Topic how do you get the perimeter: Understanding how to get the perimeter is essential for various practical tasks, from construction to crafting. This guide simplifies the process, providing easy-to-follow steps to measure the perimeter of any shape. Whether it's a rectangle, square, triangle, or circle, you'll find clear instructions to help you accurately calculate perimeters with confidence.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter Calculation
- Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
- Perimeter of Basic Geometric Shapes
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Finding the Perimeter of a Square
- Determining the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Perimeter of Polygons
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
- Perimeter of Circles (Circumference)
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
- Perimeter Calculation in Construction
- Perimeter Calculation in Landscaping
- Perimeter Calculation in Interior Design
- Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculation
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tìm chu vi các hình học cơ bản cùng Thầy J. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức về chu vi trong toán học.
Understanding Perimeter Calculation
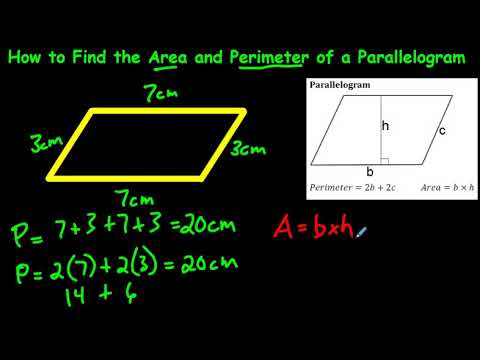
The perimeter is the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. The method to calculate the perimeter depends on the type of shape. Below are detailed steps and formulas for various shapes:
Perimeter of a Rectangle
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, use the formula:
- l: Length of the rectangle
- w: Width of the rectangle
Perimeter of a Square
For a square, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is:
- s: Side length of the square
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
- a, b, c: Lengths of the sides of the triangle
Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference)
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using:
- r: Radius of the circle
- π: Pi, approximately 3.14159
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
For a regular polygon (all sides and angles are equal), the perimeter is:
- n: Number of sides
- s: Length of each side
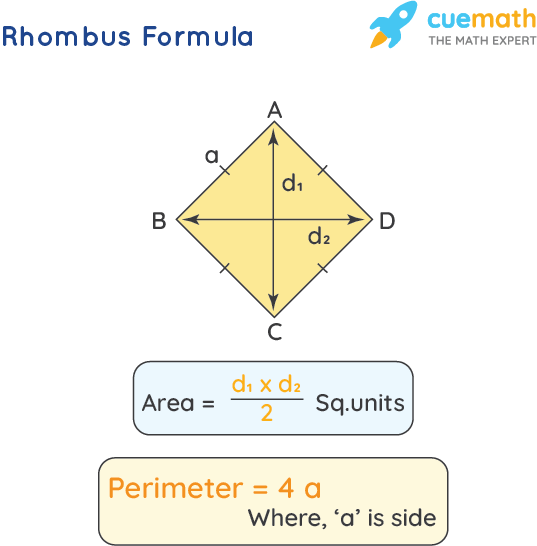
Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
For irregular shapes, sum the lengths of all the sides:
- l: Lengths of the sides
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential in various real-world applications, from construction to crafting. Practicing these formulas will help in mastering perimeter calculations for different shapes.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that represents the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. Knowing how to calculate the perimeter is crucial for various applications, from construction to design projects. Below are step-by-step methods to understand and compute the perimeter for different shapes.
To begin with, let's understand the basic principle of perimeter calculation:
- The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all the sides of a shape.
- It is measured in linear units, such as meters, feet, or inches.
Here are the detailed steps to calculate the perimeter for various common shapes:
-
Rectangle:
For a rectangle, the formula to calculate the perimeter is:
- l: Length of the rectangle
- w: Width of the rectangle
-
Square:
For a square, where all four sides are equal, the perimeter is given by:
- s: Side length of the square
-
Triangle:
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides:
- a, b, c: Lengths of the sides of the triangle
-
Circle (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using:
- r: Radius of the circle
- π: Pi, approximately 3.14159
-
Irregular Shapes:
For irregular shapes, sum the lengths of all the sides. The formula is:
- l: Lengths of the sides
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any shape, enhancing your understanding and application of this key geometric concept.
Perimeter of Basic Geometric Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of basic geometric shapes is a fundamental skill in geometry. Below are detailed methods for finding the perimeter of common shapes such as rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles.
-
Rectangle:
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated using the formula:
- l: Length of the rectangle
- w: Width of the rectangle
-
Square:
The perimeter of a square, where all sides are of equal length, is given by:
- s: Side length of the square
-
Triangle:
The perimeter of a triangle is found by adding the lengths of its three sides:
- a, b, c: Lengths of the sides of the triangle
-
Circle (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle, called the circumference, is calculated with the formula:
- r: Radius of the circle
- π: Pi, approximately 3.14159
These formulas provide straightforward methods to calculate the perimeter of basic geometric shapes. Practice using these formulas to strengthen your understanding and ability to measure the boundaries of different shapes accurately.
