Topic perimeter of a pentagon: Discover the simple and effective methods to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon. Whether you're dealing with a regular or irregular pentagon, our comprehensive guide breaks down the formulas and steps needed to find the perimeter effortlessly. Enhance your geometry skills and apply this knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Introduction to Pentagon Geometry
- Understanding the Pentagon Shape
- Basic Geometry Definitions
- Properties of a Pentagon
- Types of Pentagons
- Regular vs. Irregular Pentagons
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
- Perimeter Formula for Regular Pentagon
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Pentagon
- Perimeter Formula for Irregular Pentagon
- Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications of Pentagon Geometry
- Real-World Examples
- Advanced Topics in Pentagon Geometry
- Using Coordinate Geometry for Perimeter Calculation
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác qua video hướng dẫn chi tiết này.
Perimeter of a Pentagon
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length of all its five sides. A pentagon can be regular or irregular, and the method to calculate the perimeter differs slightly based on its type.
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has all five sides of equal length. The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon is:
where is the length of one side.
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter \( P \) of an irregular pentagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
where are the lengths of the five sides.
Example Calculations
- Regular Pentagon: If the side length \( s \) is 4 units, the perimeter \( P \) is:
- Irregular Pentagon: If the side lengths are 3, 5, 4, 6, and 7 units, the perimeter \( P \) is:
Summary
In summary, calculating the perimeter of a pentagon is straightforward whether it is regular or irregular. For regular pentagons, multiply the side length by five. For irregular pentagons, sum the lengths of all sides.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Pentagon Geometry
The pentagon is a five-sided polygon that is a fundamental shape in geometry. Understanding its properties and how to calculate its perimeter is essential for various mathematical applications. There are two main types of pentagons: regular and irregular.
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal. In contrast, an irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different measures. The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length around the shape, which can be calculated by summing the lengths of its sides.
Below is a breakdown of the properties and types of pentagons:
- Sides: 5 sides
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is \(540^\circ\)
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not equal
To calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, you can use the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \times \text{side length} \]
For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is calculated by adding the length of each side:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e\) are the lengths of the sides of the pentagon.
Understanding these basic properties and formulas provides a solid foundation for more advanced studies in geometry and practical applications involving pentagons.
Understanding the Pentagon Shape
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides and five angles. It is a significant shape in both mathematics and various real-world applications, such as architecture and design. There are two primary types of pentagons: regular and irregular.
Here are the key characteristics of a pentagon:
- Sides: 5
- Vertices: 5
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is \(540^\circ\)
- Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is \(360^\circ\)
A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal to \(108^\circ\). An irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measures. The formulas for calculating the perimeter of these pentagons differ due to their structural differences.
To further understand the structure of a pentagon, consider the following properties:
| Property | Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
| Sides | Equal | Unequal |
| Interior Angles | Equal (\(108^\circ\)) | Unequal |
| Symmetry | Symmetrical | Asymmetrical |
To visualize a regular pentagon, you can draw five equal-length sides connected end-to-end to form a closed shape. Each internal angle will be \(108^\circ\). For an irregular pentagon, the lengths of the sides and the measures of the angles can vary, creating a more complex shape.
Understanding these properties helps in various mathematical calculations and practical applications, such as determining the perimeter of the pentagon. In a regular pentagon, the perimeter can be easily calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \times \text{side length} \]
For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e\) represent the lengths of the individual sides of the pentagon.
Basic Geometry Definitions
Understanding the perimeter of a pentagon requires familiarity with basic geometry concepts. Here are some fundamental definitions to get started:
- Polygon: A closed figure formed by a finite number of straight line segments connected end-to-end.
- Side: Each straight line segment of a polygon.
- Vertex (Vertices): The point where two sides of a polygon meet.
- Angle: The space between two intersecting lines or surfaces at or close to the point where they meet.
- Perimeter: The total length around a polygon, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides.
