concept revolves around the sum of the lengths of all the sides of a shape, whether it be a regular polygon like a square or an irregular figure.
For regular shapes, the perimeter can be calculated using simple formulas:
- Square: \( P = 4a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Circle: \( P = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
For irregular shapes, measuring the perimeter often involves summing the lengths of all sides or using tools like strings or flexible measuring tapes to trace the shape's boundary. More advanced methods may involve calculus for curves and complex figures, applying integral calculus to compute the length of smooth curves.
In practical applications, accurate perimeter measurement is crucial. For instance:
- In construction, to determine the amount of materials needed for framing or fencing.
- In landscaping, to calculate the boundary for laying out paths or garden beds.
- In manufacturing, to design components that fit together precisely.
Despite its straightforward concept, measuring perimeter accurately requires attention to detail and proper tools, especially for irregular or complex shapes. Avoiding common mistakes like overlooking small sections or mismeasuring can ensure accuracy. Advanced concepts in perimeter measurement, such as those involving calculus, further broaden the scope and application of this fundamental geometric property.
Overall, mastering the measurement of perimeter not only enhances mathematical skills but also provides practical benefits across various real-world scenarios, underscoring the importance of this fundamental concept in geometry.

Học cách tính chu vi qua video bài học toán học dành cho trẻ em. Giải thích dễ hiểu và thú vị để thu hút sự chú ý của các em nhỏ.
Chu Vi Cho Trẻ Em | Video Bài Học Toán Học
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tìm chu vi qua video hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Phù hợp cho người mới bắt đầu và những ai muốn cải thiện kỹ năng toán học của mình.
Tìm Chu Vi