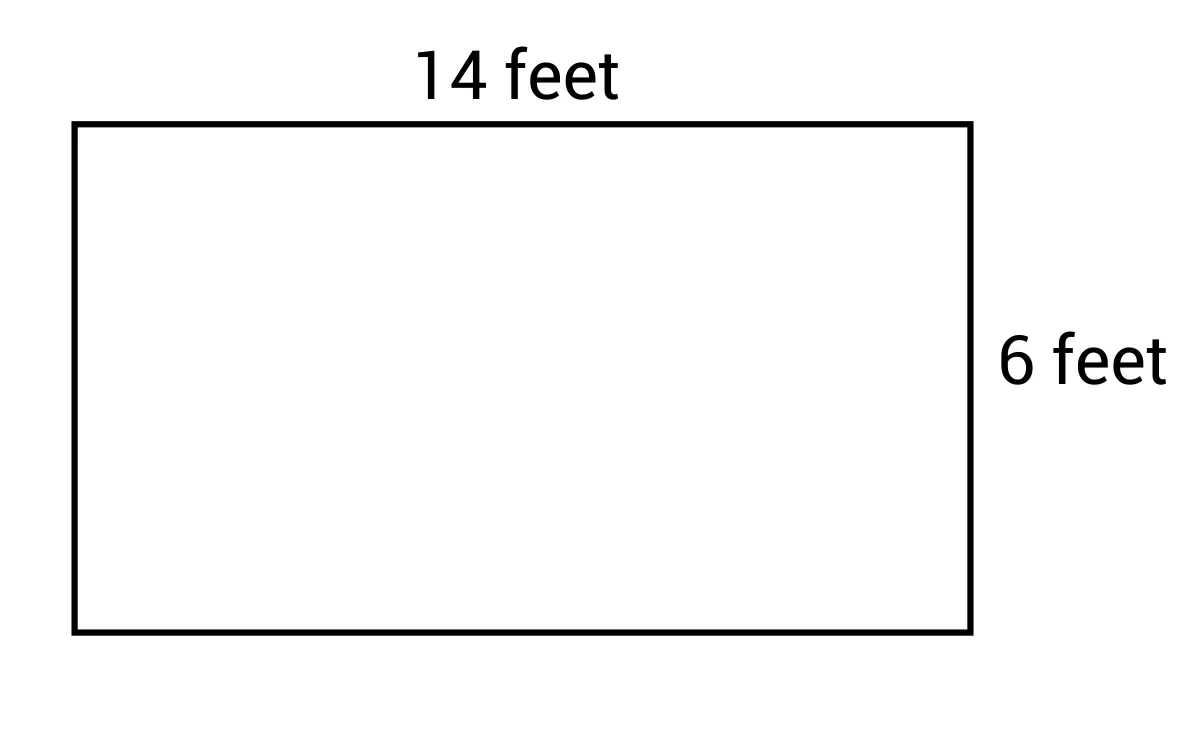
Calculating the Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total length of all its sides. To calculate the perimeter, you need to know the length and width of the rectangle. The formula for the perimeter P of a rectangle is:
\[ P = 2 \times ( \text{length} + \text{width} ) \]
Follow these steps to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Measure the length of the rectangle. Let's denote this as L.
- Measure the width of the rectangle. Let's denote this as W.
- Use the formula to calculate the perimeter:
- First, add the length and the width: \( L + W \)
- Next, multiply the result by 2: \( 2 \times (L + W) \)
- The result is the perimeter of the rectangle.
Here's an example calculation:
| Length (L) | Width (W) | Calculation | Perimeter (P) |
| 5 units | 3 units | \( 2 \times (5 + 3) \) | 16 units |
Therefore, the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units is 16 units.
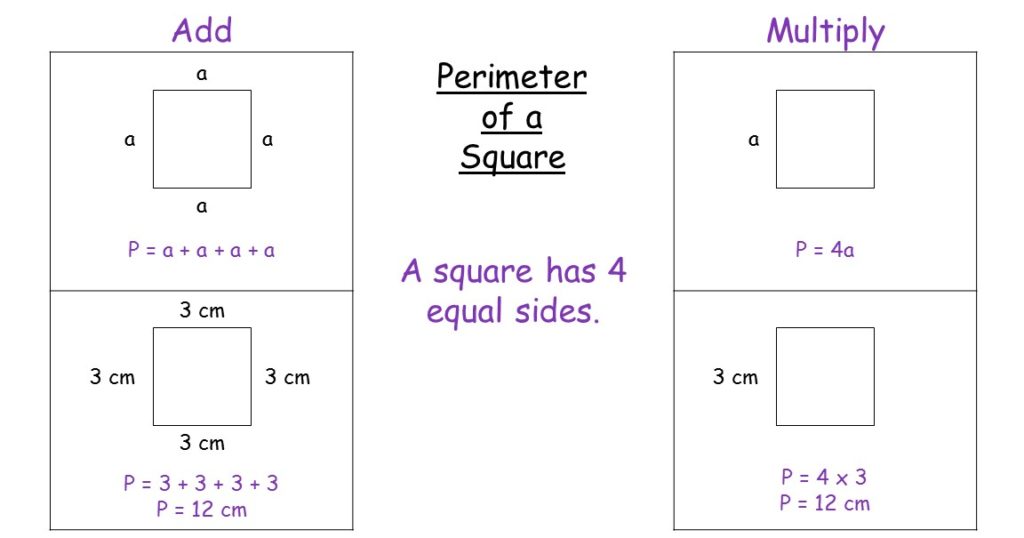
Finding the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total distance around the edge of the square. Since all four sides of a square are of equal length, finding the perimeter is straightforward. You can use the following formula:
Formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side length}
\]
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the length of one side: Measure or obtain the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply by 4: Multiply the side length by 4 to calculate the perimeter.
Example Calculation
Let's find the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 5 cm.
- Step 1: Identify the side length. Here, each side is 5 cm.
- Step 2: Multiply the side length by 4. \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{cm} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Visual Representation
Consider a square where each side is labeled as s:
| s | s | |
| (s) | ||
| s | s |
Since all sides are equal, the perimeter can be found by summing the length of all sides, which simplifies to multiplying one side by 4.