Let's delve deeper into these concepts with a focus on pentagons:
| Term | Definition | Example in a Pentagon |
| Polygon | A closed figure with multiple sides | Pentagon is a 5-sided polygon |
| Side | Each straight line segment in a polygon | A pentagon has 5 sides |
| Vertex | The point where two sides meet | A pentagon has 5 vertices |
| Angle | The space between two intersecting lines | In a regular pentagon, each interior angle is \(108^\circ\) |
| Perimeter | The total length around a polygon | Sum of all sides' lengths in a pentagon |
To further illustrate, consider the following steps for calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon:
- Measure the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply this length by 5 (since all sides are equal in a regular pentagon).
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \times \text{side length} \]
For an irregular pentagon, the process involves adding the lengths of all five sides:
- Measure the lengths of each side individually.
- Sum these lengths to find the total perimeter.
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e\) represent the lengths of the sides.
These basic geometry definitions and step-by-step methods provide a solid foundation for calculating the perimeter of any pentagon, whether regular or irregular.
Properties of a Pentagon
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides and five angles, and it has unique properties that distinguish it from other polygons. Understanding these properties is essential for various mathematical calculations, including determining the perimeter.
Here are the key properties of a pentagon:
- Sides: A pentagon has five sides.
- Vertices: A pentagon has five vertices, where each pair of adjacent sides meet.
- Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is \(540^\circ\). In a regular pentagon, each interior angle is \(108^\circ\).
- Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always \(360^\circ\).
- Diagonals: A pentagon has five diagonals. Each diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices.
Let's delve deeper into these properties:
| Property | Description | Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
| Sides | Number of edges of the polygon | 5 equal sides | 5 unequal sides |
| Vertices | Points where two sides meet | 5 vertices | 5 vertices |
| Interior Angles | Angles inside the pentagon | Each angle is \(108^\circ\) | Angles vary |
| Exterior Angles | Angles formed by one side and the extension of an adjacent side | Each angle is \(72^\circ\) | Angles vary |
| Diagonals | Line segments connecting non-adjacent vertices | 5 diagonals | 5 diagonals |
To illustrate the properties of a regular pentagon, consider the following steps to construct one:
- Draw a circle with a chosen radius. This will be the circumcircle of the pentagon.
- Divide the circle into five equal arcs using a protractor or compass.
- Connect the points where the arcs intersect the circle to form a regular pentagon.
The regular pentagon will have all sides of equal length and each interior angle measuring \(108^\circ\).
For an irregular pentagon, the sides and angles can vary. To calculate the perimeter of any pentagon, you need to sum the lengths of all five sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e\) are the lengths of the sides of the pentagon.
Understanding these properties and how they apply to both regular and irregular pentagons will enhance your comprehension of pentagon geometry and its practical applications.
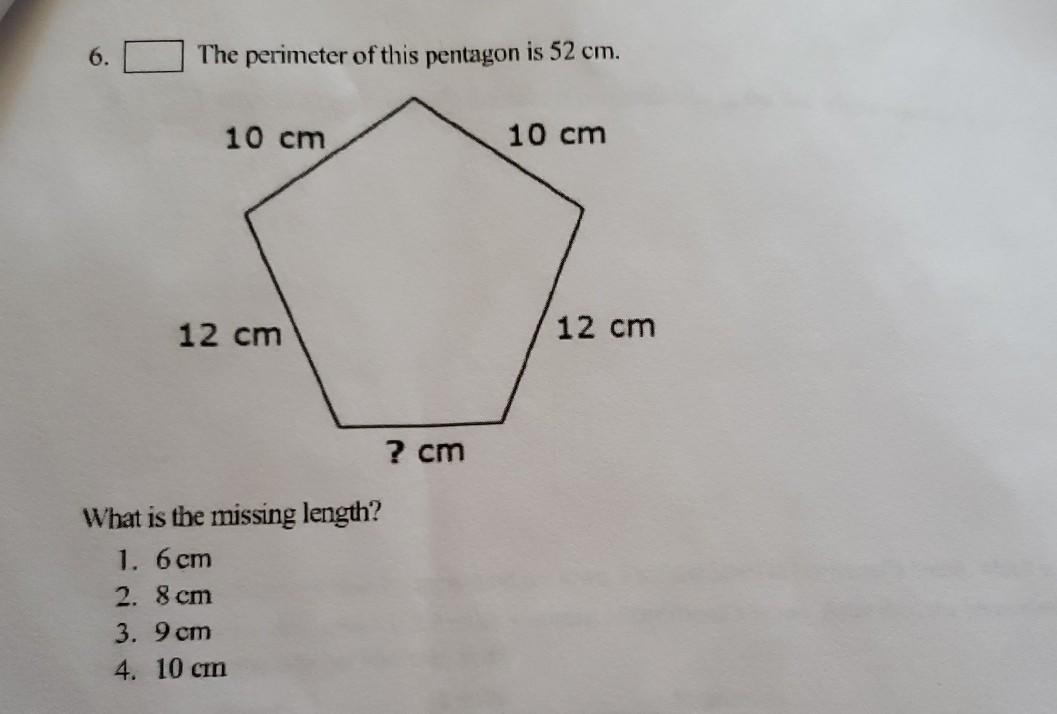
Types of Pentagons
Pentagons, which are five-sided polygons, can be categorized into various types based on the equality of their sides and angles. The two main types are regular pentagons and irregular pentagons. Understanding these types is crucial for different geometric calculations and applications.