Practical Applications
- Fencing: If you have a square-shaped garden and need to install a fence around it, knowing the perimeter will help you determine the amount of fencing material needed.
- Framing: When framing a square picture or artwork, the perimeter will help you calculate the length of the frame needed.
In conclusion, finding the perimeter of a square is a simple process involving multiplication. Whether for academic purposes or practical applications, this basic geometric calculation is both useful and easy to perform.

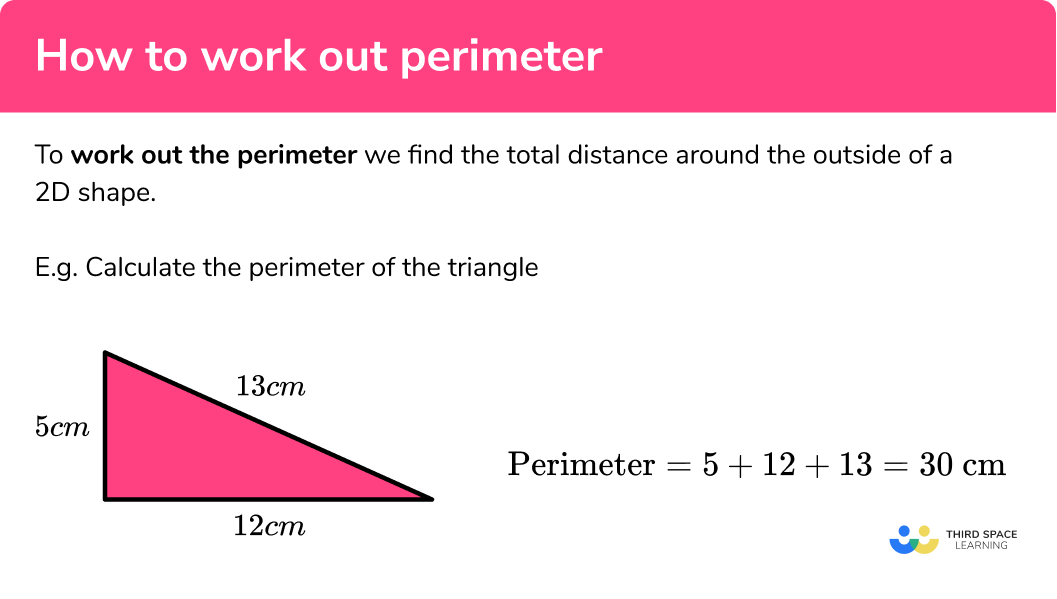
Determining the Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. To determine the perimeter of a triangle, follow these steps:
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. Let's denote them as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Add the lengths of the three sides using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
Here is a step-by-step example:
Consider a triangle with side lengths \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, and \( c = 10 \) cm:
- Step 1: Identify the side lengths: \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, \( c = 10 \) cm
- Step 2: Apply the perimeter formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm}
\] - Step 3: Calculate the sum:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 22 \, \text{cm}
\]
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 22 cm.
In cases where you are given different types of triangles, such as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene, the process remains the same:
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal. If each side length is \( a \):
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3a
\] - Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. If the equal sides are \( a \) and the base is \( b \):
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2a + b
\] - Scalene Triangle: All sides are of different lengths. Use the general formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
Ensure to measure each side accurately and sum them correctly to find the perimeter. This method applies to all types of triangles, making it a versatile approach in geometry.
Perimeter of Polygons
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. A polygon can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are different). The method to calculate the perimeter varies slightly based on the type of polygon.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of Polygons
- Identify the lengths of all the sides of the polygon.
- Add the lengths of all the sides to get the perimeter.
Regular Polygons
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length. If a regular polygon has \( n \) sides, and each side length is \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as:
\[
P = n \cdot s
\]
For example, for a regular hexagon (6 sides) with each side measuring 4 cm:
- Number of sides \( n = 6 \)
- Side length \( s = 4 \) cm
- Perimeter \( P = 6 \times 4 = 24 \) cm
Irregular Polygons
For an irregular polygon, each side can have a different length. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides.
Consider an irregular pentagon with side lengths \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 5 \) cm, \( c = 4 \) cm, \( d = 6 \) cm, and \( e = 7 \) cm:
- Step 1: Identify and list the side lengths: \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 5 \) cm, \( c = 4 \) cm, \( d = 6 \) cm, \( e = 7 \) cm
- Step 2: Apply the perimeter formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e
\] - Step 3: Calculate the sum:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 + 7 = 25 \, \text{cm}
\]
Therefore, the perimeter of the pentagon is 25 cm.
Summary
To find the perimeter of any polygon, whether regular or irregular:
- Measure the length of each side accurately.
- Sum the lengths of all the sides.
This straightforward method ensures you can calculate the perimeter of any polygon efficiently.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
A regular polygon is a geometric figure with all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure. The perimeter of a regular polygon can be calculated easily by multiplying the length of one side by the total number of sides.
Here is the step-by-step process to determine the perimeter of a regular polygon:
- Identify the length of one side of the polygon.
- Determine the total number of sides the polygon has.
- Multiply the length of one side by the total number of sides using the formula: \[ \text{Perimeter} = (\text{Number of sides}) \times (\text{Length of one side}) \]
Below are examples of how to calculate the perimeter of common regular polygons:
| Regular Polygon | Number of Sides | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | 3 | \( 3 \times \text{Length of one side} \) |
| Square | 4 | \( 4 \times \text{Length of one side} \) |
| Regular Pentagon | 5 | \( 5 \times \text{Length of one side} \) |
| Regular Hexagon | 6 | \( 6 \times \text{Length of one side} \) |
Let's look at a few specific examples:
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with each side measuring 7 feet.
- Number of sides = 6
- Length of one side = 7 feet
- Perimeter = \( 6 \times 7 = 42 \) feet
- Example 2: Calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon where each side is 6 inches.
- Number of sides = 5
- Length of one side = 6 inches
- Perimeter = \( 5 \times 6 = 30 \) inches
By following these steps, you can easily find the perimeter of any regular polygon, ensuring accurate and efficient calculation for various practical applications.
Perimeter of Irregular Polygons
Calculating the perimeter of irregular polygons can be more complex than finding the perimeter of regular polygons because the sides are not all of the same length. However, the basic principle remains the same: you need to sum the lengths of all the sides. Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of irregular polygons:
- Identify and Measure Each Side:
Begin by identifying all the sides of the irregular polygon. Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the length of each side. If the lengths are given in a problem, ensure they are all in the same unit.
- List the Side Lengths:
Write down the length of each side. This helps keep your calculations organized.
- For example, if you have a polygon with sides of 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm, list them as: 3 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm.
- Add the Lengths:
Sum all the side lengths to find the perimeter.
- Using the example above: \( 3 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} = 18 \, \text{cm} \).
- Double-check Your Measurements:
Before finalizing your calculation, re-measure each side if possible or re-check the given values to ensure accuracy.
In cases where the polygon is complex and side lengths are not directly measurable, you might need additional methods such as dividing the polygon into simpler shapes (like triangles and rectangles) or using coordinate geometry for calculation.
Example Calculation:
Let's calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with the following side lengths:
| Side | Length (cm) |
|---|---|
| Side 1 | 4.2 |
| Side 2 | 5.8 |
| Side 3 | 3.4 |
| Side 4 | 6.1 |
| Side 5 | 4.9 |
To find the perimeter, sum all the side lengths:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4.2 \, \text{cm} + 5.8 \, \text{cm} + 3.4 \, \text{cm} + 6.1 \, \text{cm} + 4.9 \, \text{cm} = 24.4 \, \text{cm}
\]
Thus, the perimeter of the pentagon is 24.4 cm.
Tips for Calculating the Perimeter of Irregular Polygons:
- Use Precision Tools: Ensure your measuring tools are precise and in good condition.
- Consistency in Units: Always measure or convert all side lengths into the same unit before adding them.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: If dealing with a very complex polygon, consider breaking it down into simpler shapes to facilitate measurement and calculation.
With these steps and tips, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any irregular polygon you encounter.
Perimeter of Circles (Circumference)
The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference. Calculating the circumference involves understanding the relationship between the circle’s diameter or radius and the constant π (pi). Here’s a detailed guide on how to find the circumference of a circle:
Basic Formulas:
The circumference (C) of a circle can be calculated using one of the following formulas:
- Using the diameter (d): \[ C = \pi \times d \]
- Using the radius (r): \[ C = 2 \pi \times r \]
Where:
- \(\pi\) (pi) is approximately equal to 3.14159.
- The diameter (d) is twice the radius (r).
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Measure the Radius or Diameter:
If you have the diameter, measure it across the circle passing through the center. If you have the radius, measure from the center to any point on the circle’s edge.
- Choose the Appropriate Formula:
If you have the diameter, use \( C = \pi \times d \). If you have the radius, use \( C = 2 \pi \times r \).
- Insert the Value:
Substitute the measured value of the radius or diameter into the formula.
- For example, if the diameter \( d = 10 \, \text{cm} \), then: \[ C = \pi \times 10 \, \text{cm} = 31.42 \, \text{cm} \]
- Or, if the radius \( r = 5 \, \text{cm} \), then: \[ C = 2 \pi \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 31.42 \, \text{cm} \]
- Calculate the Circumference:
Multiply the value by \(\pi\) (approximately 3.14159) to get the circumference.
- Use Precise Values:
For more accurate results, use the value of π to more decimal places or use a calculator with a π function.
Example Calculation:
Suppose you have a circle with a radius of 7 cm. Using the radius-based formula, the steps are:
- Identify the radius \( r = 7 \, \text{cm} \).
- Use the formula \( C = 2 \pi \times r \).
- Substitute the value of the radius: \[ C = 2 \pi \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 14 \pi \, \text{cm} \]
- Multiply by π: \[ C \approx 14 \times 3.14159 = 43.98 \, \text{cm} \]
Tips for Accurate Circumference Calculation:
- Use Precise Measurements: Ensure that the diameter or radius is measured accurately, especially in applications where precision is crucial.
- Consistent Units: Always use consistent units for measurements to avoid errors in your calculations.
- Employ Calculators: Use a calculator that includes a π function to improve the accuracy of your results.
- Understand the Role of π: Remember that π is a constant and is key to linking the diameter or radius to the circumference of a circle.
By following these steps and tips, you can accurately calculate the circumference of any circle.
Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental skill with numerous practical applications across various fields. Here, we explore some key areas where perimeter calculation is essential, and provide step-by-step guidance on how it is applied in each context:
1. Construction and Building Design
In construction, knowing the perimeter of a structure is crucial for estimating materials and planning.
- Fencing:
To determine the amount of fencing material needed to enclose a property, calculate the perimeter of the area to be fenced.
- Measure the lengths of all sides of the property.
- Sum these lengths to find the total perimeter.
- For example, if a rectangular plot has sides of 30 meters and 20 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (30 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m}) = 100 \, \text{m} \]
- Flooring and Baseboards:
To install baseboards around a room, calculate the perimeter of the room.
- Measure each wall length of the room.
- Add these lengths to get the total perimeter.