Here are the primary types of pentagons:
- Regular Pentagon: A pentagon with all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal.
- Irregular Pentagon: A pentagon with sides and angles that are not equal.
Let's explore these types in detail:
| Type | Characteristics | Examples |
| Regular Pentagon |
|
A perfect five-sided polygon, like a stop sign. |
| Irregular Pentagon |
|
Any five-sided polygon where sides and angles vary, like some building layouts. |
Understanding these types is essential for calculating the perimeter and other properties. Here are the steps to identify and work with each type:
- Regular Pentagon:
- Measure one side of the pentagon.
- Use the formula for the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 \times \text{side length} \]
- Irregular Pentagon:
- Measure all five sides of the pentagon.
- Sum the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e \] where \(a, b, c, d, e\) are the lengths of the sides.
By understanding the characteristics and differences between regular and irregular pentagons, you can accurately calculate their perimeters and apply this knowledge to practical and theoretical problems in geometry.
Regular vs. Irregular Pentagons
In geometry, pentagons can be classified into two main categories: regular and irregular. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for calculating their perimeters effectively.
Regular Pentagons
A regular pentagon is a polygon with five sides of equal length and five equal interior angles. The symmetry of a regular pentagon makes it straightforward to calculate its perimeter.
Properties of a Regular Pentagon:
- All sides are of equal length.
- All interior angles are equal, each measuring \(108^\circ\).
The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is:
where \(P\) is the perimeter and \(s\) is the length of one side.
Irregular Pentagons
An irregular pentagon, on the other hand, has sides of different lengths and angles of different measures. This lack of uniformity requires a different approach to perimeter calculation.
Properties of an Irregular Pentagon:
- Sides have different lengths.
- Angles vary in measure.
The formula for the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is:
where \(P\) is the perimeter and \(a, b, c, d, e\) are the lengths of the five sides.
Comparison
To summarize, the key differences between regular and irregular pentagons are:
| Feature | Regular Pentagon | Irregular Pentagon |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | Equal | Unequal |
| Angles | Equal | Unequal |
| Perimeter Calculation | \(P = 5s\) | \(P = a + b + c + d + e\) |
Understanding these differences is crucial for correctly calculating the perimeter of any pentagon.
Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon depends on whether the pentagon is regular or irregular. Below are the formulas for both types of pentagons.
Regular Pentagon
A regular pentagon has five sides of equal length. The formula for calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon is straightforward:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the length of one side.
For example, if each side of a regular pentagon is 7 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as:
\[ P = 5 \times 7 = 35 \text{ cm} \]
Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all the sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d + e \]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the five sides.
For example, if the sides of an irregular pentagon are 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \text{ cm} \]
Examples
- Example for Regular Pentagon:
Given a regular pentagon with each side measuring 8 cm:
\[ P = 5 \times 8 = 40 \text{ cm} \] - Example for Irregular Pentagon:
Given an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm:
\[ P = 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 20 \text{ cm} \]
Special Cases
For some special cases, such as when the radius or apothem of a regular pentagon is known, the side length can be calculated using trigonometric formulas, and then used to find the perimeter.