2. Landscaping and Garden Design
Perimeter calculations help in planning the layout and elements of a garden or landscape.
- Garden Beds:
When planning the borders of garden beds, the perimeter determines the length of edging materials needed.
- Measure each side of the garden bed.
- Sum the side lengths to get the perimeter.
- For a triangular garden bed with sides of 5 meters, 6 meters, and 7 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m} + 7 \, \text{m} = 18 \, \text{m}
- Pathways and Walkways:
To outline pathways, calculate the perimeter to estimate materials like pavers or gravel.
- Measure the length and width of the pathway.
- For a rectangular path, use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times ( \text{Length} + \text{Width} ) \).
3. Interior Design and Space Planning
Perimeter calculations assist in designing and organizing interior spaces.
- Painting and Wallpapering:
To estimate the amount of paint or wallpaper needed for a room, calculate the perimeter to cover all walls.
- Measure each wall's length in the room.
- Sum these lengths to get the total perimeter.
- For a room with walls measuring 10 meters and 8 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (10 \, \text{m} + 8 \, \text{m}) = 36 \, \text{m} \]
- Furniture Placement:
To arrange furniture in a room without overcrowding, use the perimeter to plan the available floor space.
- Measure the length of the walls where furniture will be placed.
- Ensure that the total perimeter minus furniture dimensions allows for free movement.
4. Sports and Recreation
In sports, perimeter calculations are vital for setting up fields, courts, and tracks.
- Track and Field:
Determining the distance around a running track involves calculating its perimeter, usually an oval shape.
- Measure the length of the track's straight sections and its curved sections.
- Add these to find the total perimeter.
- Playing Fields:
For soccer, baseball, or other sports fields, calculate the perimeter to install boundaries or fencing.
- Measure the length and width of the field.
- Sum the side lengths to determine the total perimeter.
5. Engineering and Manufacturing
In engineering and manufacturing, perimeter calculations are used to design and produce parts and products.
- Material Cutting:
Calculate the perimeter of shapes to determine how much material is needed for cutting parts.
- Measure all the side lengths of the shape to be cut.
- Add these lengths to find the total perimeter.
- Component Design:
Design components with precise dimensions by calculating the perimeter to ensure they fit and function properly.
- Measure each edge of the component design.
- Sum the edge lengths to determine the total perimeter.
These are just a few examples of how perimeter calculations are applied in everyday life and various professional fields. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter can be incredibly useful in planning, designing, and executing a wide range of projects and activities.
Perimeter Calculation in Construction
In construction, accurate perimeter calculations are fundamental for project planning, material estimation, and cost management. Whether you're working on a small residential project or a large commercial building, knowing how to calculate the perimeter helps ensure precision and efficiency. Here’s a detailed guide on how perimeter calculations are applied in various construction scenarios:
1. Determining the Perimeter of Building Foundations
Calculating the perimeter of a building's foundation is essential for planning the layout and estimating materials such as concrete, rebar, and formwork.
- Identify the Shape of the Foundation:
Most foundations are rectangular, but they can also be complex shapes like L-shapes or T-shapes.
- Measure the Sides:
Measure the lengths of all the sides of the foundation. Ensure measurements are taken accurately and recorded in the same unit.
- For a rectangular foundation measuring 30 meters by 20 meters, the perimeter is calculated as: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (30 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m}) = 100 \, \text{m} \]
- Sum the Lengths:
Add up the lengths of all sides to get the total perimeter. This total will help in estimating the amount of materials needed.
2. Estimating Fencing Materials
For fencing projects, the perimeter calculation determines the length of fencing materials required to enclose a site or property.
- Measure the Boundary:
Walk around the property and measure each segment of the boundary line.
- Account for Gates and Openings:
Deduct the width of any gates or openings from the total perimeter.
- Calculate the Perimeter:
Add the lengths of all boundary segments, subtracting for any gates, to get the total perimeter.
- For example, a property with sides of 50 meters, 30 meters, 50 meters, and 30 meters has a perimeter of: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 50 \, \text{m} + 30 \, \text{m} + 50 \, \text{m} + 30 \, \text{m} = 160 \, \text{m} \]
3. Planning Paving and Pathways
Perimeter calculations are crucial for planning pathways, driveways, and other paved areas.
- Measure the Edges:
For a rectangular driveway, measure the length and width. For curved or irregular paths, break them down into smaller segments and measure each segment.
- Calculate the Total Perimeter:
Sum the measurements of all sides or segments to determine the total perimeter.
- For a rectangular driveway 10 meters long and 4 meters wide, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (10 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m}) = 28 \, \text{m} \]
- Estimate Materials:
Use the perimeter to estimate the amount of edging, paving materials, or decorative elements needed.
4. Calculating Exterior Trim and Siding
When installing exterior trim or siding, knowing the perimeter helps in estimating the amount of materials required.
- Measure Wall Perimeters:
Measure each wall's length and add the measurements to get the total perimeter for trim or siding installation.
- Include Window and Door Openings:
For precise material estimation, measure and subtract the perimeter of window and door openings from the total perimeter.
- For a wall with a total length of 50 meters and window and door openings totaling 8 meters, the adjusted perimeter is: \[ \text{Adjusted Perimeter} = 50 \, \text{m} - 8 \, \text{m} = 42 \, \text{m} \]
- Estimate Material Quantities:
Use the adjusted perimeter to estimate the lengths of trim or siding required, accounting for overlaps and cuts.
5. Roofing and Gutter Installation
Calculating the perimeter of a roof is important for installing gutters, flashing, and drip edges.
- Measure Roof Edges:
Measure each edge of the roof, including any overhangs or eaves.