For example, if the radius \( r \) of a regular pentagon is known, the side length \( s \) can be calculated as:
\[ s = 2r \times \sin\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right) \]
Then, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 5s \]
Similarly, if the apothem \( a \) is known:
\[ s = 2a \times \tan\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right) \]
And the perimeter \( P \) is again:
\[ P = 5s \]
Perimeter Formula for Regular Pentagon
The perimeter of a regular pentagon, which is a polygon with five equal sides, can be calculated using a straightforward formula. Since all sides of a regular pentagon are of equal length, the perimeter is simply five times the length of one side.
The formula for calculating the perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is:
\[ P = 5 \times a \]
where \( a \) represents the length of one side of the pentagon.
Let's break down the calculation step-by-step:
- Identify the length of one side of the pentagon.
- Multiply this length by 5.
- The result is the perimeter of the pentagon.
For example, if each side of a regular pentagon is 6 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
- Length of one side, \( a = 6 \) cm
- Perimeter, \( P = 5 \times 6 \) cm = 30 cm
Therefore, the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 cm is 30 cm.

Step-by-Step Calculation for Regular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon involves straightforward steps as all sides are of equal length. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide:
-
Identify the Length of One Side
Start by measuring or noting the length of one side of the pentagon. Let's denote this length as a.
-
Write Down the Perimeter Formula
The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is given by:
\[ P = 5a \]
Where P is the perimeter and a is the length of one side.
-
Substitute the Value of the Side Length
Substitute the value of a (the side length) into the formula. For example, if each side of the pentagon is 8 units long, substitute 8 for a:
\[ P = 5 \times 8 \]
-
Calculate the Perimeter
Perform the multiplication to find the perimeter:
\[ P = 40 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the pentagon is 40 units.
Here is a summary in tabular form:
| Step | Description | Example (a = 8 units) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify the length of one side | a = 8 units |
| 2 | Write down the perimeter formula | P = 5a |
| 3 | Substitute the value of the side length | P = 5 × 8 |
| 4 | Calculate the perimeter | P = 40 units |
By following these steps, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any regular pentagon given the length of its sides.
Perimeter Formula for Irregular Pentagon
An irregular pentagon is a five-sided polygon where each side can have different lengths. Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon is straightforward:
- Identify the lengths of all five sides of the pentagon.
- Add the lengths of these sides together to find the perimeter.
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of an irregular pentagon is:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e
\]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
Let's go through a step-by-step example:
- Measure the lengths of all five sides of the pentagon. Assume the sides are 7 cm, 5 cm, 8 cm, 6 cm, and 9 cm.
- Using the formula, add all the side lengths: \[ P = 7 + 5 + 8 + 6 + 9 \]
- Calculate the sum: \[ P = 35 \text{ cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular pentagon is 35 cm.
Step-by-Step Calculation for Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon involves summing the lengths of all its sides, as the sides are not equal. Here is a step-by-step method to calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon:
-
Identify the Lengths of All Sides: Measure the lengths of all five sides of the pentagon. Let's denote these sides as \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), \(d\), and \(e\).
-
Sum the Lengths of the Sides: Add the lengths of the five sides to find the perimeter. The formula for the perimeter \(P\) of an irregular pentagon is:
P = a + b + c + d + e -
Example Calculation: Suppose the lengths of the sides of an irregular pentagon are as follows:
- Side \(a = 5\) units
- Side \(b = 7\) units
- Side \(c = 6\) units
- Side \(d = 4\) units
- Side \(e = 8\) units
Then, the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as:
P = 5 + 7 + 6 + 4 + 8 = 30 units
This simple addition of side lengths gives you the total perimeter of the irregular pentagon.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons.
Example 1: Regular Pentagon
Find the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 6 cm.
- Identify the number of sides: A regular pentagon has 5 sides.
- Identify the length of one side: Each side is 6 cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon: \( P = 5s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \) cm.
Example 2: Irregular Pentagon
Find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with sides measuring 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm.