- Sum the Edge Lengths:
Add the lengths of all roof edges to get the total perimeter for gutter or flashing installation.
- For a roof with edges of 20 meters, 15 meters, 20 meters, and 15 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 20 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m} + 20 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m} = 70 \, \text{m} \]
- Estimate Material Requirements:
Use the perimeter to estimate the lengths of gutters, drip edges, and flashing needed for the roof.
These examples illustrate how perimeter calculations are integral to various construction tasks. Accurate measurements and calculations ensure efficient material use, cost management, and successful project execution.
Perimeter Calculation in Landscaping
In landscaping, accurate perimeter calculations are essential for planning and designing outdoor spaces. Whether you are designing garden beds, installing pathways, or creating water features, understanding how to calculate the perimeter helps ensure efficient use of materials and precise project execution. Here’s a detailed guide on how to apply perimeter calculations in various landscaping tasks:
1. Designing Garden Beds
Calculating the perimeter of garden beds is crucial for determining the amount of edging, mulch, and plants needed.
- Identify the Shape of the Garden Bed:
Garden beds can be any shape: rectangular, circular, or irregular. Identify and outline the shape to measure accurately.
- Measure the Edges:
Measure each edge of the garden bed. For curved edges, use a flexible tape measure or divide the curve into smaller straight segments.
- For example, a rectangular garden bed with sides of 6 meters and 4 meters has a perimeter of: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (6 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m}) = 20 \, \text{m} \]
- Sum the Measurements:
Add the lengths of all sides to find the total perimeter. This helps in estimating the amount of edging material required.
2. Installing Pathways and Walkways
Calculating the perimeter of pathways helps in estimating the materials needed for borders, paving, or gravels.
- Outline the Pathway:
Mark the pathway using stakes and string, ensuring to follow the desired layout and curves accurately.
- Measure the Length and Width:
Measure the total length and width of the pathway. For curved paths, divide them into smaller straight segments and measure each.
- For a pathway 15 meters long and 2 meters wide, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (15 \, \text{m} + 2 \, \text{m}) = 34 \, \text{m} \]
- Calculate the Total Perimeter:
Add the lengths of all sides to get the total perimeter. This helps in planning the amount of edging or border material needed.
3. Creating Water Features
For ponds, fountains, or pools, calculating the perimeter is vital for materials estimation and design precision.
- Define the Shape:
Outline the water feature's shape on the ground. Common shapes include circular, oval, or irregular.
- Measure the Perimeter:
For circular shapes, use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi \times r \). For irregular shapes, measure each segment around the feature.
- For a circular pond with a radius of 3 meters, the perimeter (circumference) is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi \times 3 \, \text{m} \approx 18.85 \, \text{m} \]
- Sum All Measurements:
Combine the lengths of all segments or use the formula for circles to find the total perimeter. This helps in estimating materials like liner or decorative edging.
4. Planning Patios and Decks
Calculating the perimeter of patios and decks helps in determining the amount of decking, railing, and borders required.
- Measure the Layout:
Outline the patio or deck on the ground. For irregular shapes, break down the perimeter into straight segments and measure each.
- Calculate Each Segment:
Measure the length of each side or segment. For rectangular patios, use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) \).
- For a rectangular deck with sides of 10 meters and 6 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (10 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m}) = 32 \, \text{m} \]
- Sum the Perimeter:
Add the lengths of all segments to find the total perimeter. This helps in estimating the required materials for decking, railing, or borders.
5. Installing Outdoor Lighting
Perimeter calculations are important for planning the placement and quantity of outdoor lighting fixtures around a landscaped area.
- Outline the Area:
Define the area where lighting is to be installed, such as along pathways, garden beds, or around patios.
- Measure the Perimeter:
Measure each side or segment where lighting will be placed. For curved areas, use a flexible tape measure or divide into smaller segments.
- Calculate the Total Length:
Add the lengths of all segments to find the total perimeter. This helps in planning the number and placement of lighting fixtures.
By following these detailed steps, you can effectively use perimeter calculations to plan and execute various landscaping projects, ensuring efficient use of materials and precise design implementation.
Perimeter Calculation in Interior Design
In interior design, accurate perimeter calculations are essential for a variety of tasks, from planning layouts and estimating materials to creating aesthetically pleasing and functional spaces. Here's a step-by-step guide on how perimeter calculations are applied in different aspects of interior design:
1. Planning Room Layouts
Calculating the perimeter of rooms helps in determining the placement of furniture, fixtures, and decor.
- Measure Each Wall:
Use a tape measure to measure the length of each wall. Ensure that measurements are taken from corner to corner for precision.
- For a rectangular room measuring 5 meters by 4 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (5 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m}) = 18 \, \text{m} \]
- Consider Architectural Features:
Include measurements for doorways, windows, and built-in features, which can affect the usable space within the perimeter.
- Calculate the Total Perimeter:
Sum the lengths of all walls to find the total perimeter. This helps in planning the layout and ensuring furniture and decor fit comfortably within the space.
2. Estimating Paint and Wallpaper
Perimeter calculations are crucial for estimating the amount of paint or wallpaper needed to cover the walls of a room.
- Measure Wall Perimeters:
Measure the length of each wall to calculate the perimeter of the room. Multiply the perimeter by the height of the walls to get the total surface area.
- For a room with a perimeter of 18 meters and a wall height of 3 meters, the surface area is: \[ \text{Surface Area} = 18 \, \text{m} \times 3 \, \text{m} = 54 \, \text{m}^2 \]
- Subtract Openings:
Subtract the areas of doors and windows from the total surface area to get an accurate estimate of the material needed.