- Identify the lengths of all sides: 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of an irregular pentagon: \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \), where \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5 \) are the side lengths.
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 30 \) cm.
Practice Problems
Try solving these practice problems to test your understanding.
- Find the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 10 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with sides measuring 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm.
- A regular pentagon has a perimeter of 45 cm. What is the length of one side?
- An irregular pentagon has sides measuring 2.5 cm, 3.5 cm, 4.5 cm, 5.5 cm, and 6.5 cm. What is its perimeter?
Solutions
- Perimeter of regular pentagon: \( P = 5 \times 10 = 50 \) cm.
- Perimeter of irregular pentagon: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \) cm.
- Length of one side: \( s = \frac{P}{5} = \frac{45}{5} = 9 \) cm.
- Perimeter of irregular pentagon: \( P = 2.5 + 3.5 + 4.5 + 5.5 + 6.5 = 22.5 \) cm.
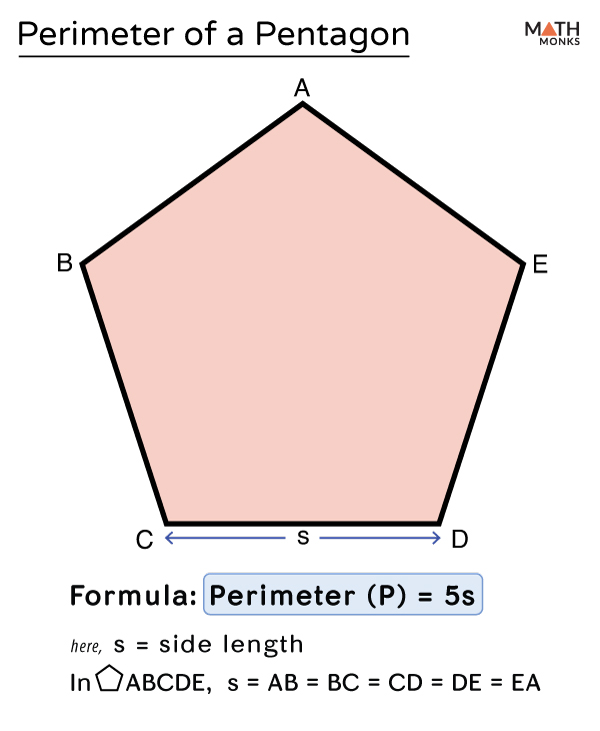
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, there are several common mistakes that students and professionals alike might make. Being aware of these errors can help ensure accurate calculations.
- Incorrect Identification of Side Lengths: Ensure that all side lengths are correctly identified and measured. In the case of an irregular pentagon, each side length may be different, so careful measurement is essential.
- Confusion Between Regular and Irregular Pentagons: Remember that the perimeter formula for a regular pentagon is different from that of an irregular pentagon. A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length, whereas an irregular pentagon does not.
- Arithmetic Errors: Simple addition errors can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations. Double-check your work to avoid mistakes in summing the side lengths.
- Unit Inconsistencies: Ensure all side lengths are in the same units before calculating the perimeter. Mixing units can lead to erroneous results.
- Overlooking Side Lengths: In complex problems, it’s easy to overlook one or more side lengths. Verify that all five sides of the pentagon have been included in your calculations.
- Misreading Diagrams: Misinterpreting a geometric diagram can lead to incorrect measurements of side lengths. Pay close attention to the given information and the scale of the diagram.
- Incorrect Use of Formulas: Ensure you are using the correct formula for the type of pentagon you are working with. For a regular pentagon, use \( P = 5s \). For an irregular pentagon, sum the lengths of all sides, \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of any pentagon, ensuring precision in your geometric work.
Applications of Pentagon Geometry
Pentagon geometry finds a wide range of applications in various fields due to its unique properties and structural characteristics. Below are some key applications of pentagon shapes:
-
Architecture and Design:
Pentagons are frequently used in architecture for aesthetic and structural purposes. The Pentagon building in the United States, which serves as the headquarters of the Department of Defense, is one of the most famous examples. The shape is also used in floor tiles and mosaics for its ability to create interesting and visually appealing patterns.
-
Natural Forms:
Pentagonal shapes are found in various natural forms, including certain flowers, sea stars, and crystals. These shapes are often admired for their symmetry and balance, which can be seen in the natural world.
-
Mathematics and Geometry:
In mathematics, pentagons are studied for their properties and their role in understanding polygons and their angles. They are also used in tiling and tessellation problems, where pentagonal shapes are explored for their ability to fill spaces without gaps.
-
Art and Symbolism:
Pentagons have been used in art and symbolism throughout history. They are often associated with the human form (as in the Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci), and they appear in various cultural and religious symbols, such as the pentagram.
-
Game Design:
In game design, especially in role-playing games (RPGs), pentagonal shapes are used for game boards, dice, and tokens. The five-sided shape provides a unique dynamic compared to more common shapes like squares and hexagons.
-
Structural Engineering:
Pentagonal structures are used in engineering for constructing geodesic domes and other frameworks that require a balance of strength and flexibility. The geometry of pentagons allows for the creation of stable and robust designs.
Real-World Examples
Pentagons are not just abstract geometric shapes; they are found in various real-world applications, showcasing their unique properties and aesthetic appeal. Below are some notable examples:
- The Pentagon Building: The headquarters of the United States Department of Defense in Washington, D.C., is a famous example of a pentagon shape. Known simply as "The Pentagon," this building's design maximizes office space and efficiency.
- Football (Soccer Ball) Design: Traditional soccer balls are made up of a combination of hexagons and pentagons. The pentagonal patches ensure that the ball maintains its spherical shape while providing structural integrity.
- Okra Cross-Section: When sliced, the cross-section of okra pods reveals a natural pentagon shape, illustrating how pentagons appear in nature.
- Geometric Art and Design: Artists and designers frequently use pentagons to create visually appealing patterns and structures. The symmetry and balance of pentagons make them a popular choice in various art forms.
- Architecture and Urban Planning: Beyond the Pentagon building, pentagonal shapes are used in the design of parks, gardens, and city layouts to create aesthetically pleasing and functional spaces.
These examples highlight the versatility and ubiquity of pentagons in different fields, from architecture and design to natural occurrences and recreational equipment.
Advanced Topics in Pentagon Geometry
Exploring advanced topics in pentagon geometry involves understanding various intricate properties and mathematical relationships associated with this unique polygon. In this section, we will delve into different types of pentagons, the use of coordinate geometry, and more sophisticated methods to calculate the perimeter.
Types of Pentagons
Pentagons can be classified based on their sides and angles into regular and irregular pentagons, as well as convex and concave pentagons.
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal. Each interior angle is 108 degrees, and each exterior angle is 72 degrees.
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not necessarily equal, leading to a variety of shapes.
- Convex Pentagon: No internal angles are greater than 180 degrees.
- Concave Pentagon: At least one internal angle is greater than 180 degrees.
Coordinate Geometry for Perimeter Calculation
Using coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a pentagon can be determined if the coordinates of its vertices are known. The distance formula between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is used to find the length of each side:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
By summing the lengths of all five sides, the perimeter \(P\) can be calculated:
\[ P = \sum_{i=1}^{5} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2} \]
Perimeter Calculation Using Trigonometry
For a regular pentagon, the side length can be found using the radius \(r\) of the circumscribed circle (the circle that passes through all the vertices of the pentagon). The formula involves the sine function:
\[ s = 2r \sin\left(\frac{180^\circ}{5}\right) = 2r \sin(36^\circ) \]
Once the side length \(s\) is known, the perimeter \(P\) is:
\[ P = 5s \]
Applications in Real World and Advanced Mathematics
Pentagon geometry is not just theoretical; it has practical applications in various fields such as architecture, art, and even molecular chemistry. For example, the famous Pentagon building in Washington, D.C., and certain molecular structures are based on pentagonal shapes.
Advanced mathematical problems involving pentagons often include finding areas, understanding symmetry properties, and exploring the relationships between inscribed and circumscribed circles. These topics may also involve deeper exploration of algebraic and trigonometric identities.