- If the room has a door (2 m2) and a window (1.5 m2), the adjusted surface area is: \[ \text{Adjusted Surface Area} = 54 \, \text{m}^2 - (2 \, \text{m}^2 + 1.5 \, \text{m}^2) = 50.5 \, \text{m}^2 \]
- Estimate Material Quantities:
Use the adjusted surface area to estimate the amount of paint or wallpaper required. This helps avoid wastage and ensures coverage is adequate.
3. Installing Molding and Trim
Calculating the perimeter of rooms or walls is essential for installing baseboards, crown molding, and other trim work.
- Measure Along the Walls:
Measure the length of each wall where molding or trim will be installed. Include any corners and detailed areas.
- Account for Variations:
For rooms with irregular shapes or additional architectural features, measure each segment separately.
- Calculate the Total Length:
Add the lengths of all segments to find the total perimeter. This will give you the total length of molding or trim required.
- For a room with sides of 6 meters, 4 meters, 6 meters, and 4 meters, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 6 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} = 20 \, \text{m} \]
4. Installing Flooring
Perimeter calculations help in planning the installation of flooring materials such as tiles, carpet, or hardwood.
- Measure Room Dimensions:
Measure the length and width of the room to determine the total perimeter and area for flooring.
- Consider Layout Patterns:
For patterned or diagonal layouts, additional material may be needed. Calculate the perimeter to ensure enough material is ordered.
- Estimate Material Requirements:
Use the perimeter and area measurements to estimate the quantity of flooring materials required, considering potential waste or cuts.
- For a rectangular room 5 meters long and 4 meters wide, the area is: \[ \text{Area} = 5 \, \text{m} \times 4 \, \text{m} = 20 \, \text{m}^2 \]
5. Hanging Curtains and Blinds
Perimeter calculations are useful for determining the length of curtain rods and the amount of fabric required for curtains or blinds.
- Measure Window Dimensions:
Measure the width and height of windows to determine the total perimeter. Add extra width if curtains will extend beyond the window frame.
- Include Rod Overhang:
Consider the overhang of the curtain rod or track beyond the window width to ensure proper coverage and aesthetics.
- Calculate Fabric Requirements:
Use the perimeter to estimate the length of curtain rods and the amount of fabric needed, including allowances for pleating and fullness.
- For a window 2 meters wide with a 0.5 meter overhang on each side, the curtain rod length is: \[ \text{Curtain Rod Length} = 2 \, \text{m} + 2 \times 0.5 \, \text{m} = 3 \, \text{m} \]
Accurate perimeter calculations play a crucial role in interior design, from planning layouts to estimating materials. These calculations help ensure that designs are executed with precision and efficiency, contributing to the overall success of the project.
Tips and Tricks for Accurate Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of various shapes and objects accurately is crucial for many applications, from construction to interior design. Here are some useful tips and tricks to ensure your perimeter calculations are precise and efficient:
1. Understand the Shape You’re Measuring
Different shapes require different formulas and approaches for perimeter calculation. Here’s a quick overview:
- Rectangles and Squares: Sum the lengths of all sides. For rectangles, use \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) \). For squares, use \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{Side} \).
- Triangles: Add the lengths of all three sides. For an equilateral triangle, use \( \text{Perimeter} = 3 \times \text{Side} \).
- Circles (Circumference): Use \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Polygons: Sum the lengths of all sides, regardless of the number of sides or irregularity.
2. Use the Right Tools for Measurement
Accurate tools are essential for precise measurements:
- Flexible Tape Measure: Ideal for measuring curved surfaces or irregular shapes.
- Laser Distance Measurer: Provides quick and accurate measurements, especially for longer distances.
- Ruler or Straightedge: Useful for smaller, straight edges and short distances.
3. Double-Check Measurements
Always verify your measurements to avoid errors:
- Measure Twice, Cut Once: Double-check each measurement to ensure accuracy, especially before making any cuts or orders.
- Cross-Verify: Compare measurements using different tools or methods for consistency.
4. Account for Irregularities
For irregular shapes, divide the perimeter into smaller, manageable sections:
- Break Down Complex Shapes: Decompose complex shapes into simpler, regular sections, then sum their perimeters.
- Use a Flexible Tape Measure: For curves and non-linear edges, a flexible tape measure provides better accuracy.
- Approximate Curved Segments: For highly irregular curves, approximate the perimeter by measuring smaller straight segments along the curve.
5. Apply Mathematical Formulas Correctly
Use the appropriate formula for the shape you are measuring:
- Rectangles and Squares: For a rectangle, use \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) \). For a square, use \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{Side} \).
- Circles: Use \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \) or \( \pi d \), where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
- Polygons: Sum the lengths of all sides. For regular polygons, multiply the length of one side by the number of sides.
6. Consider Units of Measurement
Maintain consistency in your units of measurement:
- Use the Same Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (e.g., meters, feet) before calculating the perimeter.
- Convert Units When Necessary: Convert units as needed to keep the measurements consistent throughout the calculation.
7. Use Technology to Aid Calculation
Leverage technology to enhance accuracy and efficiency:
- Perimeter Calculators: Online calculators and apps can provide quick and accurate perimeter calculations.
- CAD Software: For complex shapes, computer-aided design (CAD) software can provide precise perimeter measurements.
8. Validate with Practical Checks
After calculating the perimeter, validate it with practical measures:
- Compare to Actual Measurements: After measuring and calculating, compare the results with the actual physical dimensions to ensure accuracy.
- Physical Mock-Ups: Create physical mock-ups or use visual aids to see if the calculated perimeter aligns with real-world requirements.