Conclusion
Understanding the advanced topics in pentagon geometry enriches our knowledge of both theoretical and practical aspects of this fascinating shape. Whether through coordinate geometry or trigonometric functions, the study of pentagons reveals the intricate beauty of mathematics.

Using Coordinate Geometry for Perimeter Calculation
Coordinate geometry provides a precise method to calculate the perimeter of a pentagon by using the coordinates of its vertices. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do this:
-
Identify the coordinates of each vertex: Each vertex of the pentagon will have coordinates \((x_i, y_i)\) where \(i\) ranges from 1 to 5. Ensure the vertices are labeled in a consistent order, either clockwise or counterclockwise.
-
Use the distance formula to calculate the length of each side: The distance between two consecutive vertices \((x_i, y_i)\) and \((x_{i+1}, y_{i+1})\) is given by:
\[
\text{Distance} = \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2}
\]Repeat this for all five sides of the pentagon.
-
Sum the lengths of all sides: Add up the distances calculated in the previous step to find the perimeter \(P\) of the pentagon:
\[
P = \sum_{i=1}^{5} \sqrt{(x_{i+1} - x_i)^2 + (y_{i+1} - y_i)^2}
\]
For example, consider a pentagon with vertices at the following coordinates: \(A(1, 1)\), \(B(4, 1)\), \(C(5, 4)\), \(D(3, 6)\), and \(E(1, 4)\).
-
Distance AB:
\[
\sqrt{(4 - 1)^2 + (1 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 0^2} = 3
\] -
Distance BC:
\[
\sqrt{(5 - 4)^2 + (4 - 1)^2} = \sqrt{1^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{10}
\] -
Distance CD:
\[
\sqrt{(3 - 5)^2 + (6 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{(-2)^2 + 2^2} = \sqrt{8}
\] -
Distance DE:
\[
\sqrt{(1 - 3)^2 + (4 - 6)^2} = \sqrt{(-2)^2 + (-2)^2} = \sqrt{8}
\] -
Distance EA:
\[
\sqrt{(1 - 1)^2 + (1 - 4)^2} = \sqrt{0^2 + (-3)^2} = 3
\]
Therefore, the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
\[
P = 3 + \sqrt{10} + \sqrt{8} + \sqrt{8} + 3 \approx 3 + 3.16 + 2.83 + 2.83 + 3 = 14.82 \text{ units}
\]
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any pentagon given the coordinates of its vertices.
Conclusion and Summary
In this comprehensive guide, we explored the various aspects of calculating the perimeter of a pentagon. Understanding the geometry and properties of pentagons is crucial for accurately determining their perimeter, whether they are regular or irregular.
We began with the basics of pentagon geometry, defining the shape and its fundamental properties. We discussed different types of pentagons and highlighted the distinctions between regular and irregular pentagons. Regular pentagons have equal side lengths, simplifying perimeter calculations, while irregular pentagons require summing the lengths of all individual sides.
The formulas for calculating the perimeter of a pentagon were detailed, with a focus on both regular and irregular shapes:
- For a regular pentagon: \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the length of a side.
- For an irregular pentagon: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \), where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
Step-by-step examples illustrated how to apply these formulas in practical scenarios. Additionally, we addressed common mistakes and provided tips to avoid them. Real-world applications of pentagon geometry, from architecture to nature, were discussed, emphasizing the relevance of these mathematical principles.
Advanced topics included the use of coordinate geometry for perimeter calculations, allowing for more complex and precise measurements, especially in irregular shapes. This method involves plotting the vertices of the pentagon on a coordinate plane and using the distance formula to determine side lengths.
In summary, mastering the calculation of a pentagon's perimeter involves a solid understanding of its properties, the appropriate formulas, and the ability to apply these concepts in various contexts. This knowledge is not only academically enriching but also practically valuable in numerous fields.
For further study and practice, additional resources and references are provided to enhance your understanding and skills in pentagon geometry.
Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác qua video hướng dẫn chi tiết này.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Ngũ Giác
Khám phá cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác đều và không đều cùng với công thức và ví dụ chi tiết trong video này.
Chu Vi Ngũ Giác, Chu Vi Cho Ngũ Giác Đều và Không Đều Kèm Công Thức & Ví Dụ