By following these tips and tricks, you can ensure your perimeter calculations are accurate, whether you’re working on a simple home project or a complex design task. Accuracy in measurement not only saves time and resources but also enhances the quality and precision of your work.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Perimeter Calculation
Accurate perimeter calculation is essential for a variety of tasks, from home improvement projects to complex engineering designs. However, several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate measurements and calculations. Here are some of the most frequent errors to avoid, along with tips on how to prevent them:
1. Inconsistent Units of Measurement
Using different units within the same calculation can lead to incorrect results.
- Always Use the Same Unit: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit (e.g., meters, feet) before performing the calculation. For example, if one side of a rectangle is measured in feet and another in inches, convert them to the same unit before summing.
- Convert Units Appropriately: When necessary, convert units to maintain consistency. For instance, convert inches to feet or centimeters to meters using the appropriate conversion factors.
2. Neglecting to Measure All Sides
Failing to measure each side of an object, especially in irregular shapes, can lead to incomplete or inaccurate perimeter calculations.
- Measure Each Side Individually: For polygons and irregular shapes, measure each side separately and accurately. Summing these measurements will give the total perimeter.
- Account for All Sections: Include all sides, even those that might seem minor or insignificant. In complex shapes, missing a side can lead to significant errors.
3. Incorrect Formula Application
Using the wrong formula for the shape you are measuring can result in incorrect perimeter values.
- Identify the Shape Correctly: Ensure you correctly identify the shape you are working with and apply the appropriate formula. For example:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) \)
- Circle: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \) or \( \pi d \)
- Regular Polygon: \( \text{Perimeter} = \text{Number of Sides} \times \text{Length of One Side} \)
- Double-Check Formulas: Before calculating, review the formula to ensure it matches the shape and dimensions you are working with.
4. Overlooking Complex or Curved Edges
Ignoring curved or intricate edges can lead to underestimating the perimeter, especially in non-linear shapes.
- Approximate Curves with Straight Segments: For curved edges, approximate the perimeter by measuring small, straight segments along the curve and summing them.
- Use Flexible Measuring Tools: Employ flexible tools like a tape measure to follow the contour of curved edges accurately.
5. Rounding Errors
Excessive rounding of measurements can lead to cumulative errors in the final perimeter calculation.
- Minimize Rounding: Retain as many decimal places as practical during intermediate steps of measurement and calculation.
- Round Only at the Final Step: If necessary, round the final perimeter value, but keep intermediate calculations as precise as possible.
6. Ignoring Measurement Errors
Small inaccuracies in measurement can accumulate, leading to significant errors in the calculated perimeter.
- Use Accurate Tools: Utilize precise and calibrated measuring tools to reduce measurement errors.
- Double-Check Measurements: Verify each measurement by repeating it to ensure consistency and accuracy.
7. Not Accounting for All Sides in Irregular Shapes
In complex or irregular shapes, it’s easy to miss measuring some sides, especially smaller or less obvious ones.
- Visualize the Shape: Break down the shape into smaller, more manageable sections and measure each one individually.
- Draw a Diagram: Create a sketch of the shape and mark each side as it is measured to ensure no side is overlooked.
8. Overlooking Practical Considerations
Failing to consider practical factors such as obstacles or physical limitations can lead to incorrect measurements.
- Consider Real-World Obstacles: Account for physical barriers or obstructions that might affect the measurement process.
- Adjust for Irregularities: Modify your approach based on the physical characteristics of the object or area being measured.
By being aware of these common mistakes and applying the tips and tricks provided, you can significantly improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations. Whether for simple DIY projects or complex design tasks, accurate measurements are crucial for success.
Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter is a fundamental skill in both everyday tasks and professional fields. Understanding how to accurately measure and compute the perimeter of various shapes can enhance precision in projects ranging from simple home improvements to complex architectural designs. Here’s a recap of the key points covered in this guide:
- Basic Geometric Shapes: Knowing the perimeter formulas for common shapes like rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles simplifies the calculation process.
- Irregular Shapes: For shapes that do not follow standard patterns, summing the lengths of all sides individually is essential to obtaining an accurate perimeter.
- Practical Applications: Understanding how to apply perimeter calculations in fields such as construction, landscaping, and interior design can provide real-world benefits.
- Tools and Techniques: Using appropriate measuring tools and techniques helps ensure that measurements are precise and reliable.
- Common Mistakes: Being aware of and avoiding common pitfalls can prevent errors and save time and resources.
Accurate perimeter calculation is not only a mathematical exercise but a practical tool that supports various aspects of design and planning. Whether you're working on a personal DIY project or involved in a large-scale professional undertaking, mastering perimeter measurement can enhance the quality and success of your work.
To summarize, here’s a step-by-step approach to accurate perimeter calculation:
- Identify the Shape: Determine whether you are working with a standard geometric shape or an irregular form.
- Select the Right Formula: Use the appropriate formula based on the shape you are measuring.
- Measure Carefully: Use precise tools and measure each side accurately, especially for irregular shapes.
- Sum the Lengths: Add up the lengths of all sides to get the total perimeter.
- Double-Check: Verify your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Apply Consistently: Use the calculated perimeter for practical applications, ensuring that the results align with real-world requirements.
By following these steps, you can confidently approach any task involving perimeter calculations. Remember, attention to detail and consistent measurement practices are key to achieving accurate and useful results. Happy measuring!

Khám phá cách tìm chu vi các hình học cơ bản cùng Thầy J. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức về chu vi trong toán học.
Tìm Chu Vi | Toán Học Với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi trong toán học cơ bản. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm chu vi và cách tính toán.
Toán Học Cơ Bản - Chu Vi